- Default Location of Document flow Location
- Floating positioning float split into columns
- Layer location layer attribute is position
Document Flow Location
- From top to bottom, from left to right
- Element classification: block inline-block
- Element type conversion: display attribute
block element:
- block Element Characteristics: Monopoly Line
- Element height,width,margin,padding can be set
- common block elements < div > < p > < H1 > (< H6 > < ol > < UL > < Table > < form >
- Display the element as a block element
a{
display:block
}
//inline element a is transformed into block element, which makes a element have the characteristics of block element.
inline element
- Do not occupy a single line
- width, height is not set
- Width is the width of the text or picture that it contains and cannot be changed.
- Common inline elements: < span > < a >
- Display as inline element: display:inline;
inline-block element
- Do not occupy a single line (inline element)
- Element height,width,margin,padding can be set (block element)
- Common inline-block elements: <img>
- Display as inline-block element: display:inline-block;
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
*{
padding: 0;
margin:0;
}
#nav{
margin: 0 auto;
width: 300px;
/*The parent element definition font-size:0 removes the horizontal direction blank of the block element in the line.*/
font-size: 0;
}
a{
/*Otherwise, height and width cannot be set, etc.*/
display: inline-block;
/*Box Style*/
width: 80px;
height: 30px;
border-bottom: 1px solid #ccc;
/*Hyperlink text*/
font-size: 14px;
text-align: center;
line-height: 30px;
text-decoration: none;
}
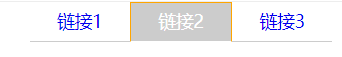
a:hover{
color: white;
background-color: #ccc;
border: 1px solid;
border-left-color: orange;
border-top-color: orange;
border-right-color: orange;
}
/*Subelement Definition vertical-align Attribute to Remove Vertical Blank of Block Element in Line*/
</style>
</head>
<body>
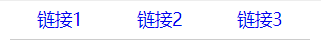
<div id="nav">
<a href="#">Link 1</a>
<a href="#">Link 2</a>
<a href="#">Link 3</a>
</div>
</body>
</html>
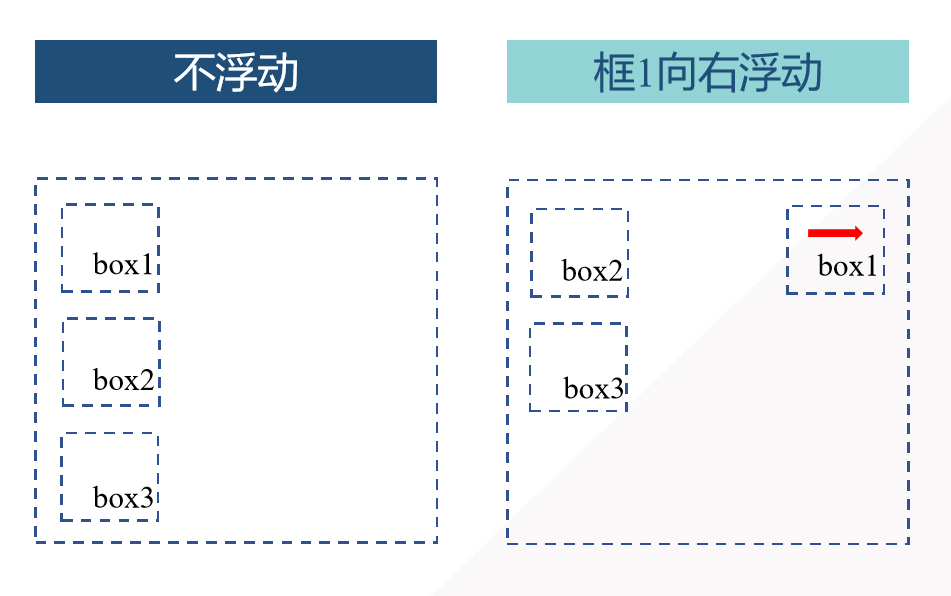
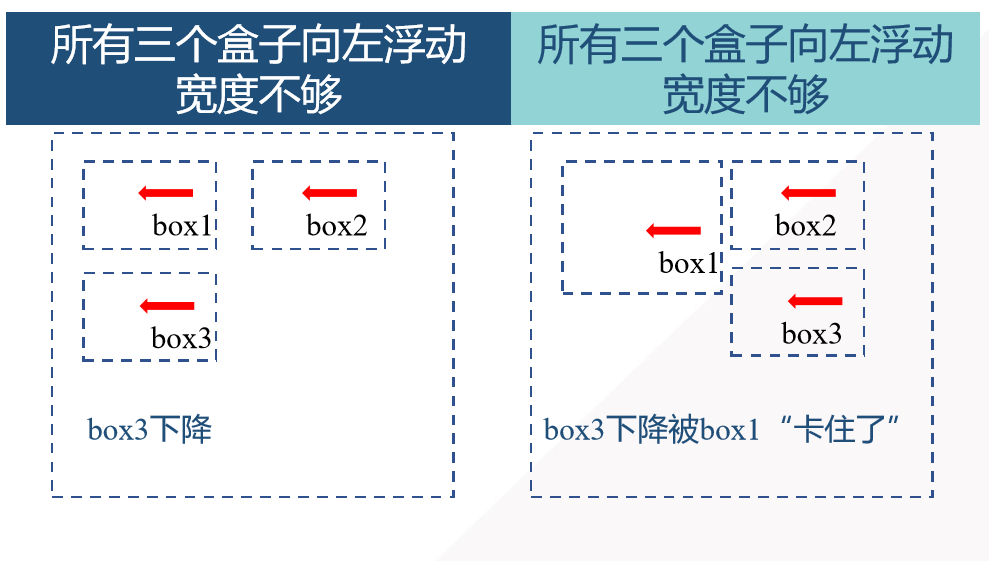
Floating positioning
- Float property: left-left float, right-right float
- clear attributes: left, right, both - clear left and right floats
<!doctype html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>4 Row 3</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="css/style.css" /> </head> <body> <div id="container"> <div id="header"> </div> <div id="nav"> </div> <div id="main"> <div id="aside1" class="aside"> </div> <div id="content"> </div> <div id="aside2" class="aside"> </div> </div> <div id="footer"> </div> </div> </body> </html>
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
body {
font-family:"Microsoft YaHei";
font-size:14px;
}
#container {
margin:0 auto;
width:900px;
}
#header {
height:100px;
background:#6cf;
margin-bottom:5px;
}
#nav{
height:30px;
background:#09c;
margin-bottom:5px;
}
#main{
height:500px;
/*background:#cff; */
margin-bottom:5px;
}
.aside{
float:left;
width:100px;
height:500px;
background:#6cf;
}
#aside1 {
}
#aside2 {
margin-left:5px;
}
#content{
float:left;
margin-left:5px;
width:690px;
height:500px;
background:#cff;
}
#footer {
height:60px;
background:#6cf;
}

Layer positioning
position attribute
-
static: The default value is not positioned, and the elements appear in the normal stream with no top, bottom, left, right, z-index validity
-
fixed: Relative to browser positioning, it does not change the elements always in sight as the browser window scrolls.
-
Relative: relative to direct parent element location
-
absolute: Locate relative to the first parent element other than static location
-
left attribute right attribute top attribute bottom attribute z-index attribute
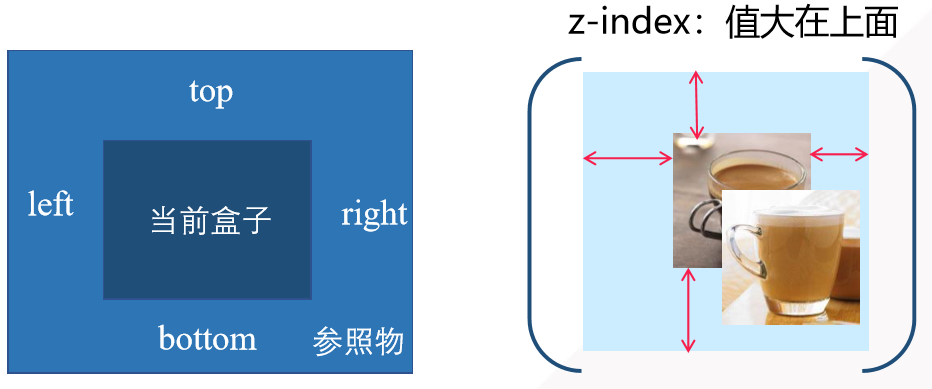
Be careful: -
Elements positioned as relative s are out of the normal document flow, but their in-situ position in the document flow still exists.
-
Layers positioned as absolute depart from the normal text stream, but differ from relative s in that their in-situ placement in the normal stream no longer exists.
-
The layer of relative location is always relative to its direct parent element, regardless of how the parent element is positioned.
-
For absolute localization, the layer is always relative to the parent layer recently defined as absolute or relation, which is not necessarily its direct parent layer.
-
For the absolute location layer, if neither absolute nor relative is defined in its parent layer, it locates the relative body.

<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
*{
margin: 0;
padding: 0;
}
div{
border:2px red solid;
color: #fff;
}
#box1{
width:170px;
height:190px;
position:relative;
}
#box2{
width:99%;
position:absolute;
bottom:0;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="box1">
<img src="2.jpg">
<div id="box2">Enjoy the warmth of coffee</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>