Database application
concept
What is a database
In short, it is a warehouse for storing and managing data.
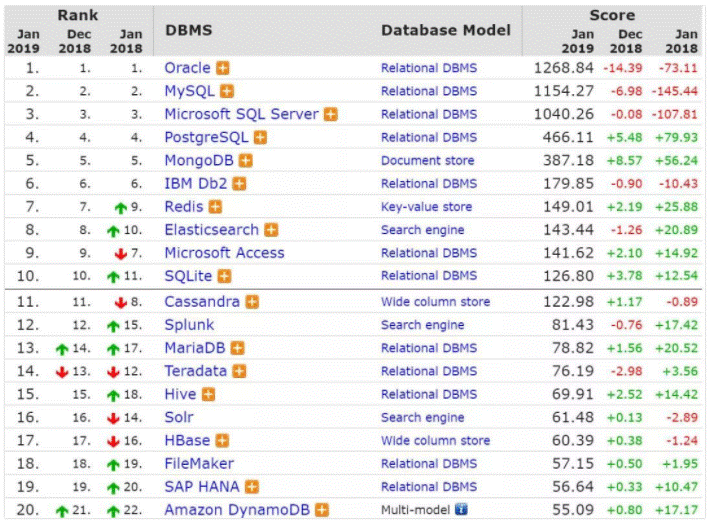
Common databases are divided into:
- Relational database, Oracle, MySQL, SQLServer, Access
- Non relational databases, MongoDB, Redis, Solr, ElasticSearch, Hive, HBase
Relational and non relational
The early developed databases were based on the close relationship of data (such as parent-child relationship and teacher-student relationship), which we call relational databases, also known as traditional databases; today's databases are based on the loose relationship of data (such as Chinese and Americans, Chinese and Indians, video and audio), which we call non relational databases nosql (not only sql). The industry is always debating whether nosql can kill traditional databases, and many beginners also have this confusion. In my opinion, there is no contradiction between the two. They have their own characteristics, and the true meaning is to complement each other according to the business situation. But generally speaking, the original pattern of unified relational databases has long been broken, the territory has been eroded, and the scale has been reduced again and again, although it can not be fully integrated It has been replaced, but it has long been lost and reduced to an even place. The decline of Oracle is the best proof. In the early days, as long as major global enterprises were all deploying Oracle, but now they are de Oracle, and Ali has completely excluded oracle.
Since we can't do it, most traditional projects focus on relational databases, so let's learn about relational databases first. At present, the most popular relational database is MySQL.
Relational database
Relational database has a specific organization. It stores data in the form of rows and columns for users to understand. The series of rows and columns in a relational database are called tables. A group of tables form a database. The user retrieves the data in the database through a query, which is an executive code used to limit some areas in the database. Relational model can be simply understood as two-dimensional table model, and a relational database is a data set composed of two-dimensional tables and their relationships.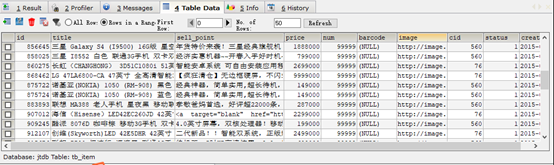
Mysql database
- mysql server, which handles specific data maintenance and saves the disk
- mysql client, CRUD, add, modify, delete, query
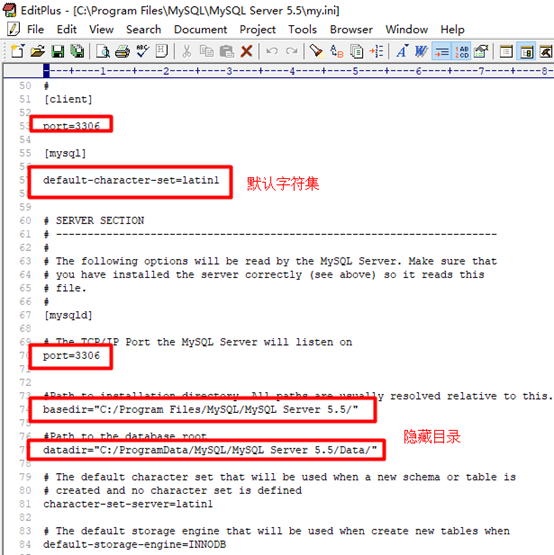
Where is MySQL data stored?
In the MySQL configuration file my Ini will be configured by default
MySQL server
mysql-5.5.27-winx64.msi
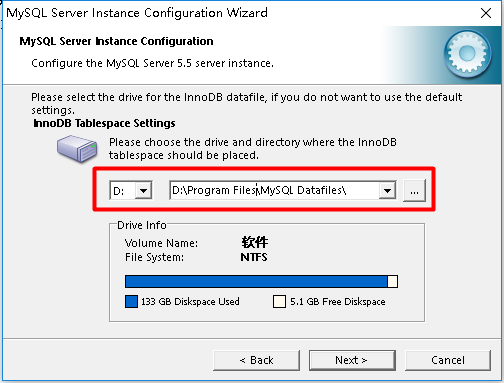
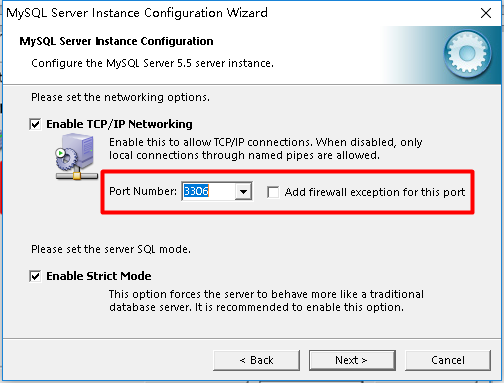
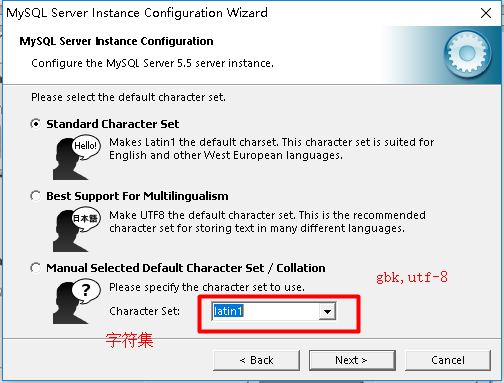
The default code of Mysql database is latin1, which is equivalent to iso-8859-1 and modified to utf-8
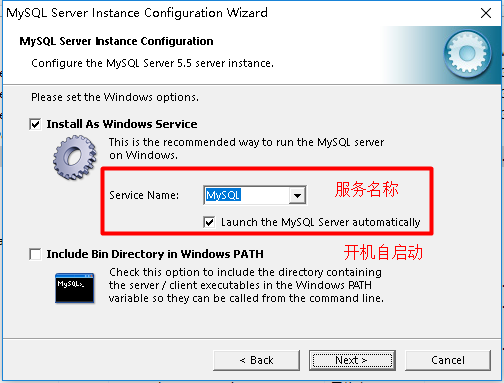
Note: after configuration, mysql starts to execute. Sometimes it can still be used if there are errors in the last step. Use SQLyog tool to test. If not, execute the installer, select remove, delete, and then reinstall. At the same time, note that it must be administrator permission.
MySQL client 1: DOS window
mysql -uroot -proot
Syntax: MySQL Exe executable
Representative parameters
-u user name, followed by
-p password, written next
MySQL client 2: visualizer
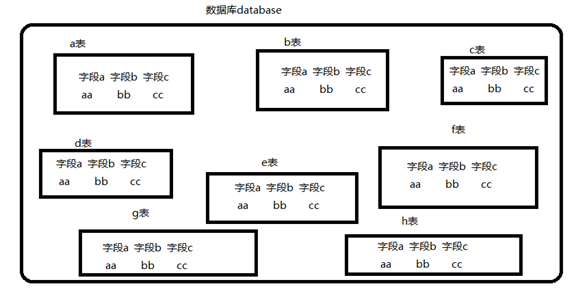
Structure of database
database structure
SQL statement
definition
Structured query language is abbreviated as SQL (pronunciation:/ ˈ es kju ː ˈ el/ "S-Q-L"), a special purpose programming language, is a database query and Programming language For accessing data and querying, updating and managing Relational database system ; Also Database script file The extension of the.
SQL was created in October 1986 by National Bureau of standards(ANSI )Passed database Language American standards, followed by the international organization for standardization( ISO )The official international standard of SQL was issued.
classification
- DML (Data Manipulation Language)
For example, insert, delete, update, select (insert, delete, modify, Retrieve) is referred to as CRUD operation, adding Create, querying Retrieve, modifying update, deleting delete
- DDL (Data Definition Language) database definition language
For example, create table
- DCL (Data Control Language)
For example, grant, deny, revoke, etc., only administrators have corresponding permissions
Note: SQL is not case sensitive
Common database operations
Build database
- Create database, database name: cbg2011
create database cbg2011 DEFAULT CHARACTER SET utf8;
- 1
Delete Library
- Delete the database whose name is cbg2011
drop database cbg2011;
- 1
View all databases
- View all databases
show databases;
- 1
Common operations of tables
Use database: use cbg2011;
- 1
Table design
Store table: * * tb_door**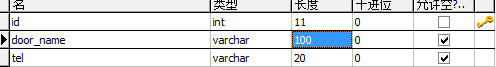
Order details: * * tb_order_detail**
Create table
- Create tb_door table with ID and door_ Name, Tel field
create table tb_door( id int primary key auto_increment, door_name varchar(100), tel varchar(50) );
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
Modify table
- Add column
alter table tb_door add column money NUMERIC(7,2)
- 1
Delete table
- The deletion name is TB_ Table for door
drop table tb_door;
- 1
View all tables
- View all tables
show tables;
- 1
View table structure / design table
- View tb_door table structure
desc tb_door;
- 1
Common operations of table records
insert record
- To TB_ Insert 2 records into the door table
insert into tb_door values(null,'Yonghe Dawang 1 store',666); insert into tb_door values(null,' Yonghe Dawang 2 store',888);
- 1
- 2
- 3
Query record
- Query TB_ All records in the door table
SELECT * FROM tb_door;
- 1
Modify record
- Modify TB_ Record with id 1 in door table
update tb_door set tel=555 where id=1;
- 1
Delete record
- Delete TB_ Data with id 2 in door table
Delete from tb_door where id=2;
- 1
sort
- Will tb_door table records are sorted by tel
Select * from tb_door order by tel desc;
- 1
Total records
- Query TB_ Total records in the door table
Select count(*) from tb_door;
- 1
data type
Naming rules
- The field name must start with a letter. Try not to use pinyin
- The length cannot exceed 30 characters (different databases, different versions)
- SQL reserved words, such as where, order and group, cannot be used
- Only the following characters AZ, AZ, 0 ~ 9, $, etc. can be used
- Oracle custom all caps: user_ Name, mysql, all lowercase: user_ name
- Multiple words are separated by underscores, rather than the hump rule of the java language
character
- char is fixed in length and cannot be filled with spaces. It can hold up to 2000 characters. char(11) stores abc, accounting for 11 bits. Query speed is very fast, but it wastes space
- varchar variable length string, which can hold up to 4000 characters. varchar(11) stores abc, accounting for only 3 bits. Query is slightly slow, but saves space. Oracle is varchar2
- Large text: large amount of text (not recommended, try to use varchar instead)
Calculated by utf8 coding, a Chinese character occupies 3 bytes under u8
Note: different database versions may have different length limits
number
- tinyint,int integer type
- float,double decimal type
- numberic(5,2) decimal(5,2) - can also represent decimals, representing a total of 5 digits, of which there can be two decimals
- decimal and numeric represent exact integer numbers
date
- date includes mm / DD / yy
- time hour minute second
- datetime includes month, day, hour, minute and second
- Timestamp timestamp is not a date, but the number of milliseconds from January 1, 1970 to the specified date
picture
- blob binary data, can store pictures and sounds, with a capacity of 4g. There was such a design in the early days. However, its disadvantages are very obvious. The database is huge and the backup is slow. It is of little value to back up multiple copies of these contents. At the same time, the database migration is too large and the migration time is too long. Therefore, at present, the mainstream will not directly store such data, but only store its access path, and the files are stored on disk.
Prepare data
Department table dept
| Field name | data type | Is it empty | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| deptno | int | Department number, PK primary key | |
| dname | varchar(20) | Y | Department name |
| loc | varchar(13) | Y | Location of Department |
CREATE TABLE dept( deptno int primary key auto_increment , dname VARCHAR(20), loc VARCHAR(13) ); INSERT INTO dept VALUES(null,'accounting','Area 1'); INSERT INTO dept VALUES(null,'research','Zone 2'); INSERT INTO dept VALUES(null,'operations','Zone 2');
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Employee form emp
| Field name | data type | Is it empty | remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| empno | int | Employee number, PK primary key | |
| ename | varchar(10) | Y | Employee name |
| job | varchar(10) | Y | position |
| mgr | int | Y | Superior number |
| hiredate | datetime | Y | Entry time |
| sal | double | Y | Monthly salary |
| comm | NUMERIC(8,2) | Y | bonus |
| deptno | int | Y | Department FK foreign key |
Mysql:
CREATE TABLE emp( empno int primary key auto_increment, ename VARCHAR(10), job VARCHAR(10), mgr int, hiredate DATE, sal double, comm NUMERIC(7,2), deptno int );
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
INSERT INTO emp VALUES(100,'jack','Vice President',NULL,'2002-05-1',90000,NULL,1); INSERT INTO emp VALUES(200,'tony','chief inspector',100,'2015-02-02',10000,2000,2); INSERT INTO emp VALUES(300,'hana','manager',200,'2017-02-02',8000,1000,2); INSERT INTO emp VALUES(400,'leo','staff',300,'2019-02-22',3000,200.12,2); INSERT INTO emp VALUES(500,'liu','staff',300,'2019-03-19',3500,200.58,2);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
Field constraints
Primary key constraint
Primary key constraint: if a primary key constraint is added to a column, the column is the primary key. The primary key is unique and cannot be empty. Usually, each table has a primary key.
Add a primary key constraint, such as setting id as primary key:
Primary key auto increment policy * * when the primary key is a numeric type, to facilitate maintenance, You can set the primary key auto increment policy (auto_increment). After the primary key auto increment policy is set, the database will save an auto_increment variable value in the table. The initial value is 1. When the id value is required, we do not need to specify the value. The database is responsible for obtaining an id value from auto_increment and inserting it into the table as the primary key value. Moreover, each time the auto_increment value is used up, it will automatically increment 1. AUTO_INCREMENT=1
create table abc( id int primary key auto_increment ); insert into abc values(null); insert into abc values(null); insert into abc values(null); select * from abc;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Non NULL constraint
Non empty constraint: if a non empty constraint is added to a column, the value of the column cannot be empty, but can be repeated.
Add a non empty constraint, such as adding a non empty constraint for password:
create table user( id int primary key auto_increment, password varchar(50) not null ); show tables; insert into user values(null,null);//Non NULL constraint not met insert into user values(null,123;);//OK
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
Unique constraint
Unique constraint: if a unique constraint is added to a column, the value of the column must be unique (that is, it cannot be repeated), but it can be empty.
Add unique constraints, such as adding unique constraints and non empty constraints for username:
create table test( id int primary key auto_increment, username varchar(50) unique--Unique constraint ); show tables; insert into test values(null,'lisi'); insert into test values(null,'lisi');--username The value of must be unique,Repeated errors will be reported select * from test;
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
Basic function
lower
SELECT 'ABC',LOWER('ABC') from dept; --Data to lowercase
- 1
upper
select upper(dname) from dept --Data to uppercase
- 1
length
select length(dname) from dept --Length of data
- 1
substr
SELECT dname,SUBSTR(dname,1,3) FROM dept; --intercept[1,3]
- 1
concat
select dname,concat(dname,'123') X from dept --Splice data
- 1
replace
select dname,replace(dname,'a','666') X from dept --hold a Replace characters with 666
- 1
ifnull
select ifnull(comm,10) comm from dept2 #Judge that if comm is null, replace it with 10
- 1
round & ceil & floor
round, ceil rounded up, floor rounded down
– direct rounding
select comm,round(comm) from emp
- 1
– round to one decimal place
select comm,round(comm,1) from emp
- 1
– ceil rounded up and floor rounded down
select comm,ceil(comm) ,floor(comm) from emp
- 1
uuid
SELECT UUID()
return uuid: a08528ca-741c-11ea-a9a1-005056c00001
- 1
now
select now() -- Year, day, hour, minute and second select curdate() --Year and day select curtime() --Hour, minute and second
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
year & month & day
– hour() minute() minute() second() second
select now(),hour(now()),minute(now()),second(now()) from emp ;
- 1
– year month day
select now(),year(now()),month(now()),day(now()) from emp ;
- 1
Escape character
'as a sql statement symbol, single apostrophe in the content will be disorderly, and can be escaped
select 'ab'cd' -- A single quotation mark is a SQL Special characters of the statement select 'ab\'cd' --When there are single quotes in the data,Use one\Escape to normal characters
Condition query
distinct
Use the distinct keyword to remove duplicate record lines
SELECT loc FROM dept; SELECT DISTINCT loc FROM dept;
- 1
- 2
- 3
where
Note: column aliases cannot be used in where!!
select * from emp select * from emp where 1=1 --Similar unconditional select * from emp where 1=0 --The condition is not tenable select * from emp where empno=100 --Unique condition select * from emp where ename='tony' and deptno=2 --Equivalent to two conditions&relationship select * from emp where ename='tony' or deptno=1 --Equivalent to two conditions|relationship select name, sal from emp where sal=1400 or sal=1600 or sal=1800; -- or select name, sal from emp where sal in(1400,1600,1800); select name, sal from emp where sal not in(1400,1600,1800);
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
like
The wildcard% represents 0 to n characters, and the wildcard is underlined_ Represents 1 character
select * from emp where ename like 'l%' --with l initial select * from emp where ename like '%a' --with a Ending select * from emp where ename like '%a%' --Intermediate inclusion a of select * from emp where ename like 'l\_\_' --l Followed by two characters _Represents a character position
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
null
select * from emp where mgr is null --Filter fields with empty values select * from emp where mgr is not null --The filter field value is not empty
- 1
- 2
- 3
between and
SELECT * FROM emp select * from emp where sal<3000 and sal>10000 select * from emp where sal<=3000 and sal>=10000--equivalent select * from emp where sal between 3000 and 10000--equivalent
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
limit
Record with the highest score: after sorting by score, limit n returns the first n records. Oracle is stupid and cumbersome to implement. It is introduced in the later stage, while MySQL is great with concise and efficient syntax. In mysql, perform paging query through limit:
select * from emp limit 2 --List the first two select * from emp limit 1,2 --Start with Article 2,Show 2 records select * from emp limit 0,3 --Start with the first one,Show 3 records--First three articles
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
order by
SELECT * FROM emp order by sal #Default ascending order SELECT * FROM emp order by sal desc #Descending order
- 1
- 2
- 3
Statistical cases
Enrollment statistics
#Old employees employed before 2015
#For employees signed after 2019, the date format is converted for comparison
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE YEAR(DATE_FORMAT(hiredate,'%Y-%m-%d'))<=2019;
- 1
#Employees from 2015 to 2019
SELECT * FROM emp WHERE STR\_TO\_DATE(hiredate,'%Y-%m-%d')\>='2015-01-01' AND STR\_TO\_DATE(hiredate,'%Y-%m-%d')\<='2019-12-31'
Annual salary statistics
The company's welfare is good, with double salary at the end of the year. The annual salary of employees = sal*13+comm*13
SELECT empno,ename,job,sal\*13+comm\*13 FROM emp; SELECT empno,ename,job,sal\*13+comm\*13 **as** **Annual salary** FROM emp;--use as List aliases for SELECT empno,ename,job,sal\*13+comm\*13 Annual salary FROM emp; --as It can also be omitted select ename, sal+comm from emp select ename, sal , comm, sal+ifnull(comm,0) from emp--Replace with 0 null
aggregation
According to a list of statistical results
count
select count(\*) from emp --The bottom layer is optimized select count(1) from emp --Effect and\*equally select count(comm) from emp --slow,Only non statistics NULL of
- min
select max(sal) from emp --Find the maximum value of the field select max(sal) sal,max(comm) comm from emp select min(sal) min from emp --Get minimum value select min(sal) min,max(sal) max from emp --Min max SELECT ename,MAX(sal) FROM emp group by ename --grouping
sum / avg
select count(\*) from emp --Total records select sum(sal) from emp --Sum select avg(sal) from emp --average
Grouping group
It is used for grouping statistics of query results
group by indicates grouping. The having clause is similar to the results returned by where filtering
group by
#The maximum salary and average salary of each position in each department, and the non aggregate column in the result must appear in the group, otherwise the business meaning is incorrect
SELECT deptno,MAX(sal),AVG(sal) FROM emp GROUP BY deptno #Group by deptno SELECT job,MAX(sal),AVG(sal) FROM emp GROUP BY job #Group by job SELECT deptno,job,MAX(sal),AVG(sal) FROM emp GROUP BY deptno,job #Both deptno and job are satisfied
having
#Departments with average wages less than 8000
select deptno, AVG(sal) from emp group by deptno #Group by Department having AVG(sal) \<8000 #Query criteria are similar to where, but group by can only be used with having #Number of deptno occurrences SELECT deptno,COUNT(deptno) FROM emp GROUP BY deptno #Group by deptno HAVING COUNT(deptno)\>1 #Frequent ## Summary ### What's the difference between char and varchar? char Is a fixed length string, char(n),n 255 Max varchar Is an indefinite length string, varchar(n),n The maximum length is 65535 char(10)and varchar(10)storage abc,What's the difference between them? char Save 10 characters, abc Three, others will be filled in with blanks; and varchar only need abc Three positions. ### What is the difference between datetime and timestamp? Database fields provide support for date types, which is the most troublesome of all data types. You will realize it slowly. date It's year and day time It's hour, minute and second datetime The storage and display are the same timestamp Timestamp, which stores not a date, but the number of milliseconds from January 1, 1970 to the specified date ### Chinese garbled code If in dos Execute under command insert Insert Chinese data, and the data is garbled. Now sqlYog The client executes the following command: set names utf8; set names gbk; Set the client character set to be the same as the server character set. If you don't know what code it uses? What shall I do? It's very simple. Try both. Whichever operation is completed and the query database is not garbled, use whichever one. Then why does it cause garbled code? Mysql The database default character set is lantin1,That is, the problems encountered in the web page in the future ISO8859-1,It is an English character set and does not support storing Chinese characters. When we create the library, we can specify the character set: create database yhdb charset utf8; However, this can easily lead to different coding sets between the server and the client, such as the server side utf8,client ISO8859-1. mysql And client tools have customary default coding settings, which should be unified in several places to ensure that there is no random code. We just need to make sure we use it when creating the database utf8,The use of visualization tools is generally correct. ### notes /\* Many comments \*/ \#Line comment content \-- Line comment content, which is used more ### What is the difference between primary key, foreign key and unique index? - Primary Key Primary key constraints, automatically creating unique indexes - Foreign Key Foreign key constraints. The content of a foreign key field refers to the content of a field in another table and cannot be written blindly - Unique Index Unique index, unique value but not primary key For the benefits of constraints, the database will check. If the constraints are violated, an error will be reported and the operation fails. Database provides rich constraint checking and other constraints, but it is rarely used under the premise of weakening relational database. Just remember the above three. ### What is the difference between drop, delete and truncate? drop Delete library or table, data and structure definitions delete and truncate Just delete the data of the table delete Can specify where Conditions, delete the records that meet the conditions, tuncate Delete all records For tables with self adding fields, delete It will not be cleared by self increment, and truncate Delete the table records and definitions, and then rebuild the table definitions, so the self incrementing primary key will start counting again