Integration of Log in SpringBoot
1, Classification of logs
1. Name classification
- log4j: log for java
- logBack log description
Note: by default, springBoot integrates logback logs
2. Log classification
Root log: Global log rootlogger (log level of springboot: info)
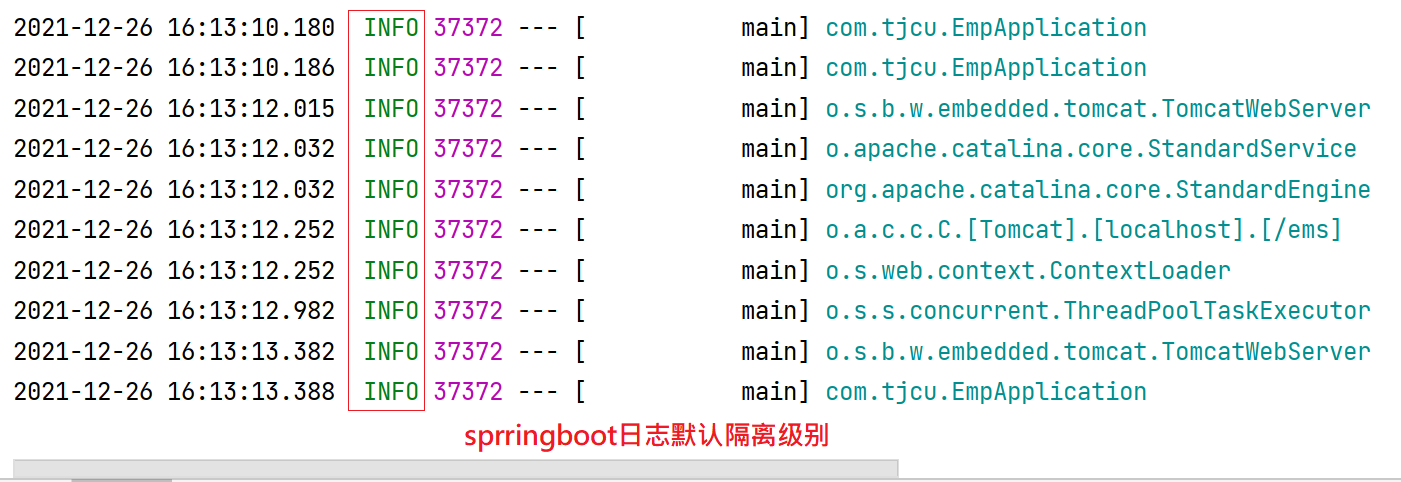
Sub log: package log logger
3. Log level
OFF = "ERROR =" WARNING = "INFO (springboot default) =" DEBUG (mybatis default level) = "ALL" the higher the level, the less output information
Log level from low to high: the higher the log level, the less log information will be output
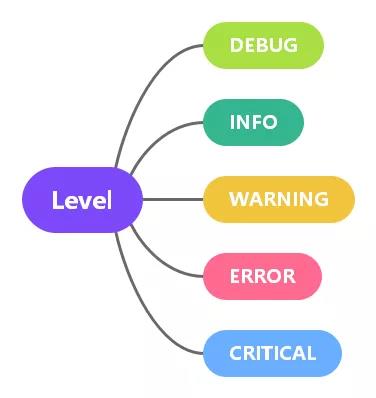
| log level | Usage scenario |
|---|---|
| DEBUG | The debug level is used to record detailed information to facilitate problem location and debugging. We generally do not open debug in the production environment |
| INFO | It is used to record the information of key code points so that the code can execute as expected. The production environment usually sets the INFO level |
| WARNING | Record some unexpected situations, such as insufficient disk |
| ERROR | Information recorded when some functions cannot function properly due to a more serious problem |
| CRITICAL | Information recorded when a serious error occurs that prevents the application from continuing to run |
2, Introduction to logback
Logback is created by log4j Another open source log component designed by the founder. At present, logback is divided into three modules: logback core, logback classic and logback access. This is a further improvement of log4j log presentation
1. Log classification in project
Logs fall into two categories
One is the rootLogger, which is used to listen to all the running logs in the project, including the logs introduced into the dependent jar
One is logger, which is used to listen to the log information in the specified package in the project
2. Used in java projects
(1) logback profile
The configuration file of logback must be placed in the project root directory and the name must be logback xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<configuration>
<!--Define the location of log output in the project-->
<appender name="stdout" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--Defines the log output format for the project-->
<!--Defines the log output format for the project-->
<layout class="ch.qos.logback.classic.PatternLayout">
<pattern> [%p] %d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} %m %n</pattern>
</layout>
</appender>
<!--Log control in project-->
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="stdout"/>
</root>
<!--Specify package log control in the project-->
<logger name="com.baizhi.dao" level="DEBUG"/>
</configuration>
(2) Use logs in specific classes
@Controller
@RequestMapping("user")
public class UserController {
private Logger logger = org.slf4j.LoggerFactory.getLogger(this.getClass());
@RequestMapping("findAll")
public String findAll(String name) {
logger.debug("debug Received name is: "+name);
logger.info("info Received name is: "+name);
logger.warn("warn Received name is: "+name);
logger.error("error Received name is: "+name);
return "index";
}
}
(3) Use default log configuration
logging:
level:
root: debug
com.baizhi.dao: debug
path: /Users/whj/aa.log
file: bbb.log
3, Log usage in SpringBoot
1. Change the default log level of Springboot to debug
#Enable log level: off > error > warn > info > debug > all
logging:
level:
root: debug
com.tjcu.controller: debug
com.tjcu.dao: debug
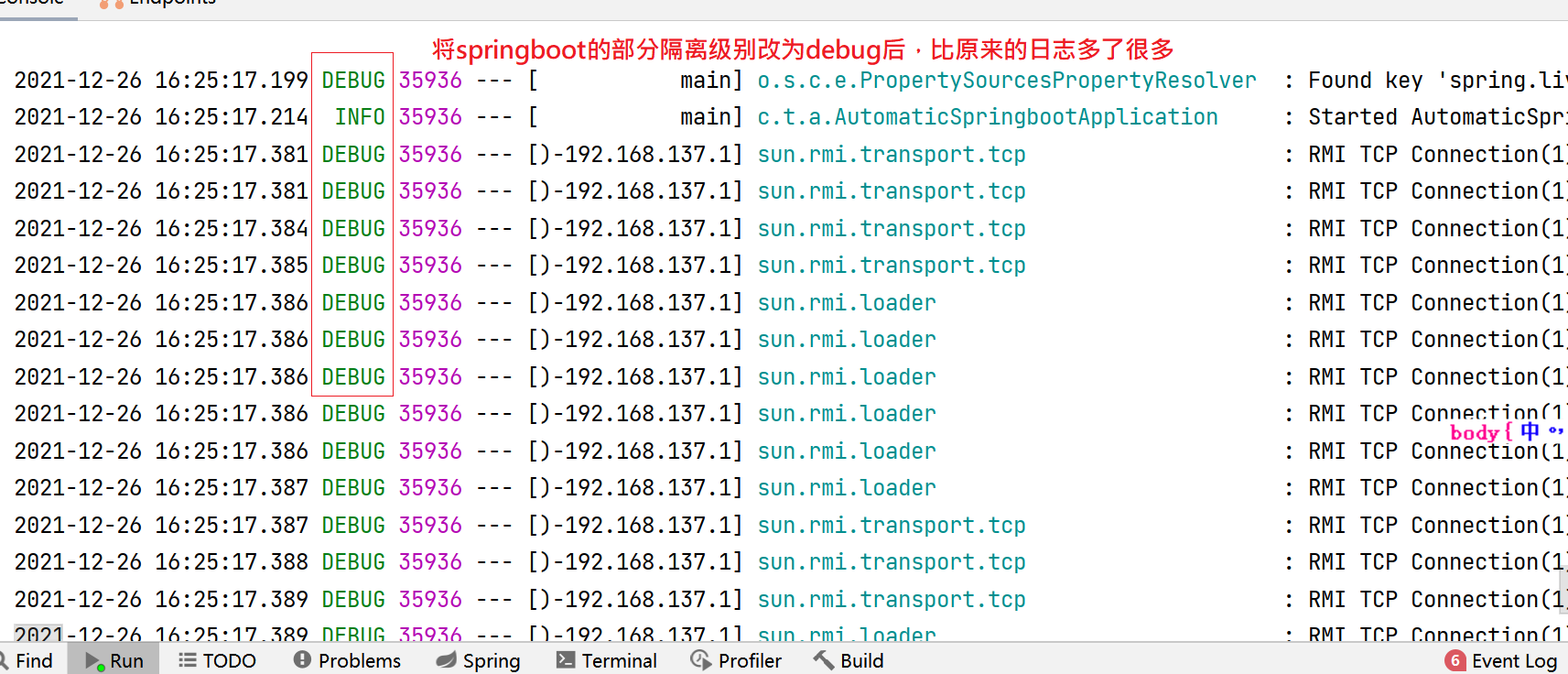
- Note: since there are too many things to print using debug as a log in spring boot, info is used as the default log level, but mybatis and others use debug as the default log level, so we need to take into account its log isolation level
2. When the SpringBoot project starts, there will be a default log object: logger
- Configure com.com first tjcu. controller: debug
#Open log
logging:
level:
root: debug
com.tjcu.controller: debug
- The log object is used in the controller
@Controller
@CrossOrigin
@ResponseBody
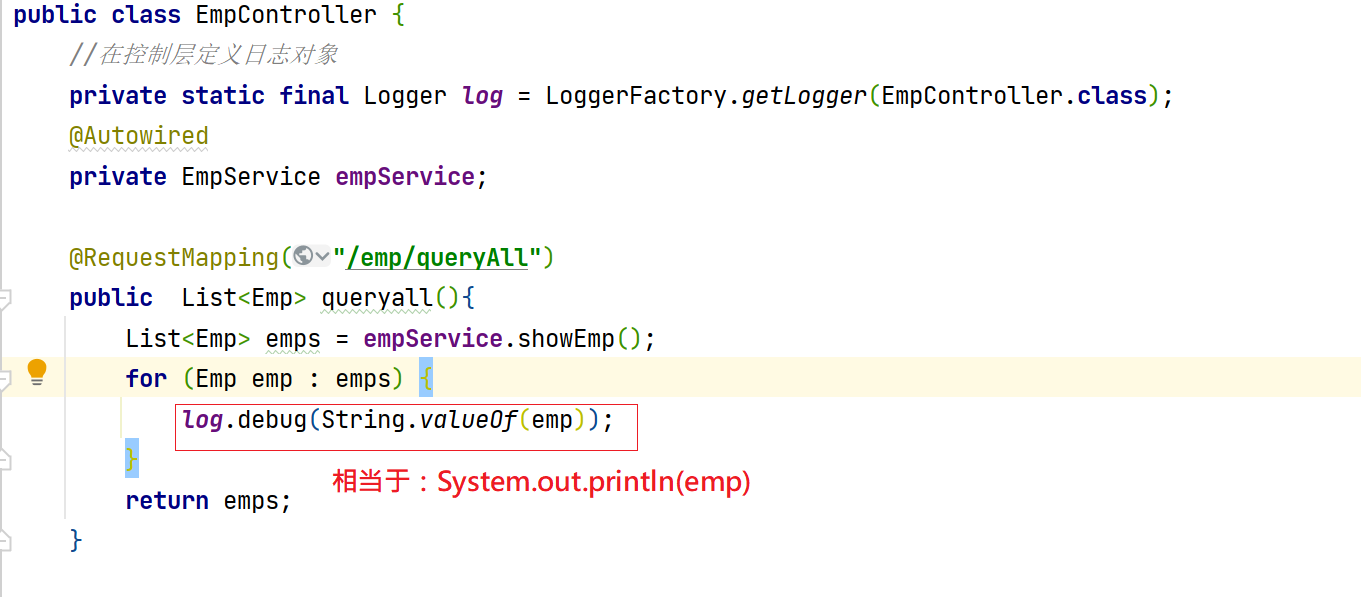
public class EmpController {
//Define log objects in the control layer
private static final Logger log = LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmpController.class);
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@RequestMapping("/emp/queryAll")
public List<Emp> queryall(){
List<Emp> emps = empService.showEmp();
for (Emp emp : emps) {
log.debug(String.valueOf(emp));
}
return emps;
}
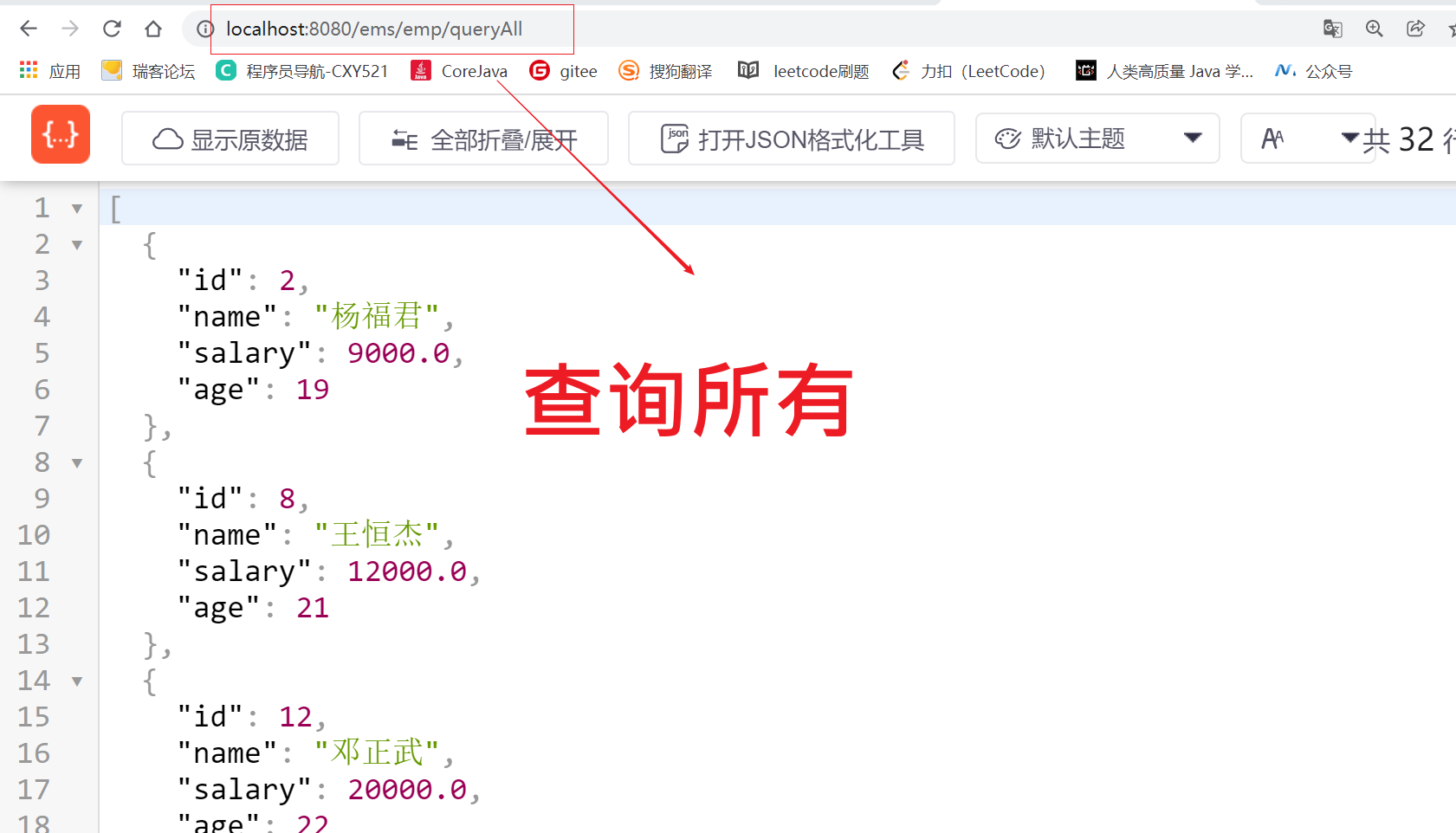
- After front-end access
http://localhost:8080/ems/emp/queryAll
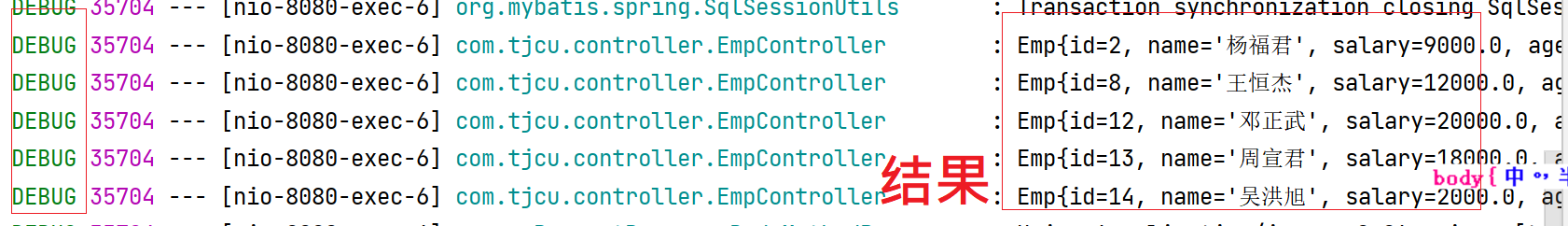
- Console results
4, Using log plug-ins in idea to simplify development
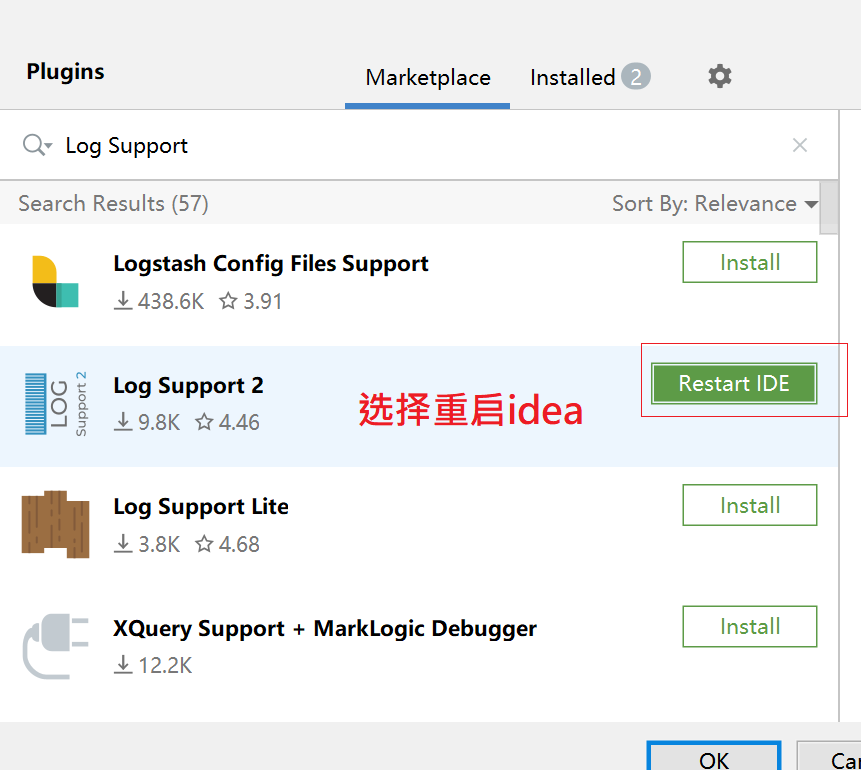
1. Download the Log Support2 plug-in
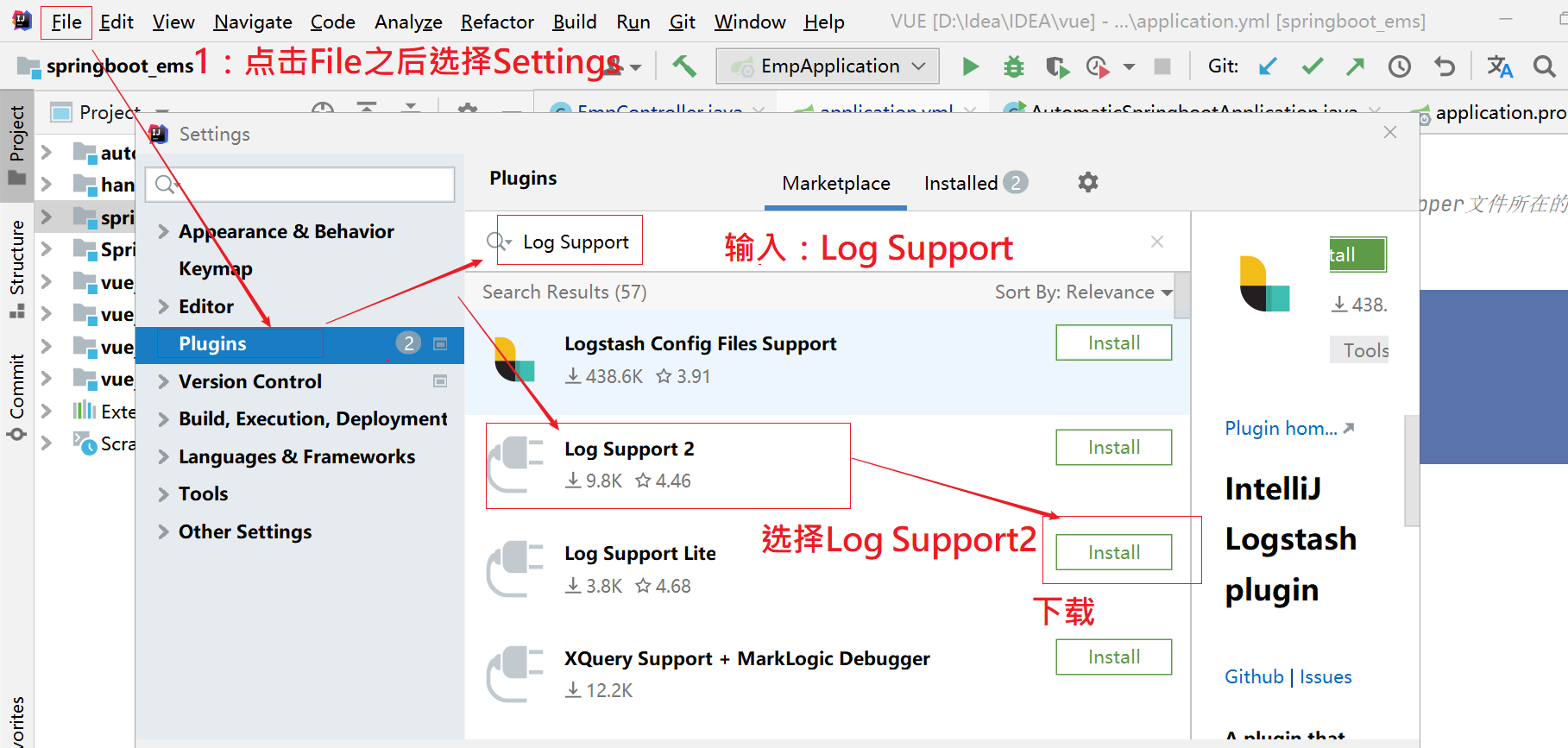
2. Restart idea
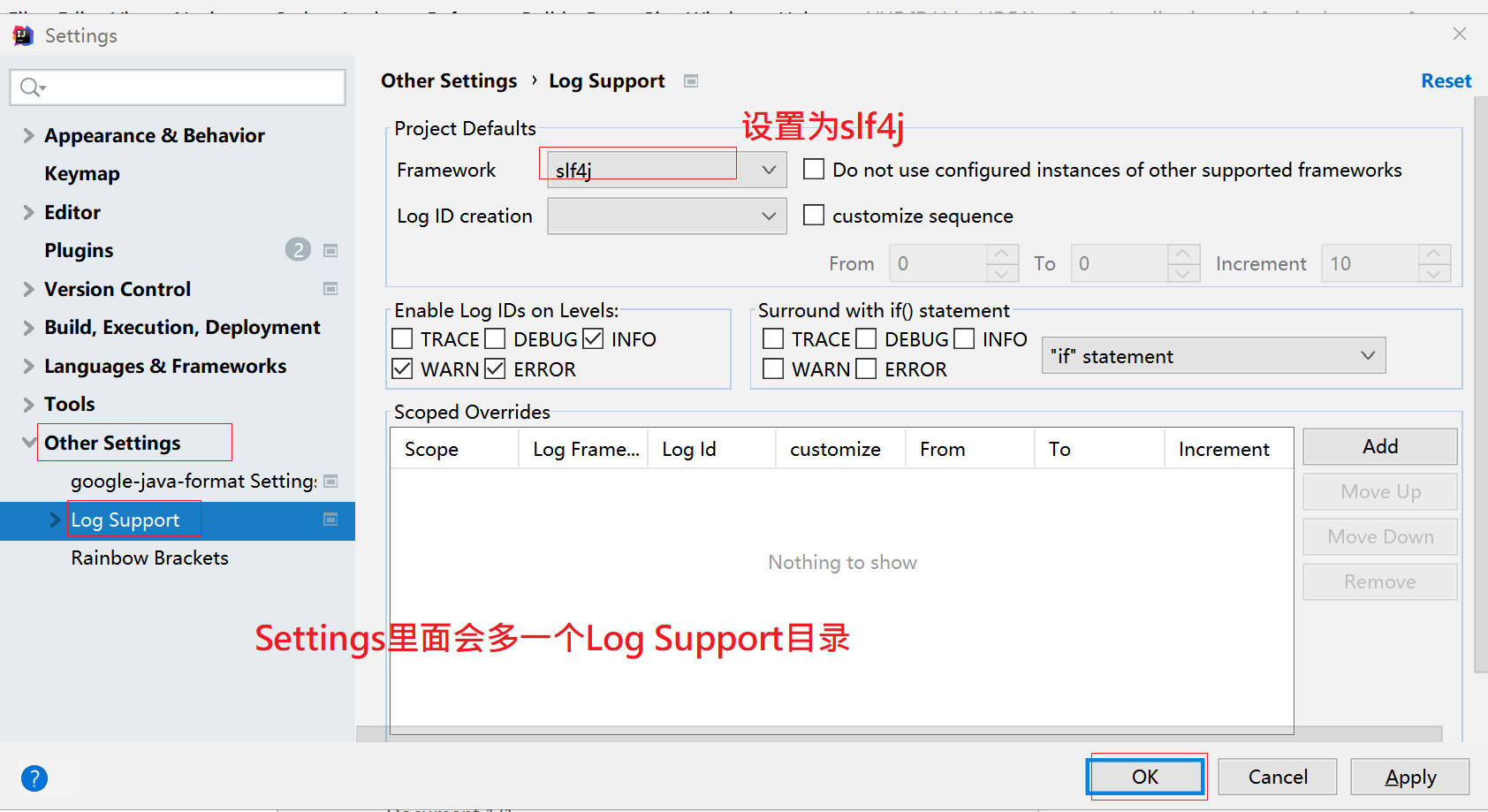
3. A Log Support directory will be added in Settings
FrameWork frame selection slf4j
- Why do we use slf4j
Used in our own system logback This log system Our system uses A.jar,A.jar The log system used in is log4j Our system is working again B.jar,B.jar The log system used in is slf4j-simple In this way, our system has to support and maintain at the same time logback,log4j,slf4j-simple Three log frameworks are very inconvenient.
Slf4j is only a logging standard, not a specific implementation of the logging system. It is very important to understand this sentence and slf4j only do two things:
- Provide log interface
- Provides methods for obtaining specific log objects
3. If you use Android directly, the logs will conflict
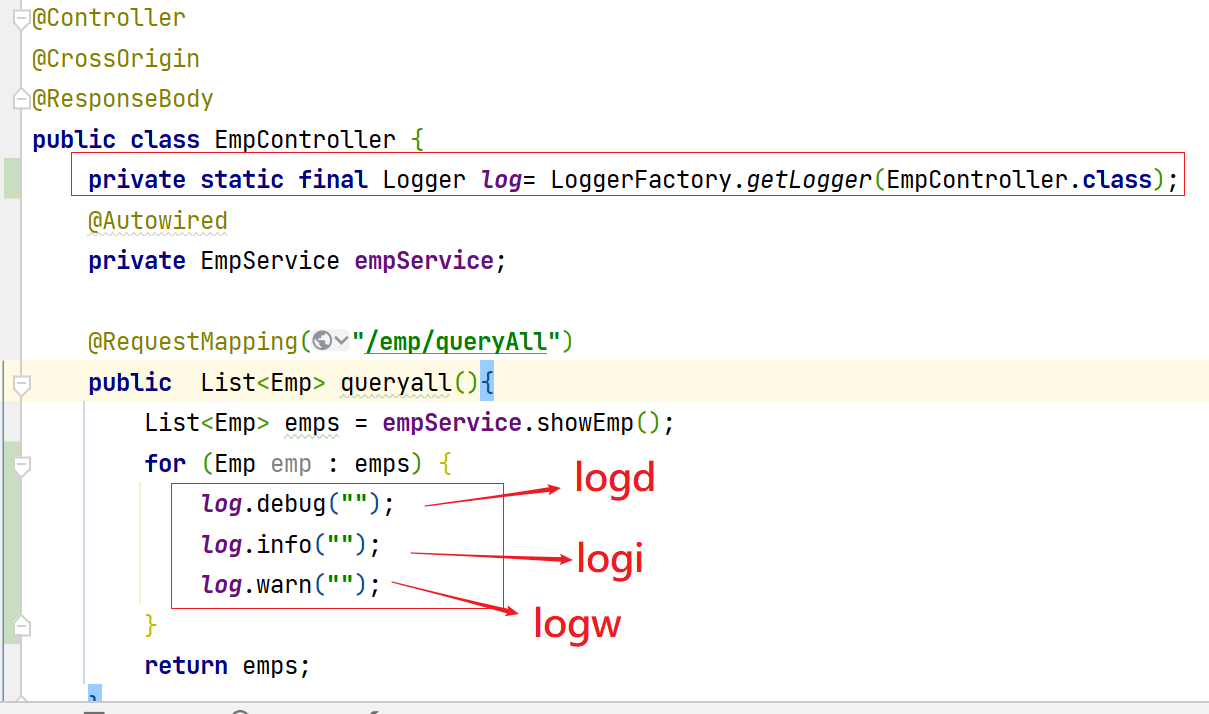
4. Testing
After logd + enter, idea will automatically add private static final logger Log1 = loggerfactory getLogger(EmpController.class);
Where d stands for debug,i for info and W for warn
@Controller
@CrossOrigin
@ResponseBody
public class EmpController {
private static final Logger log= LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmpController.class);
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@RequestMapping("/emp/queryAll")
public List<Emp> queryall(){
List<Emp> emps = empService.showEmp();
for (Emp emp : emps) {
log.debug("");
log.info("");
log.warn("");
}
return emps;
}
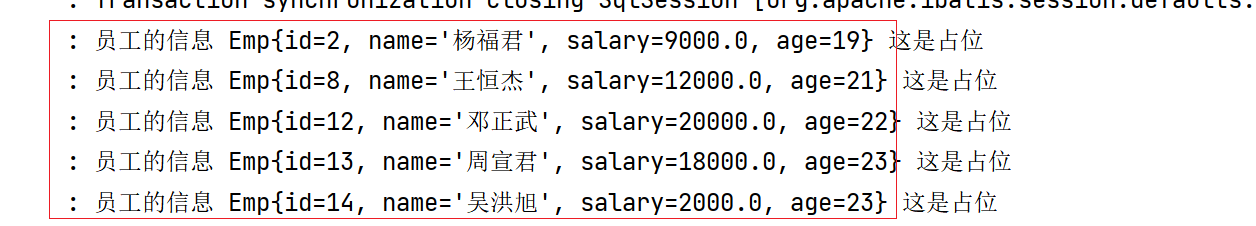
5. Write the log in a space occupying manner instead of splicing the + sign
{} stands for occupancy, one {} stands for occupancy, and one {} stands for occupancy

@Controller
@CrossOrigin
@ResponseBody
public class EmpController {
private static final Logger log= LoggerFactory.getLogger(EmpController.class);
@Autowired
private EmpService empService;
@RequestMapping("/emp/queryAll")
public List<Emp> queryall(){
List<Emp> emps = empService.showEmp();
for (Emp emp : emps) {
log.info("Employee information {} {}",emp,"This is space occupying");
}
return emps;
}