FTP, NFS, SAMBA system services
1, rsync hosted xinetd
1. Why service hosting
Independent service: independent startup script ssh ftp nfs dns
Dependent service: there is no independent startup script. rsync telnet depends on xinetd service (independent service)
2. How can rsync be managed by xinetd service?
Step 1: install xinetd service in the system
# yum -y install xinetd # rpm -ql xinetd
Step 2: write xinetd Conf file (/ etc/xinetd.conf)
# man 5 xinetd.conf
defaults
{
only_from Allow access only
no_access access denied
access_times Controls the time period for accessing the service
log_type Specify log type
interface Number of concurrent connections
per_source each IP Maximum number of connections
}
includedir /etc/xinetd.d Sub profile directory (append) rsync,telnet)
Step 3: manually create / etc / xinetd d/rsync
# vim /etc/xinetd.d/rsync
service rsync
{
disable = no
flags = IPv6
socket_type = stream
wait = no
user = root
server = /usr/bin/rsync
server_args = --daemon
log_on_failure += USERID
}
remarks:disable = no //Switch; no means to start the service; yes means to shut down the service
Step 4: restart the xinetd service (after the xinetd service is restarted, the rsync service will also be restarted to check the port occupation)
# pkill rsync
# systemctl restart xinetd
# ss -naltp |grep 873
LISTEN :::873 users:(("xinetd",pid=45079,fd=5))
When querying the occupation of port 873, it is found that there is only xinetd service and no rsync service. Reason: rsync = > xinetd
Frequently asked questions (empirical value)
If we're starting xinetd During service, it is found that port 873 in the system has not been occupied. There can only be one problem: there is an error in the configuration file! Solution: cat /var/log/messages Be sure to pay attention to the color change. If there is a color change, it means that it is the correct option. If there is no color change, it is certain that you have some invisible characters when copying.
2, FTP service overview
1. Introduction to FTP service
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) is a widely used and ancient Internet file transfer protocol.
File transfer: file upload and file download
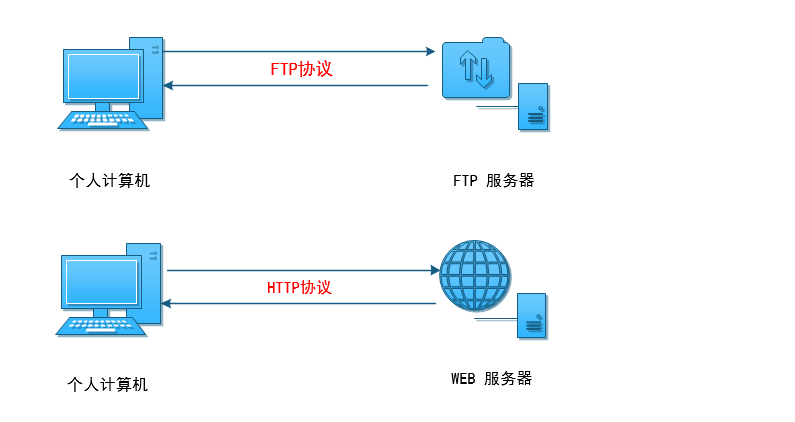
- It is mainly used for two-way transmission (upload / download) and file sharing of files on the Internet
- Cross platform Linux, Windows
- FTP is a C/S architecture, with a client and server. It uses TCP protocol as the underlying transmission protocol to provide reliable data transmission
- The default port of FTP is 21 (command port) and 20 (data port, in active mode) in passive mode by default
- FTP program (software) vsftpd
FTP software name = > vsftpd = > vs (very secure ftp daemon)
2. Client tools for FTP service
- Linux: ftp, lftp (client program)
- Windows: FlashFXP (virtual host), FileZilla, IE, Chrome, Firefox
- Differences between lftp and ftp tools:
- lftp: accessed by anonymous users by default
- ftp: accessed by user name / password by default
- lftp can batch and download directories
3. Two operating modes of FTP (understand)
In FTP service, there are two modes (active mode + passive mode)
Reference point, server side of FTP. If the FTP server actively connects to the client = > active mode, if the client actively connects to the FTP server = > passive mode.
☆ active mode
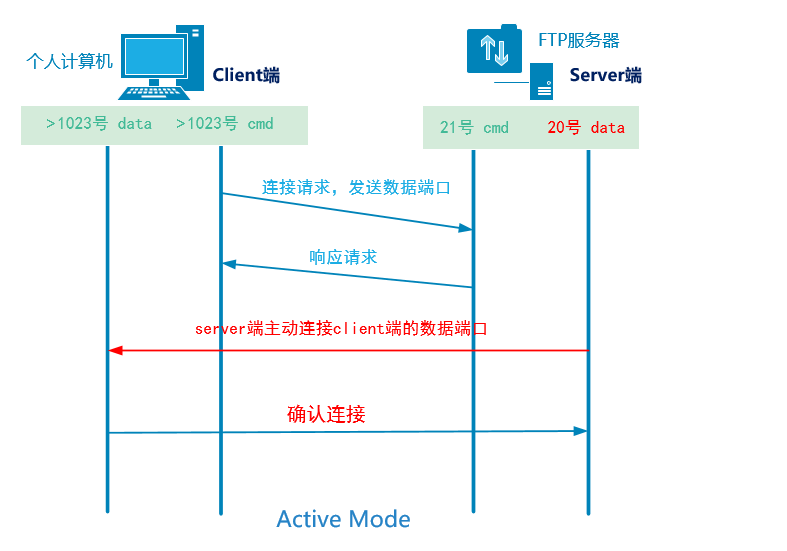
cmd: command port (send FTP request)
Data: data port (used to transmit data later)
1. The client opens the random command port greater than 1023 and the random data port greater than 1023 to initiate a request to port 21 of the service 2. The command port 21 of the server responds to the random command port of the client 3. Port 20 of the server actively requests to connect to the random data port of the client 4. Confirm the random data port of the client
☆ passive mode
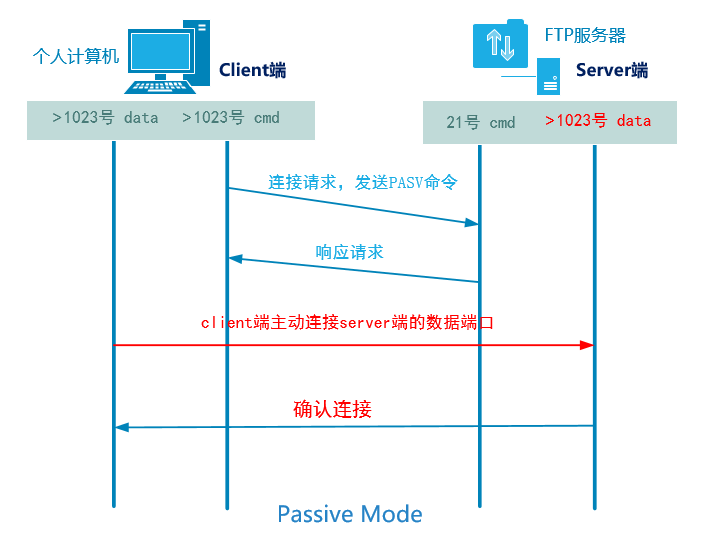
1. The client opens the random command port greater than 1023 and the random data port greater than 1023 to initiate a request to port 21 of the service 2. The command port 21 of the server responds to the random command port of the client 3. The client actively connects to the random data port larger than 1023 opened by the server 4. The server confirms
FTP uses passive mode by default!
4. Set up FTP service (important)
1. Turn off firewalls and selinux 2. to configure yum source(mount /dev/sr0 /mnt) 3. Software Trilogy 4. Understanding profiles 5. Modify the configuration file according to the requirements to complete the service construction 6. Start the service and start it automatically 7. Test verification
Step 1: turn off the firewall and SELinux
# systemctl stop firewalld # systemctl disable firewalld # setenforce 0 # vim /etc/selinux/config SELINUX=disabled
Step 2: configure YUM source
Public network with network configuration YUM Source (Alibaba, Tsinghua, Huawei) can be configured locally without a network YUM source # mount /dev/sr0 /mnt # yum clean all # yum makecache
Step 3: install vsftpd software (FTP = > vsftpd)
# yum install vsftpd -y
Step 4: start the ftp service and add it to the startup item
# systemctl start vsftpd # systemctl enable vsftpd
Step 5: test whether FTP is installed successfully
# ifconfig ens33 inet 10.1.1.10 netmask 255.255.255.0 broadcast 10.1.1.255
☆ browser based access
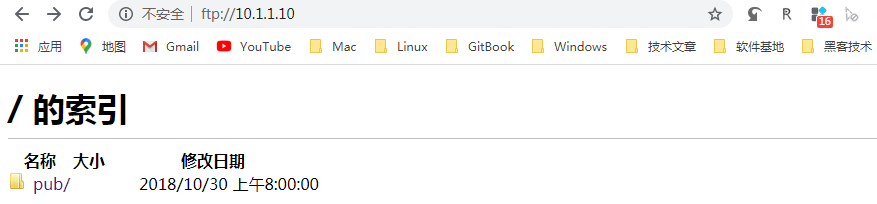
☆ Windows Explorer Based Access
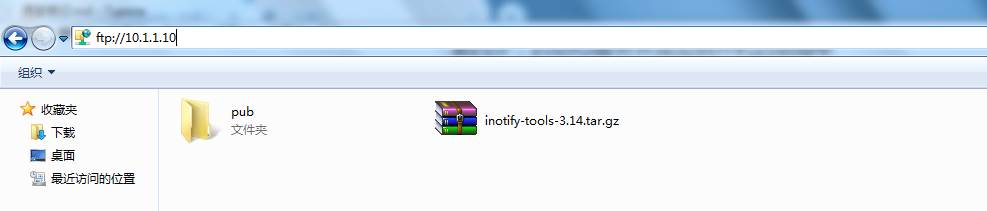
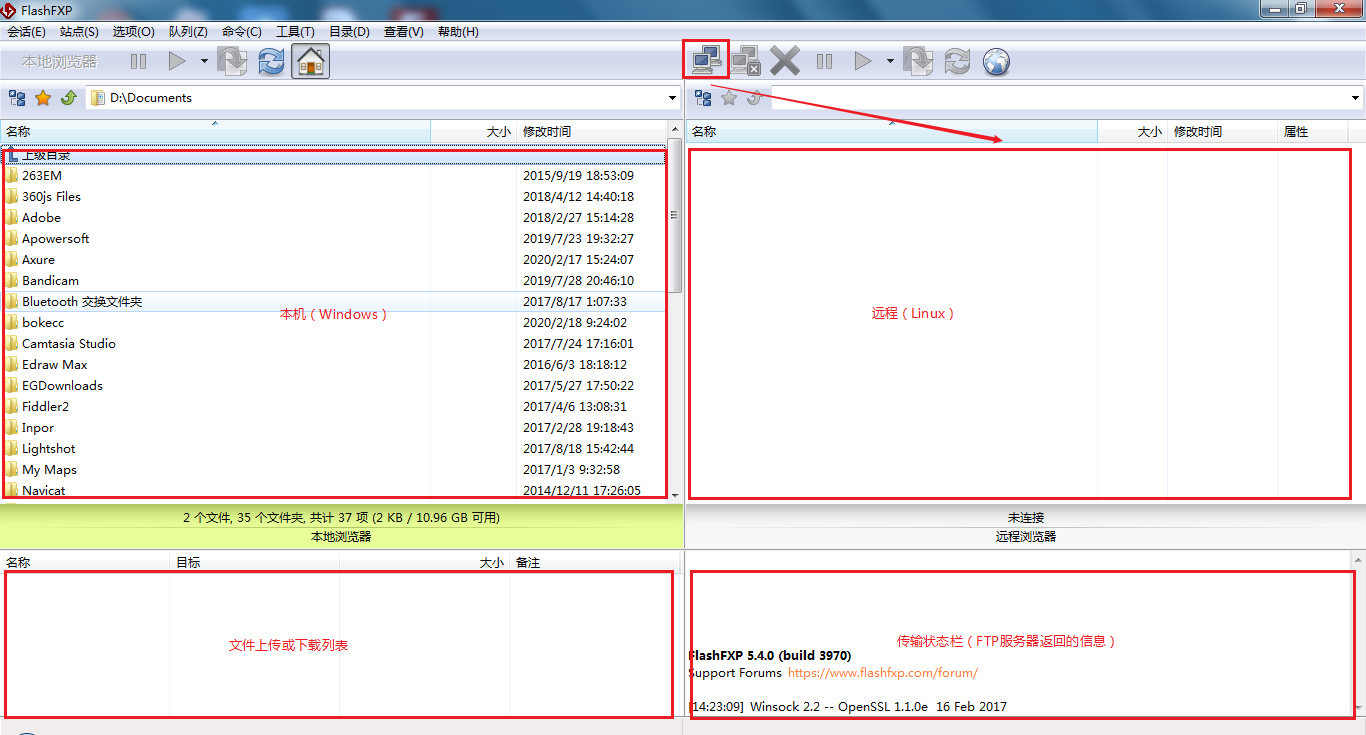
☆ based on FlashFxp and FileZilla software
☆ connection based on FTP and lftp commands (FTP file transfer between Linux and Linux)
yum install ftp lftp -y # ftp 10.1.1.10
5. Detailed description of FTP configuration file (important)
On the Server side, use rpm -ql vsftpd
# rpm -ql vsftpd /usr/lib/systemd/system/vsftpd.service Startup script /etc/vsftpd Directory of configuration files /etc/vsftpd/ftpusers User list file, blacklist /etc/vsftpd/user_list User list file, black or white (blacklist by default) /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf configuration file(Master profile) /usr/sbin/vsftpd Program itself (binary command) /var/ftp Default data root directory for anonymous users /var/ftp/pub Extended data directory for anonymous users
Details of vsftpd configuration file:
# grep -v ^# /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf anonymous_enable=YES Support anonymous user access local_enable=YES Support non anonymous users,Log in with an ordinary account and enter your home directory by default write_enable=YES Write master switch local_umask=022 Unmask file:644 rw- r-- r-- dir:755 dirmessage_enable=YES Enable message function xferlog_enable=YES Turn on or enable xferlog journal connect_from_port_20=YES Support active mode (default passive mode) xferlog_std_format=YES xferlog Log format listen=YES ftp Monitoring in service independent mode pam_service_name=vsftpd Specify certification documents userlist_enable=YES Enable user list tcp_wrappers=YES support tcp_wrappers function(FTP Speed limit operation)
# man 5 vsftpd.conf
3, FTP task solution
1. Task background
To put it simply: build a customer service system (mainly involving customer service data upload and download) according to what we have learned (FTP)
1. Customer service personnel must use user name and password(kefu/123)Log in to the server to download the corresponding documents 2. Anonymous user access is not allowed 3. The relevant documents of the customer service department are saved in the designated directory/data/kefu local_root=/data/kefu 4. Customer service user kefu/123 After logging in, you can only use the default/data/kefu Activity in directory
2. Create customer service account (Server)
# useradd kefu # echo 123 |passwd --stdin kefu
3. Anonymous user access is not allowed
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 12 that 's ok anonymous_enable=NO
After modifying the configuration, be sure to restart the vsftpd service
# systemctl restart vsftpd
4. Specify the directory accessed by the account
# mkdir /data/kefu -p # vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 17 that 's ok local_root=/data/kefu
5. kefu/123 can only be active in / data/kefu directory
Imprisoned kefu users can only be in the / data/kefu directory
# vim /etc/vsftp/vsftpd.conf 18 that 's ok chroot_local_user=YES
After the configuration modification is completed, the vsftpd service must be restarted
# systemctl restart vsftpd
4, Empirical value
1,500 OOPS
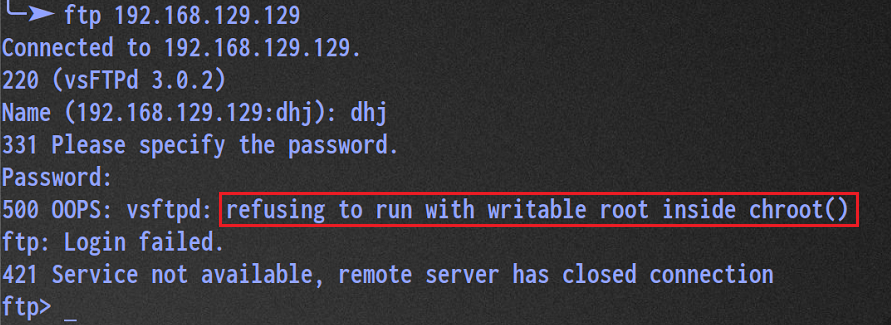
The above problems mainly occur in ftp2 In versions after 3.5, of course, you can use it
# rpm -qi vsftpd view version information
Solution:
① Remove write permission (treat symptoms but not root causes)
# chmod a-w /home/dhj
② Core solution, add an option
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 19 that 's ok allow_writeable_chroot=YES
2. Unable to upload
The reason why it cannot be uploaded is that the account kefu does not have w write permission to the / data/kefu folder
# setfacl -R -m u:kefu:rwx /data/kefu # systemctl restart vsftpd
3. Imprisonment directory supplement
18 that 's ok chroot_local_user=YES Imprison all users
Requirement: can we open non imprisoned permissions for a small number of users.
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 105 that 's ok chroot_list_enable=YES Open user list file 107 that 's ok chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list Specify user list file echo kefu >> /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list On behalf of customer service, this account will not be locked in the specified directory # systemctl restart vsftpd
3. Imprisonment directory supplement
18 that 's ok chroot_local_user=YES Imprison all users
Requirement: can we open non imprisoned permissions for a small number of users.
# vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf 105 that 's ok chroot_list_enable=YES Open user list file 107 that 's ok chroot_list_file=/etc/vsftpd/chroot_list Specify user list file echo kefu >> /etc/vsftpd/chroot_list On behalf of customer service, this account will not be locked in the specified directory # systemctl restart vsftpd