1, Perfect binary tree
It is also called full binary tree, that is, except for the leaf node of the last level, each node has two child nodes
2, Complete binary tree
Two conditions need to be met:
(1) Except for the last layer, the number of nodes in other layers reaches the maximum
(2) The nodes of the last layer are concentrated on the left, and the nodes are continuous. Only the right part can be missing nodes
3, Storage of binary tree
When using binary tree to store data, we have two options: array storage and linked list storage.
(1) Array storage
When using arrays for storage, in order to distinguish the relationship between various nodes, we will complete the tree into a full binary tree, but it will cause a waste of space.
(2) Linked list storage
Each node is packaged as an object and points to its left child node and right child node respectively through left and right, which avoids the waste of space and has clear regulations.
4, What is a binary lookup tree
Also known as binary sort tree and binary search tree. When the binary lookup tree is not empty, the following three conditions must be met:
(1) The key of the node of the non empty left subtree is less than the key of its root node
(2) The key of the node of the non empty right subtree is greater than the key of its root node
(3) The left subtree and the right subtree are also binary search trees
5, Traversal of tree
(1) Preorder traversal
Access root node = > access left subtree = > access right subtree. When accessing the left or right subtree, continue to access according to this rule.
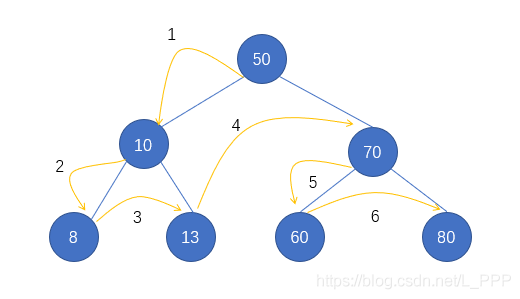
(2) Middle order traversal
Access left subtree = > access root node = > access right subtree. When accessing the left or right subtree, continue to access according to this rule.
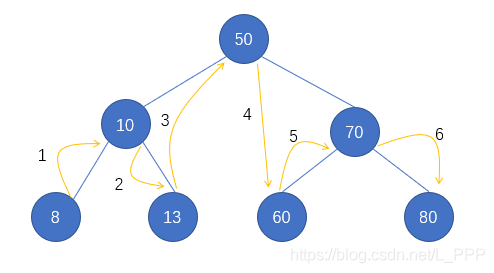
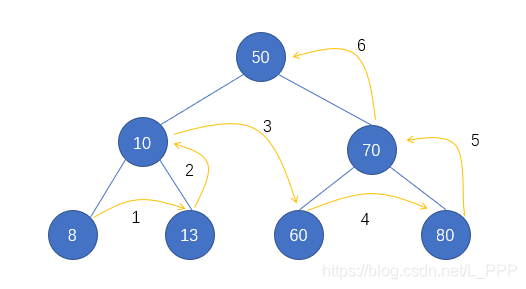
(3) Subsequent traversal
Access left subtree = > access right subtree = > access root node. When accessing the left or right subtree, continue to access according to this rule.
6, API design
6.1 node class
| Class name | Node<Key,Value> |
|---|---|
| Construction method | Node (key, value, node left, node right): creates a node object |
| Member variable | 1.public Node left: records the left child node 2.public Node right: record the right child node 3. Public key: storage key 4. Public value: store value |
6.2 binary lookup tree class
| Class name | BinaryTree<Key key,Value value> |
|---|---|
| Construction method | BinaryTree(): creates a BinaryTree object |
| Member variable | 1.private Node root: records the root node 2.private int N: number of elements in the record tree |
| Member method | 1. Public void put (key, value): insert a key value pair into the tree 2. Public value get (key): find the corresponding value from the tree according to the key 3. Public void delete (key): delete the corresponding key value pair in the tree according to the key 4.public int size(): get the number of elements in the tree |
6.3 method and realization idea
6.3.1 add
1. If there is no node in the current tree, the new node is directly used as the root node
2. If the current tree is not empty, start from the root node:
2.1 if the key of the new node is less than the key of the current node, continue to find the left child node of the current node.
2.2 if the key of the new node is greater than the key of the current node, continue to find the right child node of the current node.
2.3 if the key of the new node is equal to the key of the current node, such a node already exists in the tree. Replace the value value of the node.
6.3.2 check
Starting from the root node:
1. If the key to be queried is less than the key of the current node, continue to find the left child node of the current node;
2. If the key to be queried is greater than the key of the current node, continue to find the right child node of the current node;
3. If the key to be queried is equal to the key of the current node, the book returns the value of the current node.
6.3.3 deletion (the new order after deletion needs to be considered)
1. Find the deleted node;
2. Find the smallest node minNode in the right subtree of the deleted node
3. Delete the smallest node in the right subtree
4. Let the left subtree of the deleted node be called the left subtree of the minimum node minNode, and let the right subtree of the deleted node be called the right subtree of the minimum node minNode
5. Make the parent node of the deleted node point to the smallest node minNode
7, Code implementation
7.1 implementation of binary search tree
/**
* Binary lookup tree -- implementation of linked list
* @date 2021/5/20 14:26
*/
public class BinaryTree<Key extends Comparable<Key>, Value> {
// Root node
private Node root;
// Number of elements in the tree
private int N;
// constructor
public BinaryTree() {}
// increase
public void put(Key key, Value value){
// Start at the root node
root = put(root, key, value);
}
// Add key value to the specified tree x and return the new tree after adding elements
private Node put(Node x, Key key, Value value){
if(x == null){
N++;
return new Node(key, value, null, null);
}
int cmp = key.compareTo((Key) x.key);
if(cmp > 0){
// recursion
x.right = put(x.right, key, value);
}else if(cmp < 0){
x.left = put(x.left, key, value);
}else {
x.value = value;
}
return x;
}
// check
public Value get(Key key){
return get(root, key);
}
// From the specified tree x, find the value corresponding to the key
private Value get(Node x, Key key){
if(x == null){
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo((Key) x.key);
if(cmp > 0){// Larger than the current node, find the right
// recursion
return get(x.right, key);
}else if(cmp < 0){
return get(x.left, key);
}else {
return (Value) x.value;
}
}
// Delete
public void delete(Key key){
root = delete(root, key);
}
// Delete the value corresponding to the key in the specified tree x and return the deleted new tree
private Node delete(Node x, Key key){
if(x == null){
return null;
}
int cmp = key.compareTo((Key) x.key);
if(cmp > 0){
x.right = delete(x.right, key);
}else if(cmp < 0){
x.left = delete(x.left, key);
}else {
if(x.right == null){
return x.left; // ? Didn't you return to the new tree?
}
if (x.left == null){
return x.right;
}
Node minNode = x.right;
while (minNode.left != null){
minNode = minNode.left;
}
Node n = x.right;
while (n.left != null){
if (n.left.left == null){
n.left = null;
}else {
n = n.left;
}
}
minNode.left = x.left;
minNode.right = x.right;
x = minNode;
N--;
}
return x;
}
// Get the number of elements in the tree
public int size(){
return N;
}
}
7.2 other convenient methods of binary search tree
7.2.1 find the smallest key
// Find minimum key
public Key min(){
return (Key) min(root).key;
}
private Node min(Node x){
if(x.left != null){
return min(x.left);
}else {
return x;
}
}
7.2.2 find the largest key
// Find max key
public Key max(){
return (Key) max(root).key;
}
private Node max(Node x){
if(x.right != null){
return max(x.right);
}else {
return x;
}
}
7.3 basic traversal of binary tree
7.3.1 preorder traversal
// Preorder traversal
// Get all the keys of the specified tree and put them into the keys queue
private void preErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys){
if(x==null){
return;
}
// Root -- put the key of the x node into the keys
keys.enqueue((Key) x.key);
// Left subtree -- recursively traverses the left subtree of x node
if (x.left != null){
preErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
// Right subtree -- recursively traversing the right subtree of x node
if(x.right != null){
preErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
}
7.3.2 middle order traversal
// Middle order traversal
public Queue<Key> midErgodic(){
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
midErgodic(root, keys);
return keys;
}
private void midErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys){
if (x==null){
return;
}
// Left subtree -- recursively traverses the left subtree of x node
if (x.left!=null){
midErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
// Root -- put the key of the x node into the keys
keys.enqueue((Key) x.key);
// Right subtree -- recursively traversing the right subtree of x node
if (x.right != null){
midErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
}
7.3.3 subsequent traversal
// Postorder traversal
public Queue<Key> afterErgodic(){
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
afterErgodic(root, keys);
return keys;
}
private void afterErgodic(Node x, Queue<Key> keys){
if (x == null){
return;
}
// Left subtree -- recursively traverses the left subtree of x node
if (x.left != null){
afterErgodic(x.left, keys);
}
// Right subtree -- recursively traversing the right subtree of x node
if (x.right != null){
afterErgodic(x.right, keys);
}
// Root -- put the key of the x node into the keys
keys.enqueue((Key) x.key);
}
7.4 sequence traversal of binary tree
// Sequence traversal -- from top to bottom, from left to right
public Queue<Key> layerErgodic(){
// Create queue -- key of storage node
Queue<Key> keys = new Queue<>();
Queue<Node> nodes = new Queue<>(); //Auxiliary queue
// (1) The root node enters the queue
nodes.enqueue(root);
// (2) Bounce element -- bounce first, put the key of the node into the keys, judge whether there are left and right child nodes, and if so, put them in the queue
while (!nodes.isEmpty()){
Node x = nodes.dequeue(); // Pop up node
keys.enqueue((Key) x.key); // Put the key of the pop-up element in the queue
if(x.left!=null){
nodes.enqueue(x.left);
}
if (x.right!=null){
nodes.enqueue(x.right);
}
}
return keys;
}
7.5 maximum depth of binary tree
// Maximum depth
public int maxDepth(){
return maxDepth(root);
}
// Calculates the maximum depth of the specified tree x
private int maxDepth(Node x){
// 1. If the root node is empty, the maximum depth is 0
if (x==null){
return 0;
}
int max = 0;
int maxL = 0;
int maxR = 0;
// 2. Calculate the maximum depth of the left subtree
if (x.left!=null){
maxL = maxDepth(x.left);
}
// 3. Calculate the maximum depth of the right subtree
if (x.right!=null){
maxR = maxDepth(x.right);
}
// 4. Maximum depth of current tree = maximum depth of left subtree + maximum depth of right subtree + 1
max = maxL > maxR ? maxL+1 : maxR+1;
return max;
}