Dark horse programmer 2017 C++ STL tutorial (STL part has been completed)
STL course arrangement based on dark horse: Dark horse programmer 2017C++STL tutorial ⬅😊 Video link
special column 😬: Contents of this STL column
Article catalogue
The link is as follows:
special column: Contents of this STL column
2.2 C++STL ⭐ string container details
String is a C + + style string. In terms of early algorithm competition, cstring in C language style is enough??? (style of being y always taken) 😛)
2.3 C++STL ⭐ vector container details
Dynamic array
2.4 detailed explanation of C + + STL deque container
Double ended array, operation characteristics: the efficiency of inserting and deleting at both ends is particularly high. Inserting at the specified position will also cause the movement of data elements, and random access is supported.
2.5 C++STL ⭐ Detailed explanation of stack
Rule: first in, then out.
Traversal does not provide iterators or support random access.
while(!stack.empty())//Traversal mode
{
cout<<stack.top()<<endl;
stack.pop();
}
2.6 C++STL ⭐ queue details
Rule: first in, first out
Cannot traverse. Iterators are not provided and random access is not supported
while(!queue.empty())//Traversal mode
{
cout<<queue.front()<<endl;
queue.pop();
}
2.7 C++STL list container details
Very commonly used stl in the two-way linked list
The efficiency of inserting and deleting elements is not good at any time.
Disadvantages: random access is not supported because it costs continuous memory space. Therefore, in order to save the predecessor successor relationship between nodes, additional space overhead is required.
2.8 C++STL ⭐ Detailed explanation of set/multiset container (including pair)
// Team pair combines two values into one value
pair<string,int> pair1;
make_pair("aaa",1);
pair3=pair1;
2.9 detailed explanation of C + + STL map / Multimap container
map is different from set. map has key value and real value, and all elements are sorted automatically according to the key value. The first element of pair is called the key value, and the second element is called the real value. map also takes red black tree as the underlying implementation mechanism.
Overview of related API s
STL relevant API summary vector, Variable length array, multiplication idea size() Returns the number of elements empty() Returns whether it is empty clear() empty front()/back() push_back()/pop_back() begin()/end() [] Support comparison operation, in dictionary order pair<int, int> first, First element second, Second element Support comparison operation to first Is the first keyword, with second Is the second keyword (dictionary order) string,character string szie()/length() Return string length empty() clear() substr(Starting subscript,(Substring length)) Return substring c_str() Returns the starting address of the character array where the string is located queue, queue size() empty() push() Insert an element at the end of the queue front() Return queue header element back() Return tail element pop() Pop up queue header element priority_queue, Priority queue. The default is large root heap push() Insert an element top() Returns the top of heap element pop() Pop top element How to define as a small root heap: priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<int>> q; stack, Stack size() empty() push() Insert an element into the top of the stack top() Return stack top element pop() Pop up stack top element deque, Double ended queue size() empty() clear() front()/back() push_back()/pop_back() push_front()/pop_front() begin()/end() [] set, map, multiset, multimap, Based on balanced binary tree (red black tree), the ordered sequence is maintained dynamically size() empty() clear() begin()/end() ++, -- Return precursor and successor, time complexity O(logn) set/multiset insert() Insert a number find() Find a number count() Returns the number of a number erase() (1) The input is a number x,Delete all x O(k + logn) (2) This iterator, delete an input iterator lower_bound()/upper_bound() lower_bound(x) Return greater than or equal to x Iterator of the smallest number of upper_bound(x) Return greater than x Iterator of the smallest number of map/multimap insert() The number of inserts is one pair erase() The input parameter is pair Or iterator find() [] The time complexity is O(logn) lower_bound()/upper_bound() unordered_set, unordered_map, unordered_multiset, unordered_multimap, Hashtable Similar to the above, the time complexity of adding, deleting, modifying and querying is O(1) I won't support it lower_bound()/upper_bound(), Iterator++,-- bitset, Pressure level bitset<10000> s; ~, &, |, ^ >>, << ==, != [] count() Returns how many 1s there are any() Determine whether there is at least one 1 none() Judge whether all are 0 set() Set all positions to 1 set(k, v) Will be the first k Bit becomes v reset() Change all bits to 0 flip() Equivalent to~ flip(k) Put the first k Bit inversion Author: yxc Link: https://www.acwing.com/blog/content/404/ Source: AcWing The copyright belongs to the author. For commercial reprint, please contact the author for authorization. For non-commercial reprint, please indicate the source.
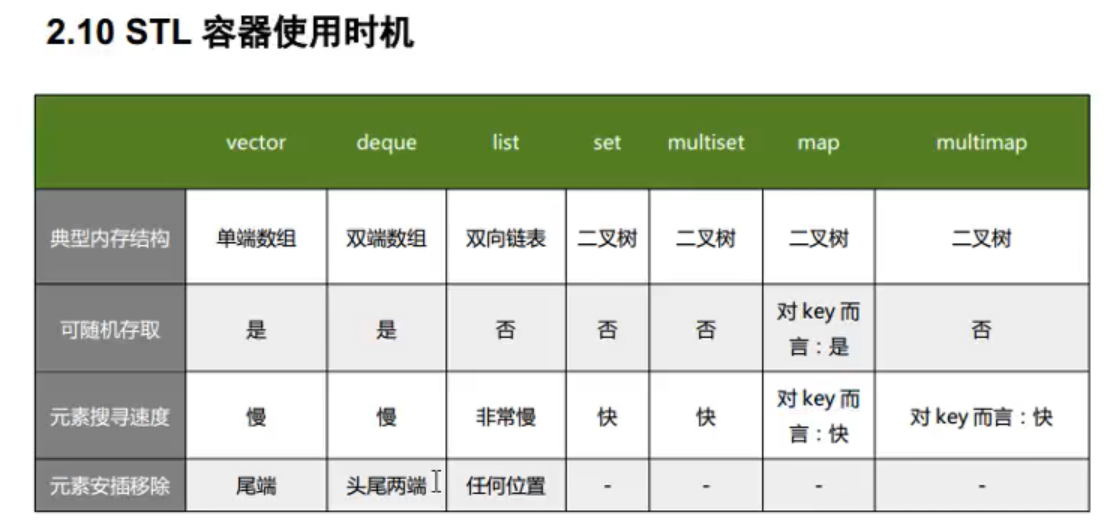
summary

Here is the reference
Thank you for reading (''▽ ''). If there are any mistakes, you are welcome to point them out. If you think they are good, you can praise them.