In some systems, in order to save memory resources and ensure the consistency of data content, only one instance can be created for some classes, which is the so-called singleton mode.
1, Definition and characteristics of singleton mode
Definition of Singleton pattern: a pattern in which a class has only one instance and the class can create the instance itself. For example, Windows can only open one task manager, which can avoid the waste of memory resources caused by opening multiple task manager Windows, or errors such as inconsistent display contents of each window.
In the computer system, there are also the recycle bin of Windows, the file system in the operating system, the thread pool in multithreading, the driver object of graphics card, the background processing service of printer, the log object of application program, the connection pool of database, the counter of website, the configuration object of Web application, the dialog box of application program The cache in the system is often designed as a singleton.
Singleton model is also widely used in real life. For example, company CEO s and some managers belong to singleton model. ServletContext and ServletContextConfig in J2EE standard, ApplicationContext in Spring framework application and connection pool in database are also single examples.
The singleton mode has three characteristics:
- A singleton class has only one instance object;
- The singleton object must be created by the singleton class itself;
- The singleton class provides a global access point for accessing singletons.
2, Advantages and disadvantages of singleton mode
Advantages of singleton mode:
- The singleton mode can ensure that there is only one instance in the memory and reduce the memory overhead;
- It can avoid multiple utilization of resources;
- The global access point is set in the singleton mode, which can optimize and share the access of resources.
Disadvantages of singleton mode:
- Singleton mode generally has no interface and is difficult to expand. If you want to expand, there is no second way except to modify the original code, which violates the opening and closing principle.
- In concurrent testing, singleton mode is not conducive to code debugging. During debugging, if the code in the single example is not executed, it cannot simulate the production of a new object.
- The function code of singleton mode is usually written in a class. If the function design is unreasonable, it is easy to violate the principle of single responsibility.
The singleton pattern looks very simple and easy to implement. Single case mode is a high-frequency interview question in the interview. I hope you can study hard, master the single case mode, improve your core competitiveness, give extra points to the interview and get the Offer smoothly.
3, Application scenario of singleton mode
For Java, the singleton pattern ensures that there is only one instance in a JVM. The application scenarios of singleton mode mainly include the following aspects:
- Some classes need to be created frequently. Using singleton can reduce the memory pressure of the system and reduce GC;
- When a class only requires to produce an object, such as a monitor in a class, the ID number of each person, etc.
- Some classes occupy more resources when creating instances, or the instantiation takes a long time and is often used;
- When a class needs frequent instantiation and the created objects are frequently destroyed, such as multi-threaded thread pool, network connection pool, etc;
- Objects that frequently access databases or files;
- For some control hardware level operations, or from the perspective of the system, it should be the operation of a single control logic. If there are multiple instances, the system will be completely disordered;
- When objects need to be shared, because singleton mode allows only one object to be created, sharing the object can save memory and speed up object access. Such as the configuration object in the Web, the connection pool of the database, etc.
4, Structure and implementation of singleton mode
Singleton pattern is one of the simplest design patterns. Generally, the constructors of ordinary classes are common, and external classes can generate multiple instances through "new constructor()". However, if the constructor of a class is set to private, the external class cannot call the constructor and cannot generate multiple instances. At this time, the class itself must define a static private instance and provide a static common function to create or obtain the static private instance.
The basic structure and implementation method are analyzed below.
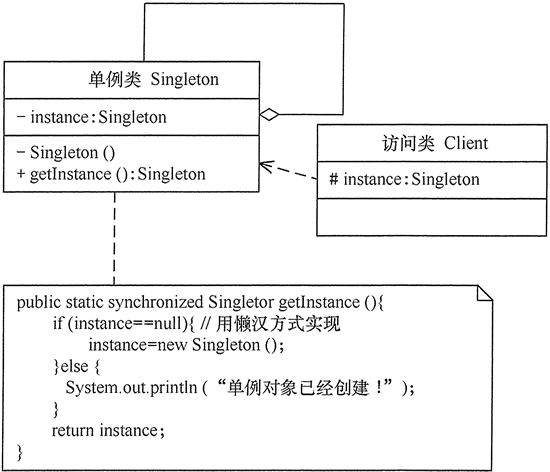
1. Mechanism of singleton mode
The main roles of singleton mode are as follows:
- Singleton class: a class that contains an instance and can create the instance itself.
- Access class: a class that uses a singleton.
Its mechanism is shown in the figure below:
2. Implementation of singleton mode
There are usually two implementations of the Singleton pattern.
Type 1: lazy single case
The feature of this mode is that no singleton is generated during class loading. This singleton is created only when the getInstance method is called for the first time. The code is as follows:
public class LazySingleton {
private static volatile LazySingleton instance = null; //Ensure that instance is synchronized in all threads
private LazySingleton() {
} //private prevents classes from being instantiated externally
public static synchronized LazySingleton getInstance() {
//Add synchronization before getInstance method
if (instance == null) {
instance = new LazySingleton();
}
return instance;
}
}
Note: if you are writing a multithreaded program, do not delete the keywords volatile and synchronized in the above example code, otherwise there will be a thread unsafe problem. If you do not delete these two keywords, you can ensure thread safety, but you need to synchronize each access, which will affect performance and consume more resources. This is the disadvantage of lazy singleton.
Section 2: hungry Han style single example
The feature of this pattern is that once the class is loaded, an instance is created to ensure that the singleton already exists before calling the getInstance method.
public class HungrySingleton {
private static final HungrySingleton instance = new HungrySingleton();
private HungrySingleton() {
}
public static HungrySingleton getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
Hungry Chinese singleton has created a static object for the system to use at the same time of class creation, which will not be changed in the future. Therefore, it is thread safe and can be directly used for multithreading without problems.
5, Application examples of singleton mode
[example 1] use lazy singleton mode to simulate the generation of current presidential objects in the United States
Analysis: in each term of office, there is only one president of the United States, so this example is suitable to be implemented in single case mode. The following figure shows the structure diagram of lazy single case implementation:
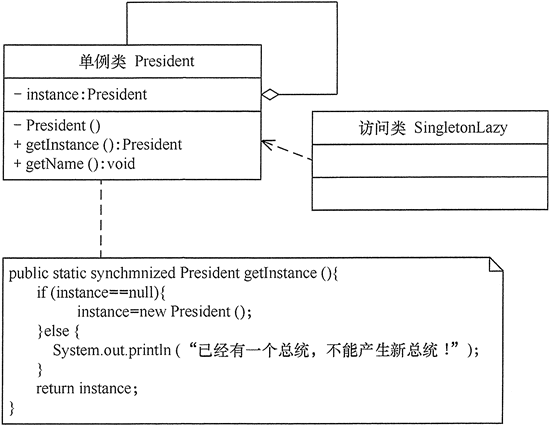
The program code is as follows:
public class SingletonLazy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
President zt1 = President.getInstance();
zt1.getName(); //Output the president's name
President zt2 = President.getInstance();
zt2.getName(); //Output the president's name
if (zt1 == zt2) {
System.out.println("They are the same person!");
} else {
System.out.println("They are not the same person!");
}
}
}
class President {
private static volatile President instance = null; //Ensure that instance is synchronized in all threads
//private prevents classes from being instantiated externally
private President() {
System.out.println("Produce a president!");
}
public static synchronized President getInstance() {
//Add synchronization to getInstance method
if (instance == null) {
instance = new President();
} else {
System.out.println("There is already a president, can not produce a new president!");
}
return instance;
}
public void getName() {
System.out.println("I am the president of the United States: trump.");
}
}
The running results of the program are as follows:
Produce a president! I am the president of the United States: trump. There is already a president, can not produce a new president! I am the president of the United States: trump. They are the same person!
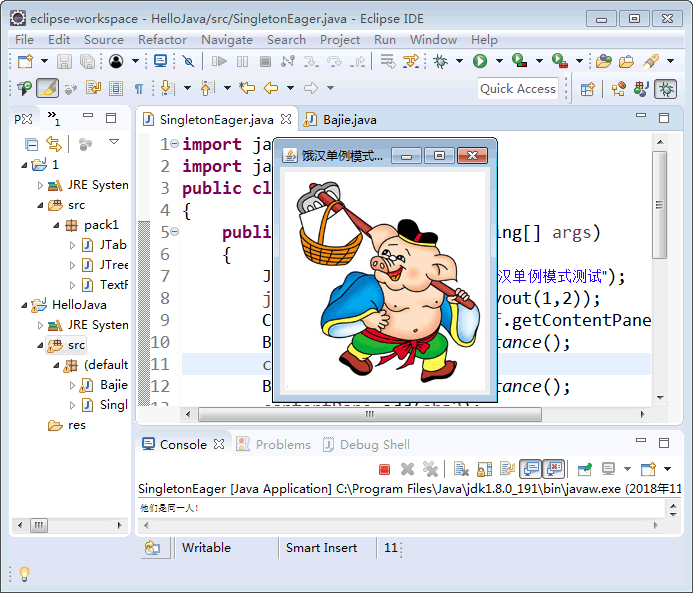
[example 2] simulate the generation of pig Bajie objects with hungry Han single case mode.
Analysis: similar to the above example, there is only one pig Bajie, so this example is also suitable for single instance mode. Because this example wants to display the image of pig Bajie, it uses the frame form JFrame component. The pig Bajie class here is a singleton class, which can be defined as a subclass of panel JPanel, which contains labels to save the image of pig Bajie. The customer form can obtain the pig Bajie object and display it. The following figure shows the structure diagram realized by hungry Han single example:
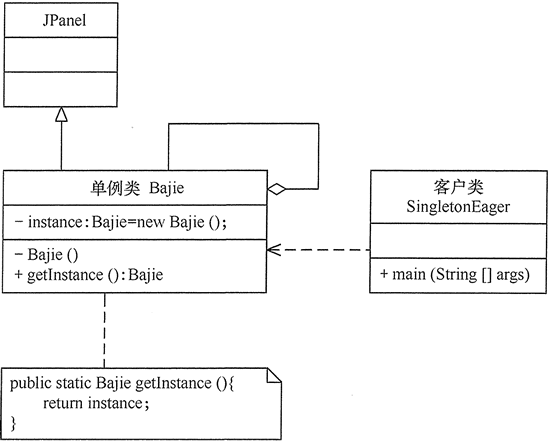
The program code is as follows:
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
public class SingletonEager {
public static void main(String[] args) {
JFrame jf = new JFrame("Hungry man single case mode test");
jf.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 2));
Container contentPane = jf.getContentPane();
Bajie obj1 = Bajie.getInstance();
contentPane.add(obj1);
Bajie obj2 = Bajie.getInstance();
contentPane.add(obj2);
if (obj1 == obj2) {
System.out.println("They are the same person!");
} else {
System.out.println("They are not the same person!");
}
jf.pack();
jf.setVisible(true);
jf.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
}
}
class Bajie extends JPanel {
private static Bajie instance = new Bajie();
private Bajie() {
JLabel l1 = new JLabel(new ImageIcon("src/Bajie.jpg"));
this.add(l1);
}
public static Bajie getInstance() {
return instance;
}
}
The running results of the program are shown in the figure below:
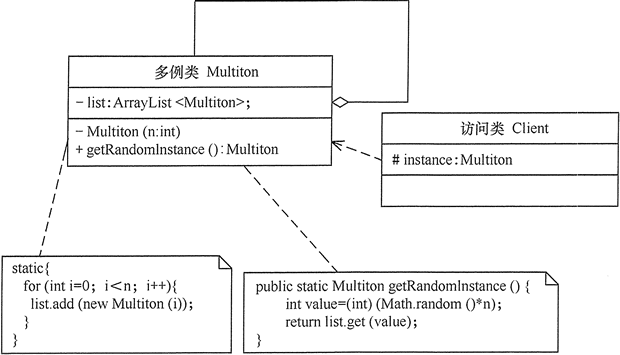
6, Extension of singleton mode
The single instance mode can be extended to the limited Multitcm mode. This mode can generate a limited number of instances and save them in the ArrayList. Customers can obtain them randomly when they need it. Its structure is shown in the following figure: