1, Functions
1. Custom method
//main entry method
void main() {
//Call method
printInfo();
//Custom methods can also be defined inside the main method
int getNum() {
return 1;
}
print(getNum());
}
//The custom method void has no return value
void printInfo() {
print("Custom method");
}
2. Location optional parameter method
It is optional to mark parameters in []:
The format in [] in the new version is: type +? + name (not in the old version?)
void main() {
String str = say("Zhang San", "ha-ha", "hehe");
print(str);
String str1 = say("Zhang San", "ha-ha");
print(str1);
}
String say(String from, String msg, [String? device]) {
var result = '$from says $msg';
if (device != null) {
result = '$result with a $device';
}
return result;
}
3. Naming optional parameter methods
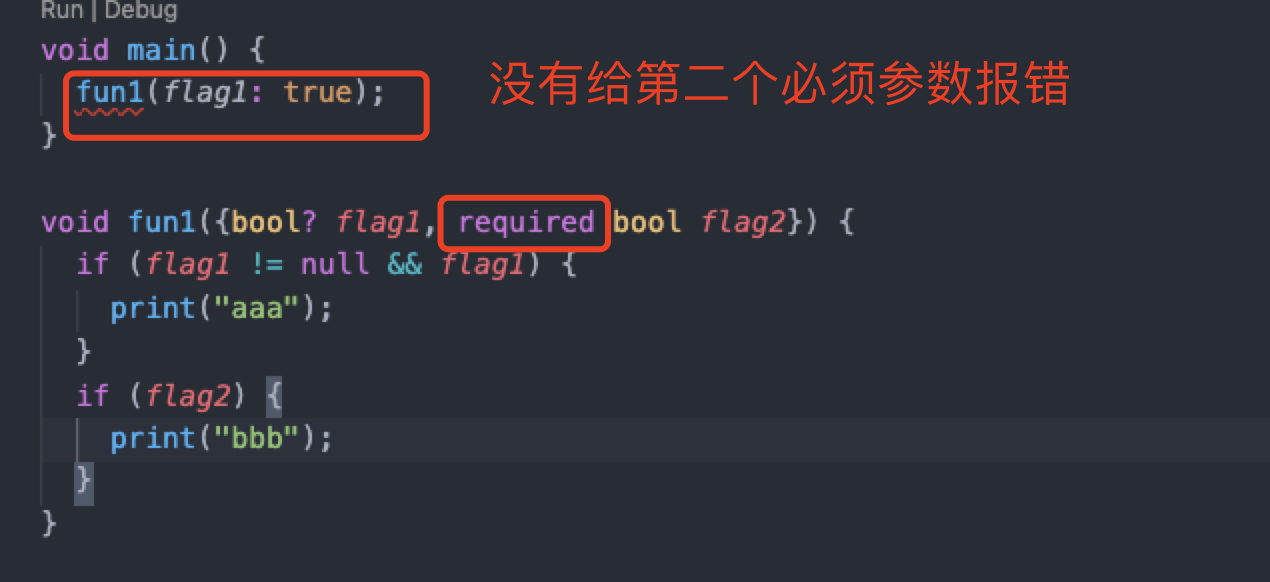
When defining a function, use {parm1,param2,...} to specify named parameters, such as:
void fun1( {bool? flag1, bool? flag2} ){
...
}
When calling the function, use the specified named parameter paramname: value. For example:
fun1(flag1 : true, flag2 : false);
example:
void main() {
fun1(flag1: true, flag2: false);
}
void fun1({bool? flag1, bool? flag2}) {
if (flag1 != null && flag1) {
print("aaa");
}
if (flag2 != null && !flag2) {
print("bbb");
}
}
When you use required to represent a parameter, you must specify the named parameter of the property
4. Default value parameter
When defining the 2 and 3 methods above, you can use = to define the default value of optional parameters. The default value can only be a compile time constant. If no default value is provided, the default value is null
void main() {
String str = say("Zhang San", "ha-ha", "hehe");
print(str);
String str1 = say("Zhang San", "ha-ha");
print(str1);
}
String say(String from, String msg, [String device = 'oo']) {
var result = '$from says $msg';
result = '$result with a $device';
return result;
}
void main() {
fun1();
}
void fun1({bool? flag1, bool flag2 = true}) {
if (flag2) {
print("bbb");
}
}
5. A method that takes a method as a parameter
void main() {
fun1(fun2);
}
fun1(fn) {
fn();
}
fun2() {
print("aaaa");
}
6. Arrow function
void main() {
List l1 = ['az', 'ss'];
//Only one line of code is allowed after the arrow function to simplify the code
l1.forEach((element) => {print(element)});
l1.forEach((element) =>print(element));
}
7. Self executing method
void main() {
//Self executing method ((formal parameter) {}) (argument)
((int n) {
print(n);
print(123);
})(12);
}
8. Closure
Closure:
1. Characteristics of global variables: global variables reside in memory, and global variables pollute the global
2. Local variable features: it is not resident in memory, will be recycled by garbage mechanism, and will not pollute the global environment
Functions to be realized:
1. Resident memory
2. No pollution
Closures are generated, and closures can solve this problem
Closure: functions are nested functions. Internal functions will call variables or parameters of external functions. Variables or parameters will not be recycled by the system
How to write closures: functions nest functions, and the functions in return form closures
void main() {
fn() {
var a = 123;
return () {
print(a);
};
}
var b = fn();
b();
}
2, Object oriented
Object oriented programming( OOP)The three basic characteristics of are encapsulation, inheritance and polymorphism dart Everything is an object, and all objects inherit from Object class dart Is an object-oriented language that uses class and singleton inheritance. All objects are instances of classes, And all classes are Object Subclass of A class usually consists of properties and methods
3, Class
1. Declaration and instantiation
void main() {
//Instantiation class
Person person = new Person();
person.getInfo();
print(person.name);
}
//Declaration class
class Person {
String name = 'zs';
int age = 23;
void getInfo() {
print("${this.age}----${this.name}");
}
}
2. Default constructor
void main() {
Person person = new Person("zs", 12);
person.getInfo();
print(person.name);
}
class Person {
String? name;
int? age;
//The default constructor can be abbreviated as Person(this.name,this.age);
Person(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
void getInfo() {
print("${this.age}----${this.name}");
}
}
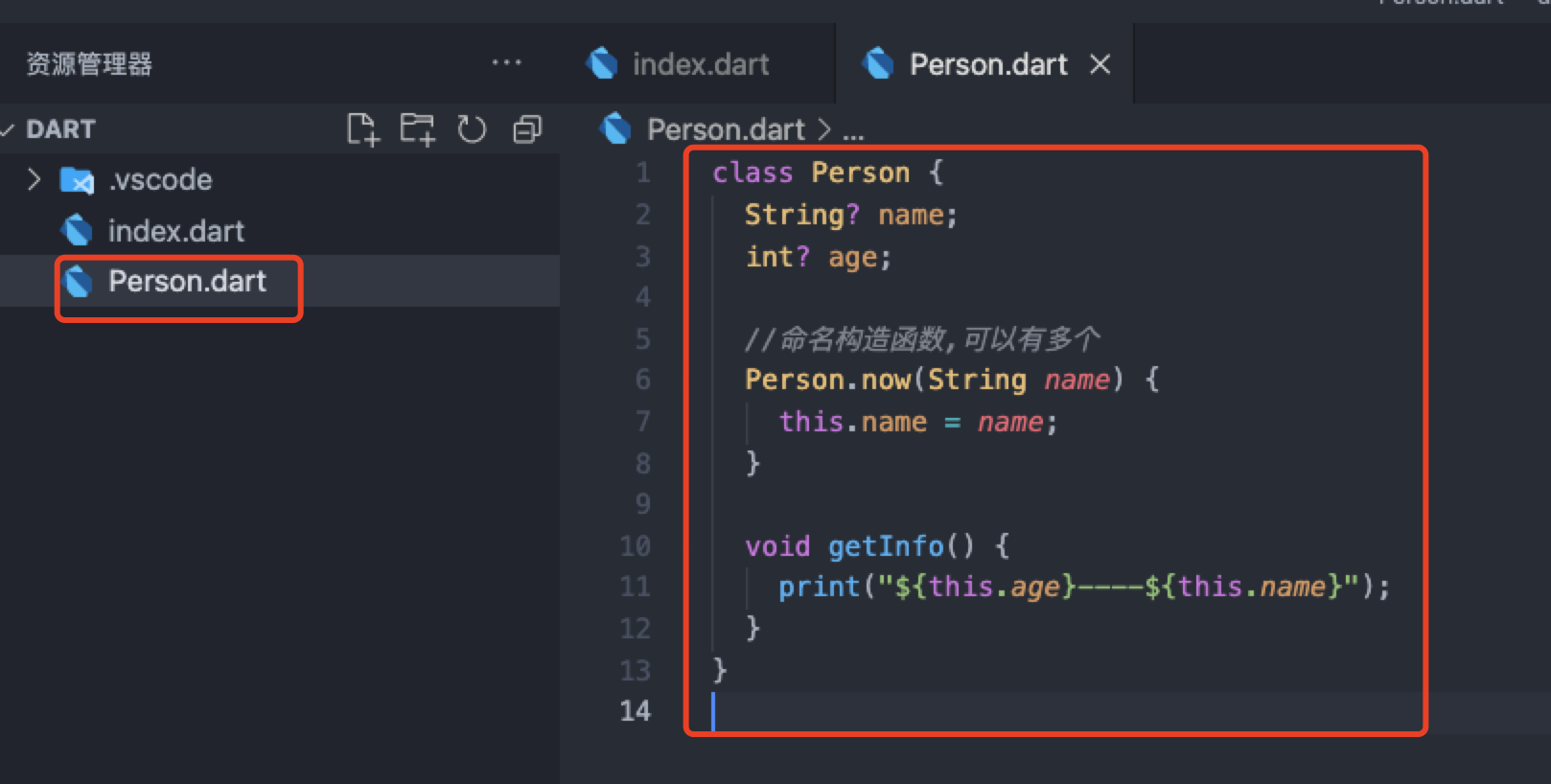
3. Named constructor
void main() {
Person p = new Person.now("ls");
print(p.name);
}
class Person {
String? name;
int? age;
//Named constructor, can have multiple
Person.now(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
void getInfo() {
print("${this.age}----${this.name}");
}
}
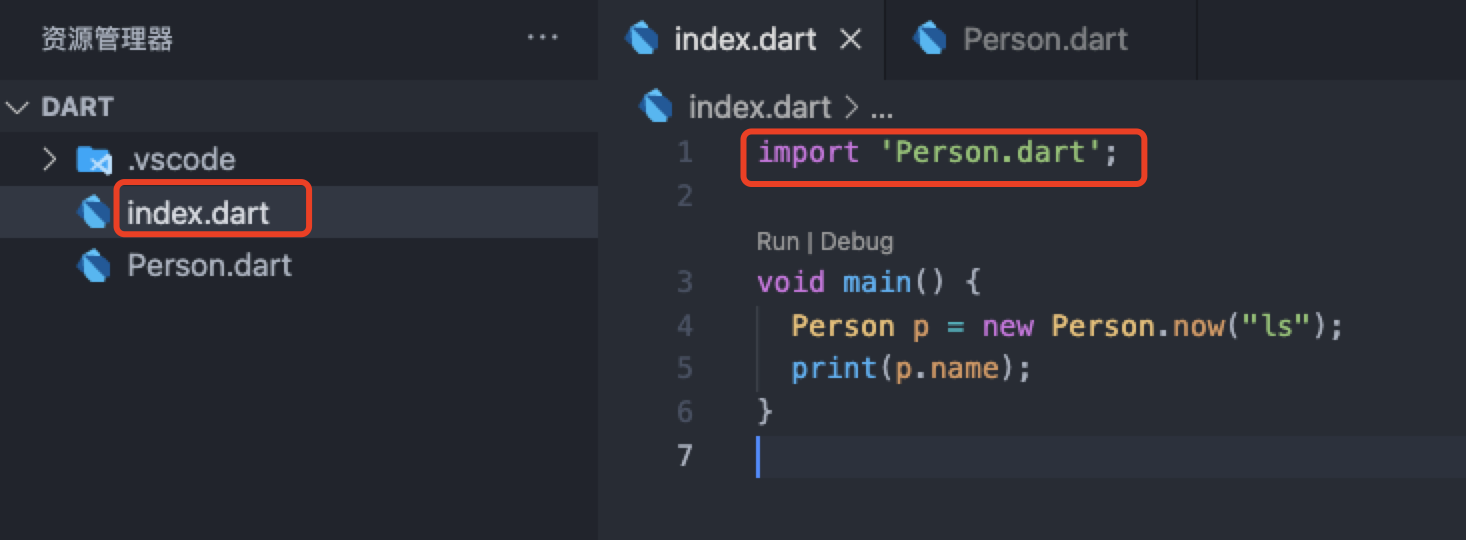
4. Extraction class and import class
5. Private methods, properties
Unlike java, dart does not have public and private access modifiers
But you can use "" Define a property or method as private. If private is to work, you need to extract the class like (4) above
Person.dart
class Person {
String? _name; //Private property
int? age;
Person(this._name, this.age);
String? getName() {
return this._name;
}
//Private method
void _run() {
print("Private method");
}
void execRun() {
this._run();
}
}
Index.dart
import 'Person.dart';
void main() {
Person p = new Person("ls", 12);
print(p.getName());
p.execRun();
}
6,setter,getter
Rect.dart
class Rect {
num height;
num width;
Rect(this.height, this.width);
//The normal method has the same effect as the getter below
num area1() {
return this.height * this.width;
}
//Define getter method, getter method has no ()
get area {
return this.height * this.width;
}
//Define setter method
set areaHeight(value) {
this.height = value;
}
}
Index.dart
import 'Person.dart';
import 'Rect.dart';
void main() {
Rect rect = new Rect(1, 3);
//Using Getters
print("use getter method:");
print("The area is: ${rect.area}");
//Using the setter method ============================================ this is different from java
rect.areaHeight = 2;
//Use common methods
print("Use common methods:");
print(rect.area1());
}
4, Static
Static members in Dart:
1. Use the static keyword to implement class level variables and functions
2. Static methods cannot access non static members. Non static methods can access static members
void main() {
Person.name; //Call static properties
Person.show(); //Call static method
Person person = new Person();
person.printInfo(); //Call non static method
}
class Person {
static String name = "Zhang San"; //Static properties
int age = 20; //Non static attribute
//Static method
static void show() {
print(name);//Static methods can access static properties, not non static properties and methods
}
//Non static method, which can access static members and non static members
void printInfo() {
print(name); //Accessing static properties
print(this.age); //Accessing non static properties
show(); //Call static method
}
}
5, Object operator
1. Is (type judgment)
void main() {
Person person = new Person();
if (person is Person) { //Type judgment
print("true");
}
person.printInfo();
}
class Person {
String name = "Zhang San";
int age = 20;
void printInfo() {
print(this.age);
}
}
2. As (type conversion)
void main() {
Person person = new Person();
(person as Person).printInfo(); //Cast type
}
class Person {
String name = "Zhang San";
int age = 20;
void printInfo() {
print(this.age);
}
}
3,. . (cascade operation (concatenation))
void main() {
Person person = new Person();
// person.name = "ls";
// person.age = 30;
// person.printInfo();
//The above code can be written in the following way
person
..name = "ls"
..age = 30
..printInfo();
}
class Person {
String name = "Zhang San";
int age = 20;
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
6, Inherit
Inheritance of classes in Dart:
1. The subclass uses the extends keyword to inherit the parent class
2. The subclass will inherit the properties and methods visible in the parent class, but will not inherit the constructor
3. The subclass can duplicate the method getter and setter of the parent class
void main() {
Web w = new Web();
print(w.age);
w.printInfo();
}
class Person {
String name = "Zhang San";
int age = 20;
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
//inherit
class Web extends Person {
}
1. super keyword
void main() {
Web w = new Web("zs", 23);
print(w.age);
w.printInfo();
}
class Person {
String? name;
int? age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person {
Web(String? name, int? age) : super(name, age);
}
2,@overried
void main() {
Web w = new Web("zs", 23);
print(w.age);
w.printInfo();
}
class Person {
String? name;
int? age;
Person(this.name, this.age);
void printInfo() {
print("${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
class Web extends Person {
Web(String? name, int? age) : super(name, age);
@override
void printInfo() {
print("Override parent method----${this.name}---${this.age}");
}
}
7, Abstract class
Abstract classes in Dart: Dart abstract classes are mainly used to define standards. Subclasses can inherit abstract classes or implement abstract class interfaces
1. Abstract classes are defined by the abstract keyword
2. Abstract methods in Dart cannot be declared with abstract. Methods not mentioned in Dart are called abstract methods
3. If the subclass inherits the abstract class, it must implement the abstract methods inside
4. If an abstract class is implemented as an interface, all properties and methods defined in the abstract class must be implemented
5. An abstract class cannot be instantiated. Only subclasses that inherit it can be instantiated
Differences between extensions abstract class and implements:
1. If you want to take the methods in the abstract class and use the abstract method to constrain the subclasses, use extensions to inherit the abstract class
2. If we only take abstract classes as the standard, we will use implents to implement abstract classes
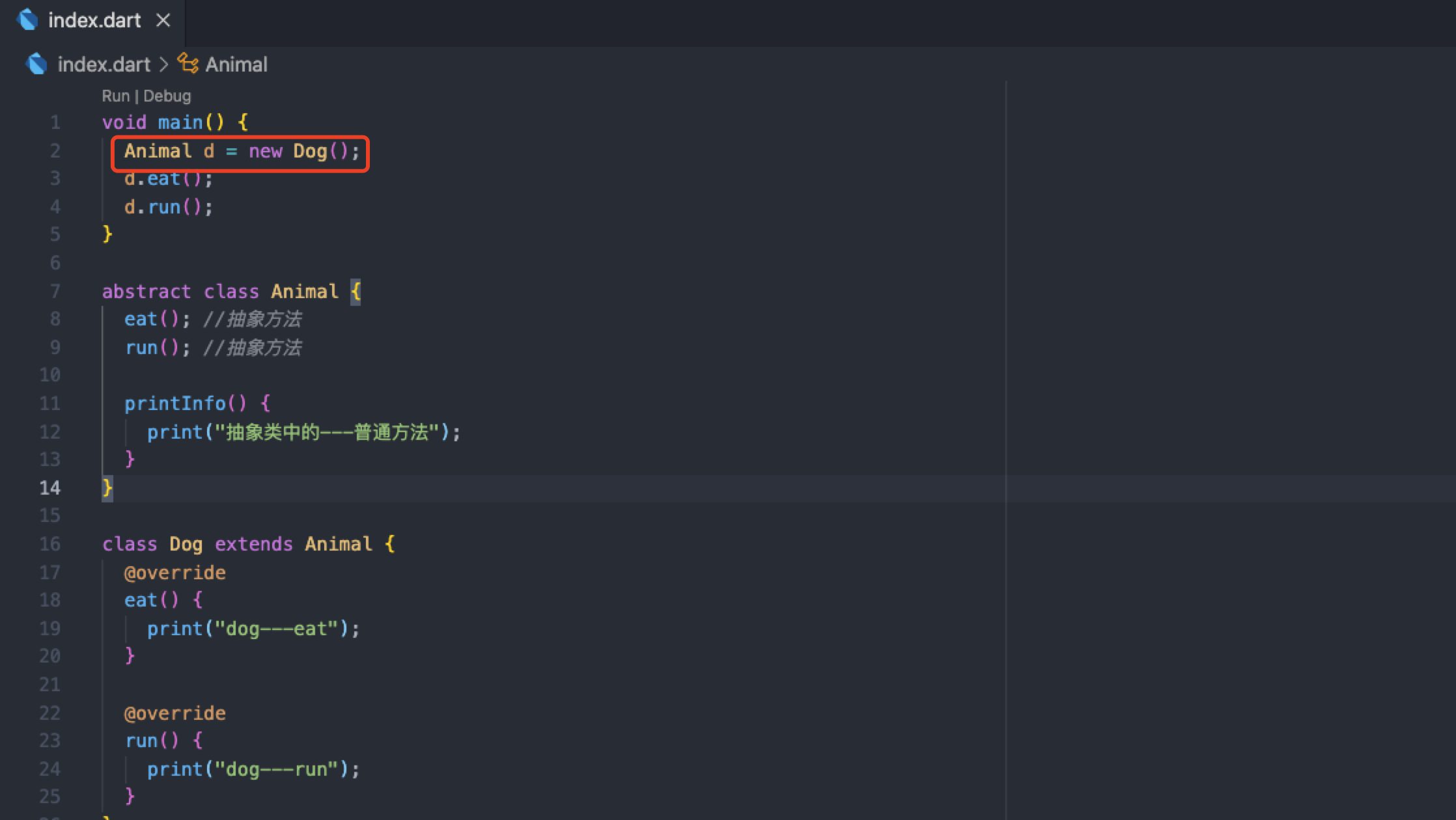
void main() {
Dog d = new Dog();
d.eat();
d.run();
}
abstract class Animal {
eat(); //Abstract method
run(); //Abstract method
printInfo() {
print("In abstract classes---Common method");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@override
eat() {
print("dog---eat");
}
@override
run() {
print("dog---run");
}
}
8, Polymorphism
Polymorphisms in Dart:
It is allowed to assign the pointer of the subclass type to the pointer of the parent type. The same function call will have different execution effects
An instance of a subclass is assigned a reference to the parent class
Polymorphism means that the parent class defines a method not to be implemented, and lets the subclasses that inherit it implement it. Each subclass has a different implementation
9, Interface
Like java, dart also has interfaces, but it is different from java:
1. The interface of dart does not have the interface keyword to define the interface, but ordinary classes or abstract classes can be implemented as interfaces
It is also implemented using the implements keyword
2. If the implemented class is an ordinary class, all the properties and methods in the ordinary class will need to be copied again
3. Because abstract classes can define abstract methods, but ordinary classes cannot, it is recommended to use abstract classes to define interfaces
abstract class Animal {
eat(); //Abstract method
run(); //Abstract method
printInfo() {
print("In abstract classes---Common method");
}
}
class Person {
String? name;
void run() {
print("run");
}
}
//Multiple implementation
class A implements Person , Animal{
@override
String? name;
@override
void run() {
// TODO: implement run
}
@override
eat() {
// TODO: implement eat
throw UnimplementedError();
}
@override
printInfo() {
// TODO: implement printInfo
throw UnimplementedError();
}
}
class Dog implements Animal {
@override
eat() {
// TODO: implement eat
throw UnimplementedError();
}
@override
printInfo() {
// TODO: implement printInfo
throw UnimplementedError();
}
@override
run() {
// TODO: implement run
throw UnimplementedError();
}
}
10, mixin mixing
mixin in Chinese means mixing in, which means mixing in other functions in the class
In Dart, you can use mixin to implement functions similar to multi inheritance
Conditions for using mixin:
1. A mixin class can only inherit from Object and cannot inherit from other classes
2. A class as a mixin cannot have a constructor
3. One class can mixin multiple mixin classes
4. mixin is neither inheritance nor interface, but a new feature
void main() {
C c = new C();
c.printA();
c.printB();
}
class A {
void printA() {
print("A");
}
}
class B {
void printB() {
print("B");
}
}
class C with A, B {}