RFM model is an important tool and means of Hengxing's customer value and profitability.Describe a customer's value by three indicators: his recent purchasing behavior, the overall frequency of purchases, and how much he spent.
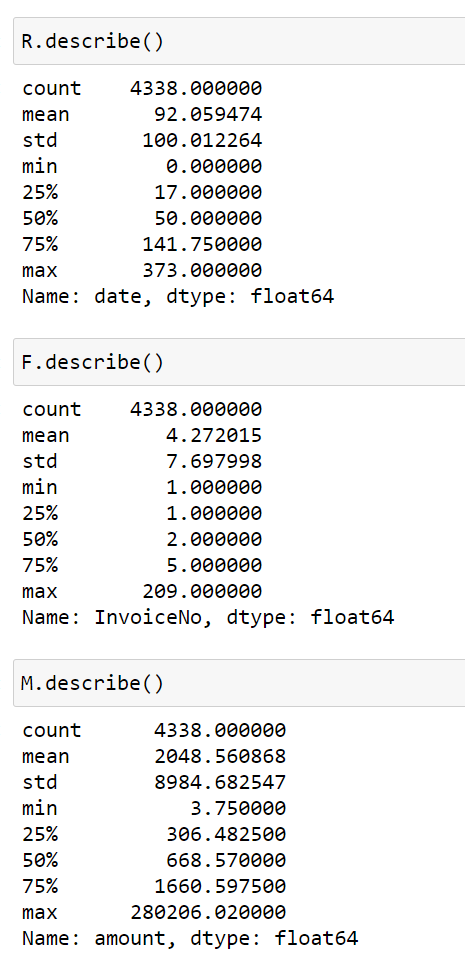
< R: Last consumption time (interval from last consumption to reference time)
F: Frequency of consumption
# M: Amount consumed (total consumption amount)
Data cleaning
data format
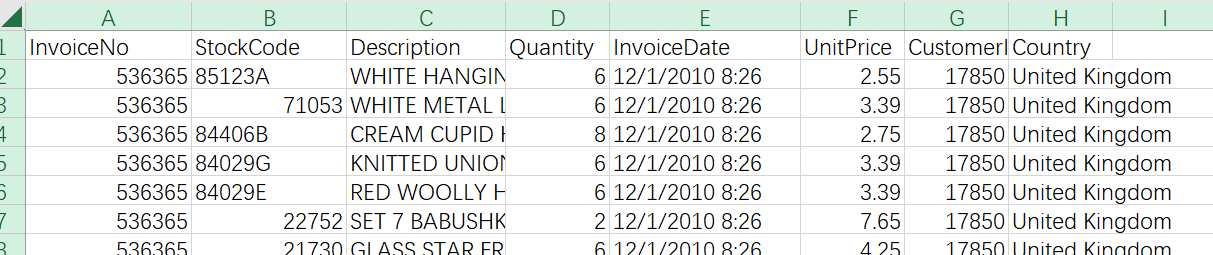
- InvoiceNo: Order number, 6 integers per transaction, return order number begins with the letter'C'.
- StockCode: The product number, which consists of five integers.
- Description: Product description.
- Quantity: Number of products, minus sign means return
- InvoiceDate: Order date and time.
- UnitPrice: Price per unit (pound sterling), price per unit product.
- CustomerID: Customer number. Each customer number consists of five digits.
- Country: Name of country, name of country/region where each customer is located.
df.shape
(541909, 8)
df.info()
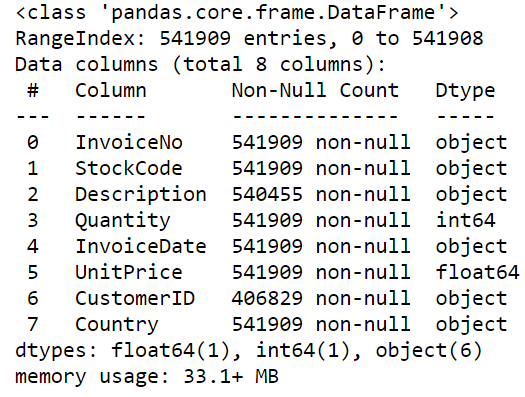
Missing Statistics Rate
df.apply(lambda x:sum(x.isnull())/len(x),axis=0)

Item descriptions don't do much to directly delete this column, then delete rows with missing user IDs
df.drop(['Description'],axis=1,inplace=True)
# how {‘Any','all'}, default'any', any: delete lines with nan;All: delete all NANs rows
df = df.dropna(how='any')
Data Standardization
#Increase Total Purchase Amount = Quantity * Amount
df['amount']= df['Quantity']*df['UnitPrice']
#Order date slicing
df['data']=[x.split(' ')[0] for x in df['InvoiceDate']]
df['time']=[x.split(' ')[1] for x in df['InvoiceDate']]
df.drop(['InvoiceDate'],axis=1,inplace=True)
df['year']=[x.split('/')[2] for x in df['data']]
df['month']=[x.split('/')[0] for x in df['data']]
df['day']=[x.split('/')[1] for x in df['data']]
#Convert date format
df['date'] = pd.to_datetime(df['data'])
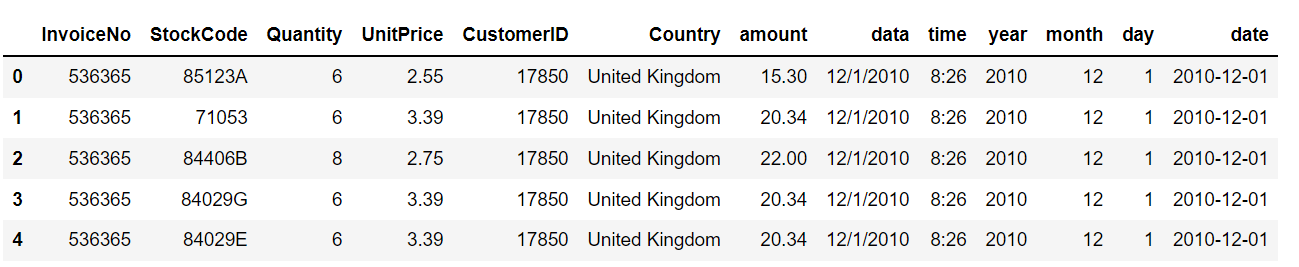
df.head()
Delete duplicate data
df = df.drop_duplicates()
Observe if there are outliers
df.describe()
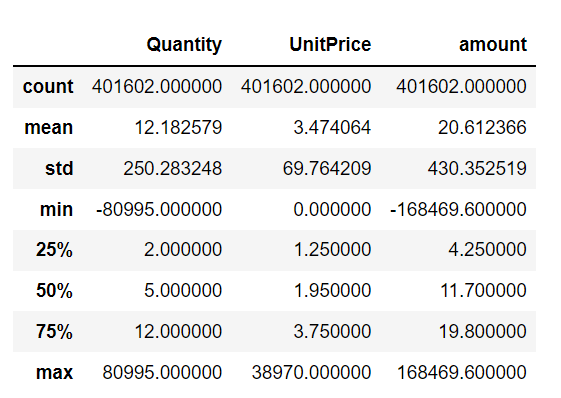
There are returned orders and items with a price of 0 (possibly gifts)
Return order percentage
df1 = df.loc[df['Quantity'] <= 0] print(df1.shape[0]/df.shape[0])
0.022091523448588404
Price is 0 commodity ratio
df2 = df.loc[df['UnitPrice'] <= 0] print(df2.shape[0]/df.shape[0])
0.0000996010976040956
Price is 0 number of items
df2['UnitPrice'].groupby(df2['UnitPrice']).count()
UnitPrice
0.0 40
Name: UnitPrice, dtype: int64
Calculate Return Rate
Number of returns/total orders
t_num = df1['Quantity'].sum() sale_num = df[df['Quantity']>0]['Quantity'].sum() t_rate = abs(t_num/sale_num) print(t_rate)
0.05285657011028571
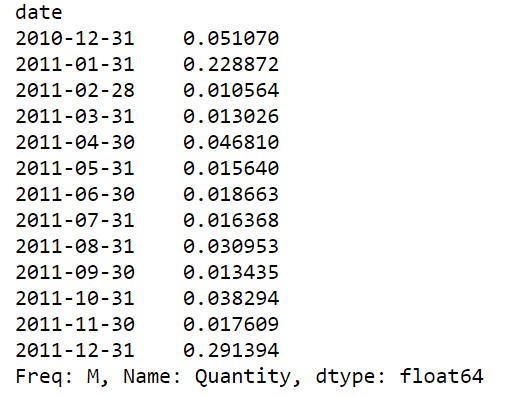
Monthly return rate
tt = df1.groupby(df1['date'])['Quantity'].sum()
tt = tt.resample('M').sum()
sale = df[df['Quantity']>0].groupby(df['date'])['Quantity'].sum()
sale = sale.resample('M').sum()
rate = abs(tt/sale)
visualization
import plotly.express as px _y = rate.values _x = rate.index fig = px.line(rate, x=_x, y=_y) fig.show()
User Classification
df2 = df[(df['Quantity'] > 0)&(df['UnitPrice'] > 0)]
# Date of latest purchase
R_value=df2.groupby('CustomerID')['date'].max()
# Calculate customer's last consumption distance in days to deadline
R = (df2['date'].max()- R_value).dt.days
print(R)
print('-'*50)
#Customer consumption frequency, nunique:Number of calculations after weight removal
F = df2.groupby('CustomerID')['InvoiceNo'].nunique()
print(F)
print('-'*50)
#Customer consumption amount
M = df2.groupby('CustomerID')['amount'].sum()
print(M)
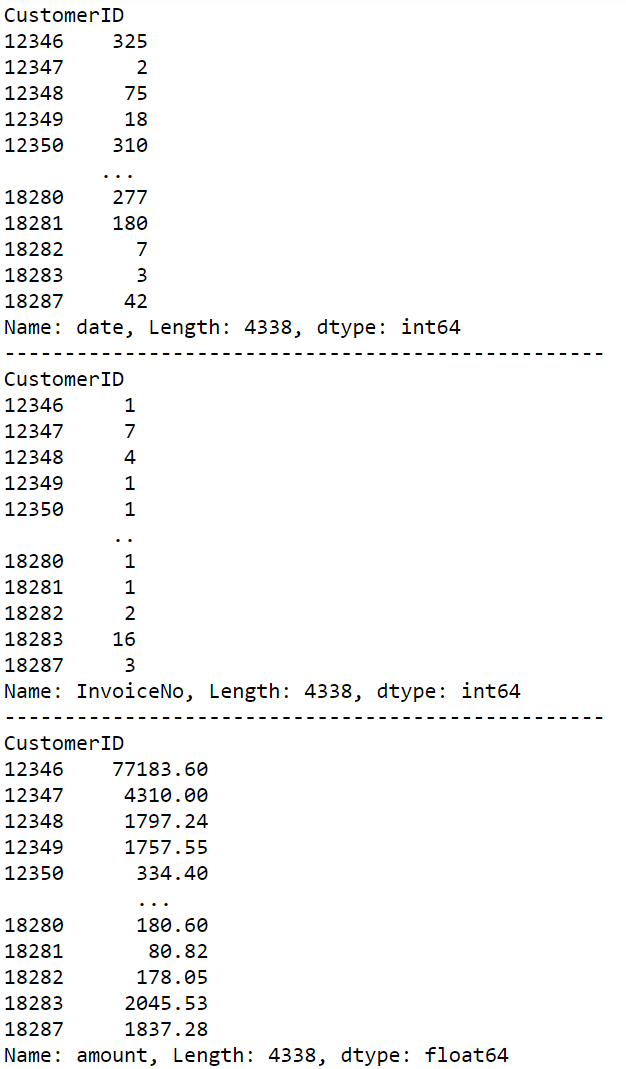
Find thresholds using describe() method
visualization
Visually display the distribution of data
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False plt.hist(R,bins =30) plt.show()
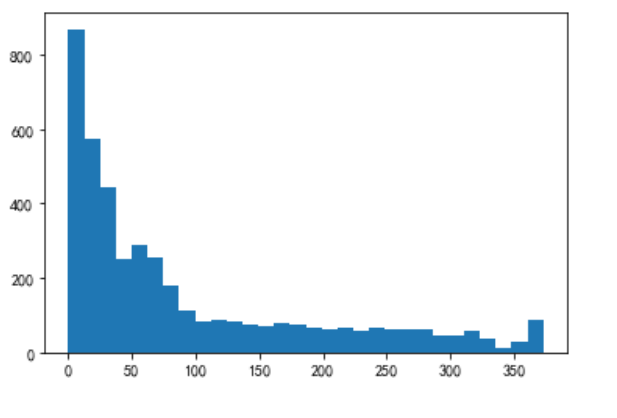
plt.hist(F,bins =30) plt.show()
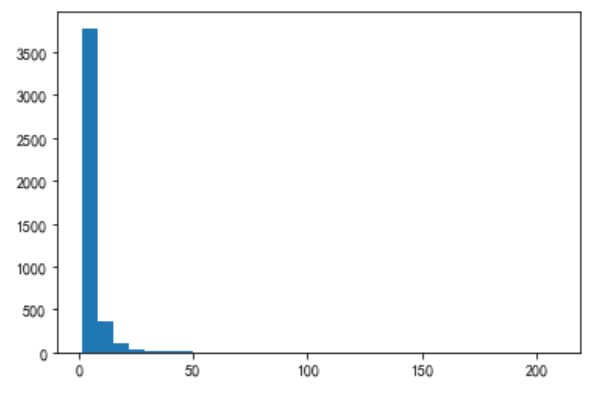
Visualization is not obvious affected by extreme values, observed within 10 days
print(F[F<10].count()/F.count()) plt.hist(F[F<10],bins =10) plt.show
0.9098662978331028
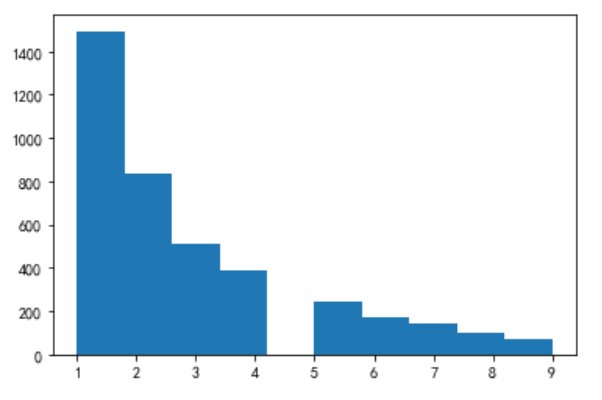
plt.hist(M,bins =30) plt.show
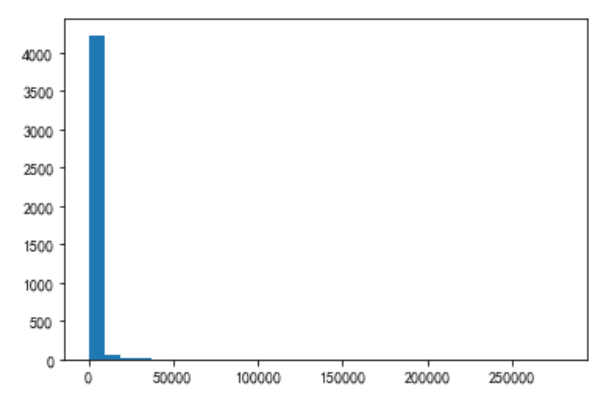
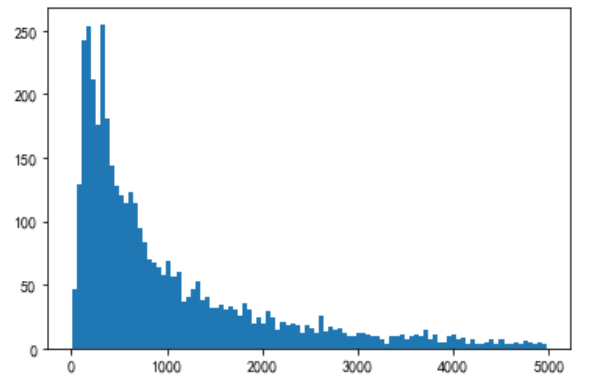
print(M[M<5000].count()/M.count()) plt.hist(M[M<5000],bins=100) plt.show()
0.9368372521899493
Calculate rfm score
pd.cut() Inter-Zonal Statistics
Divide the data according to the above RFM distribution
R_bins = [0,30,90,180,360,720] #Smaller is better F_bins = [1,2,5,10,20,500] #Larger is better M_bins = [0,500,2000,5000,10000,300000] #Larger is better R_score = pd.cut(R,R_bins, labels = [5,4,3,2,1], right=False) F_score = pd.cut(F,F_bins, labels = [1,2,3,4,5], right=False) M_score = pd.cut(M,M_bins, labels = [1,2,3,4,5], right=False)
Data consolidation
rfm = pd.concat([R_score,F_score,M_score],axis=1) print(rfm)
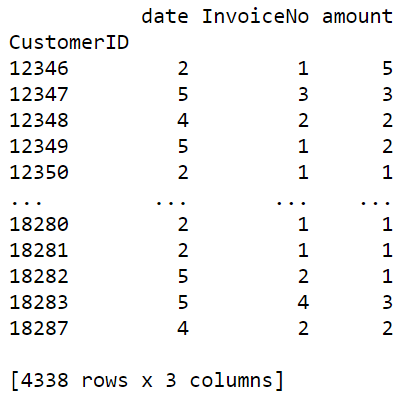
rfm.rename(columns={'date':'R_score','InvoiceNo':'F_score','amount':'M_score'},inplace = True)
Data Type Conversion
for i in ['R_score','F_score','M_score']:
rfm[i] = rfm[i].astype(float)
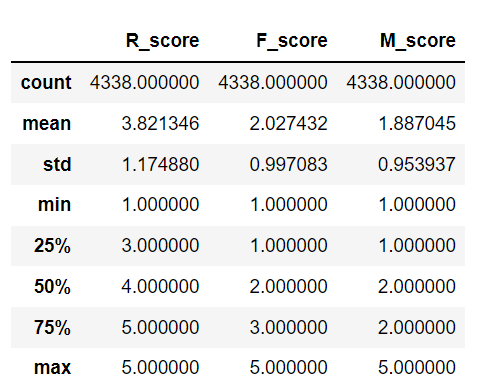
View RFM Score Information
rfm.describe()
Ranking
rfm['R'] = np.where(rfm['R_score']>3.82,'high','low') rfm['F'] = np.where(rfm['F_score']>2.03,'high','low') rfm['M'] = np.where(rfm['M_score']>1.89,'high','low') rfm['value'] = rfm['R'].str[:] + rfm['F'].str[:]+rfm['M'].str[:] # Remove whitespace rfm['value'] = rfm['value'].str.strip()
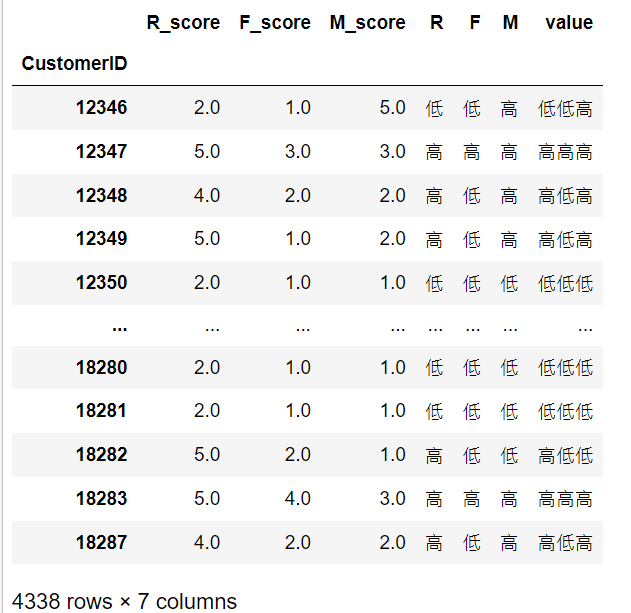
def trans_value(x):
if x=='High and High':
return 'Important Value Customer'
elif x =='High and low':
return 'Important Customer Development'
elif x =='Low High':
return 'Important customer retention'
elif x =='Low Low High':
return 'Important customer retention'
elif x == 'High or low':
return 'General Value Customer'
elif x =='High or low':
return 'General Customer Development'
elif x =='Low or low':
return 'Maintain customer in general'
else:
return 'Customer retention in general'
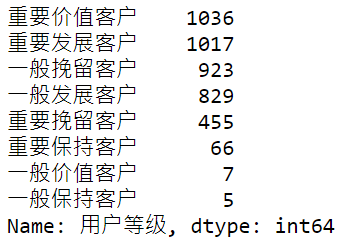
rfm['User Level'] = rfm['value'].apply(trans_value)
rfm['User Level'].value_counts()
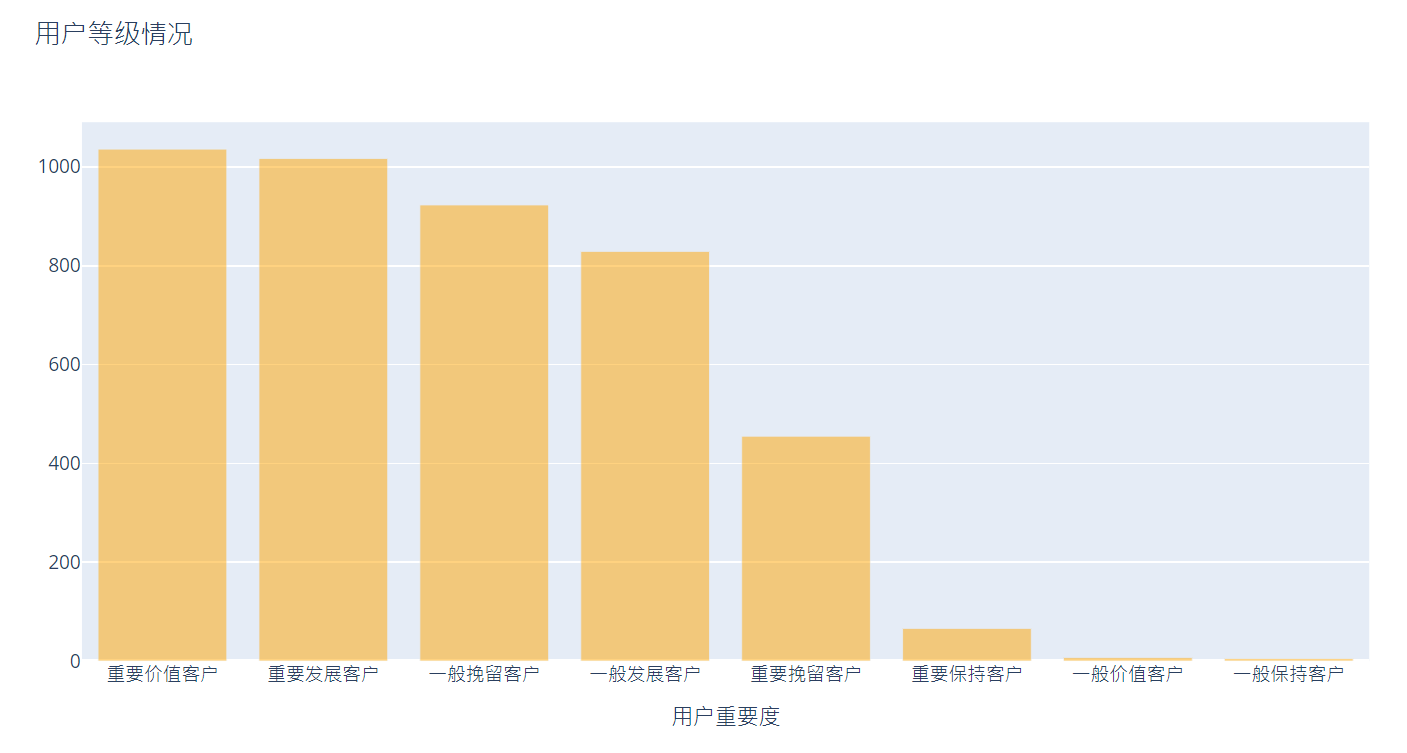
Visualize user level
trace_basic = [go.Bar(x =rfm['User Level'].value_counts().index.tolist(),
y =rfm['User Level'].value_counts().values.tolist(),
marker=dict(color='orange'),opacity=0.50)] #transparency
layout = go.Layout(title = 'User ratings',xaxis =dict(title ='User Importance'))
figure_basic = go.Figure(data = trace_basic,layout=layout)# data and layout form an image object
pyplot(figure_basic)
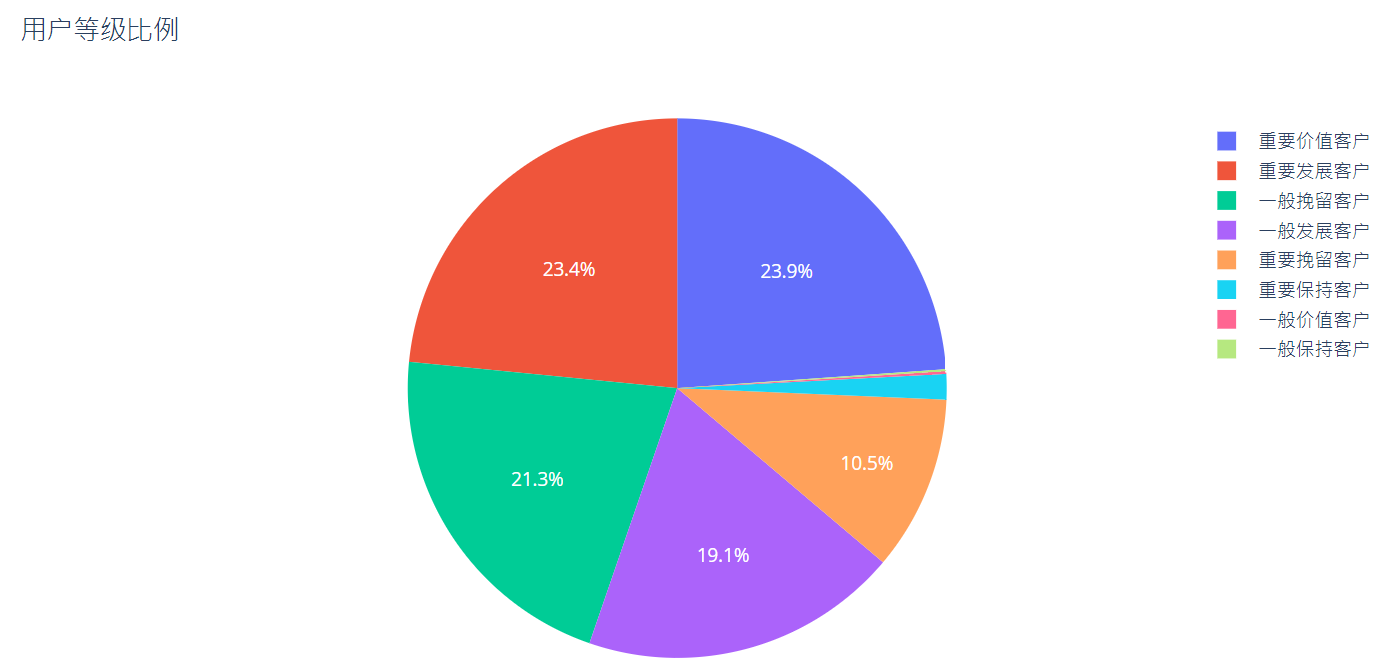
trace = [go.Pie(labels = rfm['User Level'].value_counts().index,values=rfm['User Level'].value_counts().values,
textfont =dict(size=12,color ='white'))]
layout = go.Layout(title ='User Rating Scale')
fig = go.Figure(data = trace,layout=layout)
pyplot(fig)