Defcon 2018 Qualify: Easy Pisy
1. Source Code
The title is given to two people:
- execute.php
<?php
include 'common.php';
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET') {
print highlight_string(file_get_contents("execute.php"), TRUE);
exit(0);
}
$keys = get_keys();
$privkey = $keys[0];
$pubkey = $keys[1];
$file_info = $_FILES['userfile'];
check_uploaded_file($file_info);
$data = file_get_contents($file_info['tmp_name']);
$signature = hex2bin($_POST['signature']);
if (openssl_verify($data, $signature, $pubkey)) {
print 'Signature is OK.<br/>';
} else {
die('Bad signature.');
}
$text = pdf_to_text($file_info['tmp_name']);
print "Text: \"$text\"<br/>";
$execute_query = "EXECUTE ";
$echo_query = "ECHO ";
if (substr($text, 0, strlen($execute_query)) === $execute_query) {
$payload = substr($text, strlen($execute_query));
print "About to execute: \"$payload\".<br/>";
$out = shell_exec($payload);
print "Output: $out";
} else if (substr($text, 0, strlen($echo_query)) === $echo_query) {
$payload = substr($text, strlen($echo_query));
print "About to echo: \"$payload\".<br/>";
echo $payload;
} else {
print "I can't recognize the command type. Go away.<br/>";
}
?>
- shellme.php
<?php
include 'common.php';
if ($_SERVER['REQUEST_METHOD'] === 'GET') {
print highlight_string(file_get_contents("sign.php"), TRUE);
exit(0);
}
$keys = get_keys();
$privkey = $keys[0];
$pubkey = $keys[1];
if ($privkey === FALSE || $pubkey === FALSE) {
die("Could not load keys. Contact admin.<br/>");
}
$file_info = $_FILES['userfile'];
check_uploaded_file($file_info);
$text = pdf_to_text($file_info['tmp_name']);
print "Extracted text: \"$text\"<br/>";
$execute_query = "EXECUTE ";
$echo_query = "ECHO ";
if (substr($text, 0, strlen($execute_query)) === $execute_query) {
print "I don't sign EXECUTE commands. Go away.<br/>";
} else if (substr($text, 0, strlen($echo_query)) === $echo_query) {
print "I'm OK with ECHO commands. Here is the signature: <br/>";
$data = file_get_contents($file_info['tmp_name']);
openssl_sign($data, $signature, $privkey);
print bin2hex($signature);
} else {
print "I can't recognize the command type. Go away.<br/>";
}
?>
2. Writeup
-
shellme.php is the portal. Users upload the pdf with ECHO as the first place to get signature
-
Upload signature and pdf to execute php
- First check the signature consistency
- If ECHO is the first place of PDF, the PDF content is displayed
- If the first place of PDF is EXECUTE, EXECUTE the PDF content
The test site of this question is to check the consistency of signature,
Note that the function used to verify the signature in the title is openssl_verify
This function uses the sha1 algorithm for signature by default
Due to sha1 unsafe , we can use tool Collide the pdf content with the same signature, which is the first to EXECUTE instead of ECHO, so as to RCE.
3. Info
challenge source code https://gist.github.com/janmasarik/232381eec3918313b5b4d2c20ca1ed0f
CTF Time writeup https://ctftime.org/task/6094
Writeup provider teams:
- mhackeroni
- EmpireCTF
- tuna$laves
Author: Not Found, But Maybe
- https://gist.github.com/janmasarik/ This guy has a problem
- https://github.com/nneonneo/ The elder brother wrote the corresponding tools before the topic
- Marc Stevens(CWI Amsterdam) this is the work of announcing the first SHA1 collection
- Elie Bursztein (Google) "announcing the first SHA1 collection"
writeup for study: https://github.com/0e85dc6eaf/CTF-Writeups/tree/05ad6a9ecbc19ceb8890f4581dfee36f16d164aa/DEF%20CON%20CTF%20Qualifier%202018/Easy%20Pisy#easy-pisy
tools used:
4. Analysis of Author
Since it is still uncertain who the author of this question is, we should first face the top four who are more likely at present.
4.1 janmasarik
- languages
- python\go\php
- Social media
- https://twitter.com/s14ve
- https://masarik.sh/
- Recent
- resolvers Check tool for DNS interception? twenty million two hundred and ten thousand four hundred and sixteen
- low-hanging Madleets Jscan
- bucketsperm Cloud storage bucket privilege vulnerability scanner made with low hanging above?
- Automating Bug Bounty Thesis: automatic vulnerability digging? This seems to be dedicated to tapping cloud storage vulnerabilities. It should be linked with bucketsperm
Mr. jan.masarik's dynamic since 19 years is mainly in the automatic mining of cloud storage vulnerabilities.
4.2 nneonneo (Robert Xiao)
- languages
- python
- Social media
- https://twitter.com/nneonneo
- https://www.robertxiao.ca
- Recent
At the end of 2020, the github dynamics of nneonneo boss are all engaged in RE and PWN, and the research work is relatively low-level. There should be no problem with the web ⑧
And it seems that the boss of nneonneo is CTFer rather than the person who makes the question, but how did he design the question making tool before making the question
That means he read Marc's article
4.3 Marc Stevens
-
languages
- C/C++
-
Social media
-
Recent
- Non-interactive cryptographic timestamping based on verifiable delay functions 2020
- Real World Cryptanalysis 2019
- The general sieve kernel and new records in lattice reduction
- sha1collisiondetection But this seems to be the easypasy test site of defcon for 18 years
- snippets Marc personal script collection warehouse
-
Learn about non interactive cryptographic timing based on verifiable delay functions
-
Take a closer look at the update details of sha1collisiondetection. Maybe new knowledge points can be updated to make a question?
-
The teacher also wrote an article on blockchain On immutability of blockchains
4.4 Elie Bursztein (Google)
- languages
- Python/PHP
- Social media
- Recent
Although it is the second work of announcing the first SHA1 collection, Elie's main energy is still invested in the fields of Phishing, Malware, Abuse and so on.
I prefer these popular science articles without mathematical formulas in his blog, which are as happy as reading novels. My girlfriend likes things with logical derivation and mathematical calculus, which will be more beautiful and artistic
From the perspective of field matching degree, Elie is also more in line with the portrait of EasyPisy's questioner.
But I hardly see anything about CTF in my blog.
This idea of "defense against bypass attack based on deep learning" is publicized in Defcon 28 & Black Hat USA 2020 / / todo
Cryptography bypass attack: Intermediate variable vulnerability of AES algorithm based on bypass attack // TODO
5. Signature function in language
First find the signature functions in the standard libraries of various languages, and then further find the signature functions introduced in the third-party libraries.
5.1 php
https://www.php.net/manual/zh/function.hash-hmac-file.php
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000020201103
https://www.php.net/manual/zh/ref.openssl.php
5.1.1 standards library
5.1.1.1 Hash
Since PHP 5.1.2, Hash has become a built-in extension.
Since PHP 7.4.0, Hash has become the core extension, and its functions can be used directly.
Hash function
- hash_algos -- returns a list of registered hash algorithms
- hash_copy - copy hash context
- hash_equals - string comparison that prevents timing attacks
- hash_file - generates a hash value for the contents of the specified file
- hash_final - ends the incremental hash and returns the summary result
- hash_hkdf — Generate a HKDF key derivation of a supplied key input
- hash_hmac_algos — Return a list of registered hashing algorithms suitable for hash_hmac
- hash_hmac_file - generates a hash value with a key using the HMAC method and the contents of the given file
- hash_hmac -- generates a hash value with a key using the HMAC method
- hash_init -- initializes the incremental hash operation context
- hash_pbkdf2 - PBKDF2 key export that generates the supplied password
- hash_update_file -- populates data from a file into the context of an active hash operation
- hash_update_stream -- populates data from an open stream to an active hash context
- hash_update - populates the active hash context with data
- Hash - generate hash value (message digest)
There is no default value for the algo parameter of Hash series functions.
5.1.1.2 Cryptographic hash algorithm function
The following functions can be called directly
If you want to use Argon2 password hash, PHP must be built with -- with password Argon2 [= dir] configuration option and libargon2.
Cryptographic hash algorithm function
- password_algos — Get available password hashing algorithm IDs
- password_get_info - returns information about the specified hash
- password_hash - create hash of password (hash)
- password_needs_rehash -- detects whether the hash value matches the specified option
- password_verify - verify that the password matches the hash value
password_hash all available signature algorithms as follows - PASSWORD_BCRYPT (default) Learning links
- PASSWORD_ARGON2I Learning links
- PASSWORD_ARGON2ID
- PASSWORD_ARGON2_DEFAULT_MEMORY_COST
- PASSWORD_ARGON2_DEFAULT_TIME_COST
- PASSWORD_ARGON2_DEFAULT_THREADS
Hash function slow Learning links //What's this? I don't understand... Let's talk about it after my girlfriend reads it
ARGON2Learning links
5.1.2 third party Library
5.1.2.1 OpenSSL
To use the OpenSSL module of PHP, you must use the -- with OpenSSL [= dir] parameter to compile PHP.
All functions of OpenSSL library are as follows
openssl_cipher_iv_length — Get password iv length openssl_cms_decrypt — Decrypt a CMS message openssl_cms_encrypt — Encrypt a CMS message openssl_cms_read — Export the CMS file to an array of PEM certificates openssl_cms_sign — Sign a file openssl_cms_verify — Verify a CMS signature openssl_csr_export_to_file — take CSR Export to file openssl_csr_export — take CSR Export as string openssl_csr_get_public_key — return CSR Public key of openssl_csr_get_subject — return CSR Theme of openssl_csr_new — Generate a CSR openssl_csr_sign — Sign with another certificate CSR (Or itself) And generate a certificate openssl_decrypt — Decrypt data openssl_dh_compute_key — Computing remote DH secret key(Public key)And local DH Shared key for key openssl_digest — Calculation summary openssl_encrypt — Encrypted data openssl_error_string — return openSSL Error message openssl_free_key — Release key resource openssl_get_cert_locations — Retrieve available certificate locations openssl_get_cipher_methods — Get available encryption algorithms openssl_get_curve_names — get ECC List of available curve names for openssl_get_md_methods — Get available summary algorithms openssl_get_privatekey — alias openssl_pkey_get_private openssl_get_publickey — alias openssl_pkey_get_public openssl_open — Open sealed data openssl_pbkdf2 — Generate a PKCS5 v2 PBKDF2 character string openssl_pkcs12_export_to_file — Output one PKCS#12 compatible certificate storage files openssl_pkcs12_export — take PKCS#12 export compatible certificate storage file to variable openssl_pkcs12_read — take PKCS#The certificate store is parsed into an array openssl_pkcs7_decrypt — Decrypt a S/MIME Encrypted message openssl_pkcs7_encrypt — Encrypt one S/MIME news openssl_pkcs7_read — take PKCS7 Export file as PEM Array of format certificates openssl_pkcs7_sign — Yes, one S/MIME Sign messages openssl_pkcs7_verify — Verify a signed S/MIME Signature of message openssl_pkey_derive — Computes shared secret for public value of remote and local DH or ECDH key openssl_pkey_export_to_file — Export key to file openssl_pkey_export — Converts the exportable representation of a key to a string openssl_pkey_free — Release a private key openssl_pkey_get_details — Returns an array containing key details openssl_pkey_get_private — Get private key openssl_pkey_get_public — Resolve the public key from the certificate for use. openssl_pkey_new — Generate a new private key openssl_private_decrypt — Decrypt data using private key openssl_private_encrypt — Encrypt data with private key openssl_public_decrypt — Decrypt data using public key openssl_public_encrypt — Encrypt data using public key openssl_random_pseudo_bytes — Generate a pseudo-random byte string openssl_seal — seal up (encryption) data openssl_sign — Generate signature openssl_spki_export_challenge — Export challenge string related to signature public key and challenge openssl_spki_export — Export an available public key by signing the public key and challenge PEM Format public key openssl_spki_new — Generate a new signature public key and challenge openssl_spki_verify — Verify signature public key and challenge. openssl_verify — Verify signature openssl_x509_check_private_key — Check whether the private key corresponds to the certificate openssl_x509_checkpurpose — Verify that certificates can be used for specific purposes openssl_x509_export_to_file — Export certificate to file openssl_x509_export — Export certificate in string format openssl_x509_fingerprint — Calculate a given x.509 Fingerprint or abstract of the certificate openssl_x509_free — Release certificate resources openssl_x509_parse — Parse a X509 Certificate and return information as an array openssl_x509_read — Parse a x.509 Certificate and returns a resource identifier openssl_x509_verify — Verifies digital signature of x509 certificate against a public key
The openssl library functions are classified with the default algorithm as follows:
Default encryption algorithm: OpenSSL_ CIPHER_ RC2_ Function of 40
- openssl_cms_encrypt
- openssl_pkcs7_encrypt
Default encoding method: OpenSSL_ ENCODING_ Functions of smime
- openssl_cms_verify
- openssl_cms_sign
Default encryption and decryption method: RC4 function
- openssl_open
- openssl_seal
Default signature function: SHA1
- openssl_pbkdf2
- openssl_sign
- openssl_verify
- openssl_x509_fingerprint
Default signature flag: pkcs7_ Function of detached
- openssl_pkcs7_sign
Default padding: OpenSSL_ PKCS1_ Function of padding
- openssl_private_decrypt
- openssl_private_encrypt
- openssl_public_decrypt
- openssl_public_encrypt
5.2 python
5.2.1 standards library
5.2.1.1 hashlib
The underlying code of hashlib is the openssl open source library. The methods supported by openssl can be supported by hashlib.
All supported methods are:
DSA, DSA-SHA, MD4, MD5, RIPEMD160, SHA, SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512, blake2b, blake2s, dsaEncryption, dsaWithSHA, ecdsa-with-SHA1, md4, md5, ripemd160, sha, sha1, sha224, sha256, sha384, sha3_224, sha3_256, sha3_384, sha3_512, sha512, shake_128, shake_256, whirlpool
Among them, no matter what operating system the execution and operation environment is, the methods that must be available are:
blake2b, blake2s, md5, sha1, sha224, sha256, sha384, sha3_224, sha3_256, sha3_384, sha3_512, sha512, shake_128, shake_256
Algorithms in different environments_ Guaranteed different
The environment here is Python 3 7.7 MacOS 10.14.6
hashlib can be used as follows:
import hashlib
h = hashlib.md5()
h.update("hello".encode('utf-8'))
print(h.hexdigest())
h = hashlib.sha1()
h.update("hello".encode('utf-8'))
print(h.hexdigest())
hashlib is initialized with the method name. The code is as follows:
hash_name = "sha1"
h = hashlib.new(hash_name)
h.update(args.data.encode('utf-8'))
print(h.hexdigest())
This kind of unclear statement uses what hash writing method, which is more convenient to write the title.
5.2.1.2 hmac
Normative hmac RFC standard
hmac is a standardized implementation for checking message integrity in communication
The usage is as follows
import hmac import hashlib h = hmac.new(b'secret-shared-key', 'hello', hashlib.sha1) digest = h.hexdigest() print(digest)
hmac. The new function has three parameters: secret key, message and signature algorithm
The signature algorithm defaults to md5
5.2.2 third party Library
5.2.2.1 cryptography
Cryptography : a python package that provides encryption algorithms and primitives.
5.2.2.2 VoidSpace
VoidSpace Is a Hashlib decorator for IronPython
5.3 go
5.3.1 standards library
5.3.1.1 crypto
All available Hash methods are as follows
const (
MD4 Hash = 1 + iota // import golang.org/x/crypto/md4
MD5 // import crypto/md5
SHA1 // import crypto/sha1
SHA224 // import crypto/sha256
SHA256 // import crypto/sha256
SHA384 // import crypto/sha512
SHA512 // import crypto/sha512
MD5SHA1 // no implementation; MD5+SHA1 used for TLS RSA
RIPEMD160 // import golang.org/x/crypto/ripemd160
SHA3_224 // import golang.org/x/crypto/sha3
SHA3_256 // import golang.org/x/crypto/sha3
SHA3_384 // import golang.org/x/crypto/sha3
SHA3_512 // import golang.org/x/crypto/sha3
SHA512_224 // import crypto/sha512
SHA512_256 // import crypto/sha512
BLAKE2s_256 // import golang.org/x/crypto/blake2s
BLAKE2b_256 // import golang.org/x/crypto/blake2b
BLAKE2b_384 // import golang.org/x/crypto/blake2b
BLAKE2b_512 // import golang.org/x/crypto/blake2b
)
Use MD5 as an example
func GetMd5String(s string) string {
h := md5.New()
h.Write([]byte(s))
return hex.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
}
5.3.1.2 other encryption packages under crypto package
aes,cipher,des,dsa,ecdsa,elliptic,hmac,md5,rand,rc4,rsa,sha1,sha256,sha512,subtle,tls,x509
5.3.2 third party Library
It seems that Golang does not have a particularly mainstream third-party encryption library, and the standard library can solve most of the needs.
6. Cryptography knowledge points
md5
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MD5
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37257569
Hash function slow
https://tate-young.github.io/2019/05/21/bcrypt.html
By the way, this kind of slow hash function is designed to resist the attackers who break the dictionary.
In addition to the feature that all Hash functions have "give Hash, let reverse calculation, and can not calculate the original text", at the same time, "with the original text, it is very slow to calculate Hash"
For example, bcrypt,scrypt,PBKDF2, etc
python bcrypt is written as follows:
import bcrypt passwd = b's$cret12' salt = bcrypt.gensalt() hashed = bcrypt.hashpw(passwd, salt) print(salt) print(hashed)
ARGON2
https://github.com/P-H-C/phc-winner-argon2/raw/master/argon2-specs.pdf
Towards Practical Attacks on Argon2i and Balloon Hashing
It is also a slow hash function.
Memory hard Hash function: improve the time consumption of Hash of the algorithm by increasing the memory usage in the algorithm.
RC2_40
http://cryptowiki.net/index.php?title=RC2/40_english
https://github.com/SaschaWessel/rc2-40-cbc
SMIME
https://www.cse.scu.edu/~tschwarz/coen350_03/Lectures/smime.html
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/S/MIME
Secure email encryption
How to use SMIME
S box
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/S%E7%9B%92
Generally, S-Box accepts a specific number of input bits m and converts it into a specific number of output bits n, where n is not necessarily equal to m[1]. One m × The S-Box of N can be realized by a lookup table containing 2m entries and N bits of each item.
S-boxes are usually fixed (such as DES and AES encryption algorithms), and some S-boxes of encryption algorithms are dynamically generated based on keys (such as Blowfish and Pisces encryption algorithms).
RC4
https://zh.wikipedia.org/zh-hans/RC4
SHA1
https://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/SHA-1
PKCS7_DETACHED
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000019793040
OPENSSL_PKCS1_PADDING
https://blog.csdn.net/liuxianbing119/article/details/7405628
ecdsa
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/97953640
subtle
subtle is not only the name of golang encrypted bag, but also a brand of men's satchel.
It seems to be the kind of style that is obviously luxurious, but it is dressed as a floor stall on me
Ah, I'm distracted again

https://documentation.help/Golang/crypto_subtle.htm
7. Bucket configuration error
Mr. jan.masarik's dynamic since 19 years is mainly in the automatic mining of cloud storage vulnerabilities.
- bucketsperm
- Automating Bug Bounty
First, let's learn about the Bucket misconfiguration vulnerability.
Thousands of patient data were destroyed due to the misconfigured Amazon S3 bucket
When using OSS, you must first create a Bucket storage space.
How does alicloud create a Bucket
In Mr. jan.masarik's paper, he summarized the mistakes that users often make when creating buckets:
- No permission restriction ACL is configured, and all contents are public Lead to the disclosure of sensitive information
- At the same time, many people will name buckets according to the purpose of buckets, just like naming variables.
So that many buckets that store sensitive information can be accessed by breaking sub domain names.
Mr. jan.masarik summarized these bucket name s that may store sensitive information into Group2 in the following table
At the same time, Bucket name Group 1, which is often used but generally does not store sensitive information, is given
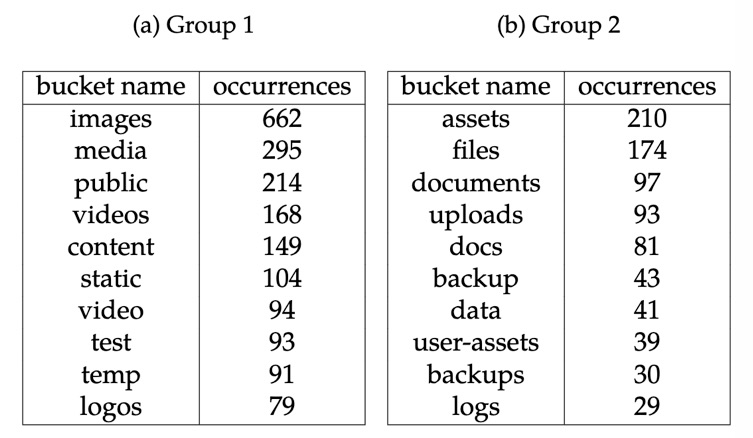
At the end of the paper, jan.masarik suggests that these OSS providers set up bucket name blacklists.
Alibaba cloud OSS does not have this restriction when viewing documents.

I found several oss tutorials on google and github,
Visited the oss link in the tutorial. - When the bucket exists and the path exists, but the ACL is private, the following error is reported.

- When the bucket exists but the path does not exist, the following error is reported

- When the bucket does not exist, the following error is reported

- When the bucket exists, the path exists, and the access permission exists, you can access the corresponding file or folder.
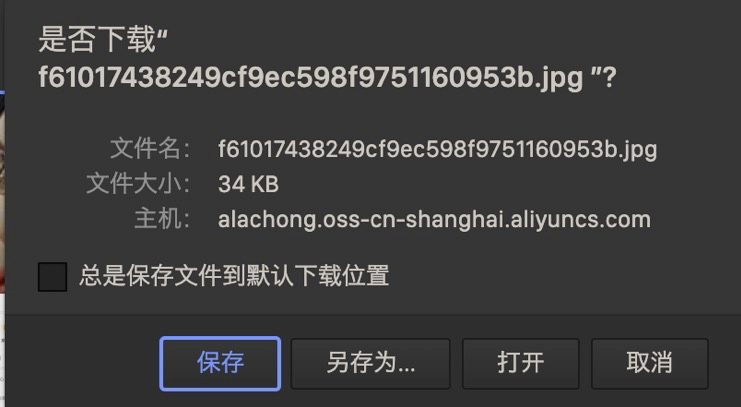
The oss bucket with the wrong ACL configuration has not been found yet
Some oss links are collected through subdomain name resolution, and there are indeed keywords in Group2. It does look tempting.

However, the access result is not good. It should be that the sub domain name corresponding to the bucket has cancelled the oss service.
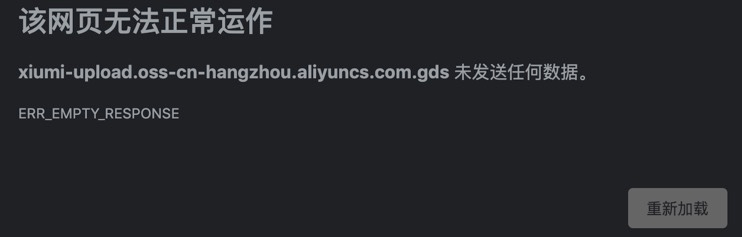
For the time being, we have not encountered the oss configuration error vulnerability instance mentioned in Mr. jan's paper.
8. <Non-interactive cryptographic timestamping based on verifiable delay functions>
We usually rely on an authoritative server for timestamp verification in web applications.
In order to achieve decentralization, Marc Stevens proposed this decentralized timestamp scheme based on VDF.
9. sha1collisiondetection
TODO
10. <On immutability of blockchains>
TODO
11. collect Crypto 2021 Paper
TODO
12. A Hacker's guide to reducing side-channel attack surfaces using deep-learning
This idea of "defense against bypass attack based on deep learning" is publicized in Defcon 28 & Black Hat USA 2020 / / todo
13. Intermediate variable vulnerability of AES algorithm based on bypass attack
Cryptography bypass attack: Intermediate variable vulnerability of AES algorithm based on bypass attack // TODO
summary
There are four possible questions for EasyPisy, and the possible directions of each person are as follows
- janmasarik: buckets unauthorized access vulnerability (WEB)
- nneonneo (Robert Xiao): ios reverse (RE)
- Marc Stevens: decentralized timestamp based on VDF (BLOCKCHAIN)
- Elie Bursztein (Google): AES bypass attack (CRYPTO)