Collection query
INTERSECT and INTERSECT operations include INTERSECT and INTERSECT
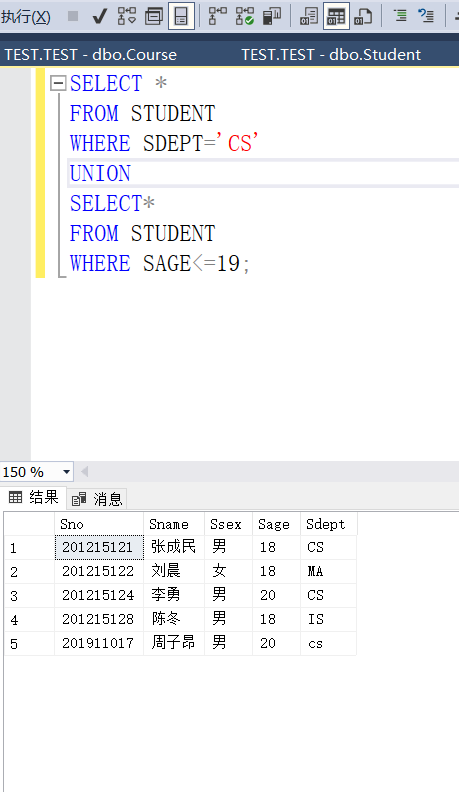
Query students in the Department of computer science and students under the age of 19
SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='CS' UNIOM SELECT* FROM STUDENT WHERE SAGE<=19;
Example 3.65 query the students who have elective course 1 or elective course 2
SELECT * FROM SC WHERE SNO='1' UNION SELECT * FROM SC WHERE SNO='2';
Example 3.66 query the intersection of students in the Department of computer science and students who are not old and 19 years old
SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='CS' INTERSECT SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SAGE<=19;
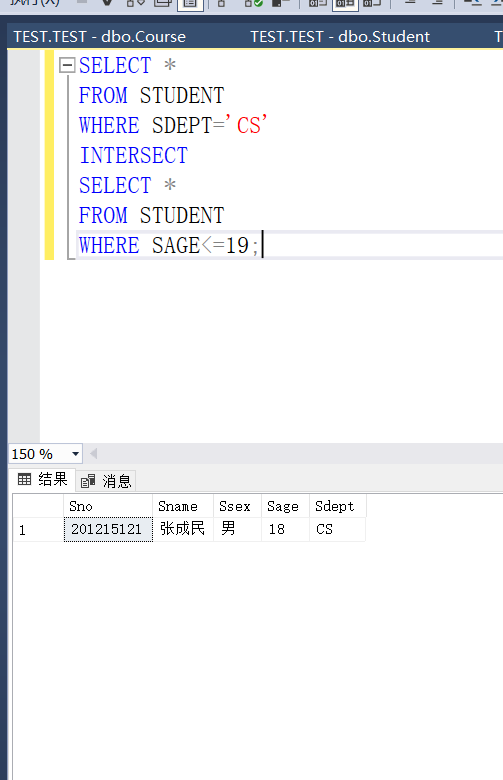
In fact, it is to query students under the age of 19 in the Department of computer science
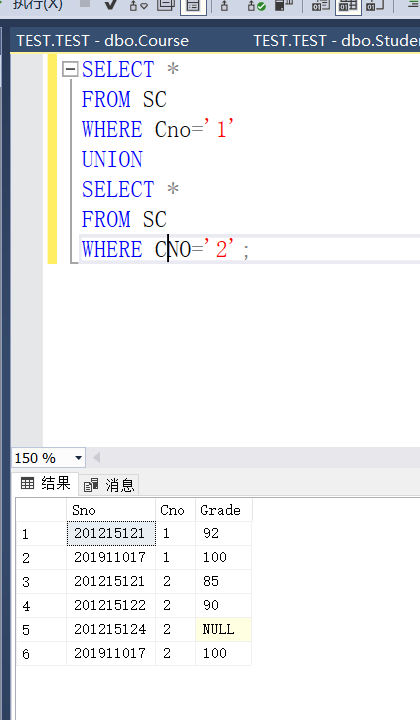
Example 3.67 query students who have both elective courses 1 and 2 (intersection)
SELECT * FROM SC WHERE CNO='1' INTERSECT SELECT * FROM SC WHERE CNO='2';
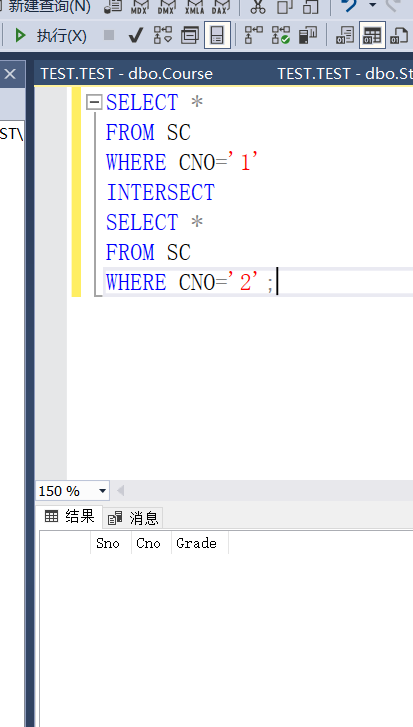
There is no choice between two
Example 3.68 query the difference set of students in the Department of computer science at the age of no more than 19 years old
It's actually looking for students older than 19 in the computer department
SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SAGE<=19 EXCEPT SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='CS';
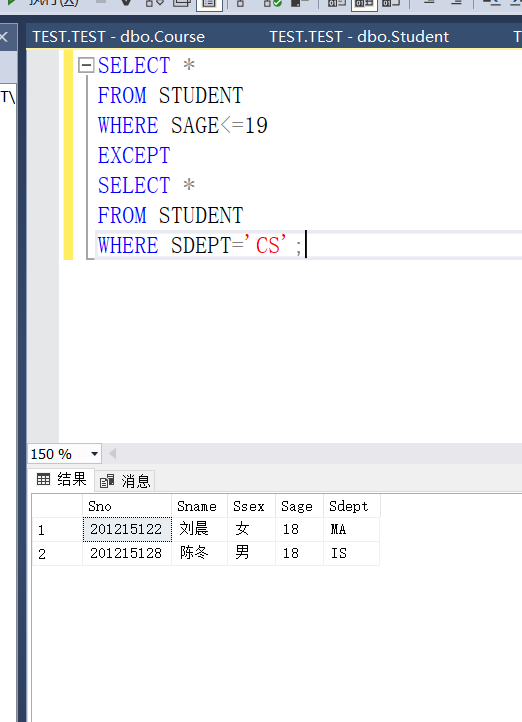
At the beginning, it was found that the result was wrong. Think about two sets a and B
A-B and B-A are different
According to the requirements of the title, the code should be written like this
SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='CS' EXCEPT SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SAGE<=19;
Query based on derived table
Derived table can be understood as creating a table temporarily and then querying in the help of this virtual table
Example 3.57 find out the course number that each student exceeds the average score of his own elective courses
SELECT SNO,CNO FROM SC,(SELECT SNO,AVG(GRADE) FROM SC GROUP BY SNO ) AS AVG_SC(AVG_SNO,AVG_GRADE) WHERE SC.SNO=AVG_SC.AVG_SNO AND SC.GRADE>=AVG_SC.AVG_GRADE;
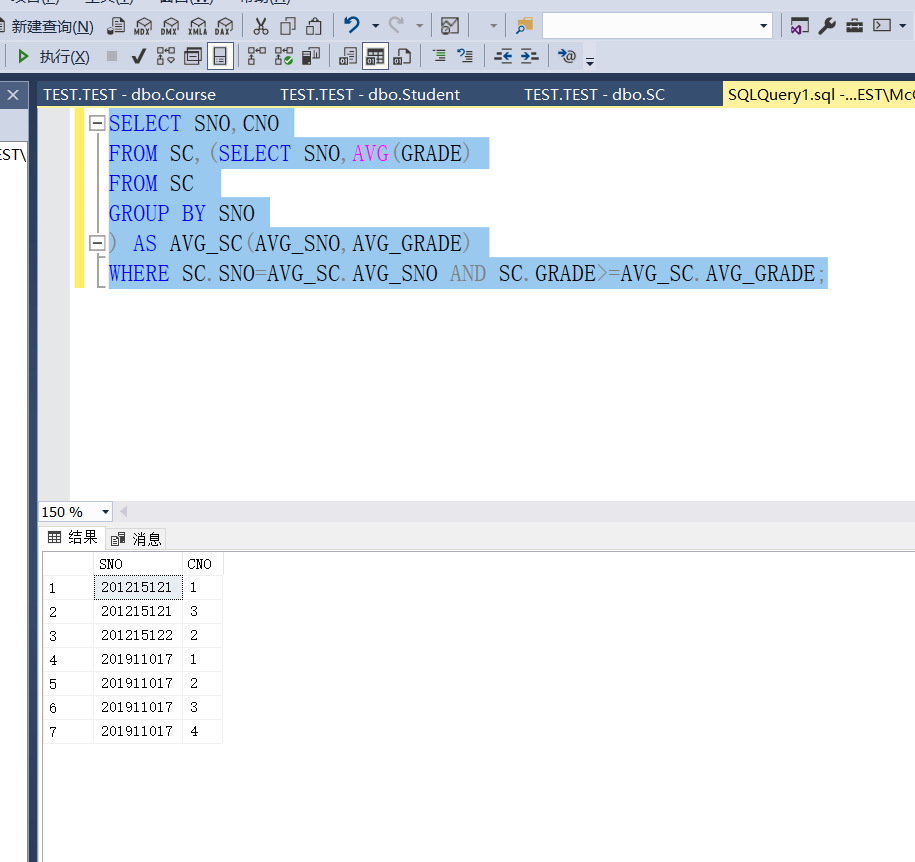
Note the difference between underline - and - English underline seems to have other meanings in TSQL. Column names cannot be used in creating derived tables-


Data update
Example 3.69 insert a new Student tuple (Student No.: 201215128 Name: Chen Dong gender male department IS age 18) into the Student table
INSERT
INTo STUDENT(SNO,SNAME,SSEX,SDEPT,SAGE)
VALUES('201215128','Chen Dong','male','IS',18);
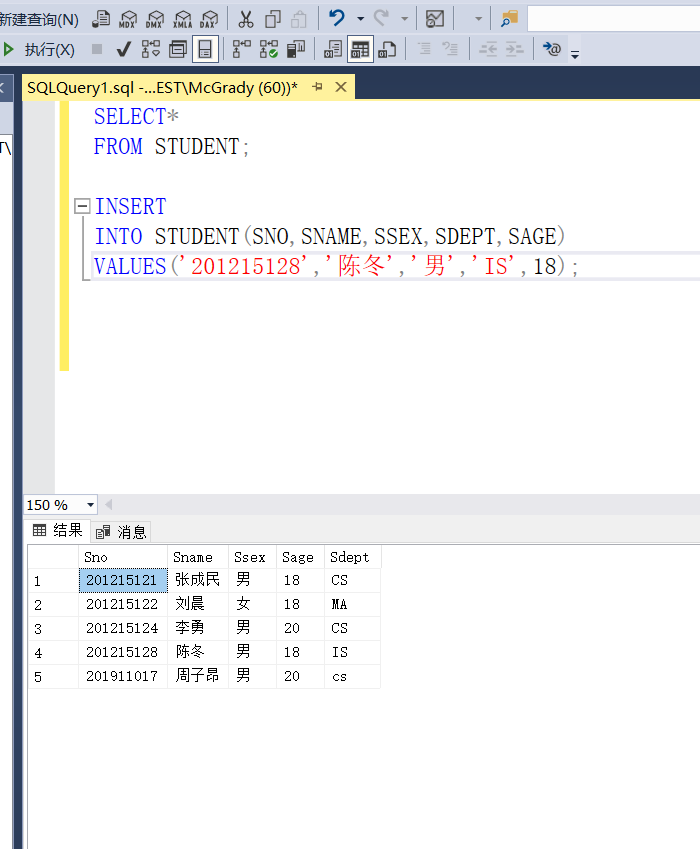
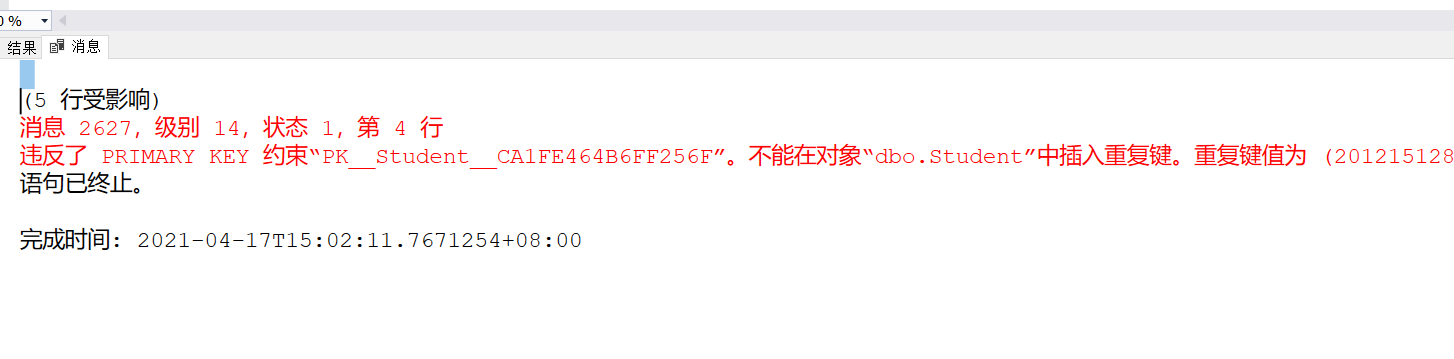
Because Chen Dong has been a student before, it shows failure when inserting 201215128
Example 3.69 insert the information of student Zhang Chengmin into the student table
INSERT
INTO STUDENT
VALUES('201215126','Zhang Chengmin','male'. '18','CS');
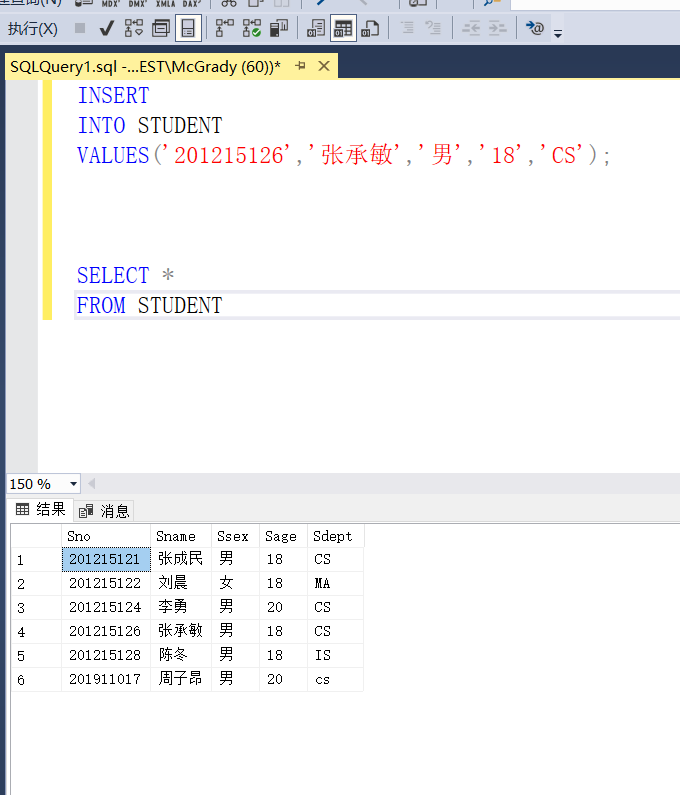
In the INTO clause, only the table name is given, but the attribute name is not given, indicating that the new element group should specify values on all attribute columns of the table in the same order
Example 3.71 insert a course selection record
INSERT
INTO SC(SCO,CNO)
VALUES('201215128','1');
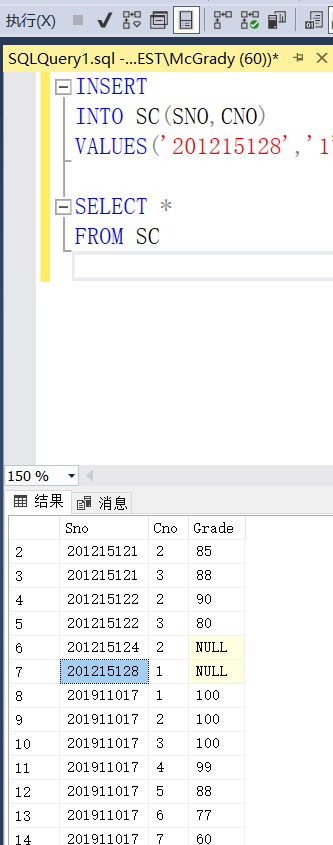
If GRADE does not give a value, the system will automatically give a null value or use the following code
INSERT
INTO SC
VALUES('201215128','1',NULL);
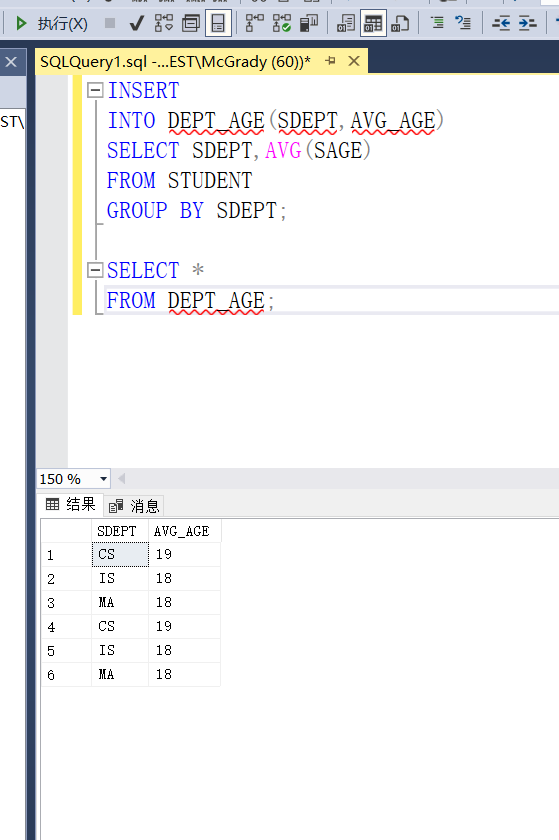
Example 3.72 find the average age of students in each department and store the results in the database
First, create a new table in the database, in which one column stores the Department name and the other column puts the corresponding average age of students
CREATE TABLE DEPT_AGE (SDEPT CHAR(15) AVG_AGE SMALLINT);
Then calculate the average age of student s by department grouping, and then store the Department name and average age in the new table
INSERT INTO DEPT_AGE(SDEPT,AVG_AGE) SELECT SDEPT,AVG(SAGE) FROM STUDENT GROUP BY SDEPT;
Modify data
Example 3.73 change the age of students 201215121 to 22
UPDATE STUDENT SET SAGE=22 WHERE SNO='201215121';
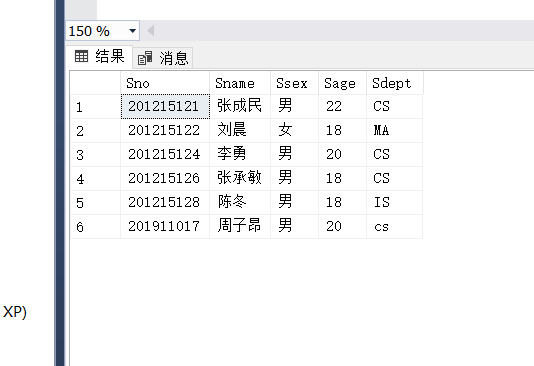
The age of all students will increase by 3.74 years
UPDATE STUDENT SET SAGE=SAGE+1;
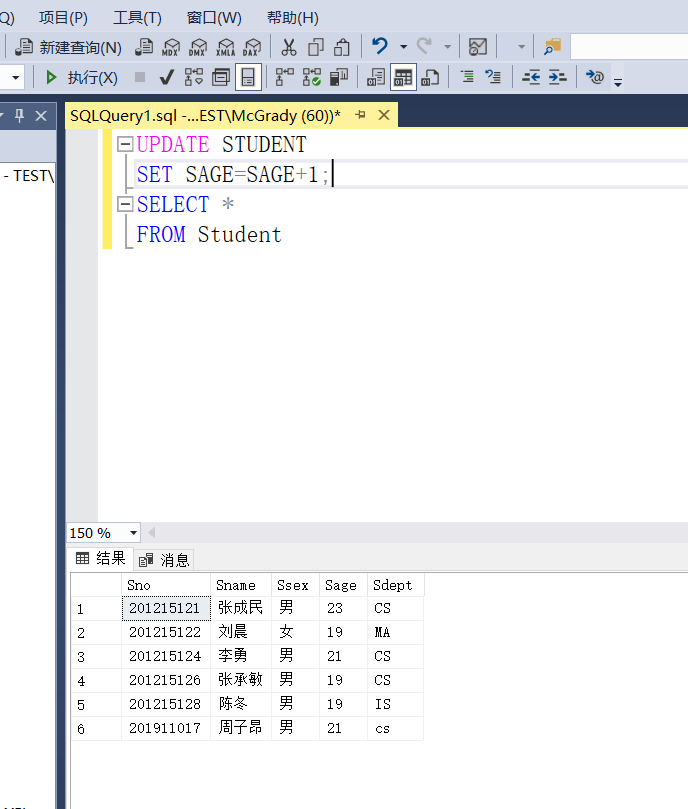
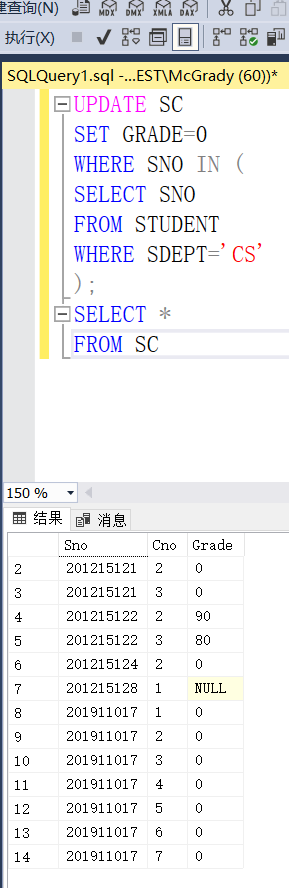
Example 3.75 set the scores of all students in the computer science department to zero
UPDATE SC SET GRADE=0 WHERE SNO IN ( SELECT SNO FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='CS' );
Delete data
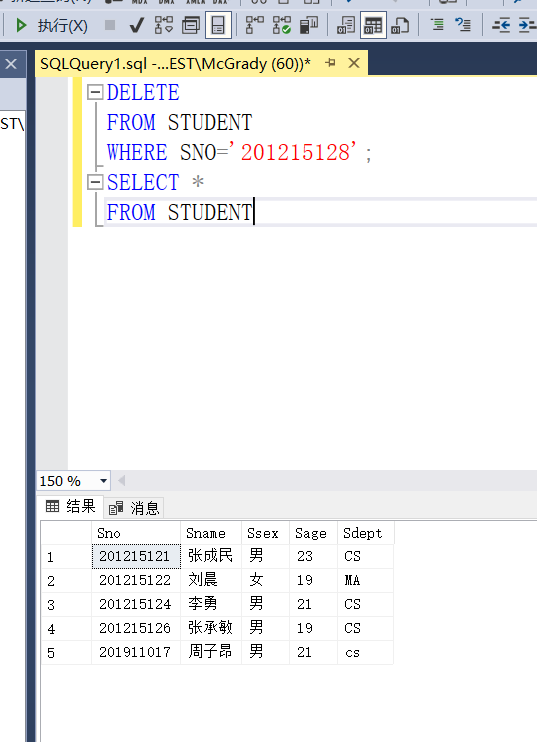
Example 3.76 delete student records with student number 201215128
DELETE FROM STUDENT WHERE SNO='201215128';
Delete the course selection records of all students
DELETE FROM SC;
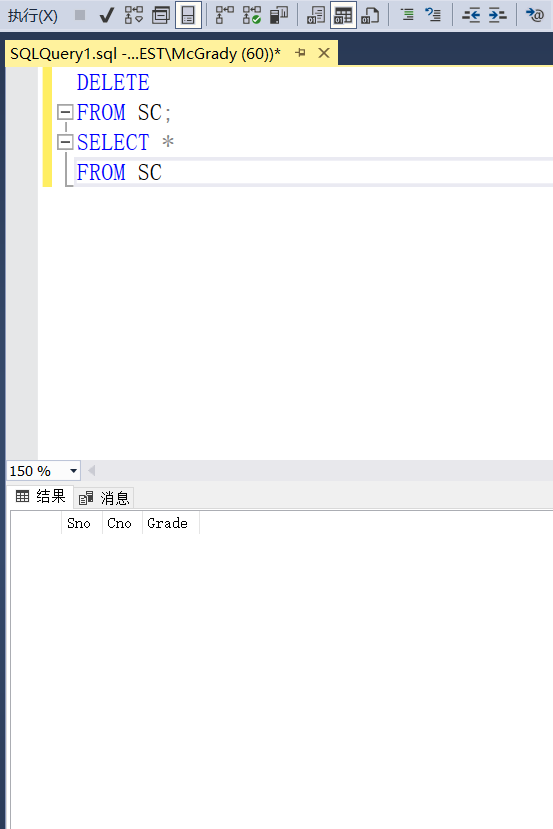
Delete the course selection records of all students in the computer science department
DELETE FROM SC WHERE SNO IN( SELECT SNO FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPY='CS' );
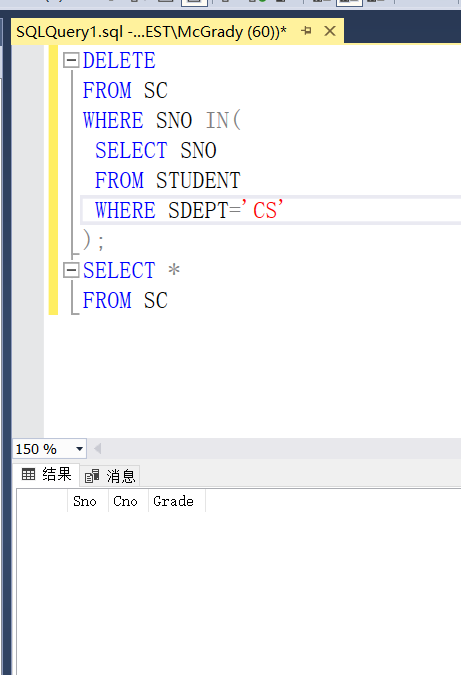
Because the SC table has been cleared in the previous example, it is still empty this time
Processing of null values
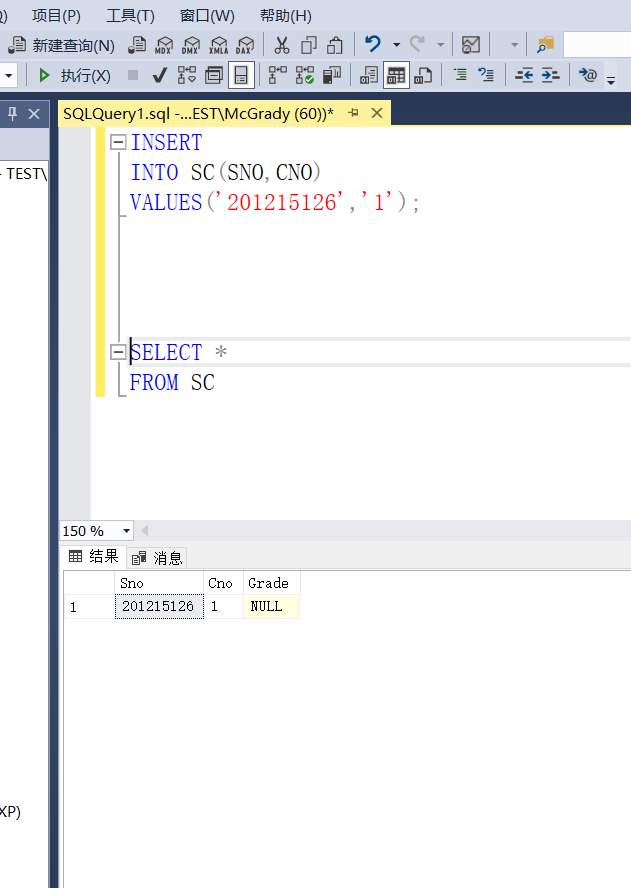
Example 3.79 insert a tuple into the SC table, the student number is 201215126, the course number is 1, and the score is empty
INSERT
INTO SC(SNO,CNO,GRADE)
VALUES('201215126','1',NULL);
or
INSERT
INTO SC(SNO,CNO)
VALUES('201215126','1');
Example 3.80 change the Department of the STUDENT whose middle school number is 201215200 in the STUDENT table to blank
UPDATE TUDENT SET SDEPT=NULL WHERE SNO='201215200';
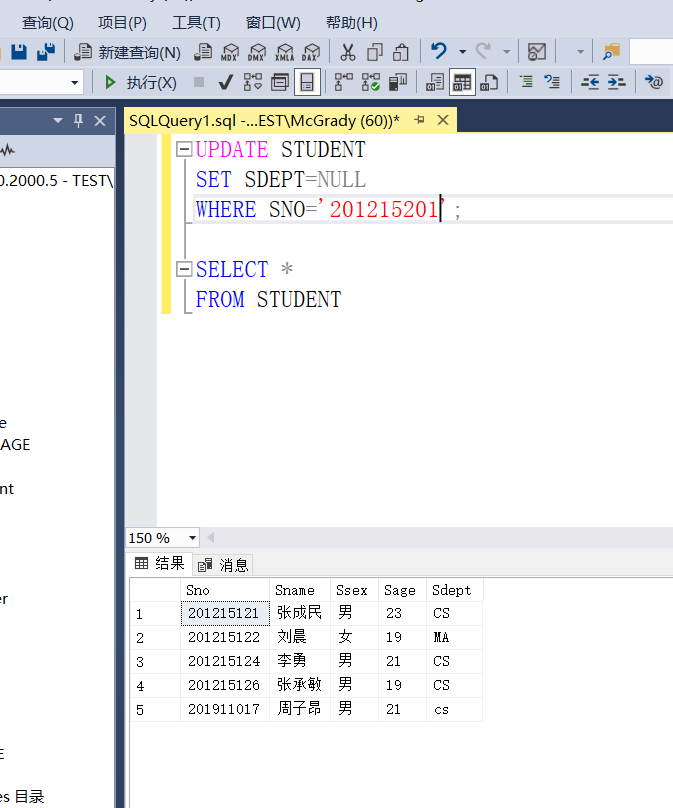
It is found here that if there is no STUDENT with STUDENT number 201215201 in the STUDENT table, the query will be successful and no error will be reported
So I manually insert a 201215201
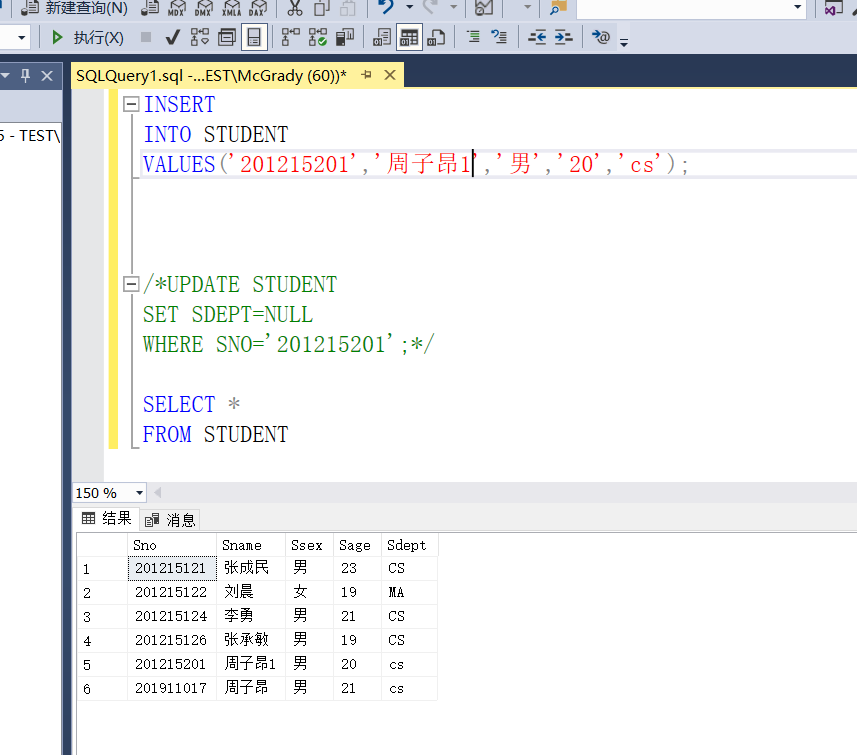
Modify again
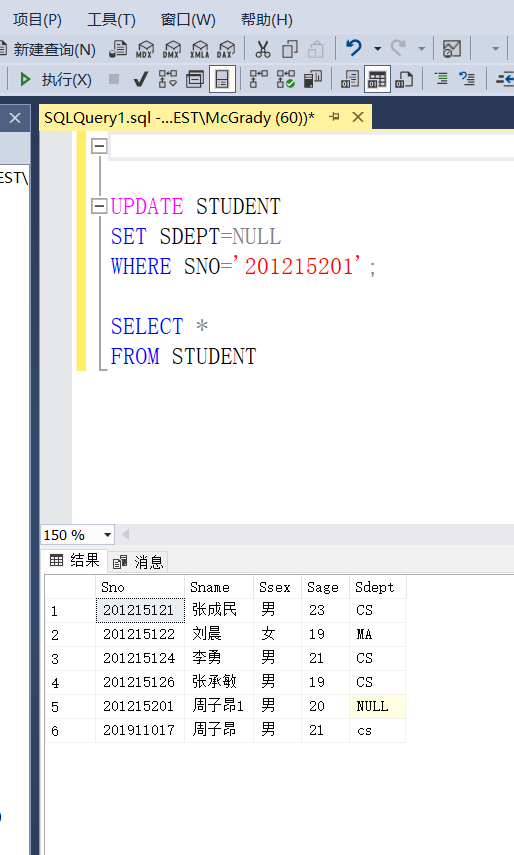
Judge whether the value of a property IS NULL. Use IS NULL or IS NOT NULL. You cannot use the equal sign
Example 3.81 find out the student information with missing data from the student table
SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SNAME IS NULL OR SSEX IS NULL OR SAGE IS NULL OR SDEPT IS NULL;
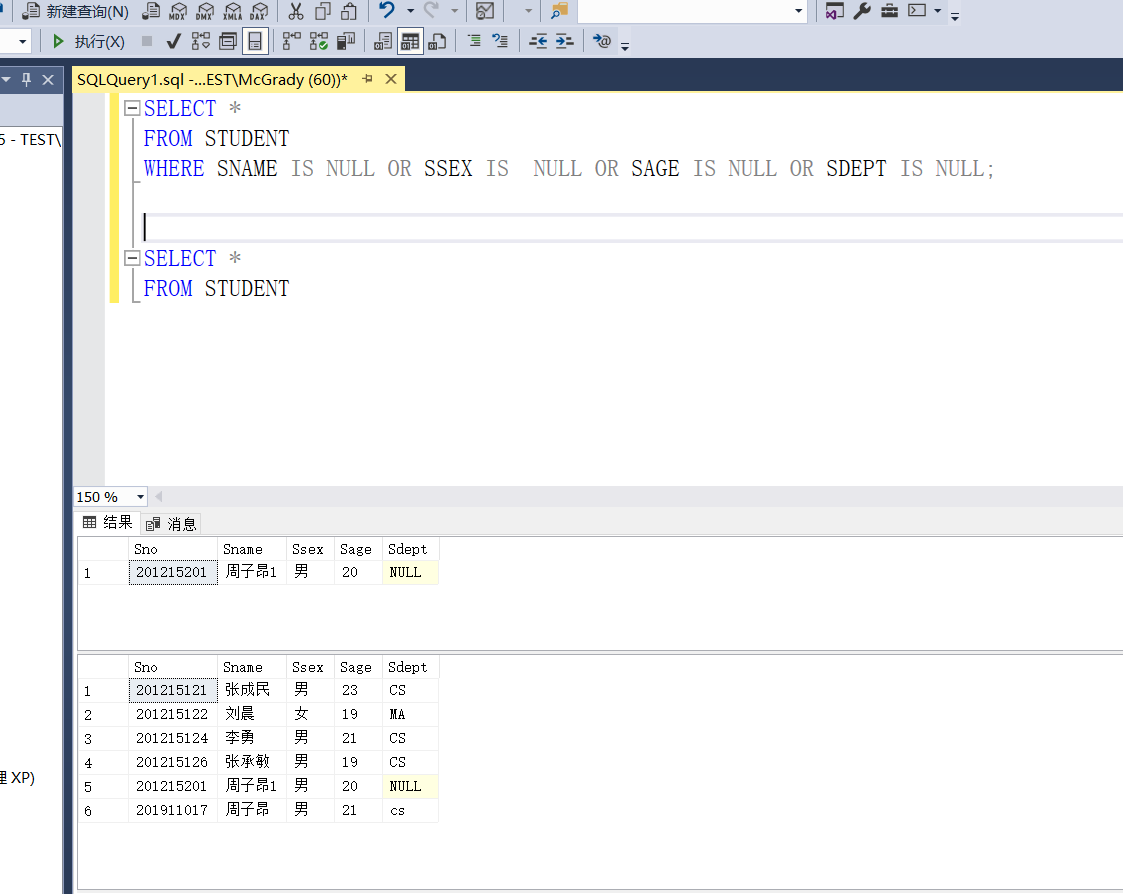
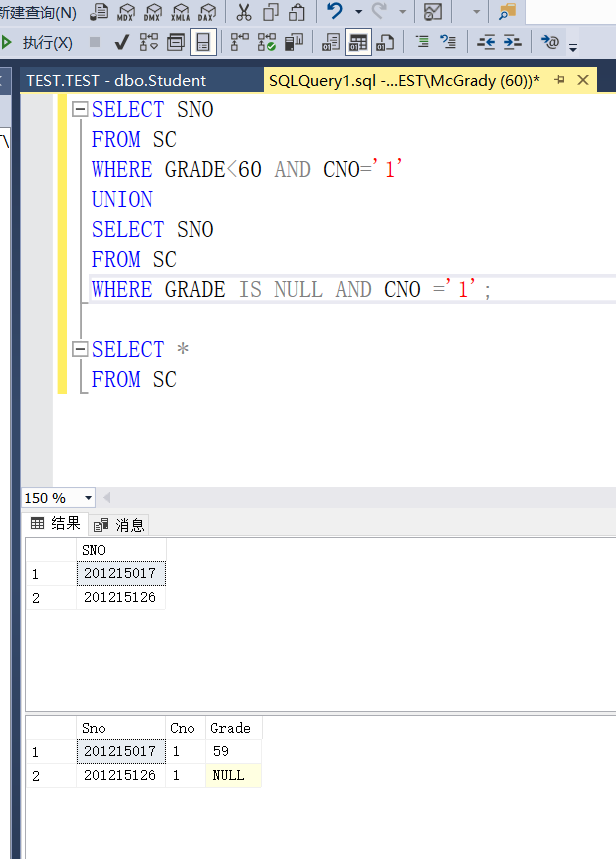
Example 3.82 find out the failed students who take the No. 1 course
SELECT SNO FROM SC WHERE GRADE <60 AND CNO='1';
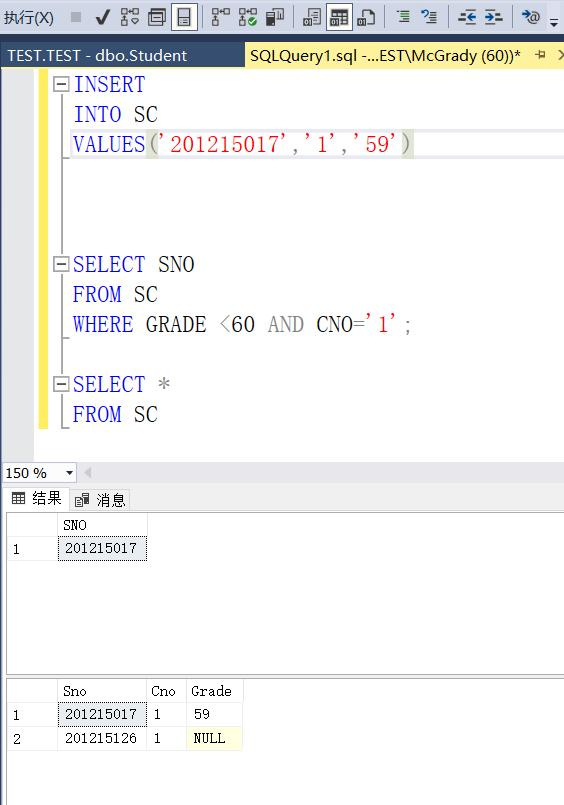
Example 3.83 select the students who fail the No. 1 course and the students who are absent from the exam
SELECT SNO FROM SC WHERE GRADE<60 AND CNO='1' UNION SELECT SNO FROM SC WHERE GRADE IS NULL AND CNO ='1';
view
The view is not a basic table, but a virtual table. Only the attempted definition is stored in the database, and the corresponding data is not stored
My understanding is that view is a way for you to see data
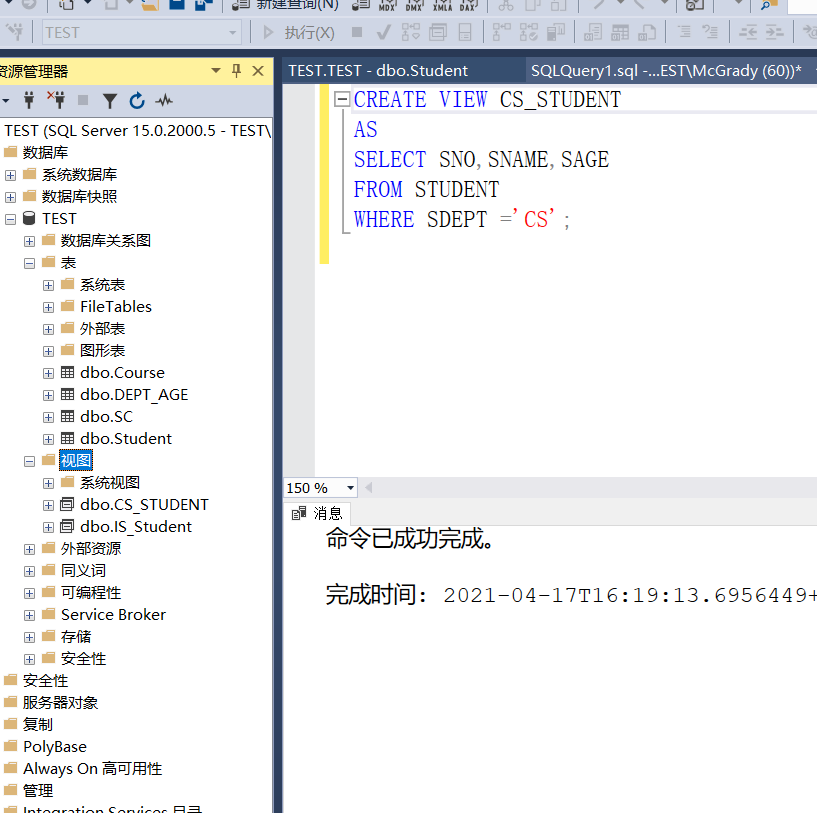
Example 3.84 establishing a view of Information Department Students
CREATE VIEW IS_STUDENT AS SELECT SNO,SNAME,SAGE FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT ='IS';
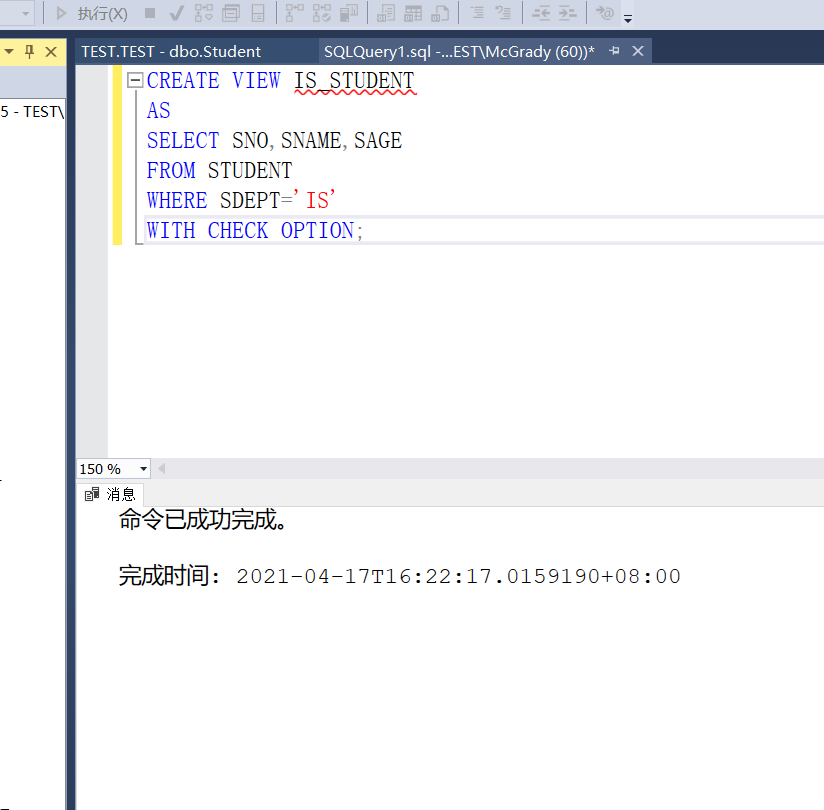
Example 3.85 when establishing the view of information department students and requiring modification and insertion, it is still necessary to ensure that the view is only for information department students
CREATE VIEW IS_STUDENT AS SELECT SNO,SNAME,SAGE FROM STUDENT WHERE SDEPT='IS' WITH CHECK OPTION;
Example 3.86 establish a view of students who have taken No. 1 course in the information department (including student number, name and score)
CREATE VIEW IS_S1(SNO,SNAME,GRADE) AS SELECT STUDENT.SNO,SNAME,GRADE FROM STUDENT,SC WHERE SDEPT='IS' AND STUDENT.SNO=SC.SNO AND SC.CNO='1';
Example 3.87 establish a view of students who have taken No. 1 course in the information department and scored more than 90 points
CREATE VIEW IS_S2 AS SELECT SNO,SNAME,SAGE FROM IS_S1 WHERE GRADE>=90;
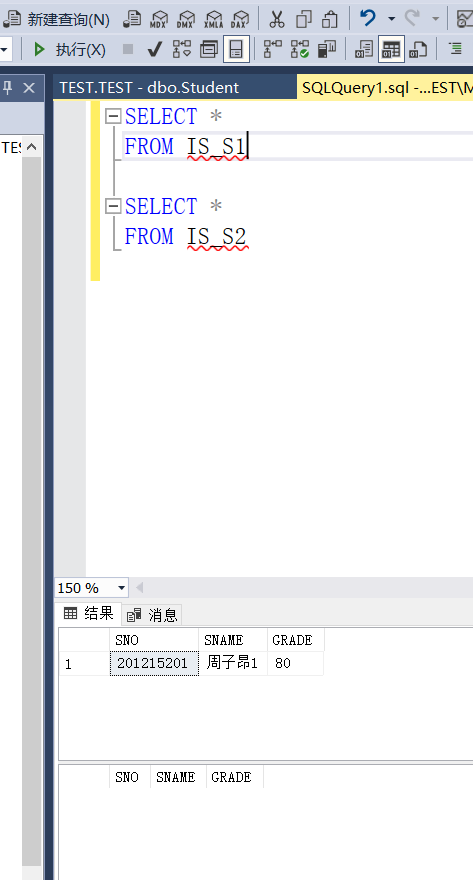
There are no information department students who have taken No. 1 course and scored more than 90 points in the data
Example 3.88 define a view that reflects a student's year of birth
CREATE VIEW BT_S(SNO,SNAME,SBIRTH) AS SELECT SNO,SNAME,2020-SAGE FROM STUDENT;
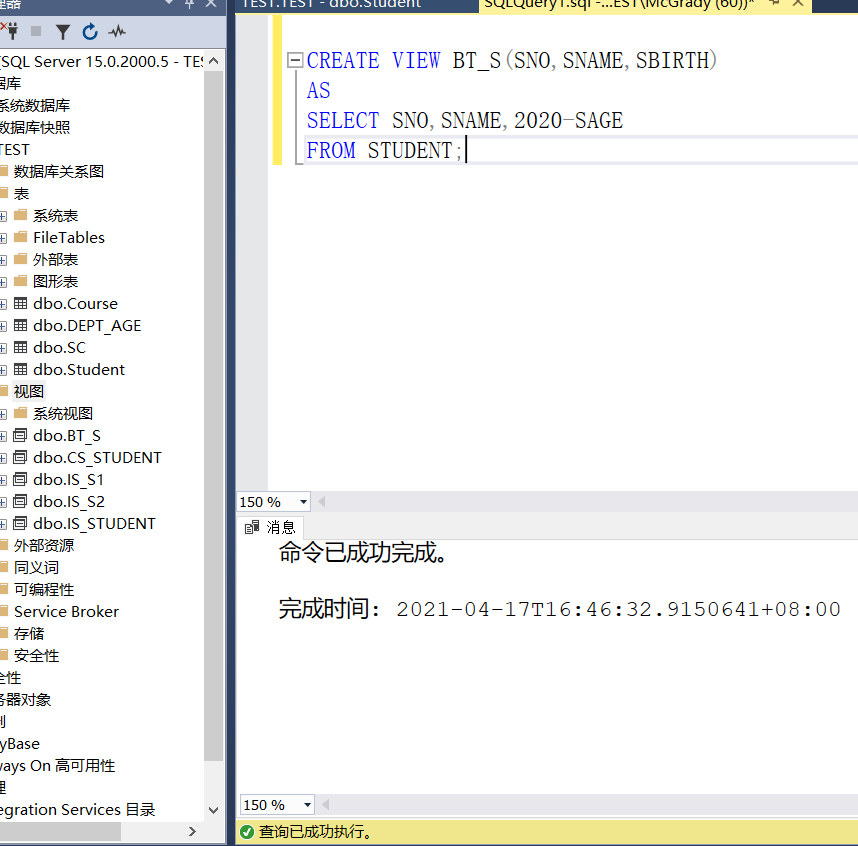
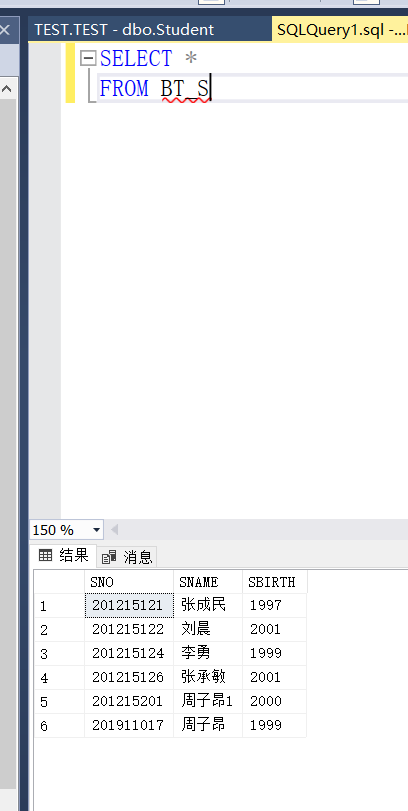
This is the data of the generated view
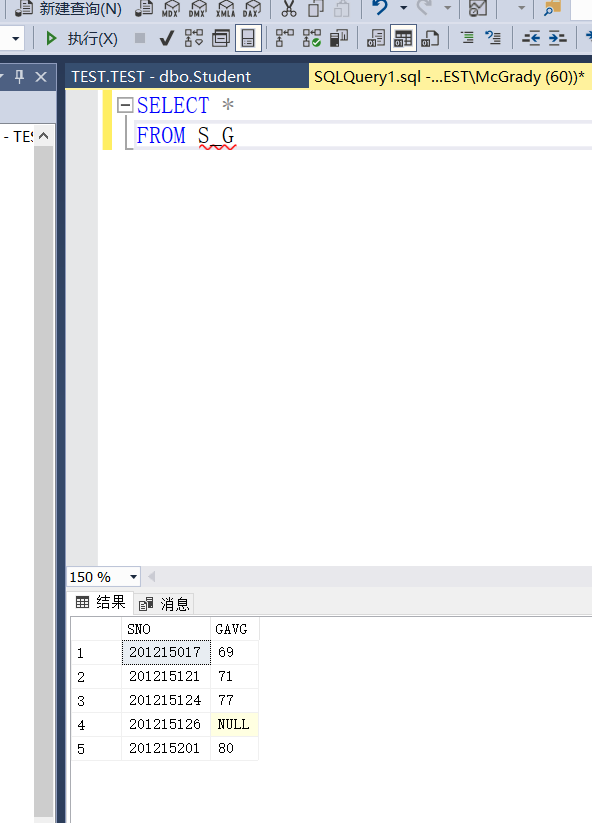
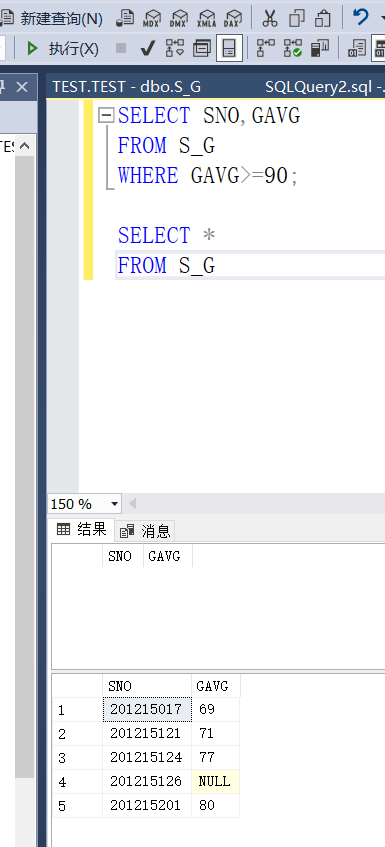
Example 3.89 defines the student number and average score of students as a view
CREATE VIEW S_G(SNO,GAVG) AS SELECT SNO,AVG(GRADE) FROM SC GROUP BY SNO;
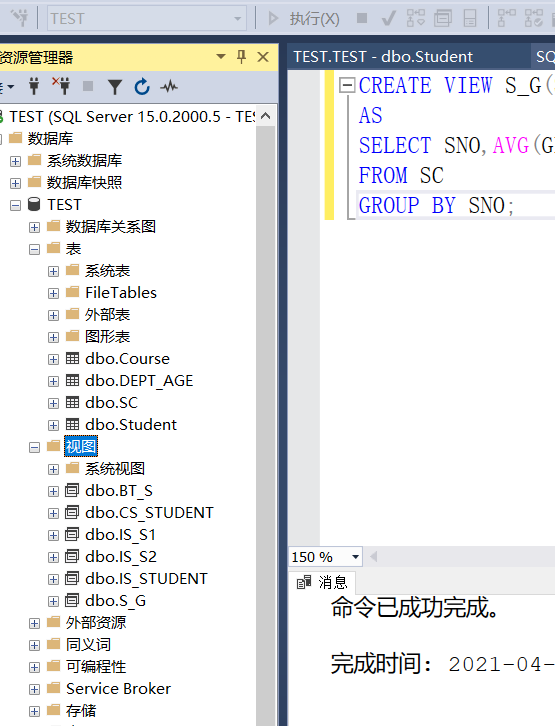
Example 3.90 define all female records in the student table as one view
CREATE VIEW F_STUDENT(F_SNO,NAME,SEX,AGE,DEPT) AS SELECT * FROM STUDENT WHERE SSEX='female';
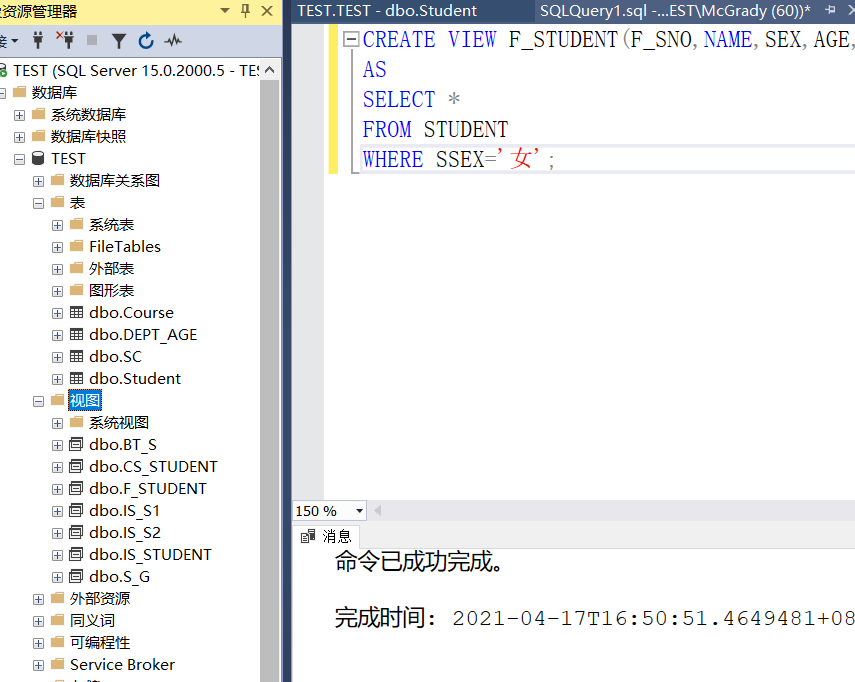
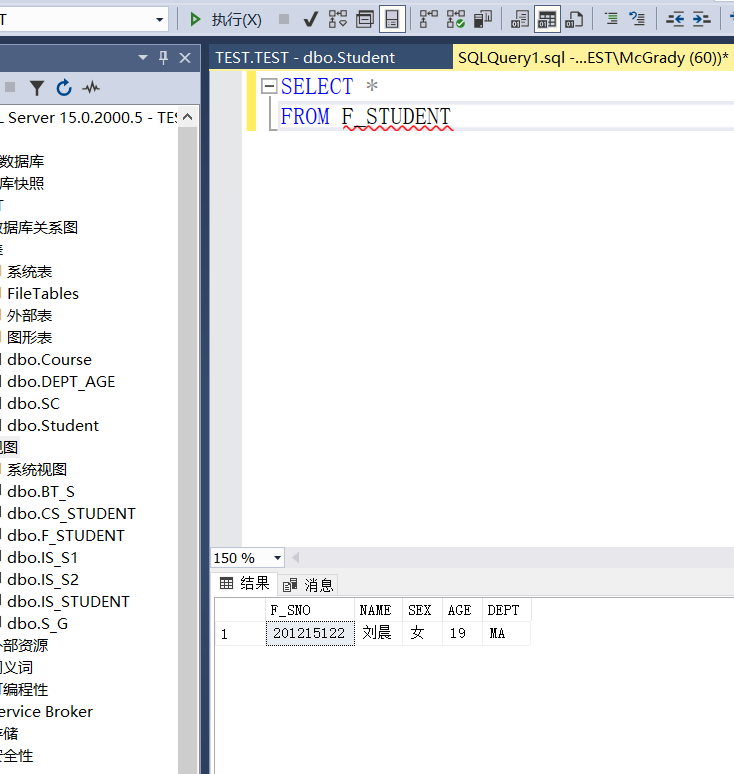
There's F_ The attribute column of student view is the same as that of student. If the attribute column of student is modified later, the image relationship between the two will be destroyed_ There was an error in the student view, so
Delete view
Example 3.91 delete view BT_S and view IS_S1
DROP VIEW BT_S; DROP VIEW IS_S1;
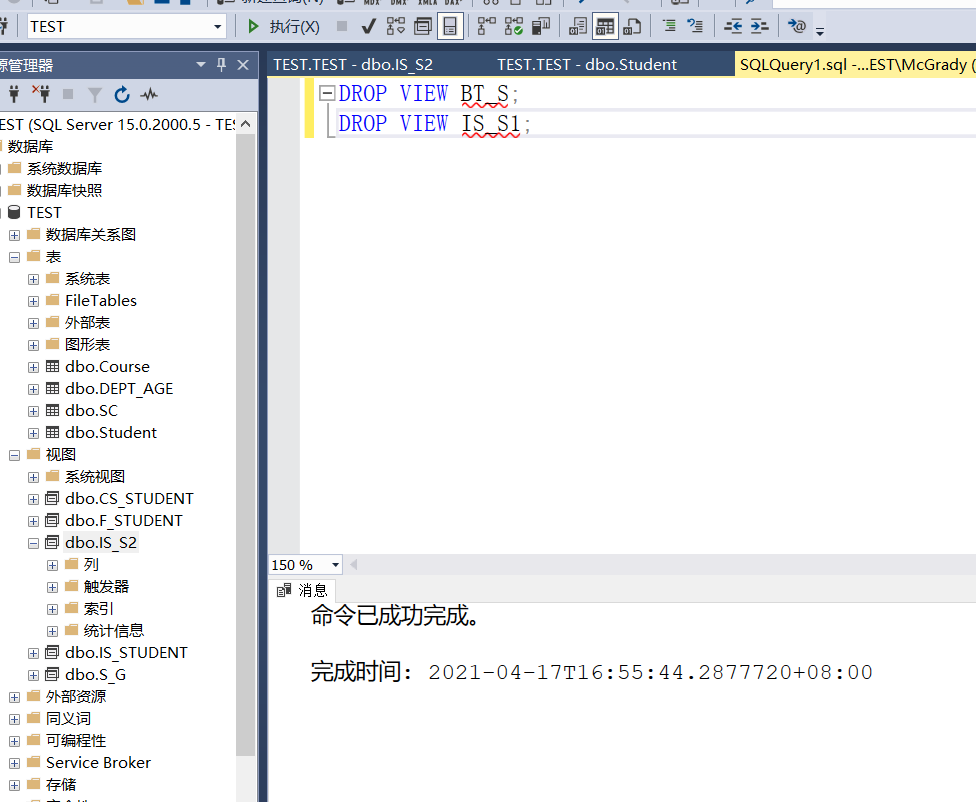
This is a little different from the book
Here because of creating is_ Is is used in S2_ S1 according to the book, it should be an error
But I found that is was deleted directly in T-SQL_ S2, but an error will be reported when you want to open it
Example 3.92 find students younger than 20 years old in the view of planning students.
select * from CS_Student where Sage<20;
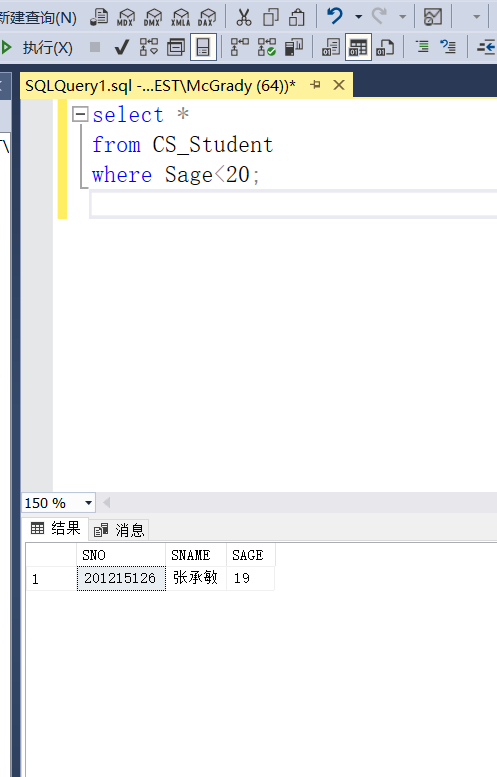
Example 3.94 in S_ Query the student number and average score of students with an average score of more than 90 in the G view
SELECT SNO,G_AVG FROM S_G WHERE G_AVG>=90;
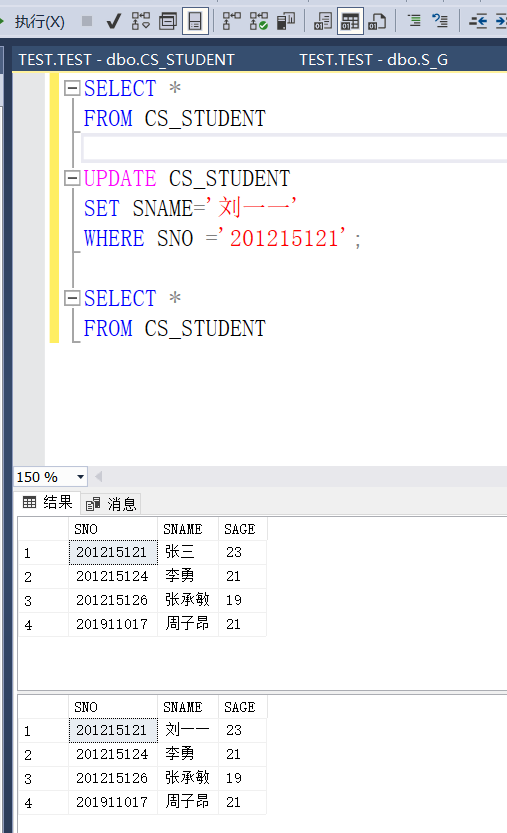
[example 3.95] the information department student view CS_ The student's middle school number "201215131" is changed to "Liu 11".
UPDATE CS_STUDENT SET SNAME='Liu Yiyi' WEHER SNO='201215131';
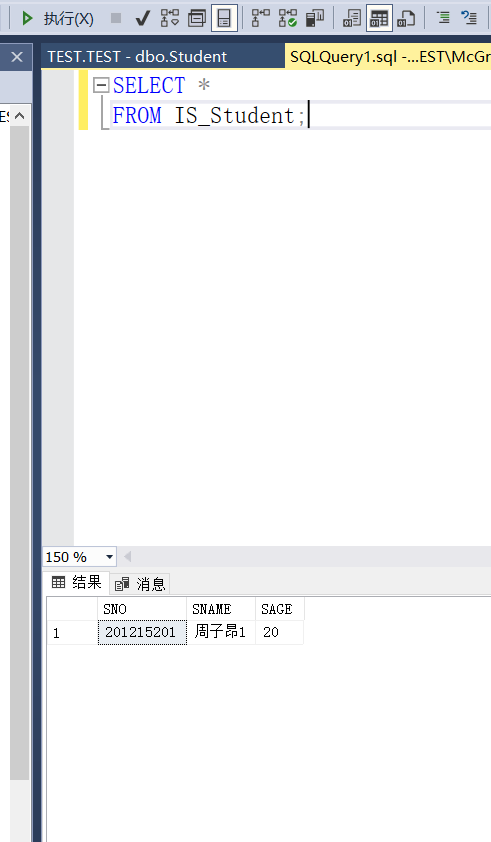
Example 3.96 view is to information students_ Insert a new student record into the student record, in which the student number is' 201215129 ', the name is' Zhao Xin', and the age is 20 years old
INSERT
INTO IS_STUDENT
VALUES('201215129','Zhao Xin','20');
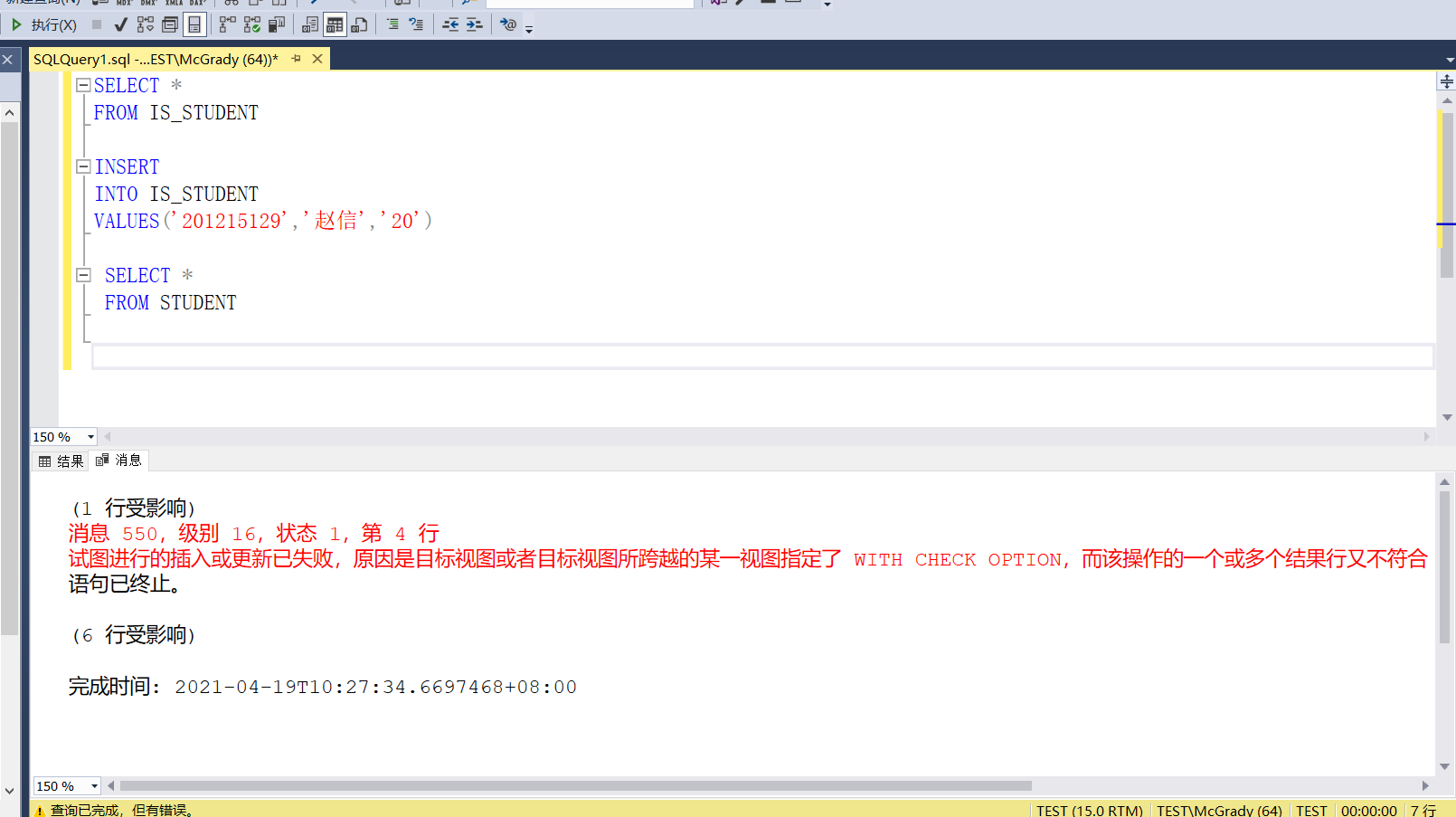
Write it in according to the code in the book and find the error
The attempted insert or update has failed because the target view or a view across which the target view spans specifies WITH CHECK OPTION, and one or more result rows of the operation do not comply with the CHECK OPTION constraint.
Baidu found that this is the difference between standard sql and tsql
Creating is_ In the student view, we added the with check option statement
First, the view only operates on the data it can query. For the data it cannot query, even if the base table has, it cannot be operated through the view.
For update, there is a with check option, which ensures that after update, the data will be queried by the view
For delete, whether there is a with check option or not is the same
For the insert, there is a with check option, which ensures that the data will be queried by the view after the insert
For views without a where clause, it is redundant to use the with check option.
In tsql, we need to ensure that the insert ed data can be represented in the view
Because we didn't specify that the new Zhao Xin IS a student of IS department
So tsql will report an error
But in the standard sql, when we add it, we will automatically add a message: that IS, the condition for creating the view IS automatically added. Zhao Xin IS a student of IS department
So when I was doing this experiment
Insert data directly into the student table
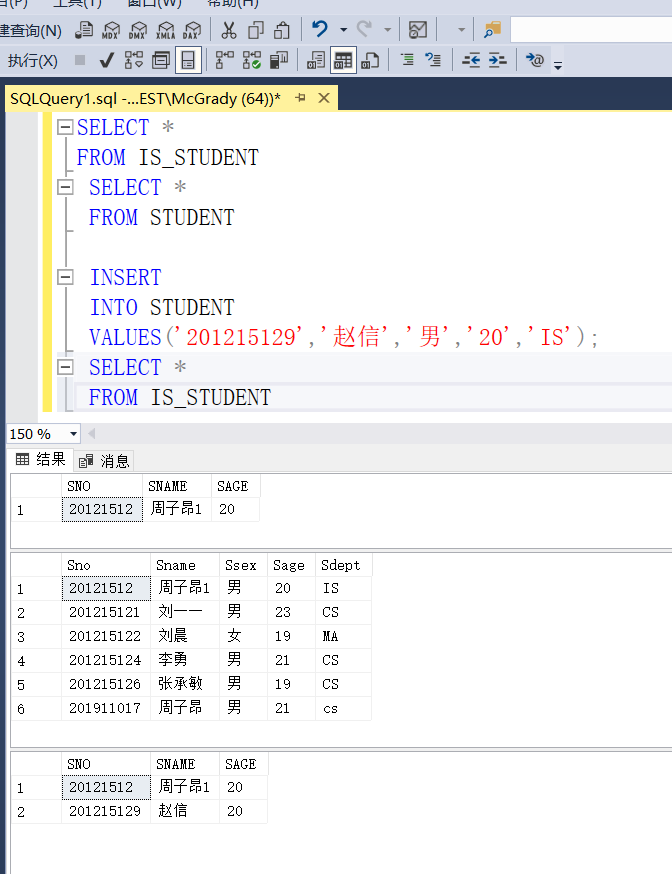
At this time, it was found that Zhao Xin was automatically in this view
[example 3.97] delete the CS of the students' View_ Student's middle school record No. "201215131"
delete from CS_Student where Sno='201215131';
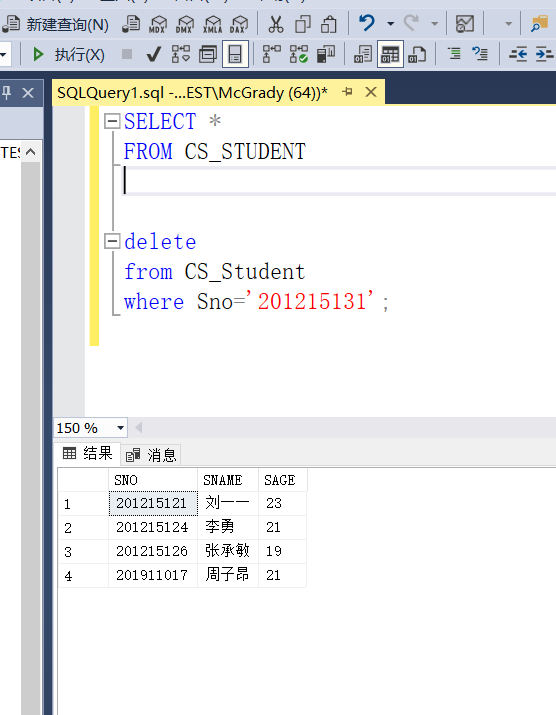
Finally, there are many differences between sql and tsql. At present, it is unclear whether there is any convenient way to add data to tsql with check option