catalogue
The essence of variable identification in python
Comparison between single linked list and sequential list
Chapter III
Proposal of linked list
Linear list: sequential list + linked list
The sequential list is arranged in order, and the linked list is connected by lines (elements can be added or deleted at will)
The key point of linked list operation is to find out who is cut off first and who is connected again
Li=[200,400,600]
The three single linked list nodes are as follows:
| Data area | Link area | |
| 0×11 | 200 | 0×34 |
| Data area | Link area | |
| 0×34 | 400 | 0×88 |
| Data area | Link area | |
| 0×88 | 600 | None |
The essence of variable identification in python
What data type is the address in python?
a = 10
b = 20
a. B = B, a (only the address in a,b storage unit is changed)
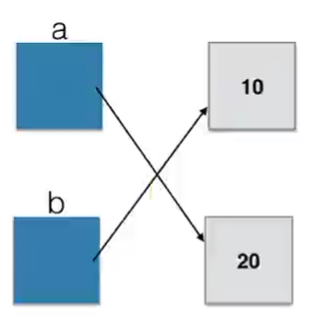
a and b are storage units, which store the addresses of the two values of 10 and 20
In python, = is the link that generates a reference
Single linked list
Unidirectional linked list means that the arrow direction must point from the previous node to the next node (data area + subsequent node)
The first node is called the head node and the last node is called the tail node (empty)
Each cell (node) in the single linked list has two parts, one is the element and the other is the identification of the next node
class SingleNode(object):
def __init__(self,item):
"""Node of single linked list"""
self.item = item # _ item stores data elements
self.next = None # _ Next is the identification of the next nodeThe basic operation will have two classes, one is the node class and the other is the linked list class
is_empty()Is the linked list empty length()Linked list length travel()Traverse the entire linked list: you can print out each node in the linked list add(item)Add elements to the head of the linked list append(item)Add elements at the end of the linked list insert(pos,item)Add element at specified location remove(item)Delete node---Delete the first element found from the column header search(item)Find whether the node exists
| __head | __head.next | ||||
| 100 | 20 | " " | 300 | None |
# coding:utf-8
class Node(object):
""""Class of node"""
def __init__(self,elem):
self.elem = elem
self.next = None
pass
# node = Node(100)
class SingleLinkList(object):
"""Class of single linked list"""
def __init__(self,node=None):
self.__head = node # Private attribute headers that are not exposed to the outside world__
def is_empty(self): # These are all object operations self
"""Is the linked list empty"""
return self.__head == None #Judged to be empty
def length(self):
"""Linked list length"""
cur = self.__head # cur cursor, used to move traversal nodes
count = 0 # Number of Records last
while cur != None: # cur is not equal to None
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count
def travel(self):
"""Traverse the entire linked list"""
cur = self.__head
while cur != None:
print(cur.elem,end=' ') # In python3, end = '' means that line wrapping is prohibited -- in python2, just use it
cur = cur.next
# print("") #Line feed
def add(self,item): # Back pass parameters required
"""Add elements to the head of the linked list, head insertion method"""
node = Node(item) #First construct the node to insert
node.next = self.__head #Let the tail of the node point to the head of the original linked list
self.__head = node
def append(self,item):
"""Add elements at the end of the linked list"""
node = Node(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head = node # First judge whether the linked list is empty. If it is empty, the_ head points to the new node
else:
cur = self.__head # If it is not empty, find the tail and point the next of the tail node to the new node
while cur.next != None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
def insert(self,pos, item):
"""Add element at specified location
:param pos Index from 0
"""
if pos <= 0:
self.add(item)
elif pos > (self.length()-1):
self.append(item)
else:
node = Node(item)
pre = self.__head # piror
count = 0
while count < (pos-1):
pre = pre.next
count +=1
# When the cycle is pushed out, pre points to pos-1
node.next = pre.next
pre.next = node
def remove(self,item):
"""Delete node"""
cur = self.__head
pre = None
while cur != None:
if cur.elem == item:
# First judge whether this node is the head node
if cur == self.__head:
self.__head = cur.next
else:
pre.next = cur.next
break #Exit the loop after deletion
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
def search(self,item):
"""Find whether the node exists"""
cur = self.__head
while cur != None: #cur is not equal to none before entering the cycle
if cur.elem == item:
return True
else:
cur = cur.next
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
ll = SingleLinkList()
print(ll.is_empty())
print(ll.length())
ll.append(1)
print(ll.is_empty())
print(ll.length())
ll.append(2)
ll.add(8)
ll.append(3)
ll.append(4)
ll.insert(-1,9)
ll.insert(2,100)
ll.insert(10,200)
ll.travel()
print("")
print(ll.search(100))
ll.remove(9)
ll.travel()Successor node: the next node of the current node
To traverse, you need to use the loop while
Comparison between single linked list and sequential list
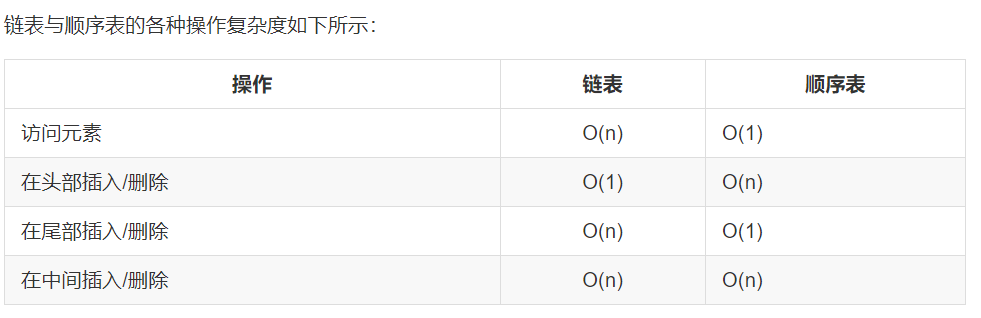
The linked list cannot be located to pos at one time and needs to be cycled. The sequence table can be located at one time.
The nodes of the linked list can be dispersed in memory, but the time complexity is high. The space of the sequential table must be continuous, and it is necessary to re apply for space when the storage space of the sequential table is insufficient.
Bidirectional linked list
The nodes in a two-way linked list are different from those in a single linked list. In addition, the location of the previous nodes is saved. As follows:
Precursor node + data area + successor node
The code of the class can be encapsulated. When building a new class later, the previous class can be regarded as an object to achieve class inheritance
class Node(object):
def __init__(self,item):
self.elem = item
self.next = None
self.prev = None
class DoubleLinkList(object):
def __init__(self,node=None):
self.__head = node
def is_empty(self):
"""Is the linked list empty"""
return self.__head is None
def length(self):
"""Linked list length"""
cur = self.__head
count = 0
while cur != None:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count
def travel(self):
"""Traverse the entire linked list: you can print out each node in the linked list"""
cur = self.__head
while cur != None:
print(cur.elem,end=" ")
cur = cur.next
def add(self,item):
"""Add elements to the head of the linked list"""
node = Node(item)
node.next = self.__head
self.__head = node # self.__head.prev = node self.__head = node is also OK
node.next.prev = node
def append(self,item):
"""Add elements at the end of the linked list"""
node = Node(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head = node
else:
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != None:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
node.prev = cur
def insert(self,pos, item):
"""Add element at specified location"""
if pos <=0: #Count from 0
self.add(item)
elif pos > (self.length()-1):
self.append(item)
else:
cur = self.__head
count = 0
while count < pos :
count +=1
cur = cur.next
node = Node(item)
node.next = cur
node.prev = cur.prev
cur.prev.next = node
cur.prev = node
def remove(self,item):
"""Delete node - --Delete the first element found from the column header"""
cur = self.__head
while cur != None:
if cur.elem == item:
if cur == self.__head:
self.__head = cur.next
if cur.next: #If cur If next exists, enter if, otherwise exit
# Determine whether the linked list has only one node
cur.next.prev = None
else:
cur.prev.next = cur.next
if cur.next:
cur.next.prev = cur.prev
break
else:
cur = cur.next
def search(self,item):
"""Find whether the node exists"""
cur = self.__head
while cur != None:
if cur.elem == item:
return True
else:
cur = cur.next
return False
if __name__ == "__main__" :
dll = DoubleLinkList()
print(dll.is_empty())
print(dll.length())
dll.append(1)
print(dll.is_empty())
print(dll.length())
dll.append(2)
dll.add(8)
dll.append(9)
dll.append(3)
dll.append(4)
dll.insert(-1, 9)
dll.insert(2, 100)
dll.insert(10, 200)
dll.travel()
print("")
print(dll.search(100))
dll.remove(9)
dll.travel()One way circular linked list
Unidirectional circular linked list is a deformation of single linked list. The next of the last node in the linked list is no longer None, but points to the head node of the linked list.
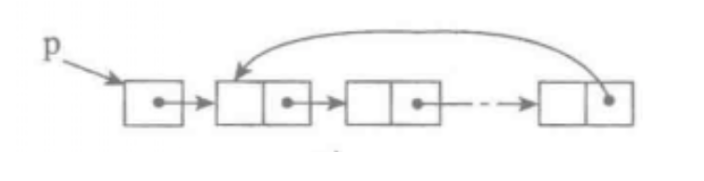
class Node(object):
def __init__(self,elem):
self.elem = elem
self.next = None
class SingleCycleLinkList(object):
def __init__(self,node=None):
self.__head = node
if node:
node.next = node
def is_empty(self):
"""Is the linked list empty"""
return self.__head == None
def length(self):
"""Linked list length"""
if self.is_empty():
return 0
cur = self.__head
count = 1
while cur.next != self.__head:
count += 1
cur = cur.next
return count
def travel(self):
"""Traverse the entire linked list: you can print out each node in the linked list"""
if self.is_empty():
return
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != self.__head:
print(cur.elem,end=" ")
cur = cur.next
print(cur.elem)
def add(self,item):
"""Add elements to the head of the linked list"""
node = Node(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head = node
node.next = node
else:
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != self.__head:
cur = cur.next
node.next = self.__head
self.__head = node
cur.next = self.__head # node
def append(self,item):
"""Add elements at the end of the linked list"""
node = Node(item)
if self.is_empty():
self.__head = node
node.next = node
else:
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != self.__head:
cur = cur.next
cur.next = node
node.next = self.__head
def insert(self,pos, item):
"""Add element at specified location"""
if pos <=0: #Count from 0
self.add(item)
elif pos > (self.length()-1):
self.append(item)
else:
node = Node(item)
pre = self.__head
count = 0
while count < (pos-1) :
pre = pre.next
count +=1
node.next = pre.next
pre.next = node
def remove(self,item):
"""Delete node - --Delete the first element found from the column header"""
if self.is_empty():
return
cur = self.__head
pre = None
while cur.next != self.__head:
if cur.elem == item:
if cur == self.__head:
# Head node
rear = self.__head
while rear.next != self.__head:
rear = rear.next
self.__head = cur.next
rear.next = self.__head
else:
# Intermediate node
pre.next = cur.next
return
else:
pre = cur
cur = cur.next
# Exit the loop and cur points to the tail node
if cur.elem == item:
if cur == self.__head:
self.__head = None
else:
pre.next = self.__head
def search(self,item):
"""Find whether the node exists"""
if self.is_empty():
return False
cur = self.__head
while cur.next != self.__head:
if cur.elem == item:
return True
else:
cur = cur.next
# Exit the loop and point to the tail node
if cur.elem == item:
return True
return False
if __name__ == "__main__":
ll = SingleCycleLinkList()
print(ll.is_empty())
print(ll.length())
ll.append(1)
print(ll.is_empty())
print(ll.length())
ll.append(2)
ll.add(8)
ll.append(9)
ll.append(3)
ll.append(4)
ll.insert(-1, 9)
ll.insert(2, 100)
ll.insert(10, 200)
ll.travel()
print("")
print(ll.search(100))
ll.remove(9)
ll.travel()