Refer to data structure (C Language Edition) - Yan Weimin, WU Weimin, Tsinghua University Press
Structure definition of sparse matrix
typedef struct
{
int i, j; //Row and column subscripts of the non-zero element
ElemType e; //Value corresponding to non-zero element
}Triple;
typedef struct
{
Triple data[MAX_SIZE]; //Nonzero element triple table
int rpos[MAX_RC]; //Position table of the first non-zero element in each row
int mu, nu, tu; //Number of rows, columns and non-zero elements of matrix
}RTSMatrix;
Sparse matrix initialization
void Init_Matrix(RTSMatrix &M, int i)
{
int x, y, z;
int M_row = 0; int M_col = 0;
M.tu = 0;
printf("Please press row.,column,Form input of data-1 End input at\n");
for (int i = 0; ; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d,%d,%d", &x, &y, &z);
if (x == -1 || y == -1)
break;
M.data[i].i = x; M.data[i].j = y; M.data[i].e = z;
M.tu++;
if (M_row < x)
M_row = x;
if (M_col < y)
M_col = y;
}
M.mu = M_row;
M.nu = M_col;
printf("\n The first%d A matrix is\n", i);
Show_Matrix_1(M);
}
Calculate the position of the first non-zero element in each line
void non_zero_elements(RTSMatrix &M)
{
int num[100]; //num [] save the number of non-zero elements in each line cpot [] save the starting address of each line
for (int i = 0; i < M.mu; i++)
num[i] = 0; //Initialize num
for (int j = 0; j < M.tu; j++)
num[M.data[j].i - 1]++; //Count the number of non-zero elements in each row, because the matrix starts from the first row, and the data array starts from 0, so - 1
M.rpos[0] = 0; //The starting point is 0.
for (int k = 1; k < M.mu; k++)
M.rpos[k] = M.rpos[k - 1] + num[k - 1];
}
Fast multiplication
void FastMultSMatrix(RTSMatrix A, RTSMatrix B, RTSMatrix &C)
{
if (A.nu != B.mu) //The number of columns in the front matrix should be equal to the number of rows in the back matrix
return;
C.mu = A.mu; //The number of rows of the result matrix is the number of rows of the previous matrix
C.nu = B.nu; //The number of columns of the result matrix is the number of columns of the post matrix
C.tu = 0; //Result matrix initialization
int ctemp[MAX_SIZE]; //accumulator
int arow, brow, t, tp, ccol;
non_zero_elements(A); //Calculate the position of the first non-zero element in each row
non_zero_elements(B);
if (A.tu * B.tu != 0)
{ //Multiplication matrix is not 0
for (arow = 0; arow < A.mu; arow++)
{ //From the first line to the last
for (int i = 0; i <= A.nu; i++)
ctemp[i] = 0; //Accumulator clear 0
C.rpos[arow] = C.tu; //The first non-zero position is 0
if (arow < A.mu - 1) //Get the non 0 element number of A
tp = A.rpos[arow + 1];
else
tp = A.tu;
for (int j = A.rpos[arow]; j < tp; j++)
{ //For each non-zero number in A's row, take its column index and multiply it with each number in B's row
brow = A.data[j].j; //Take column index
if (brow < B.mu) //Take the non-zero number of column marked row of B
t = B.rpos[brow];
else
t = B.tu;
for (int k = B.rpos[brow - 1]; k < t; k++)
{ //Each non-zero element of the column standard row of B
ccol = B.data[k].j;
ctemp[ccol] += A.data[j].e * B.data[k].e;
}
}
for (ccol = 1; ccol <= C.nu; ccol++) //Copy the results of the accumulator to the result array in order
if (ctemp[ccol])
{
C.tu++;
if (C.tu > MAX_SIZE)
return;
C.data[C.tu - 1].i = arow + 1;
C.data[C.tu - 1].j = ccol;
C.data[C.tu - 1].e = ctemp[ccol];
}
}
}
printf("The result is\n");
Show_Matrix_1(C);
}
Output sparse matrix in matrix form
void Show_Matrix_1(RTSMatrix T) {
int data[100] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < T.tu; i++) //Store non-0 yuan in the specified location, and the rest are 0
data[(T.data[i].i - 1) * T.nu + T.data[i].j - 1] = T.data[i].e;
for (int j = 0; j < T.mu * T.nu; j++) {
printf("%5d", data[j]);
if ((j + 1) % T.nu == 0)
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
Output sparse matrix in the form of three tuples
void Show_Matrix_2(RTSMatrix T)
{
printf("\n Three yuan table for\n");
for (int t = 0; t < T.tu; t++)
printf("%4d %4d %4d\n", T.data[t].i, T.data[t].j, T.data[t].e);
printf("\n");
}
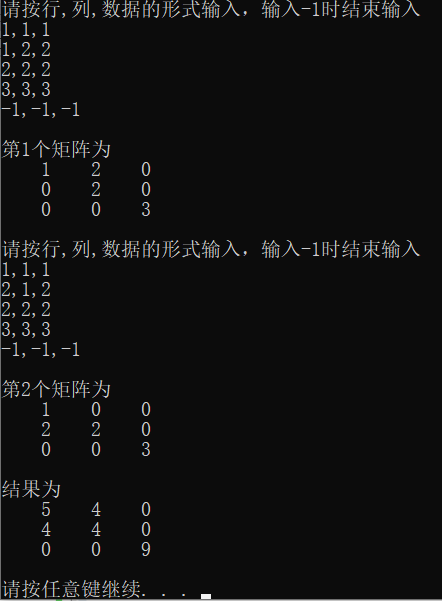
Test set
Matrix A:1 2 0
0 2 0
0 0 3
Matrix B:1 0 0
2 2 0
0 0 3
Whole code
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 1000
#define MAX_RC 1000
#define ElemType int
typedef struct
{
int i, j; //Row and column subscripts of the non-zero element
ElemType e; //Value corresponding to non-zero element
}Triple;
typedef struct
{
Triple data[MAX_SIZE]; //Nonzero element triple table
int rpos[MAX_RC]; //Position table of the first non-zero element in each row
int mu, nu, tu; //Number of rows, columns and non-zero elements of matrix
}RTSMatrix;
void Show_Matrix_1(RTSMatrix T) {
int data[100] = { 0 };
for (int i = 0; i < T.tu; i++)
data[(T.data[i].i - 1) * T.nu + T.data[i].j - 1] = T.data[i].e;
for (int j = 0; j < T.mu * T.nu; j++) {
printf("%5d", data[j]);
if ((j + 1) % T.nu == 0)
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
}
void Show_Matrix_2(RTSMatrix T)
{
printf("\n Three yuan table for\n");
for (int t = 0; t < T.tu; t++)
printf("%4d %4d %4d\n", T.data[t].i, T.data[t].j, T.data[t].e);
printf("\n");
}
void Init_Matrix(RTSMatrix &M, int i)
{
int x, y, z;
int M_row = 0; int M_col = 0;
M.tu = 0;
printf("Please press row.,column,Form input of data-1 Time end input\n");
for (int i = 0; ; i++)
{
scanf_s("%d,%d,%d", &x, &y, &z);
if (x == -1 || y == -1)
break;
M.data[i].i = x; M.data[i].j = y; M.data[i].e = z;
M.tu++;
if (M_row < x)
M_row = x;
if (M_col < y)
M_col = y;
}
M.mu = M_row;
M.nu = M_col;
printf("\n The first%d A matrix is\n", i);
Show_Matrix_1(M);
}
void non_zero_elements(RTSMatrix &M)
{
int num[100]; //num [] save the number of non-zero elements in each line cpot [] save the starting address of each line
for (int i = 0; i < M.mu; i++)
num[i] = 0; //Initialize num
for (int j = 0; j < M.tu; j++)
num[M.data[j].i - 1]++; //Count the number of non-zero elements in each row, because the matrix starts from the first row, and the data array starts from 0, so - 1
M.rpos[0] = 0; //The starting point is 0.
for (int k = 1; k < M.mu; k++)
M.rpos[k] = M.rpos[k - 1] + num[k - 1];
}
void FastMultSMatrix(RTSMatrix A, RTSMatrix B, RTSMatrix &C)
{
if (A.nu != B.mu) //The number of columns in the front matrix should be equal to the number of rows in the back matrix
return;
C.mu = A.mu; //The number of rows of the result matrix is the number of rows of the previous matrix
C.nu = B.nu; //The number of columns of the result matrix is the number of columns of the post matrix
C.tu = 0; //Result matrix initialization
int ctemp[MAX_SIZE]; //accumulator
int arow, brow, t, tp, ccol;
non_zero_elements(A); //Calculate the position of the first non-zero element in each row
non_zero_elements(B);
if (A.tu * B.tu != 0)
{ //Multiplication matrix is not 0
for (arow = 0; arow < A.mu; arow++)
{ //From the first line to the last
for (int i = 0; i <= A.nu; i++)
ctemp[i] = 0; //Accumulator clear 0
C.rpos[arow] = C.tu; //The first non-zero position is 0
if (arow < A.mu - 1) //Get the non-zero element of A
tp = A.rpos[arow + 1];
else
tp = A.tu;
for (int j = A.rpos[arow]; j < tp; j++)
{ //For each non-zero number in A's row, take its column index and multiply it with each number in B's row
brow = A.data[j].j; //Take column index
if (brow < B.mu) //Take the non-zero number of column marked row of B
t = B.rpos[brow];
else
t = B.tu;
for (int k = B.rpos[brow - 1]; k < t; k++)
{ //Each non-zero element of the column standard row of B
ccol = B.data[k].j;
ctemp[ccol] += A.data[j].e * B.data[k].e;
}
}
for (ccol = 1; ccol <= C.nu; ccol++) //Copy the results of the accumulator to the result array in order
if (ctemp[ccol])
{
C.tu++;
if (C.tu > MAX_SIZE)
return;
C.data[C.tu - 1].i = arow + 1;
C.data[C.tu - 1].j = ccol;
C.data[C.tu - 1].e = ctemp[ccol];
}
}
}
printf("The result is\n");
Show_Matrix_1(C);
}
void main() {
RTSMatrix A;
RTSMatrix B;
RTSMatrix C;
Init_Matrix(A, 1);
Init_Matrix(B, 2);
FastMultSMatrix(A, B, C);
system("pause");
}
Result