preface
Nginx is the Rambler with the second largest number of visitors in Russia Ru site design and development. Since its release in 2004, with the power of open source, it has been close to maturity and perfection.
Nginx has rich functions and can be used as HTTP server, reverse proxy server and mail server. Support FastCGI, SSL, Virtual Host, URL Rewrite, Gzip and other functions. It also supports many third-party module extensions.
Nginx's stability, feature set, sample configuration files and low consumption of system resources make it catch up from behind, with a utilization rate of 12.18% among the world's active websites, about 22.2 million websites.
You can find such boasting on Baidu Encyclopedia or some books if you are not satisfied.
Nginx common functions
1. Http proxy, reverse proxy: as one of the most commonly used functions of web server, especially reverse proxy.
Here I'll give you two pictures to explain the positive agency and response agency. You can look through the information for the specific details.
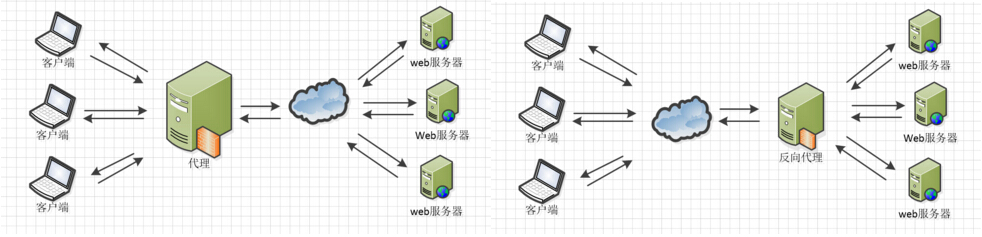
When working as a reverse proxy, nginx provides stable performance and flexible forwarding function. Nginx can adopt different forwarding strategies according to different regular matching, such as file server at the end of image file and web server for dynamic page. As long as you have no problem writing regular and have corresponding server solutions, you can play as you like. In addition, nginx performs error page Jump and exception judgment on the returned results. If the distributed server has an exception, it can re forward the request to another server, and then automatically remove the exception server.
2. Load balancing
There are two load balancing strategies provided by Nginx: built-in strategy and expansion strategy. The built-in policies are polling, weighted polling and Ip hash. The expansion strategy is unrestrained. There are only things you can't think of and nothing he can't do. You can refer to all load balancing algorithms and find them one by one for implementation.
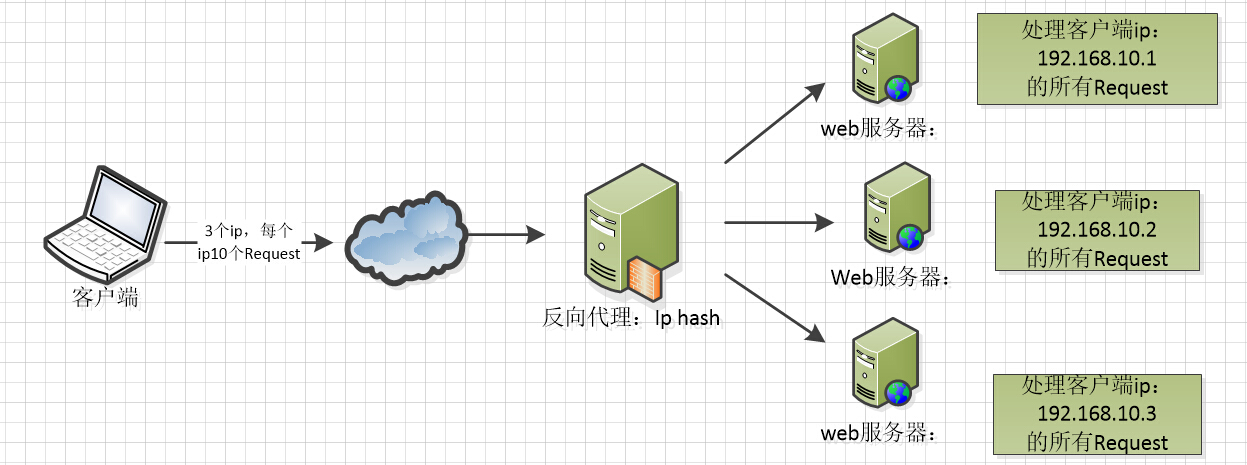
In the above three figures, understand the implementation of these three load balancing algorithms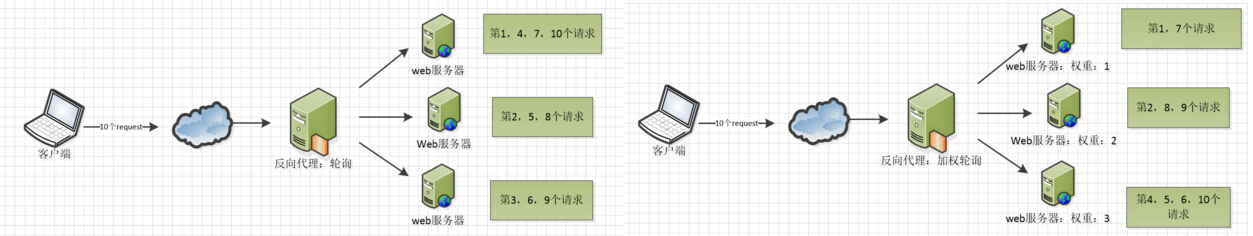
Ip hash algorithm, hash the ip requested by the client, and then distribute the request of the same client ip to the same server for processing according to the hash result, which can solve the problem of session non sharing.
3. web cache
Nginx can cache different files with flexible configuration and supports FastCGI_Cache is mainly used to cache the dynamic programs of FastCGI. With the third party's ngx_cache_purge, which can add and delete the specified URL cache content.
4. Nginx related address
Source code: https://trac.nginx.org/nginx/browser
Official website: http://www.nginx.org/
Nginx configuration file structure
If you have downloaded your installation files, you might as well open Nginx. Exe in the conf folder Conf file, the basic configuration of Nginx server, and the default configuration are also stored here.
In nginx Annotation symbol bit of conf#
The structure of nginx file can be seen by students who have just started.
Default config
#user nobody;
worker_processes 1;
#error_log logs/error.log;
#error_log logs/error.log notice;
#error_log logs/error.log info;
#pid logs/nginx.pid;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
#log_format main '$remote_addr - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
# '$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
# '"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
#access_log logs/access.log main;
sendfile on;
#tcp_nopush on;
#keepalive_timeout 0;
keepalive_timeout 65;
#gzip on;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
#charset koi8-r;
#access_log logs/host.access.log main;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
#error_page 404 /404.html;
# redirect server error pages to the static page /50x.html
#
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
# proxy the PHP scripts to Apache listening on 127.0.0.1:80
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1;
#}
# pass the PHP scripts to FastCGI server listening on 127.0.0.1:9000
#
#location ~ \.php$ {
# root html;
# fastcgi_pass 127.0.0.1:9000;
# fastcgi_index index.php;
# fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME /scripts$fastcgi_script_name;
# include fastcgi_params;
#}
# deny access to .htaccess files, if Apache's document root
# concurs with nginx's one
#
#location ~ /\.ht {
# deny all;
#}
}
# another virtual host using mix of IP-, name-, and port-based configuration
#
#server {
# listen 8000;
# listen somename:8080;
# server_name somename alias another.alias;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
# HTTPS server
#
#server {
# listen 443 ssl;
# server_name localhost;
# ssl_certificate cert.pem;
# ssl_certificate_key cert.key;
# ssl_session_cache shared:SSL:1m;
# ssl_session_timeout 5m;
# ssl_ciphers HIGH:!aNULL:!MD5;
# ssl_prefer_server_ciphers on;
# location / {
# root html;
# index index.html index.htm;
# }
#}
}
nginx file structure
... #Global block
events { #events block
...
}
http #http block
{
... #http global block
server #server block
{
... #server global block
location [PATTERN] #location block
{
...
}
location [PATTERN]
{
...
}
}
server
{
...
}
... #http global block
}
1. Global block: configure instructions that affect nginx global. Generally, there are user groups running nginx server, pid storage path of nginx process, log storage path, introduction of configuration file, number of worker process es allowed to be generated, etc.
2. events block: the configuration affects the nginx server or the network connection with the user. There is the maximum number of connections per process, which event driven model is selected to process connection requests, whether multiple network connections are allowed to be accepted at the same time, and starting multiple network connection serialization.
3. http block: it can nest multiple server s, configure most functions such as proxy, cache and log definition, and configure third-party modules. Such as file import, MIME type definition, log customization, whether to use sendfile to transfer files, connection timeout, number of single connection requests, etc.
4. server block: configure the relevant parameters of the virtual host. There can be multiple servers in one http.
5. location block: configure the routing of requests and the processing of various pages.
Let's give you a configuration file. As an understanding, it is also configured into a testing machine I built to give you examples.
########### Each instruction must end with a semicolon.#################
#user administrator administrators; #Configure users or groups. The default is nobody.
#worker_processes 2; #The number of processes allowed to be generated. The default is 1
#pid /nginx/pid/nginx.pid; #Specify the storage address of nginx process running files
error_log log/error.log debug; #Make log path and level. This setting can be put into the global block, http block and server block. The level is: debug|info|notice|warn|error|crit|alert|emerg
events {
accept_mutex on; #Set the network connection serialization to prevent group panic. The default is on
multi_accept on; #Set whether a process accepts multiple network connections at the same time. The default is off
#use epoll; #Event driven model, select|poll|kqueue|epoll|resig|/dev/poll|eventport
worker_connections 1024; #The maximum number of connections is 512 by default
}
http {
include mime.types; #File extension and file type mapping table
default_type application/octet-stream; #The default file type is text/plain
#access_log off; #Cancel service log
log_format myFormat '$remote_addr–$remote_user [$time_local] $request $status $body_bytes_sent $http_referer $http_user_agent $http_x_forwarded_for'; #Custom format
access_log log/access.log myFormat; #combined is the default value for log format
sendfile on; #sendfile mode is allowed to transfer files. The default is off. It can be in http block, server block and location block.
sendfile_max_chunk 100k; #The number of transfers per call of each process cannot be greater than the set value. The default value is 0, that is, there is no upper limit.
keepalive_timeout 65; #The connection timeout, which is 75s by default, can be set in http, server and location blocks.
upstream mysvr {
server 127.0.0.1:7878;
server 192.168.10.121:3333 backup; #Hot standby
}
error_page 404 https://www.baidu.com; # Error page
server {
keepalive_requests 120; #Maximum number of single connection requests.
listen 4545; #Listening port
server_name 127.0.0.1; #Listening address
location ~*^.+$ { #Request url filtering, regular matching, ~ is case sensitive, ~ * is case insensitive.
#root path; #root directory
#index vv.txt; #Set default page
proxy_pass http://mysvr; # The request goes to the list of servers defined by mysvr
deny 127.0.0.1; #Rejected ip
allow 172.18.5.54; #Allowed ip
}
}
}
The above is the basic configuration of nginx. Note the following:
1,1. r e m o t e a d d r And remote_addr and remotea ddr and http_x_forwarded_for is used to record the ip address of the client; two r e m o t e u s e r : use come remember record passenger household end use household name call ; 3. remote_user: used to record the client user name; three Remoteuser: used to record the client user name; 3.time_local: used to record access time and time zone; 4.$request: used to record the url and http protocol of the request;
5. s t a t u s : use come remember record please seek shape state ; become Merit yes 200 , 6. Status: used to record request status; Success is 200, 6 Status: used to record request status; Success is 200, 6 body_ bytes_ S ent: record the content size of the file body sent to the client; seven h t t p r e f e r e r : use come remember record from that individual page noodles chain meet interview ask too come of ; 8. http_referer: used to record the links accessed from that page; eight httpr # eferer: used to record the links accessed from that page; 8.http_user_agent: record the relevant information of the client browser;
2. Group shock: when a network connection arrives, multiple sleeping processes are awakened by colleagues, but only one process can get the link, which will affect the system performance.
3. Each instruction must end with a semicolon.
summary
If you use these technologies in the development process, or you encounter any problems when you want to use them, welcome to join the group in the upper left corner. Let's discuss and learn together. This article will not be finished.