Day0 four hex and encoding
Course objective: to explain some necessary common sense knowledge in computer and let students understand the meaning behind some common nouns (focusing on understanding).
Course overview:
- How python code works
- Base system
- Units in a computer
- code
1.Python code operation mode
-
Scripted
python3 ~/PycharmProjects/day03/6.Explanation of homework questions.py
-
interactive
python3

2. Binary
All data at the bottom of the computer exists in the form of 010101 (picture, text, video, etc.).
-
Binary
0 1 10

-
octal number system
-
decimal system
-
hexadecimal

2.1 binary conversion
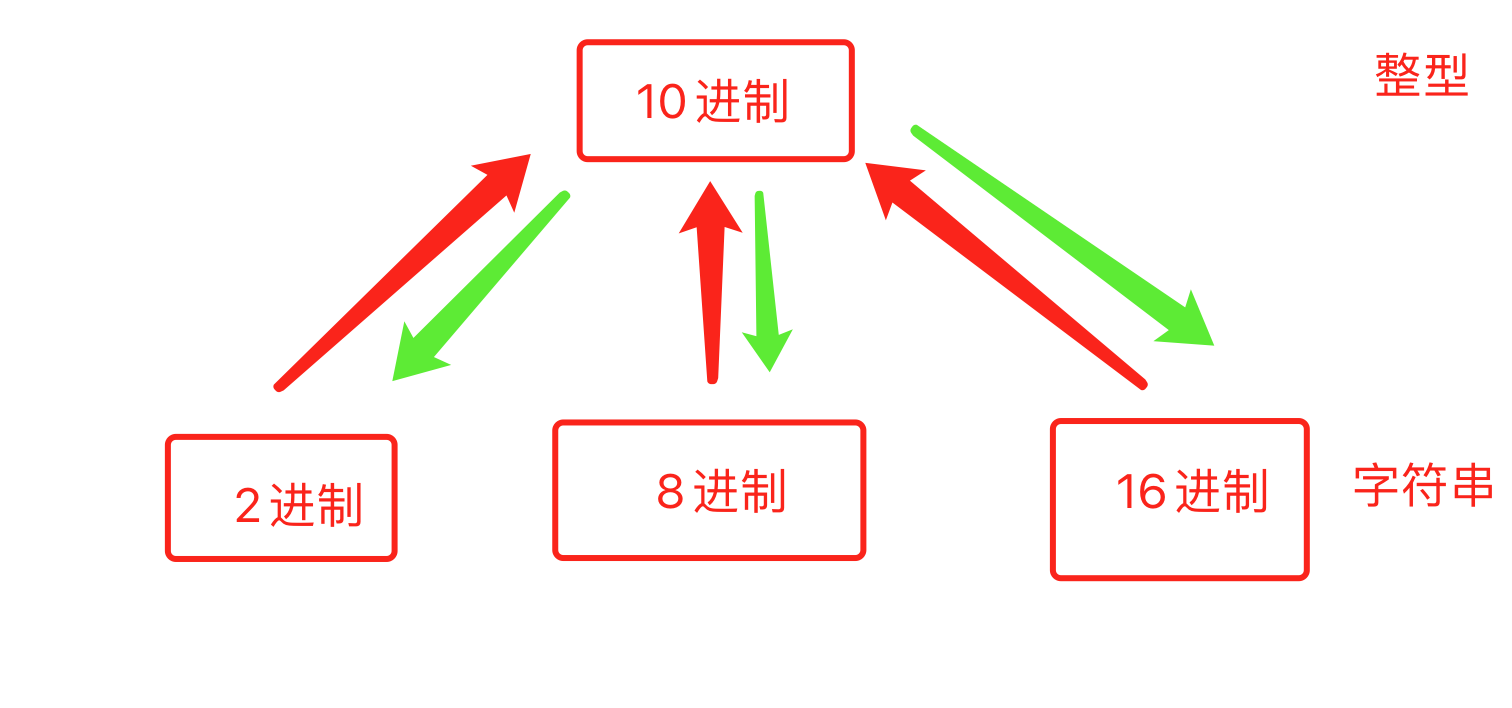
25 vl = bin(25) # Replace decimal with binary v2 = oct(25) # Replace decimal With Octal v3 = hex(25) # Convert decimal to hexadecimal
i1 = int("0b11001", base=2) # Binary to decimal
i1 = int("0b11001", base=8) # Binary to decimal
i1 = int("0b11001", base=16) # Replace binary with hexadecimal
3. Units in the computer
Since virtually everything in the computer is stored and operated as binary, in order to facilitate the representation of binary size, some units have been made
-
b (bit), bit
1 # One 10 # both of you 110 # Three
-
B (byte), byte
8 Bit is a byte 10010110 # 1 byte 10010110 10010110 # 2 bytes
-
KB, (kilobyte), kilobyte
1024 A byte is a kilobyte 1KB = 1024B 10101010 10101010 ..... 1KB 1KB = 1024B= 1024 * 8 b
-
M (Megabyte), Megabyte
1MB = 1024KB 1M = 1024KB = 1024*1024B = 1024*1024*8b
-
G (Gigabyte), Gigabit
1024M = 1GB
-
T (Terabyte), Terabyte
1024GB = 1TB
-
... Other larger units PB/EB/ZB/YB/BB/NB/DB will not be repeated.
4. Coding
Encoding, a correspondence table between text and binary.
4.1 ASCII encoding
ascii specifies that one byte is used to represent the correspondence between letters and binary.
0000000 00000001 w 00000010 B 00000011 a ... 11111111 2**8 = 256


4.2 gb-2312 coding
gb-2312 code, produced by the National Information Standards Committee (1980).
gbk code extends gb2312 to include Chinese, Japanese and Korean characters (1995).
When corresponding to binary, the following logic is used:
- Single byte representation, with one byte representing the corresponding relationship. 2 * * 8 = 256 possibilities
- Two bytes represent, and two bytes represent the corresponding relationship. 2 * * 16 = 65536 possibilities.
4.3 unicode
unicode, also known as universal code, assigns a code point (binary representation) to every word in the world.
-
ucs2
Use a fixed two bytes to represent a text. 00000000 00000000 Comprehend ... 2**16 = 65535
-
ucs4
Use a fixed 4 bytes to represent a text. 00000000 00000000 00000000 00000000 nothing ... 2**32 = 4294967296
written words hexadecimal Binary ȧ 0227 1000100111 ȧ 0227 00000010 00100111 ucs2 ȧ 0227 00000000 00000000 00000010 00100111 ucs4 Joe 4E54 100111001010100 Joe 4E54 01001110 01010100 ucs2 Joe 4E54 00000000 00000000 01001110 01010100 ucs4 😆 1F606 11111011000000110 😆 1F606 00000000 00000001 11110110 00000110 ucs4
Both ucs2 and ucs4 have disadvantages: waste of space?
written words hexadecimal Binary A 0041 01000001 A 0041 00000000 01000001 A 0041 00000000 00000000 00000000 01000001
Application of unicode: in file storage and network transmission, unicode will not be used directly, but in memory.
4.4 utf-8 coding
Containing the correspondence between all words and binary, it is the most widely used coding in the world (standing on the shoulders of Giants).
In essence: utf-8 is a compression of Unicode, which uses as few binaries as possible to correspond to text. When storing data, Unicode is converted to utf-8 for storage and optimization
unicode Code point range utf-8 0000 ~ 007F Expressed in 1 byte 0080 ~ 07FF Represented by 2 bytes 0800 ~ FFFF Represented by 3 bytes 10000 ~ 10FFFF Represented by 4 bytes
Specific compression process:
-
Step 1: select a conversion template
Code point range (HEX) Conversion template 0000 ~ 007F 0XXXXXXX 0080 ~ 07FF 110XXXXX 10XXXXXX 0800 ~ FFFF 1110XXXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX 10000 ~ 10FFFF 11110XXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX For example: "B" Corresponding unicode If the code point is 0042, it should select a template. "ǣ" Corresponding unicode The code point is 01 E3,The second template should be selected. "martial" Corresponding unicode The code point is 6 B66,The third template should be selected. 😆 Corresponding unicode The code point is 1 F606,The fourth template should be selected. Note: generally, the third template (3 bytes) is used in Chinese, which means that people usually speak Chinese in English utf-8 The reason why it will occupy 3 bytes in. -
Step 2: fill in data in the template
- "martial" -> 6B66 -> 110 101101 100110 - Insert data according to template 1110XXXX 10XXXXXX 10XXXXXX 1110XXXX 10XXXXXX 10100110 1110XXXX 10101101 10100110 11100110 10101101 10100110 stay UTF-8 Code "Wu" 11100110 10101101 10100110 - 😆 -> 1F606 -> 11111 011000 000110 - Insert data according to template 11110000 10011111 10011000 10000110
4.5 Python related coding
String( str) "Hammer" unicode handle Generally in memory Byte( byte) b"alexfdsfdsdfskdfsd" utf-8 code or gbk code Generally used for file or network processing
v1 = "martial"
# Convert Unicode processed encoding to utf-8 encoding
v2 = "martial".encode("utf-8")
# Convert Unicode processed encoding to gbk encoding
v2 = "martial".encode("gbk")
Writes a string to a file.
name = "Hammer"
# Use utf-8 format for storage
data = name.encode("utf-8")
# Open a file
file_object = open("log.txt",mode="wb")
# Write content in file
file_object.write(data)
# Close file
file_object.close()
summary
The knowledge points in this chapter are mainly understanding. Understanding these foundations is conducive to the learning of the following knowledge points. Next, all the knowledge points in this section are summarized:
-
Everything on the computer will eventually be converted into binary and run.
-
ascii encoding, unicode character set and utf-8 encoding are essentially the relationship between characters and binary.
- ascii, character and binary comparison table.
- Comparison table of unicode, character and binary (code point).
- utf-8 compresses the code points of unicode character set, and indirectly maintains the comparison table between characters and binary.
-
ucs2 and ucs4 refer to the number of bytes used to represent the code point of the unicode character set.
-
At present, the most extensive coding is utf-8, which can represent all characters, and the storage or network transmission will not waste resources (the code bits are compressed).
-
Binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal are actually different times of carry.
-
Realize the conversion between binary, octal, decimal and hexadecimal based on Python.
-
One byte 8 bits
-
The relationship between common units b/B/KB/M/G in computer.
-
For Chinese characters, 2 bytes are required for gbk encoding; Encoding with utf-8 requires 3 bytes.
-
Converting strings to bytes (utf-8 encoding) based on Python implementation
# String type name = "Hammer" print(name) # Hammer # Convert string to byte type data = name.encode("utf-8") print(data) # b'\xe9\x93\x81\xe9\x94\xa4' # Convert bytes to strings old = data.decode("utf-8") print(old) -
Converting strings to bytes (gbk encoding) based on Python implementation
# String type name = "Hammer" print(name) # Hammer # Convert string to byte type data = name.encode("gbk") # print(data) # B '\ xe9 \ X93 \ x81 \ xe9 \ x94 \ Xa4' utf8, Chinese 3 bytes print(data) #B '\ Xcc \ xfa \ xb4 \ xb8' GBK, Chinese 2 bytes # Convert bytes to strings old = data.decode("gbk") print(old)