4.2. Implementation of circular queue function
Cyclic queue characteristics
In order to make full use of vector space and overcome the phenomenon of "false overflow", the method is to imagine vector space as a ring with head and tail connected, and call this vector cyclic vector. The queue stored in it is called Circular Queue. Circular Queue is to connect the sequential queue end to end, and logically regard the table storing queue elements as a ring to become a Circular Queue.
Circular queue is to circle the last position of the queue storage space to the first position to form a logical ring space for the cyclic use of the queue. In the cyclic queue structure, when the last location of the storage space has been used and you want to enter the queue operation again, you only need the first location of the storage space to be idle, you can add elements to the first location, that is, the first location of the storage space is the end of the queue. [1] Circular queue can prevent pseudo overflow more simply, but the queue size is fixed.
In a circular queue, when the queue is empty, there is front=rear, and when all queue spaces are full, there is also front=rear. In order to distinguish the two cases, it is stipulated that the circular queue can only have MaxSize-1 queue elements at most. When there is only one empty storage unit left in the circular queue, the queue is full. Therefore, the condition of empty queue is front=rear, while the condition of full queue is front = (rear+1)%MaxSize.
0. Definition and implementation of circular queue class
//Sequential storage of queues
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Elemtype;
#define MAX_SIZE 25
class queue{
private:
int head;
int rear;
Elemtype *data;
int size;
int cnt;//count
public:
//1. Parameterless constructor of queue
queue();
//2. Parameterized constructor of queue
queue(int s);
//3. Queue destructor
~queue();
//4. Join the team
void push(Elemtype t);
//5. Out of team operation
bool pop(Elemtype&k);
//6. Judge whether the queue is empty
bool isEmpty();
//7. Determine whether the queue is full
bool isFull();
//8. Return to the tail element
Elemtype GetRear();
//9. Return the header element
Elemtype GetHead();
//10. Clear the queue
void Clear();
//11. Print queue
void PrintQueue();
};
1. Nonparametric constructor of circular queue
//1. Parameterless constructor of queue
queue::queue()
{
cnt=0;
head=0;
rear=-1;
size=MAX_SIZE;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
2. Parametric constructor of circular queue
//2. Parameterized constructor of queue
queue::queue(int s)
{
head=0;
rear=-1;
cnt=0;
if(size>MAX_SIZE)
{
size=MAX_SIZE;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
else
{
size=s;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
}
3. Destructor of circular queue
//3. Queue destructor
queue::~queue()
{
delete []data;
}
4. Loop queue incoming operation
//4. Join the team
void queue::push(Elemtype t)
{
if(!isFull())
{
rear=(rear+1)%size;
data[rear]=t;
cnt++;
}
else
{
cout<<"The queue is full"<<endl;
return ;
}
}
5. Out of line operation of circular queue
//5. Out of team operation
bool queue::pop(Elemtype&k)
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
k=data[head];
head=(head+1)%size;
cnt--;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
6. Loop queue to judge whether the queue is empty
//6. Judge whether the queue is empty
bool queue::isEmpty()
{
return cnt==0;
}
7. Cycle the queue to determine whether the queue is full
//7. Determine whether the queue is full
bool queue::isFull()
{
return cnt==MAX_SIZE;
}
8. Loop queue return end of queue element
//8. Return to the tail element
Elemtype queue::GetRear()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
return data[rear];
}
return 0;
}
9. Loop queue return queue header element
//9. Return to the header element
Elemtype queue::GetHead()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
return data[head];
}
return 0;
}
10. Cycle the queue and clear the queue
//10. Clear the queue
void queue::Clear()
{
head=-1;
rear=-1;
cnt=0;
}
11. Cycle queue print queue
//11. Print queue
void queue::PrintQueue()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
int p=head;
int q=rear;
while(p%size!=q)
{
cout<<data[p]<<" ";
p=(p+1)%size;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
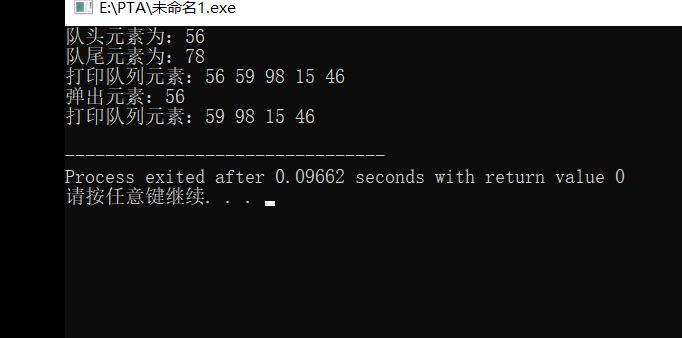
12. Cyclic queue test case
//12. Test cases
void test01()
{
int k;
queue Queue;
Queue.push(56);
Queue.push(59);
Queue.push(98);
Queue.push(15);
Queue.push(46);
Queue.push(78);
cout<<"The team head elements are:"<<Queue.GetHead()<<endl;
cout<<"The tail element is:"<<Queue.GetRear()<<endl;
cout<<"Print queue elements:";
Queue.PrintQueue();
Queue.pop(k);
cout<<"Pop up elements:"<<k<<endl;
cout<<"Print queue elements:";
Queue.PrintQueue();
}
5. Total source code of circular queue
//Sequential storage of queues
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef int Elemtype;
#define MAX_SIZE 25
class queue{
private:
int head;
int rear;
Elemtype *data;
int size;
int cnt;//count
public:
//1. Parameterless constructor of queue
queue();
//2. Parameterized constructor of queue
queue(int s);
//3. Queue destructor
~queue();
//4. Join the team
void push(Elemtype t);
//5. Out of team operation
bool pop(Elemtype&k);
//6. Judge whether the queue is empty
bool isEmpty();
//7. Determine whether the queue is full
bool isFull();
//8. Return to the tail element
Elemtype GetRear();
//9. Return to the header element
Elemtype GetHead();
//10. Clear the queue
void Clear();
//11. Print queue
void PrintQueue();
};
//1. Parameterless constructor of queue
queue::queue()
{
cnt=0;
head=0;
rear=-1;
size=MAX_SIZE;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
//2. Parameterized constructor of queue
queue::queue(int s)
{
head=0;
rear=-1;
cnt=0;
if(size>MAX_SIZE)
{
size=MAX_SIZE;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
else
{
size=s;
data=new Elemtype[size];
}
}
//3. Queue destructor
queue::~queue()
{
delete []data;
}
//4. Join the team
void queue::push(Elemtype t)
{
if(!isFull())
{
rear=(rear+1)%size;
data[rear]=t;
cnt++;
}
else
{
cout<<"The queue is full"<<endl;
return ;
}
}
//5. Out of team operation
bool queue::pop(Elemtype&k)
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
k=data[head];
head=(head+1)%size;
cnt--;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
//6. Judge whether the queue is empty
bool queue::isEmpty()
{
return cnt==0;
}
//7. Determine whether the queue is full
bool queue::isFull()
{
return cnt==MAX_SIZE;
}
//8. Return to the tail element
Elemtype queue::GetRear()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
return data[rear];
}
return 0;
}
//9. Return to the header element
Elemtype queue::GetHead()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
return data[head];
}
return 0;
}
//10. Clear the queue
void queue::Clear()
{
head=-1;
rear=-1;
cnt=0;
}
//11. Print queue
void queue::PrintQueue()
{
if(!isEmpty())
{
int p=head;
int q=rear;
while(p%size!=q)
{
cout<<data[p]<<" ";
p=(p+1)%size;
}
cout<<endl;
}
}
//12. Test cases
void test01()
{
int k;
queue Queue;
Queue.push(56);
Queue.push(59);
Queue.push(98);
Queue.push(15);
Queue.push(46);
Queue.push(78);
cout<<"The team head elements are:"<<Queue.GetHead()<<endl;
cout<<"The tail element is:"<<Queue.GetRear()<<endl;
cout<<"Print queue elements:";
Queue.PrintQueue();
Queue.pop(k);
cout<<"Pop up elements:"<<k<<endl;
cout<<"Print queue elements:";
Queue.PrintQueue();
}
int main()
{
test01();
}
Cyclic queue test results