1. Closure function: Define a function inside the function, and the internal function refers to the variable of the external function
def outer(x,y): def my_max(): if x > y: # Referenced outer Parameters,Quite like a reference outer The variable of is a closure function return x return y return my_max res = outer(80,90) print(res())
2. Decorators: Opening and Closing Principle (Opening to Extension and Closing to Modification)
The decorator must abide by two principles 1: do not change the source code of the decorated object 2 do not change the call method of the decorated object
Insert: time module:
def outer(x,y): def my_max(): if x > y: # Referenced outer Parameters,Quite like a reference outer The variable of is a closure function return x return y return my_max res = outer(80,90) print(res())
- Decorate parameterless functions
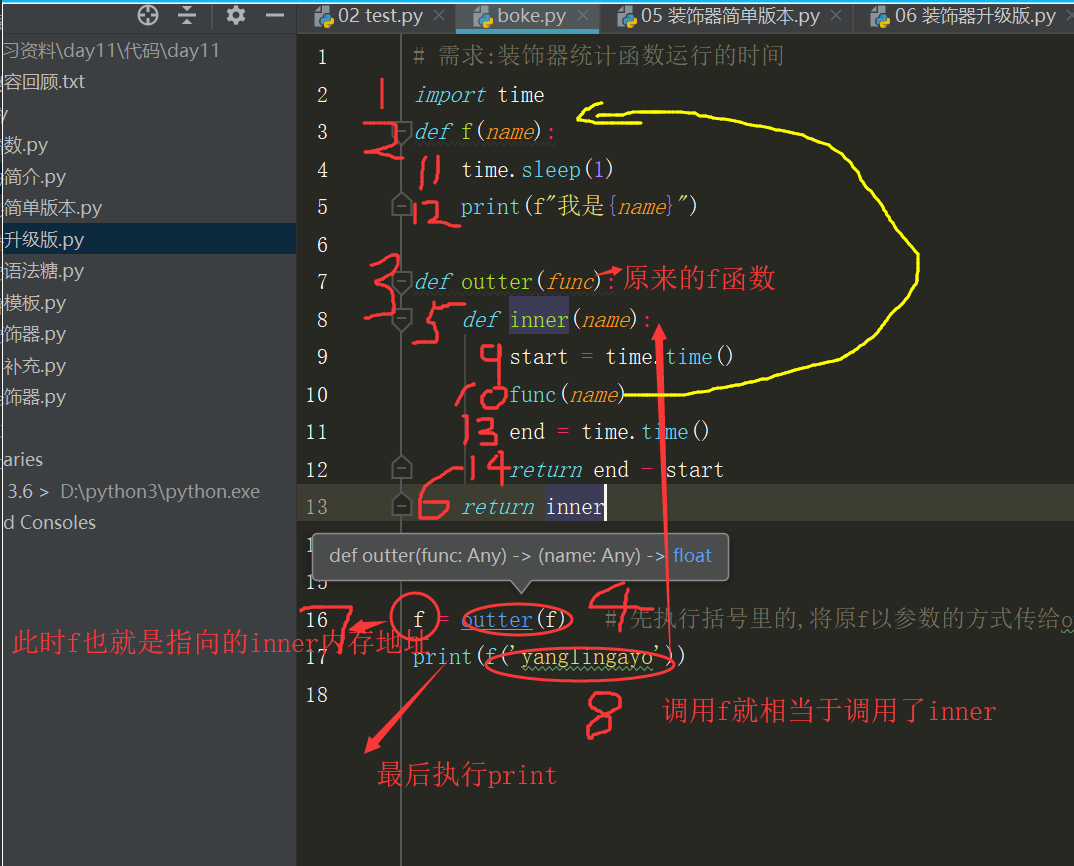
# demand:Running time of decorator statistical function import time def f(): time.sleep(1) print("I am f") def outter(func): # There func The parameter is passed in as an argument f Memory address of function def inner(): start = time.time() func() # The call here is from the beginning f function end = time.time() return end - start return inner # take inner Function's memory address return f = outter(f) # Execute first in parentheses,Make original f Passed as a parameter to outter Return inner Memory Address,Then call the newly defined f,Is equivalent to calling inner print(f()) # f() Is equivalent to calling inner
- Functions decorated with parameters
import time def f(name): time.sleep(1) print(f"I am{name}") def outter(func): # There func The parameter is passed in as an argument f Memory address of function def inner(name): # parameter name yes f Parameters name start = time.time() func(name) # The call here is from the beginning f function end = time.time() return end - start return inner f = outter(f) # Execute first in parentheses,Make original f Passed as a parameter to outter Return inner Memory Address,Then call the newly defined f,Is equivalent to calling inner print(f('yanglingayo')) # f() Is equivalent to calling inner
- Decorator Grammatical Sugar: Grammatical sugar is next to the decorated function when decorating. When multiple decorators decorate a function, the order is top-down, while executing from bottom-up
import time def outter(func): def inner(name): start = time.time() func(name) end = time.time() return end - start return inner @outter # use@Add decorator function name to represent,Placed above the decorated function is equivalent to f = outter(f) def f(name): time.sleep(1) print(f"I am{name}") print(f('yanglingayo'))
- Templates for Decorators
def outter(func): def inner(*args,**kwargs): print('What you can do before performing the decorated function') res = func(*args,**kwargs) print('What you can do after performing the decorated function') return res return inner
- Multiple decorators decorate a function
- Decorator Final Template
from functools import wraps def outter(func): @wraps(func) # Decorator Repair Technology def inner(*args,**kwargs): print('What you can do before the decorated function is executed') res = func(*args,**kwargs) print('What you can do after the decorated function is executed') return res return inner
- Multilayer Decoration
def outter1(func1): print('Loaded outter1') def wrapper1(*args,**kwargs): print('Executed wrapper1') res1=func1(*args,**kwargs) return res1 return wrapper1 def outter2(func2): print('Loaded outter2') def wrapper2(*args,**kwargs): print('Executed wrapper2') res2=func2(*args,**kwargs) return res2 return wrapper2 def outter3(func3): print('Loaded outter3') def wrapper3(*args,**kwargs): print('Executed wrapper3') res3=func3(*args,**kwargs) return res3 return wrapper3 @outter1 # index = outter1(wapper2) @outter2 # wrapper2 = outter2(wrapper3) @outter3 # wrapper3 = outter3(ancestral index Function memory address) def index(): print('from index')
This is my understanding that the decorated function is treated as a center, and he adds a shell to it without being decorated once. When I call to execute this decorated function, it is as if he is going to pull the shell apart. Dialing one layer from the outside to the inside will be executed before each decorated function is executed from the outside to the inside.Operation, when the decorated function is finally executed, execute each decorator from the inside out to execute the decorated function on each layer, just like a needle through an egg with three layers of eggs