preface
This article belongs to the column "100 problems to solve the installation and deployment of big data". This column is original by the author. Please indicate the source of quotation. Please help point out the deficiencies and errors in the comment area. Thank you!
For the directory structure and references of this column, see 100 questions to solve the installation and deployment of big data
text
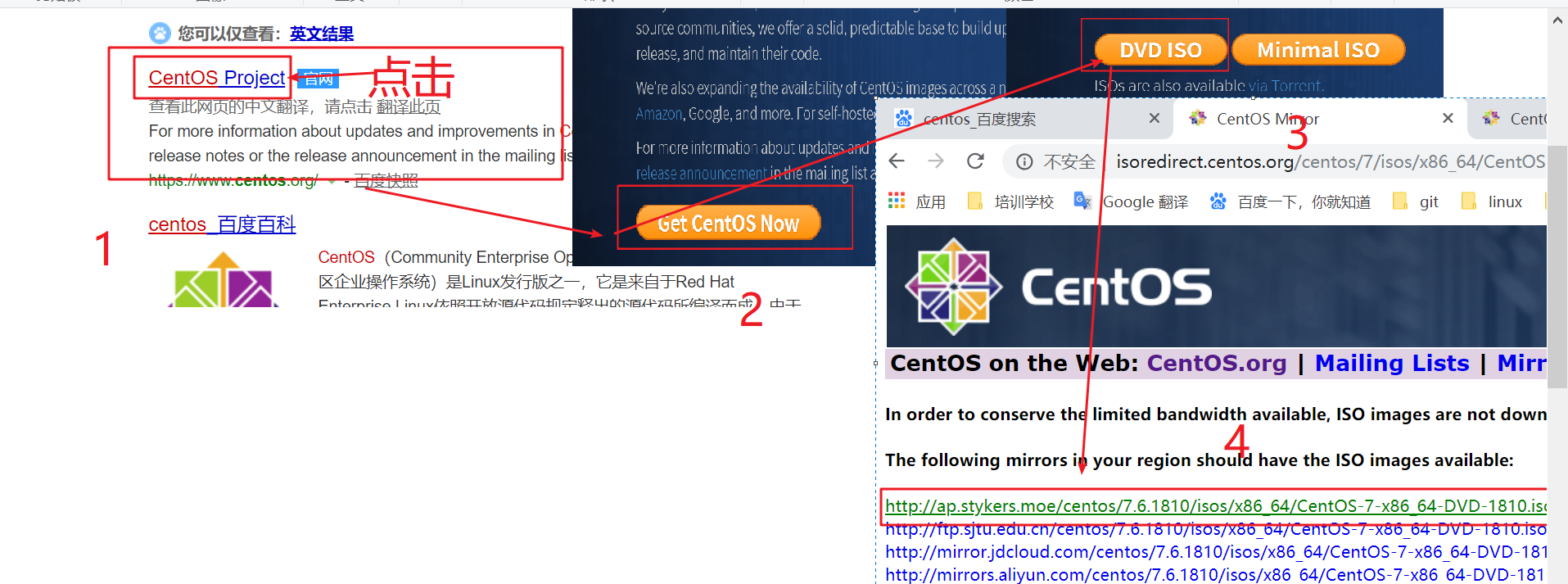
1. Download CentOS7
- Baidu search centos – >
- Click centos official website to connect – >
- Click DVD ISO – >
- click http://ap.stykers.moe/centos/7.6.1810/isos/x86_64/CentOS-7-x86_64-DVD-1810.iso Connect to download
2. Install virtual machine management software
VMware Fusion configuring Nat static IP - zhishengqianjun's blog - CSDN
After the installation is completed, the virtual opportunity generates a virtual machine shortcut on the desktop
3. Create virtual machine
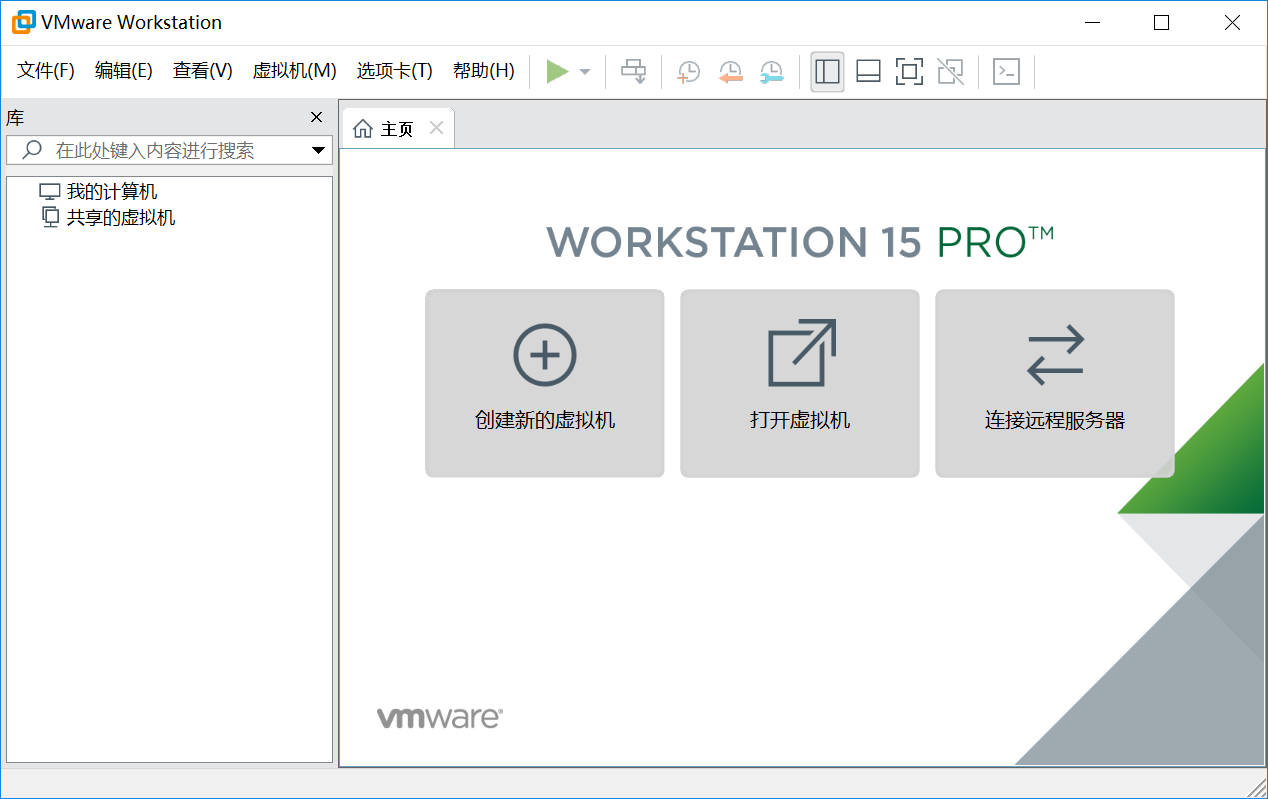
3.1 start the virtual machine management software
After installing the virtual machine management software, double-click the shortcut of the desktop

Start the virtual machine management software, as shown in the following figure:
As shown in the figure below, click file – > click new virtual machine – > select typical (recommended) by default – > click next
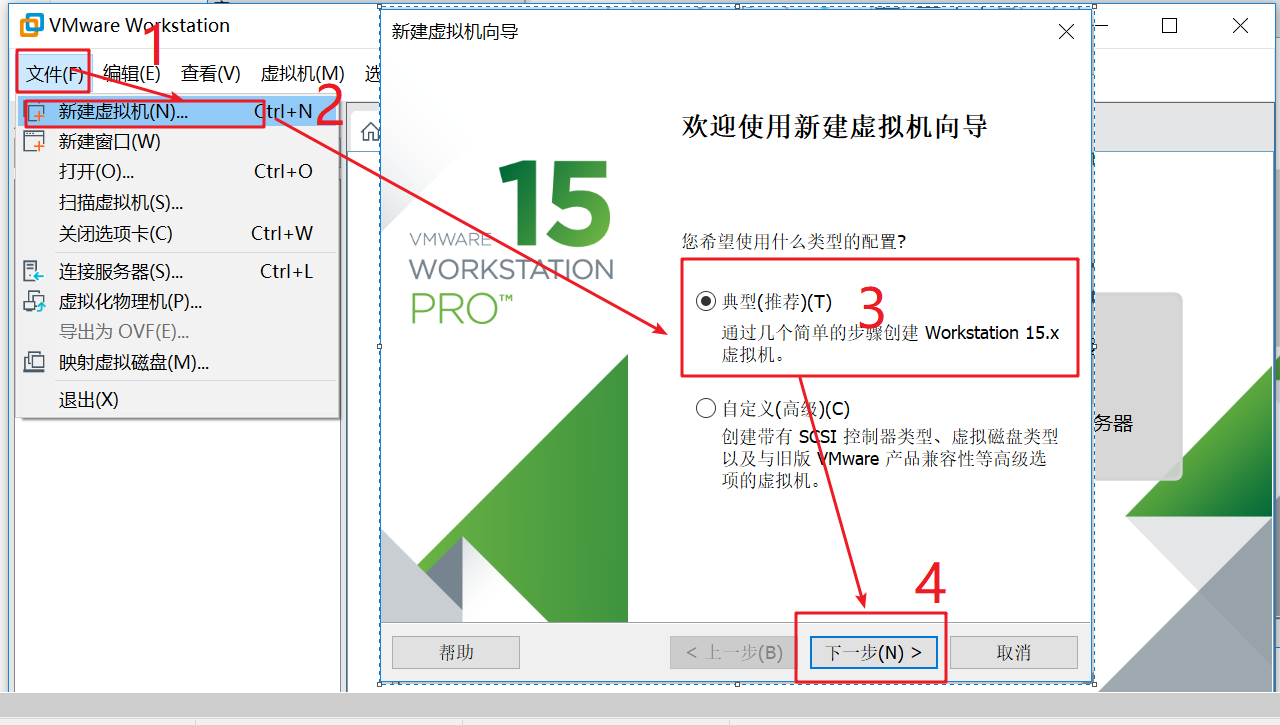
As shown in the figure below, click "install operating system later" – > click next
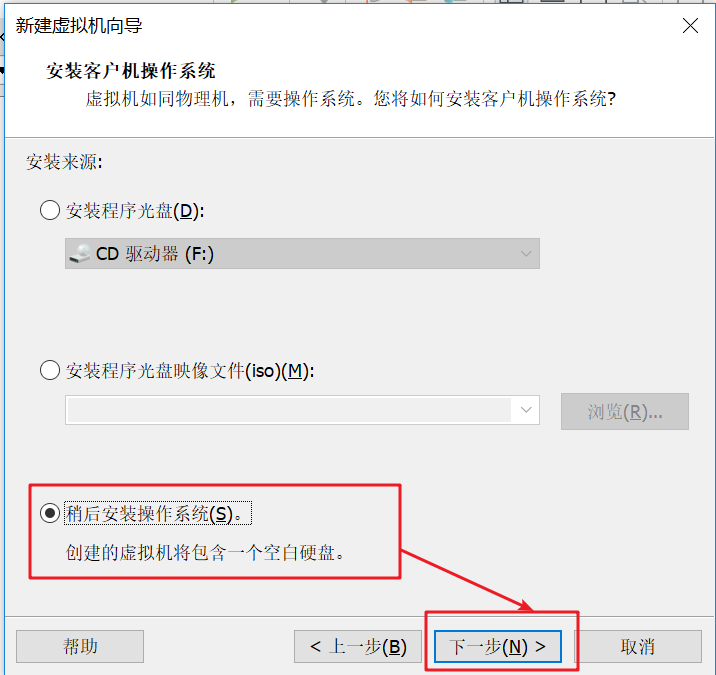
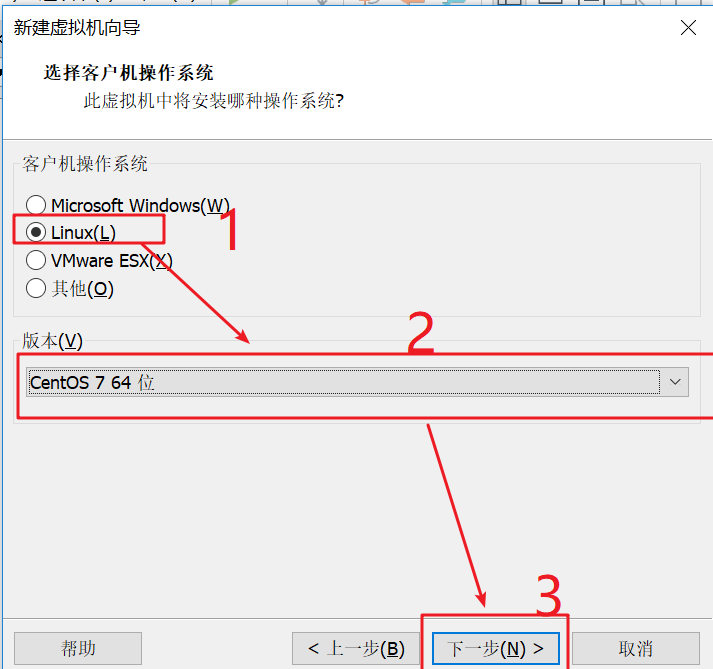
As shown in the figure below, select Linux(L) – > select CentOS7 64 bit – > click next
As shown in the following figure, enter the name: BaseCentos7, select to create a basic virtual machine, and subsequent cluster nodes will be cloned from this virtual machine
After entering the virtual machine name,
1. Click Browse – > select virtual machine location – > select this computer – > select and expand local disk C
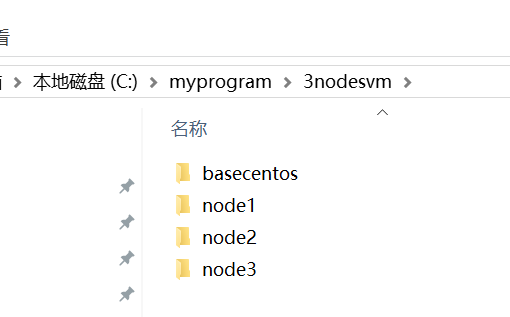
2. Create a hierarchical folder myprogram (virtual machine storage root directory) – > 3nodesvm – > basecentos (virtual machine storage directory) on the disk
3. Select C:\myprogramnodesvm\basecentos directory as the storage directory of BaseCentos7
4. Create node1, node2 and node3 under C:\myprogramnodesvm \ directory to store the virtual machine disk files of the following three nodes respectively.
5. After selecting basecentos directory, click next

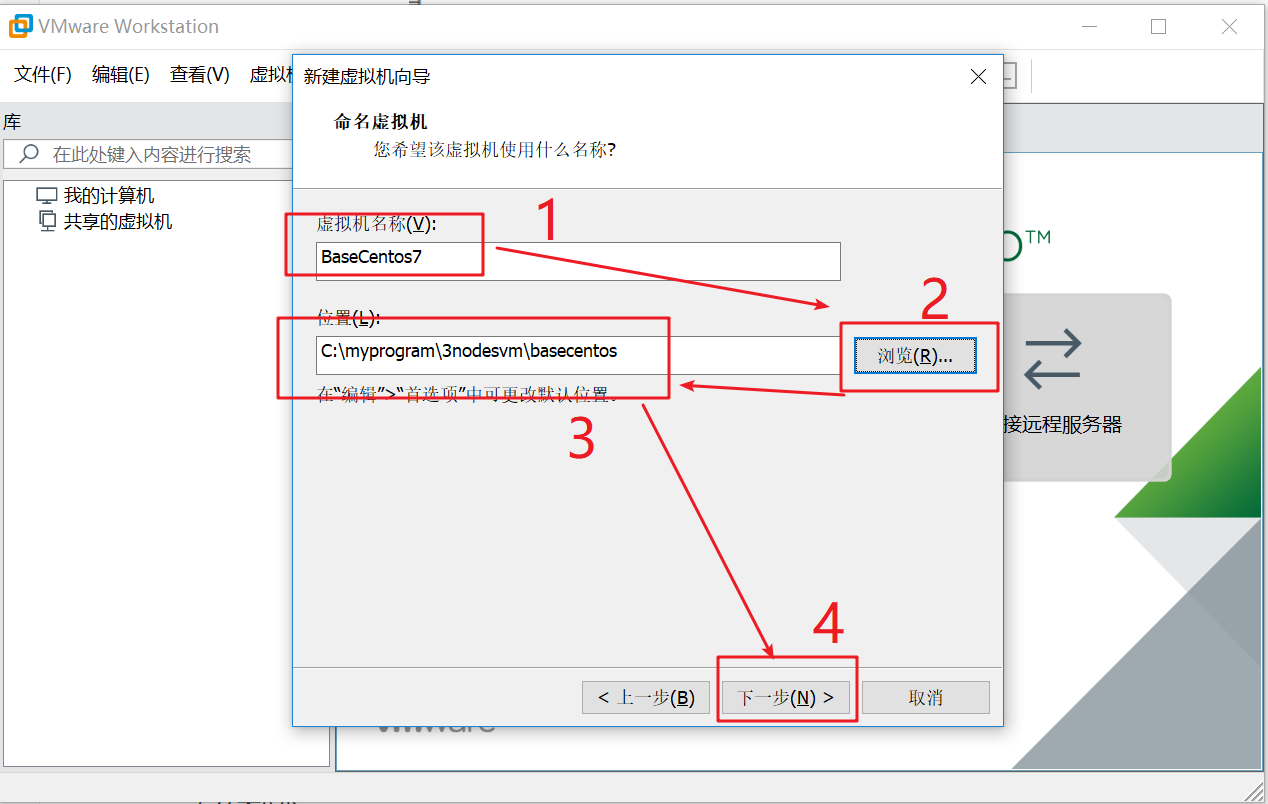
As shown in the following figure, the maximum disk size is modified from the default 20G to 200G (the one-time modification is larger, a large number of files will be generated during cluster operation, and the default 20G is not enough)
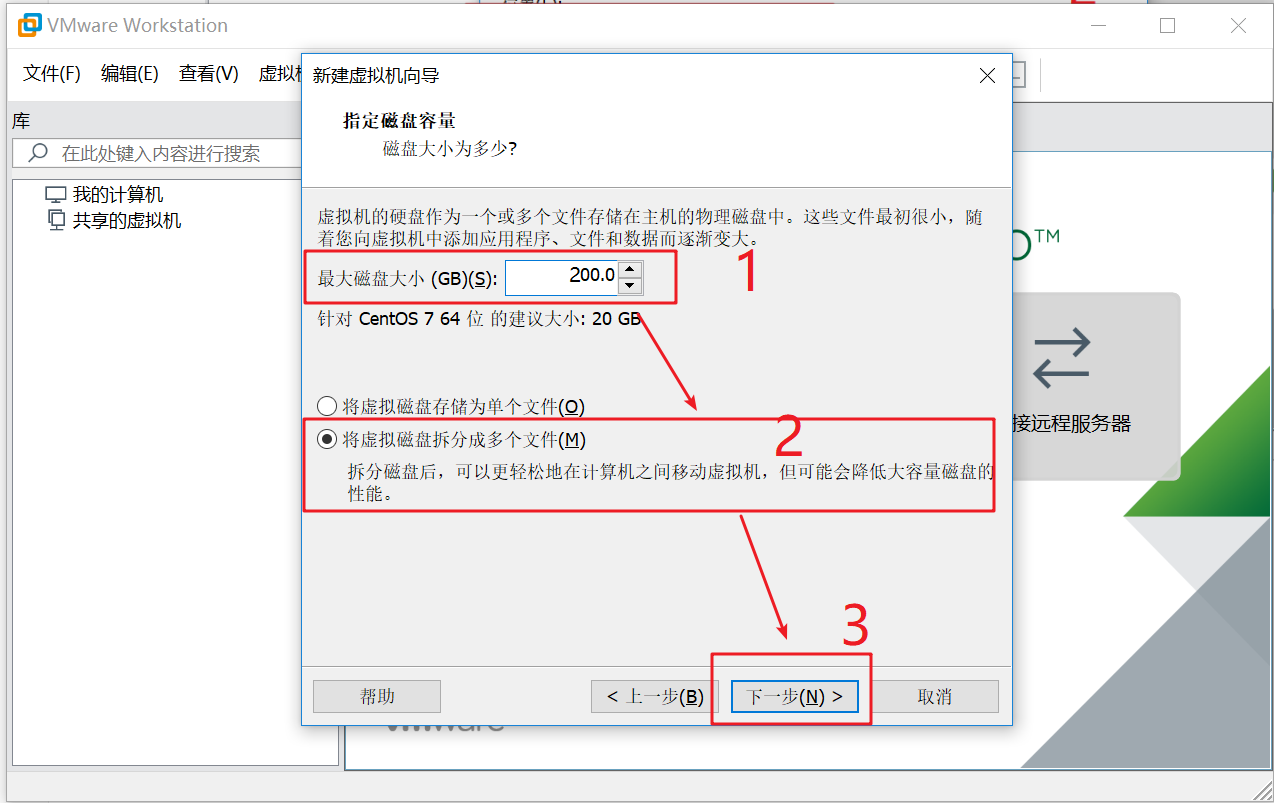
As shown in the figure below, click Finish to complete the creation of the virtual machine. Wait two or three seconds to see the created virtual machine
The virtual machine created is as follows:
3.2 modifying memory and CPU
As shown in the figure below, click memory – > select memory – > Enter 2048 on the right to adjust the virtual machine memory to 2G
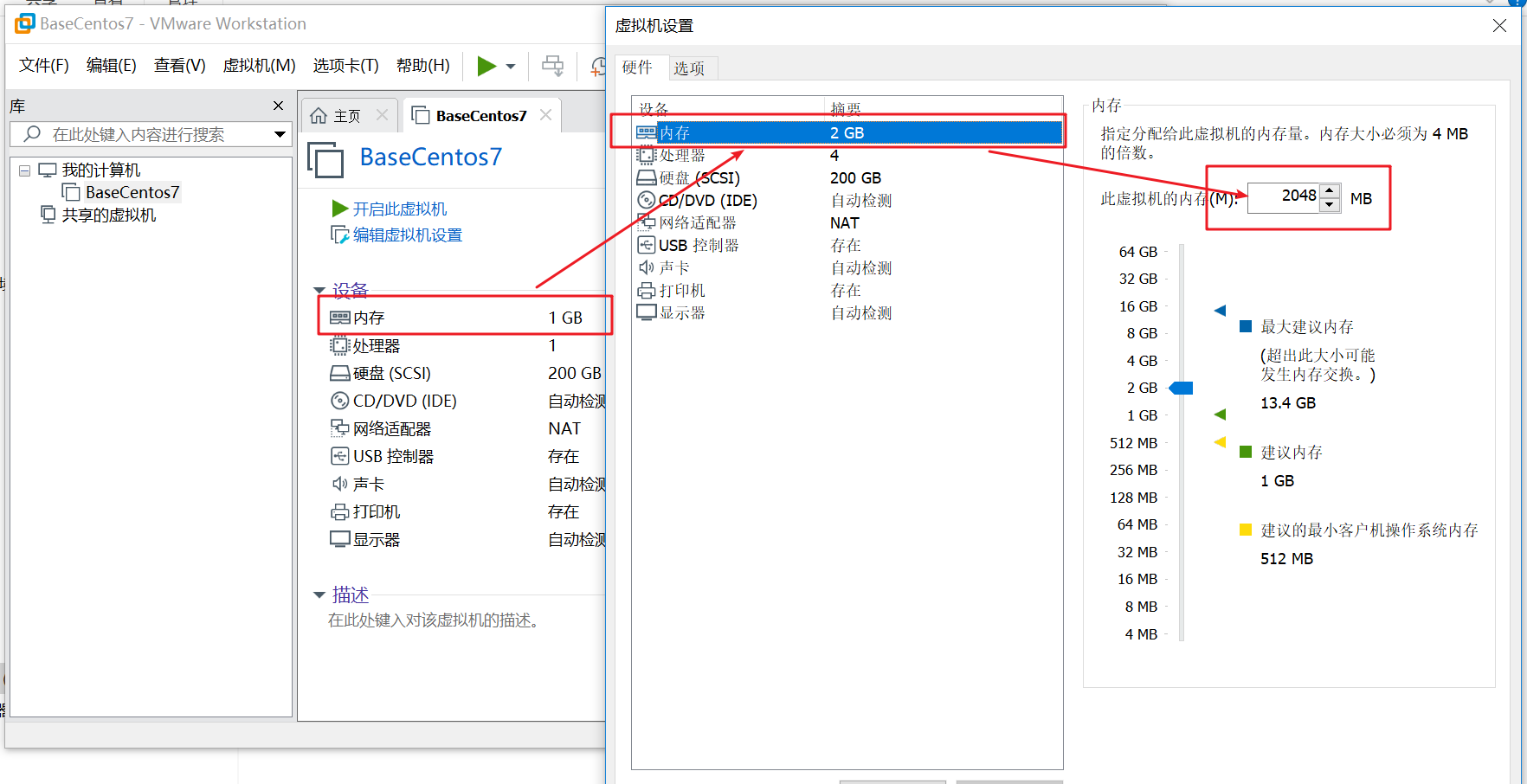
Following the previous operation, after entering the memory value, select CPU, and the number of processors and cores is 2
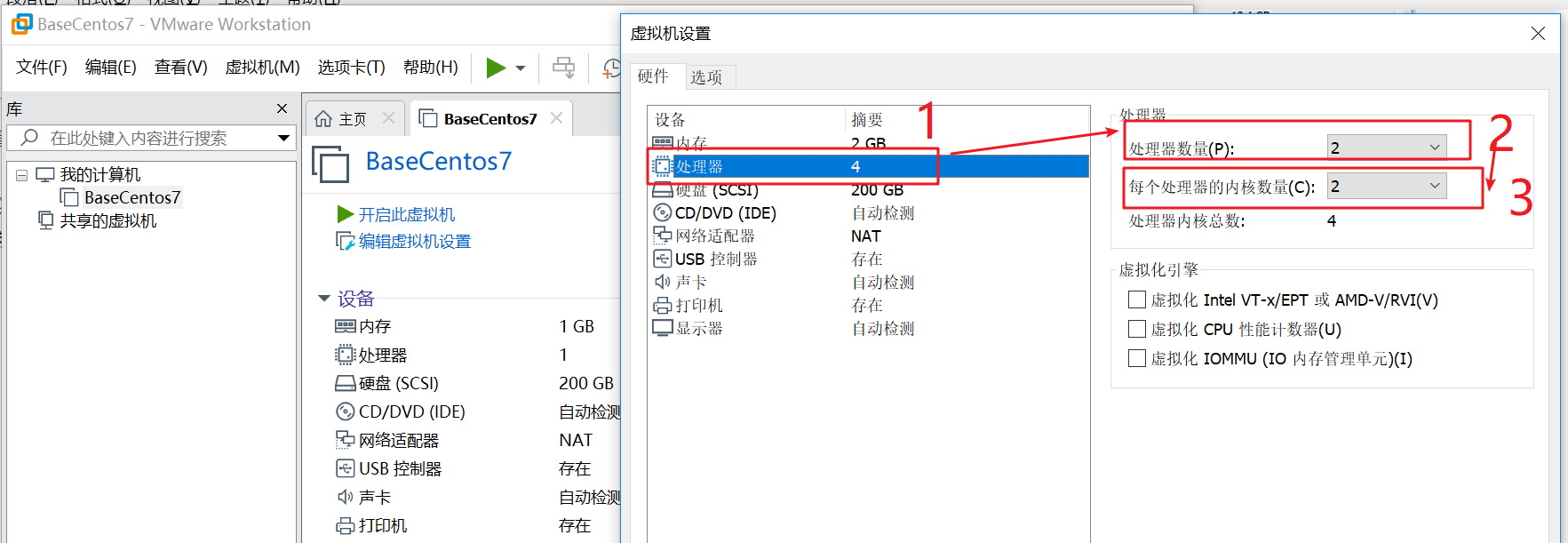
Click OK as shown below
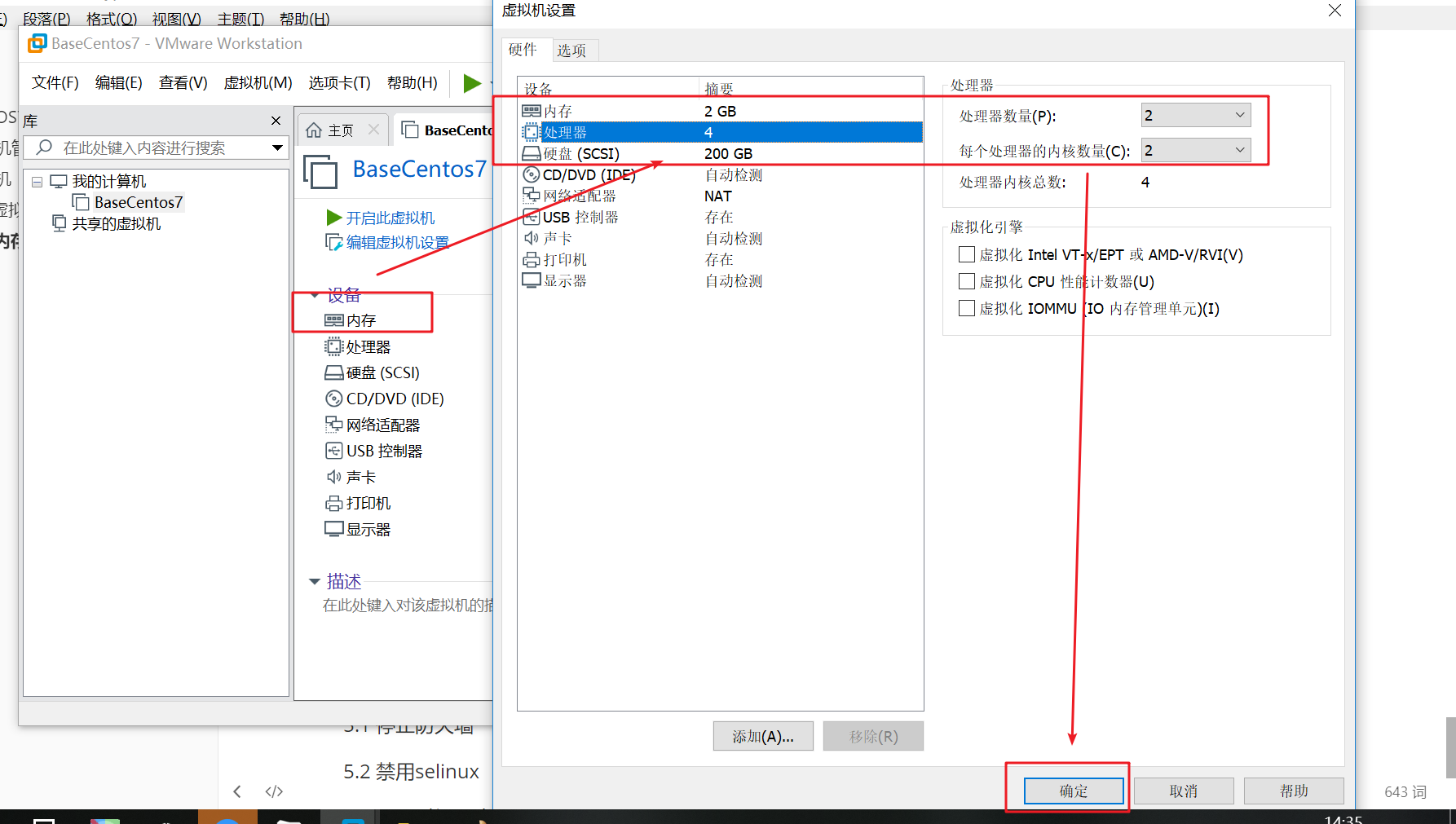
As shown in the figure below, it is set to memory and cpu.
3.3 select the image file of Centos7
The following two figures:
1. Click CD/DVD
2. Click CD/DVD(IDE)
3. Click use ISO image file
4. Click Browse
5. Select the image file of the centos7 system you just downloaded
6. Click open
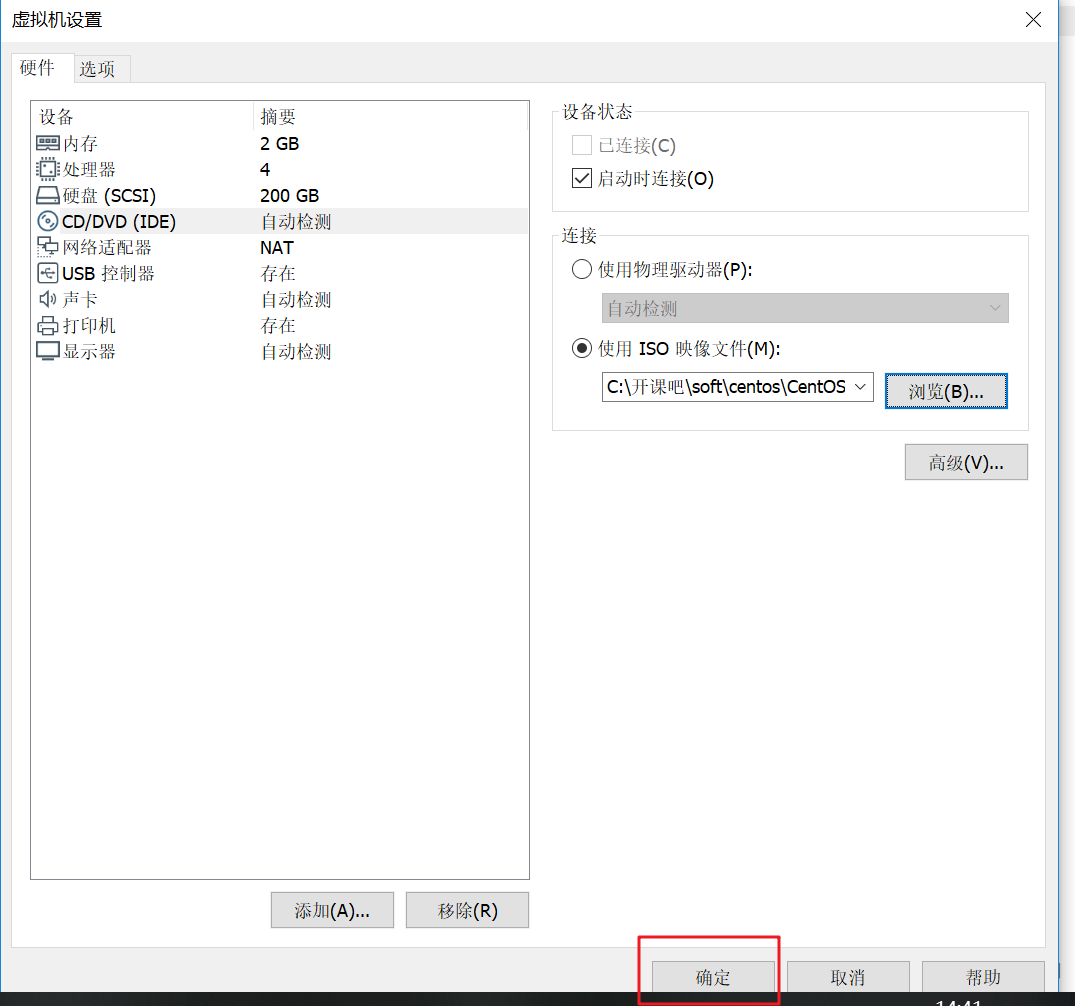
7. Click OK to complete the selection of image file
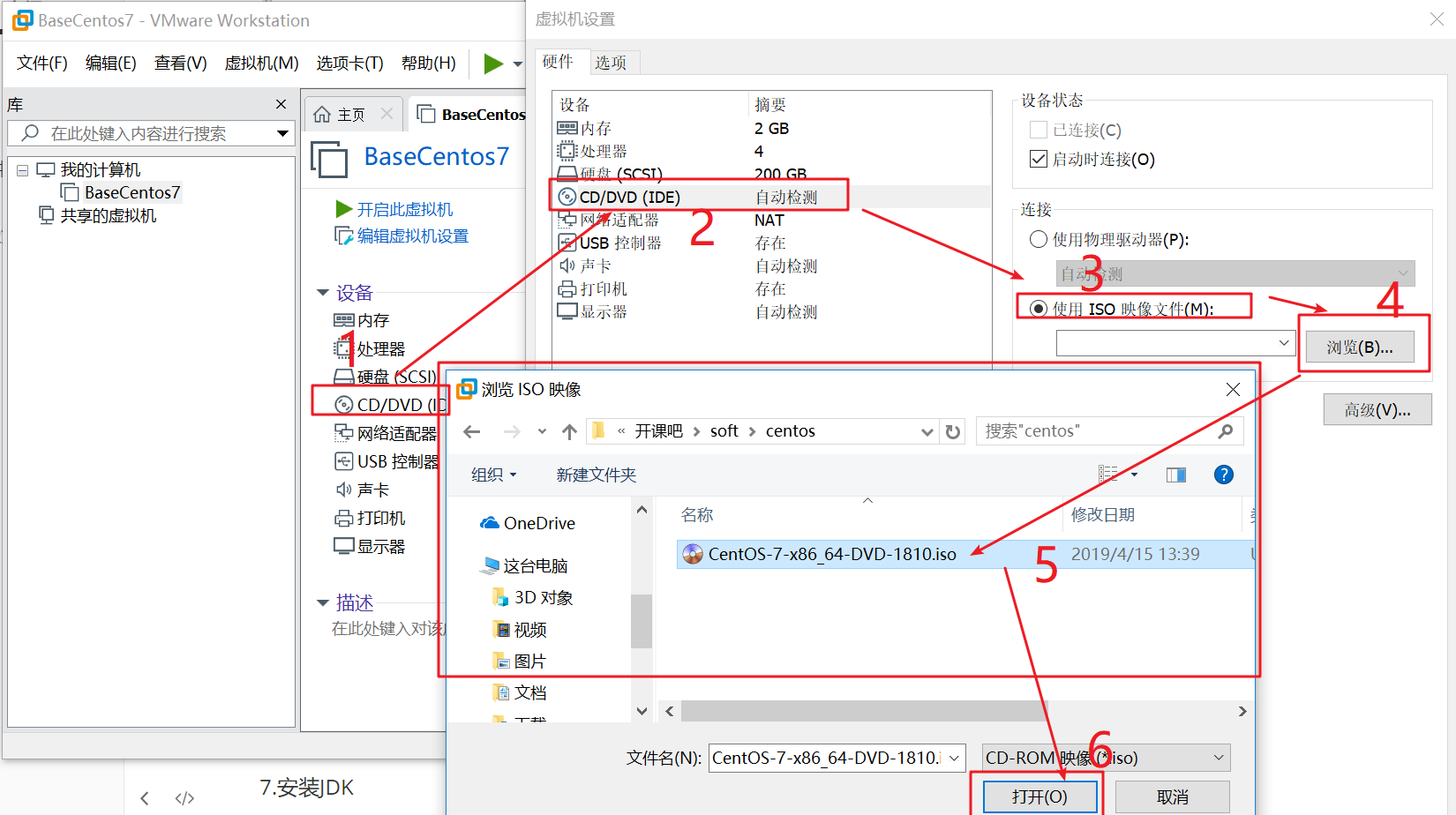
Click OK as shown below
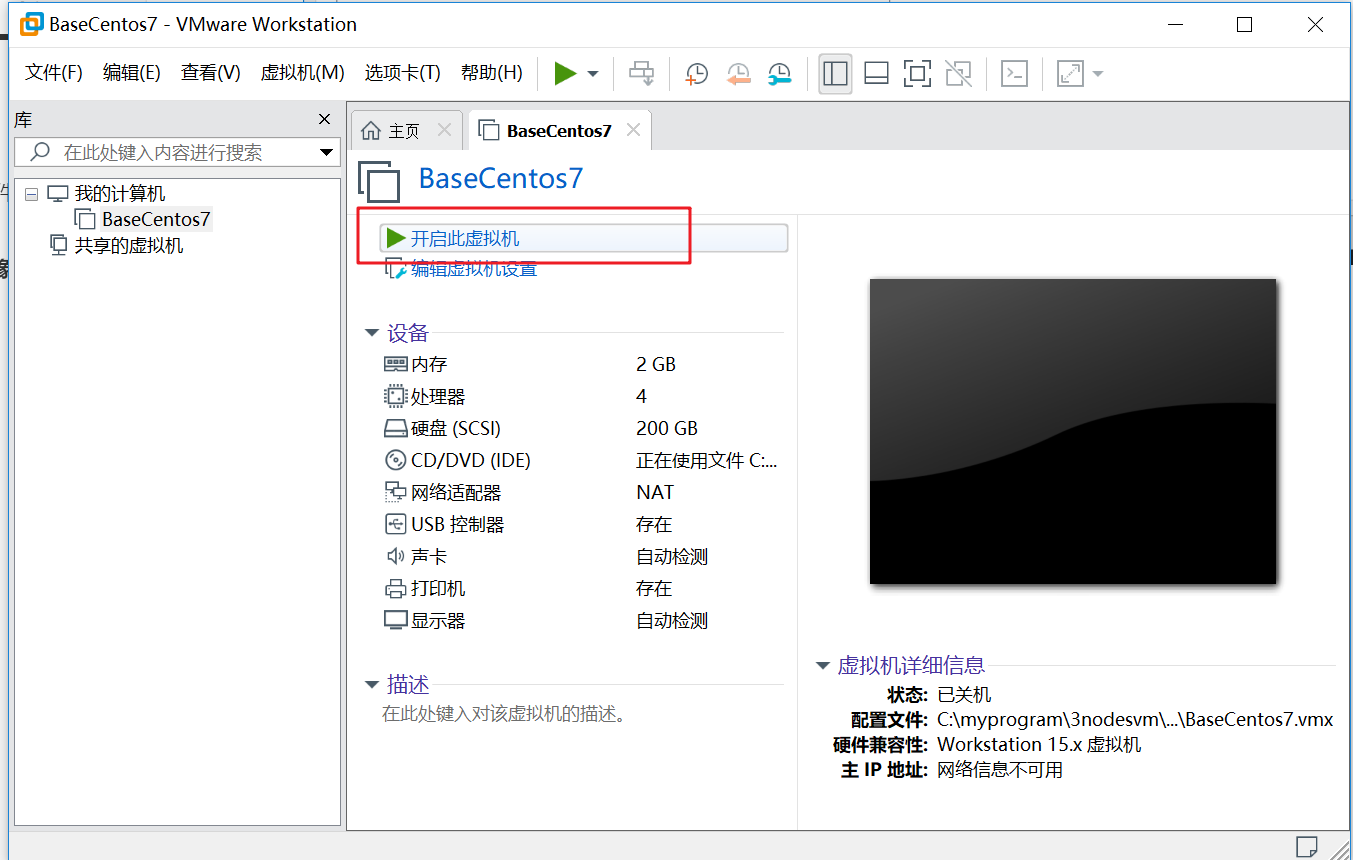
3.4 centos system installation
As shown in the figure below, click start this virtual machine
If the following figure appears, click I have completed the installation
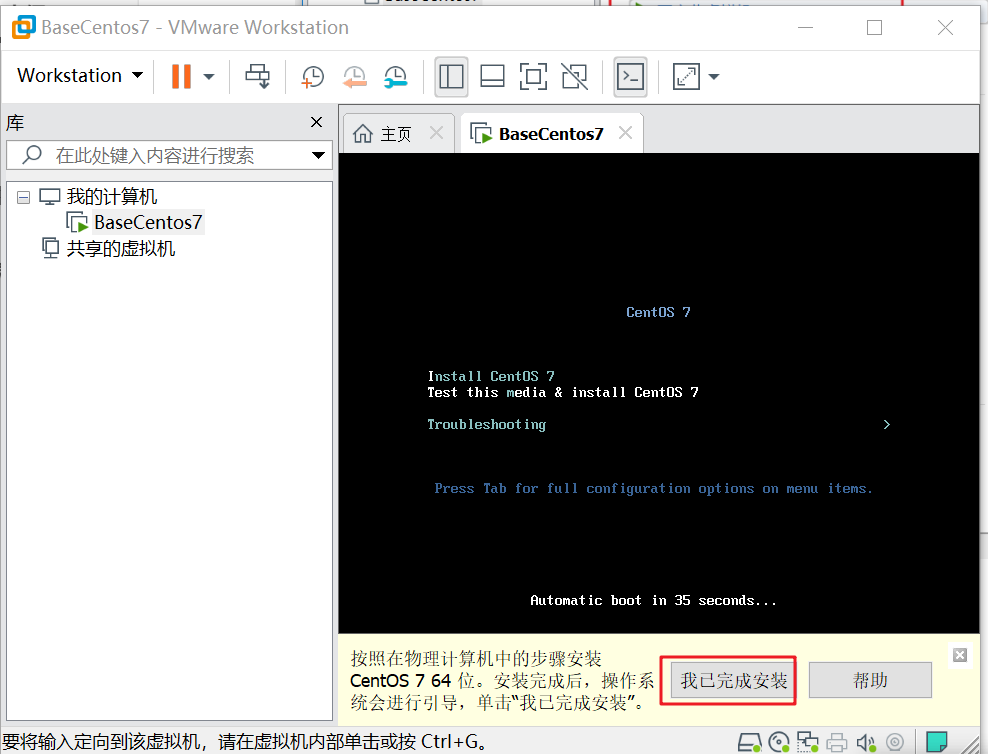
Wait for the automatic countdown to 0 and start the system installation automatically
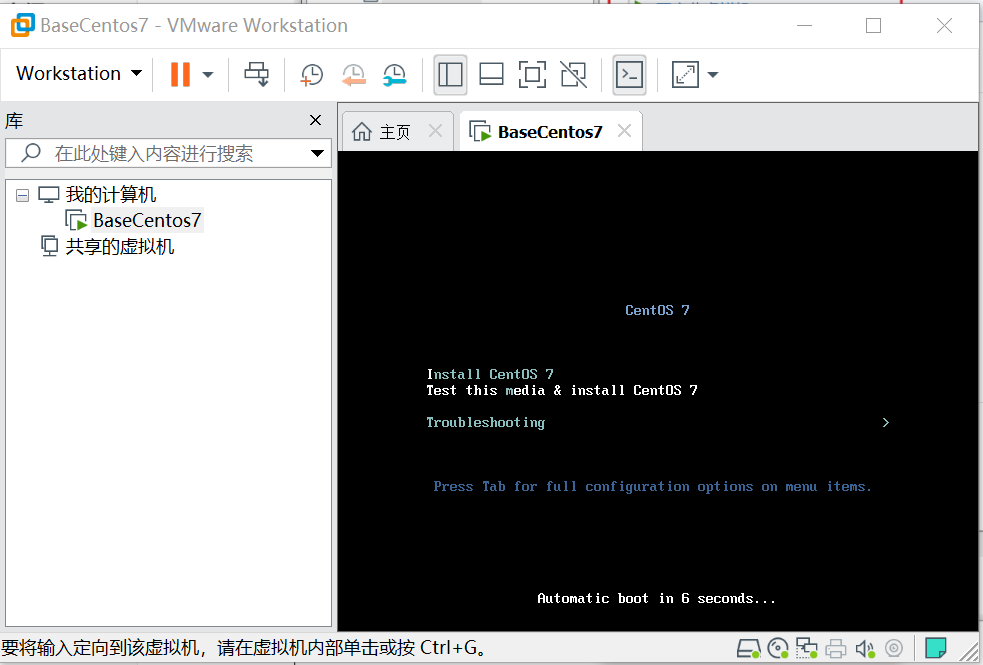
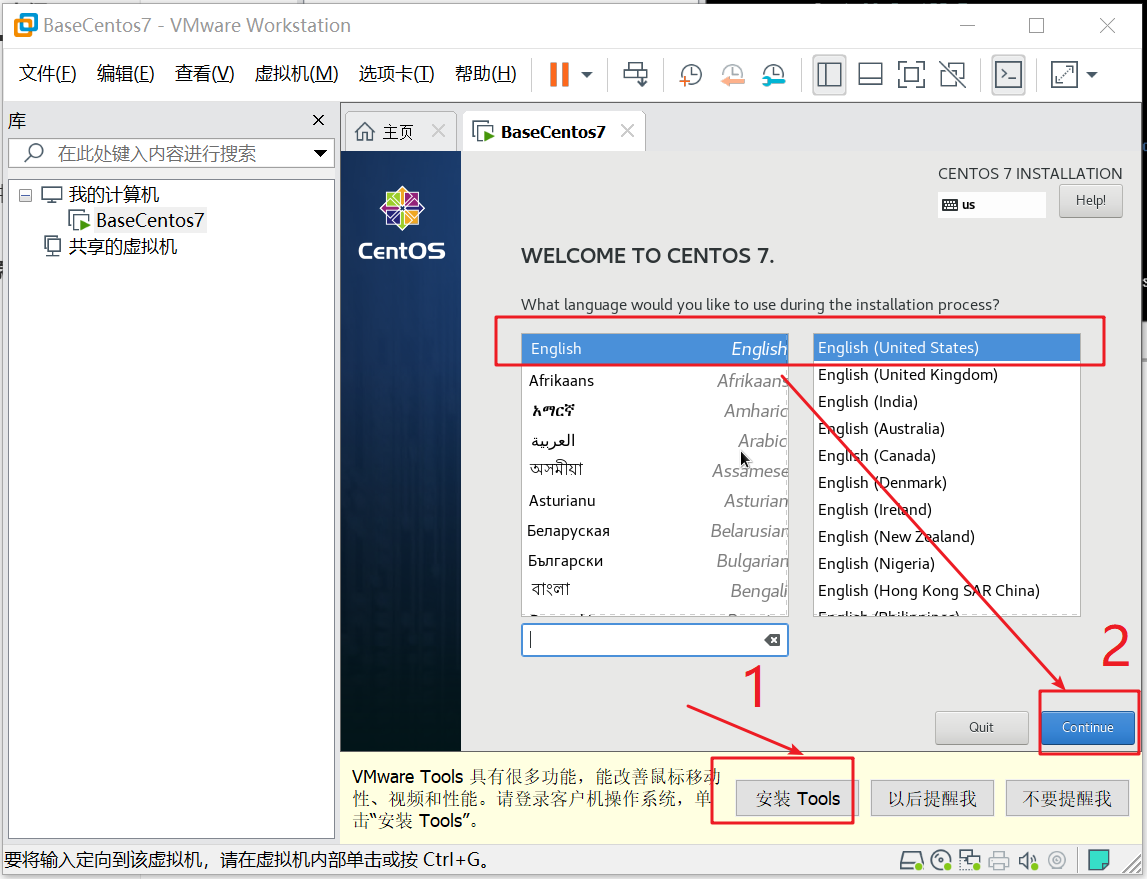
1. Click Install Tools,2 Click Continue
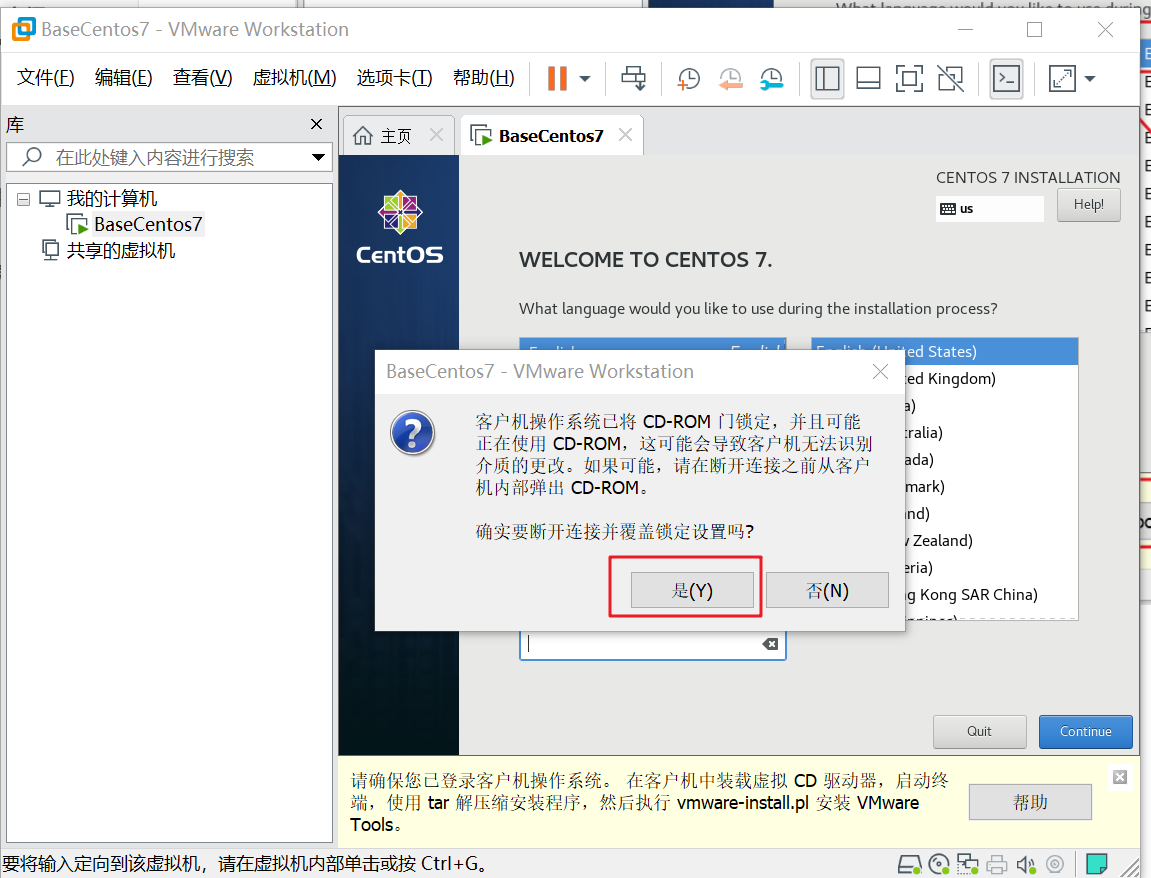
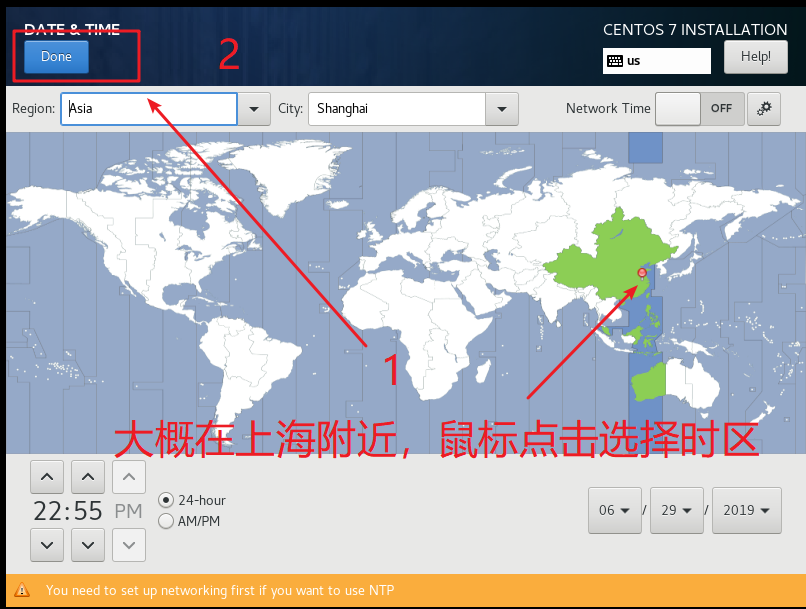
Click date & time as shown below
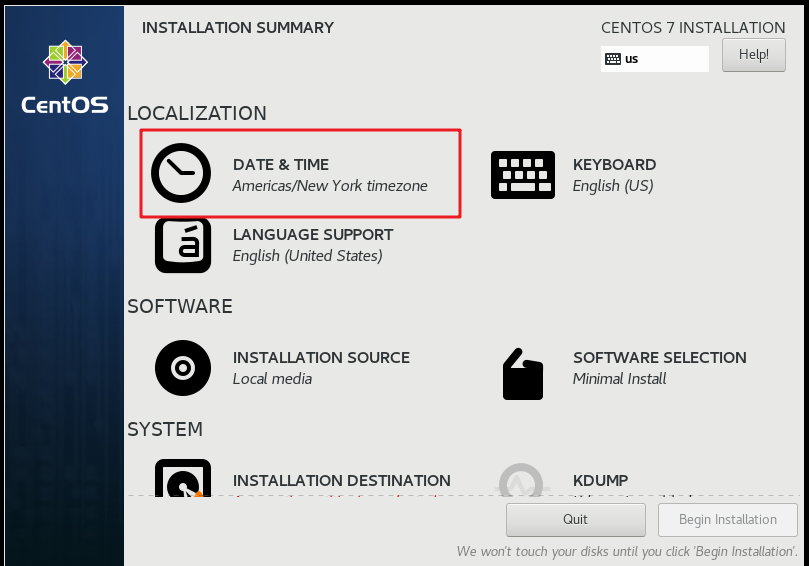
As shown in the figure below, select the time zone and click Done
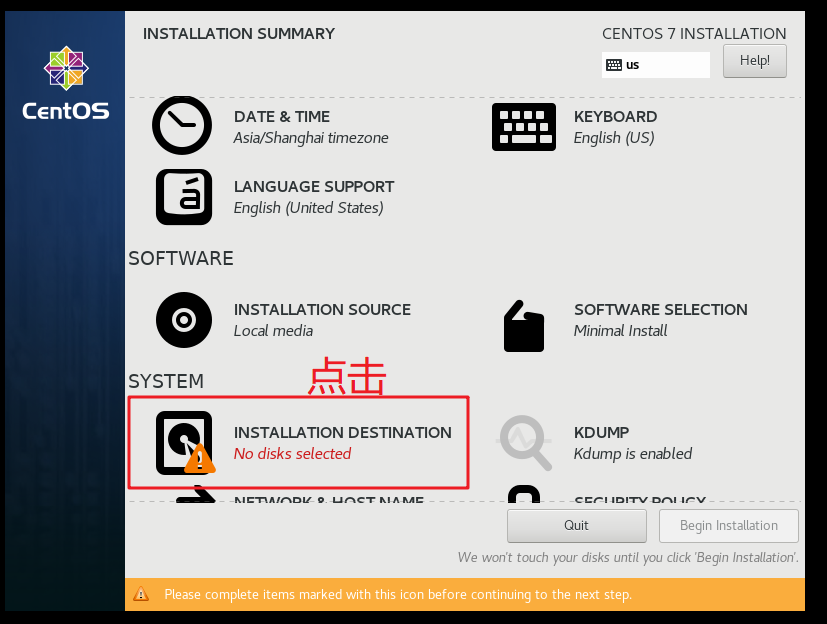
Click INSTALLATION SOURCE as shown below
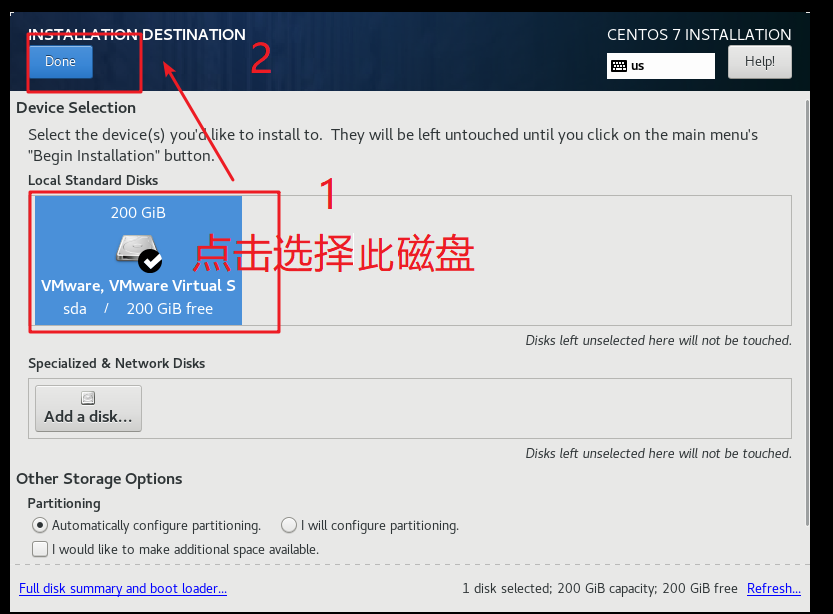
As shown in the figure below, select the disk and click Done
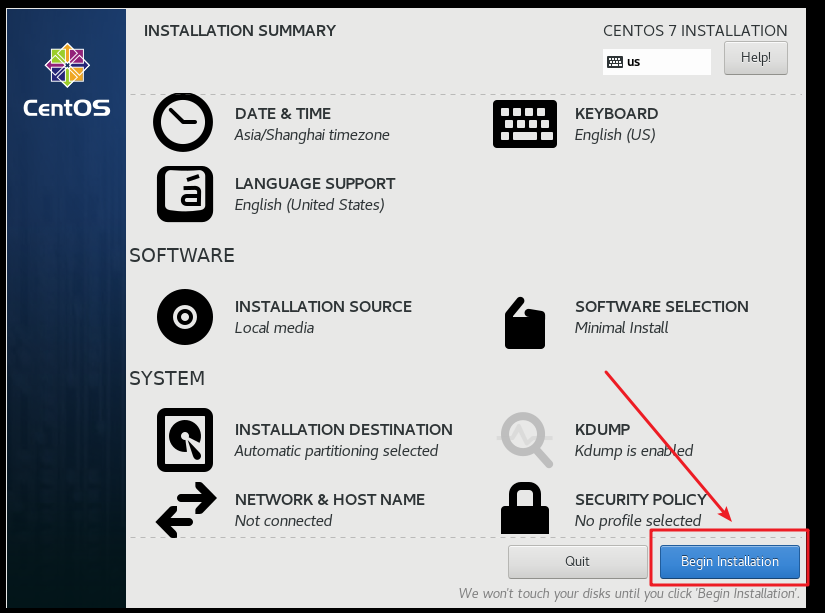
After the disk selection is completed, Begin installation will become available in blue. Click Begin installation to continue to the next step
As shown in the figure below, click to set the password of administrator root as root, which is the same as the user name for easy memory
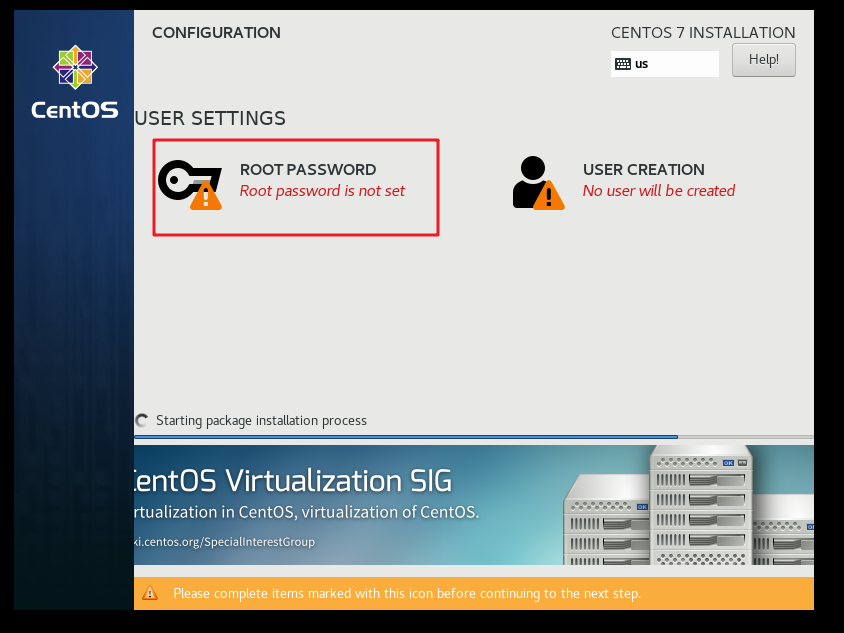
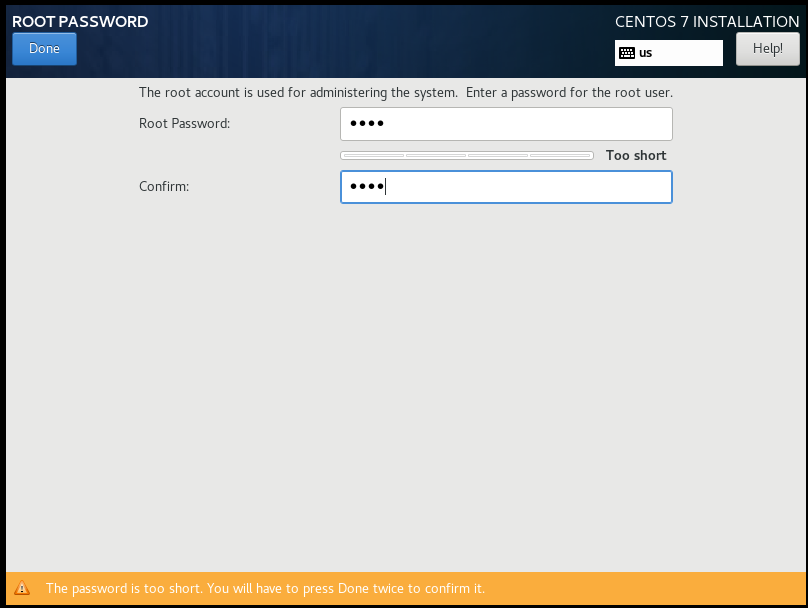
Wait for the installation progress to complete. So far, the perfect start has been half successful. Wait patiently
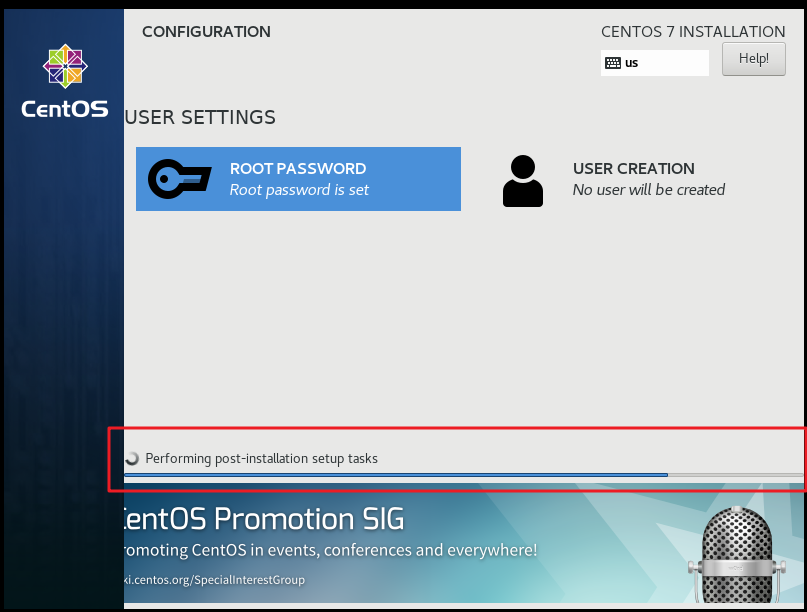
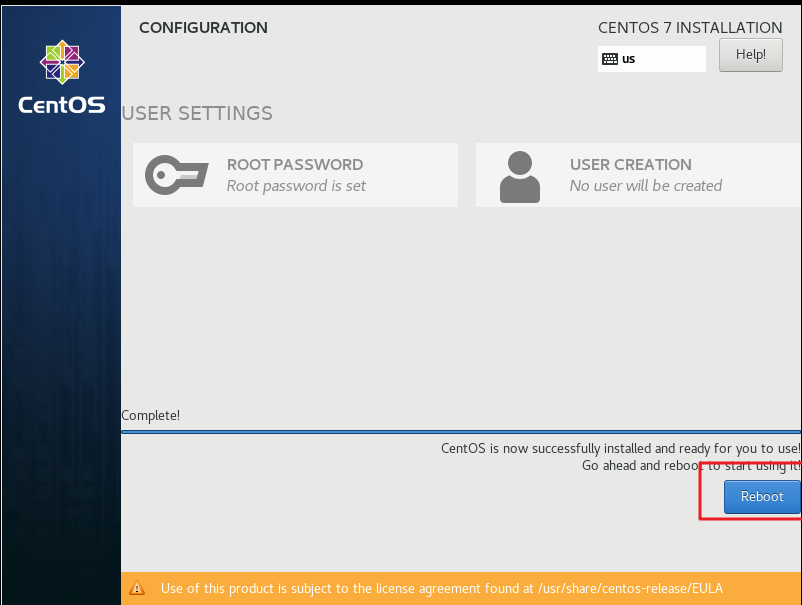
After the installation is completed as shown in the figure below, click Reboot to restart
After restart, as shown in the figure below, a flashing white short bar is displayed after localhost login: (colon), where localhost represents the current host name. So far, the virtual machine installation is completed
Enter the user name root and the password: root. At this time, you only need to enter the password, but it is not displayed on the interface. Press enter after entering. The login is successful, as shown in the figure below:
Displayed after successful login[ root@localhost ~]#
Enter the init 0 command and press enter to close the centos linux system. After downloading, take a snapshot of the newly installed virtual machine to prevent errors during software installation. You can use the snapshot to restore the system to the newly installed state
4. Create a snapshot
For example, follow the steps 1-5 to create a snapshot, view the created snapshot in 6, 7 and 8, and recommend you to create a snapshot in the key steps of later operation
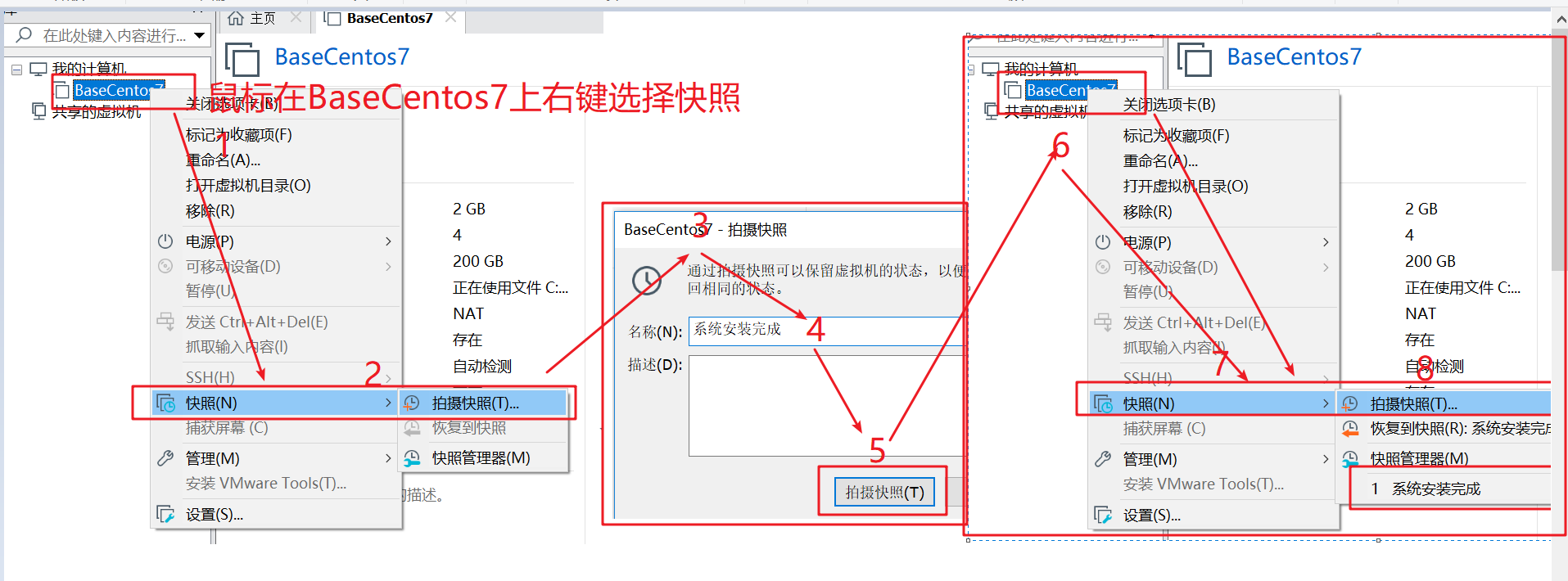
4. Environment configuration
After creating the snapshot, start the virtual machine and log in to the system with root user and root password

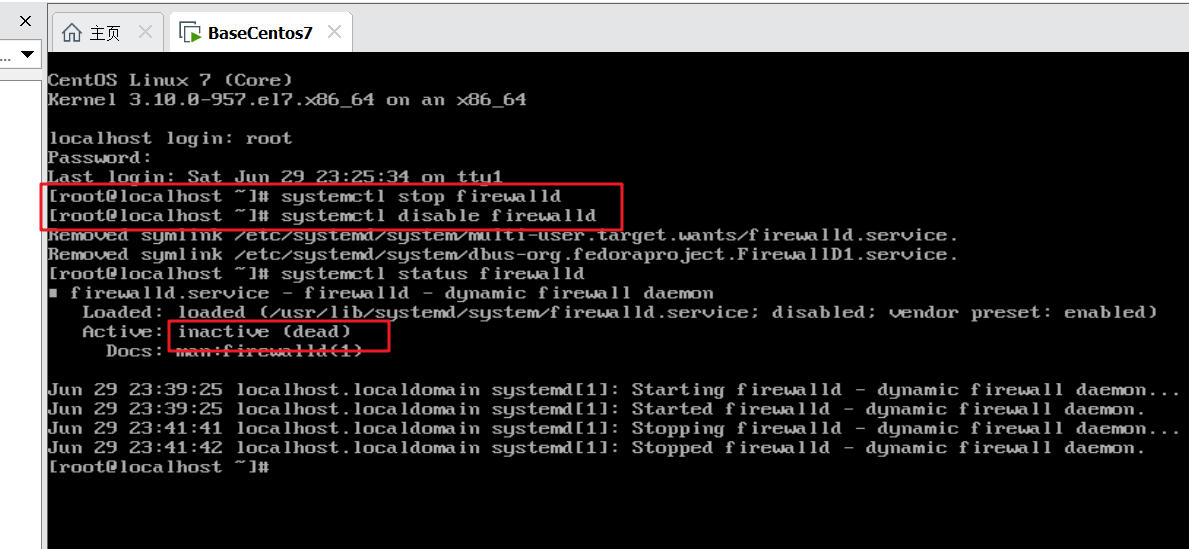
4.1 stop firewall
#Stop firewall [root@localhost ~]#systemctl stop firewalld #Prohibit firewall from starting with system startup [root@localhost ~]#systemctl disable firewalld #View firewall status [root@localhost ~]#systemctl status firewalld
The firewall operation is as follows:
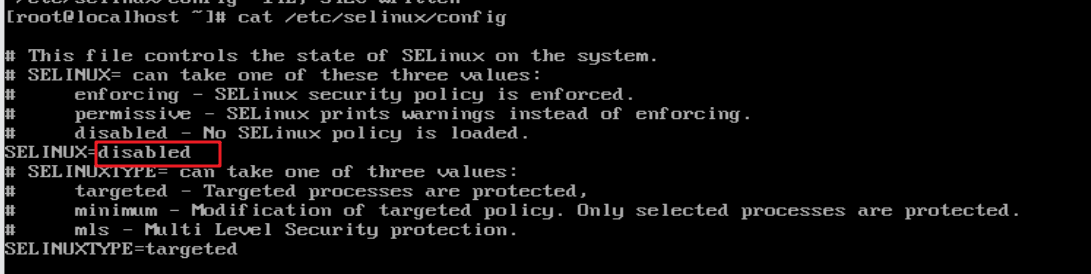
4.2 disabling selinux
#Set the value of SELINUX to disabled [root@localhost ~]# vi/etc/selinux/config #Check whether the setting is complete [root@localhost ~]# cat /etc/selinux/config
5. Configure virtual machine network
5.1 open virtual network editor
5.2 setting up virtual network and subnet
As shown in the figure below, select VMnet8, click change settings, and click Yes
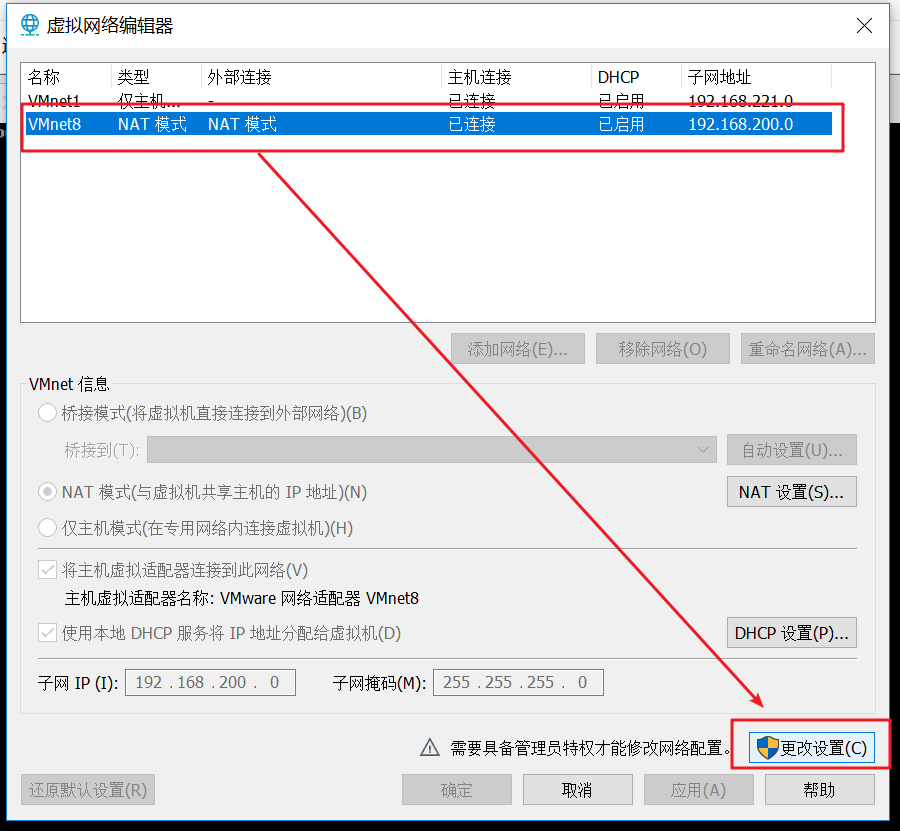
Select VMnet8 here, enter 192.168.200.0 for subnet IP and 255.255.255.0 for subnet mask
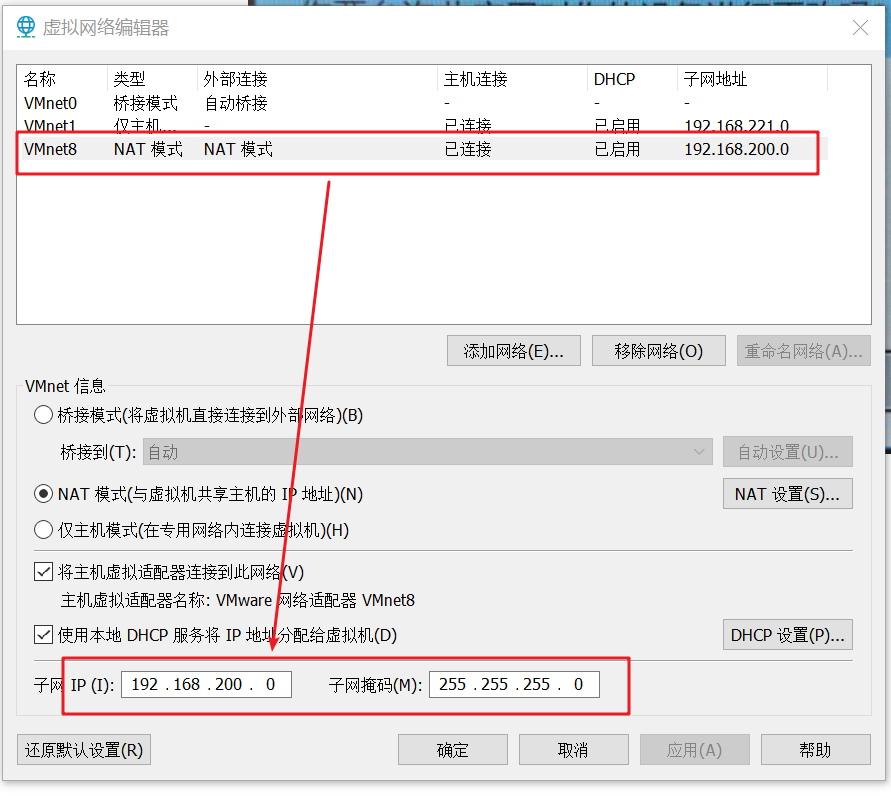
Click NAT settings and enter gateway ip192 168.200.2 (this IP address must be 192.168.200.2, not 192.168.200.1. This IP has a special purpose. Just know it). Click OK
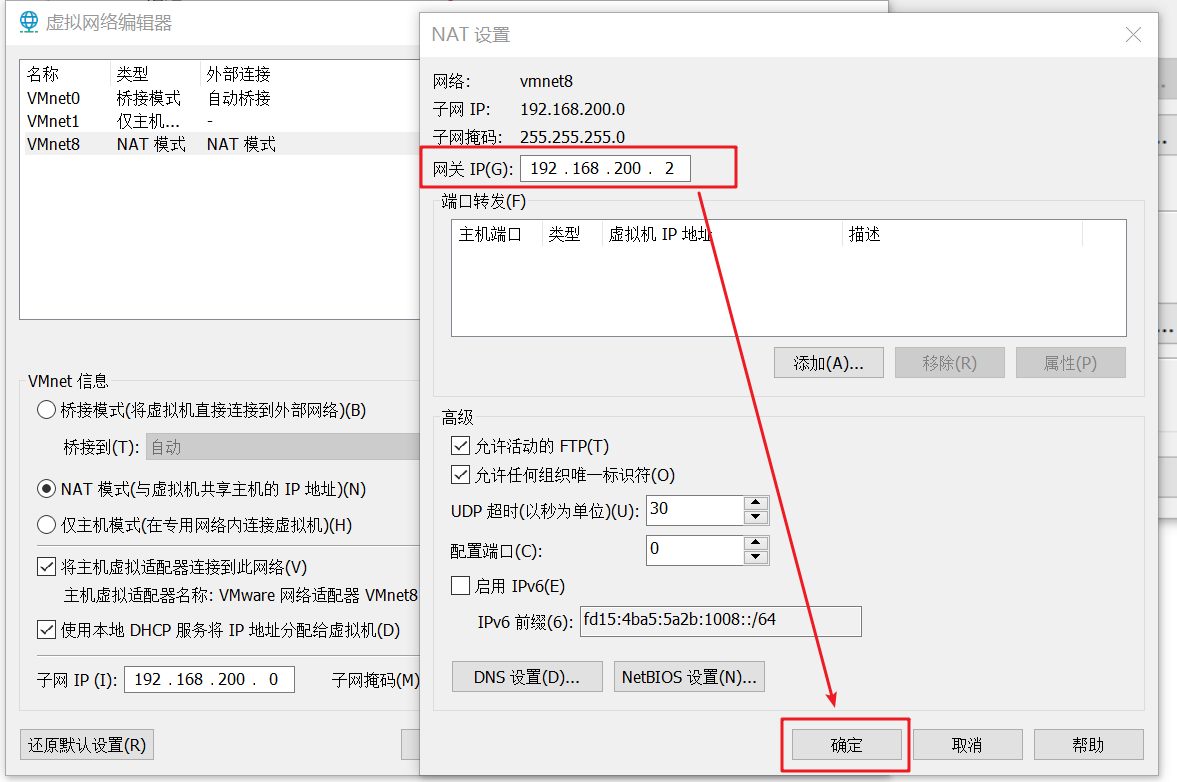
Click OK here to complete the virtual network configuration
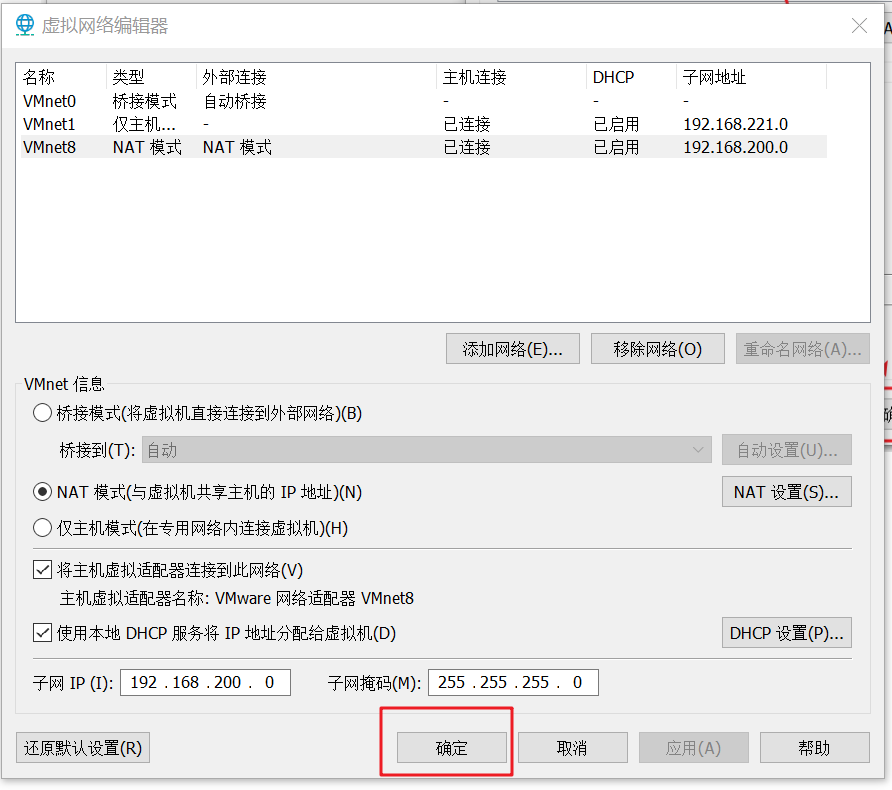
5.3 setting up virtual machine network
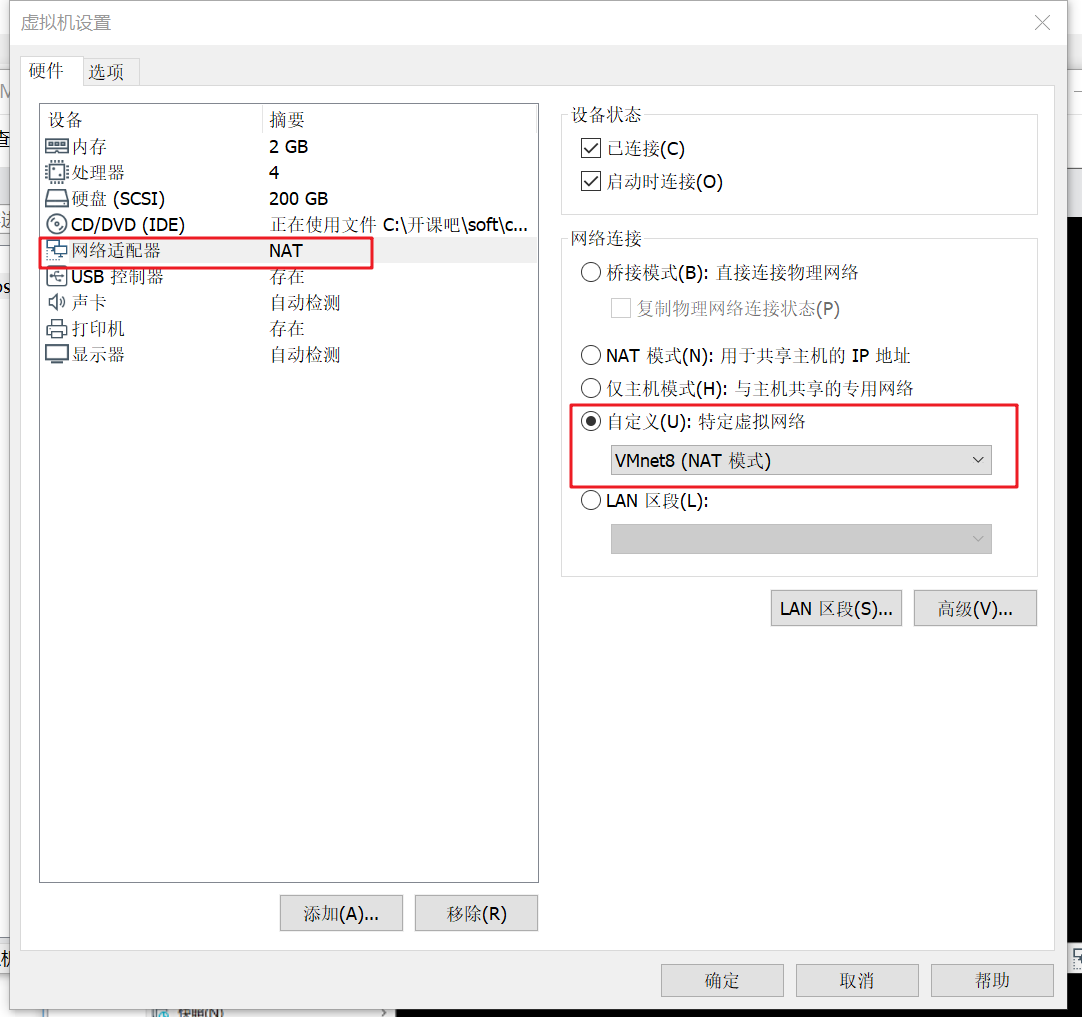
BaseCentos – > right click to select settings to open virtual machine settings
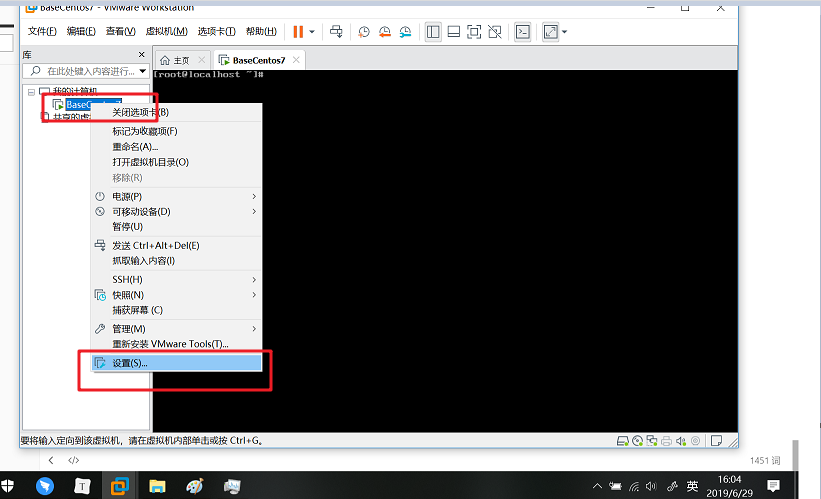
Select network adapter – > select custom: specific virtual network – > OK, complete the virtual machine network settings
5.4 configuring virtual machine IP
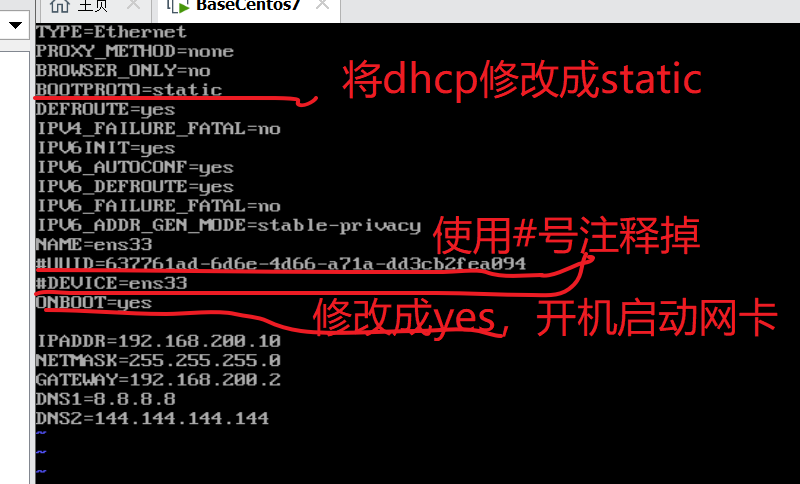
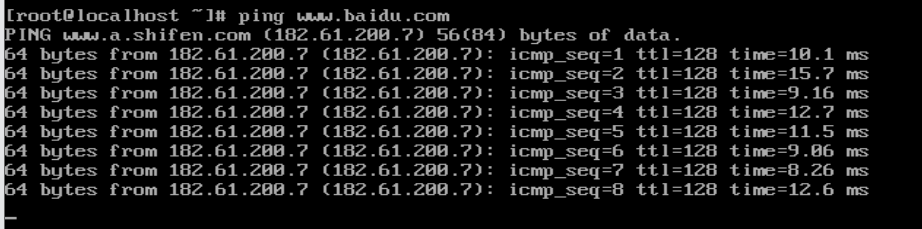
[root@localhost ~]#vi /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-ens33 In file ifcfg-ens33 Add the following at the end of: IPADDR=192.168.200.10 NETMASK=255.255.255.0 GATEWAY=192.168.200.2 #Consistent with the gateway in the configured virtual network DNS1=8.8.8.8 DNS2=144.144.144.144 Save the file when the configuration is complete #Restart the network card [root@localhost ~]#systemctl restart network #ping Baidu's official website ensures that the virtual machine can access the external network to facilitate the online installation of some dependent software in the later stage [root@localhost ~]#ping www.baidu.com
6. Install xshell tool
Using this tool, you can easily operate linux. For example, you can connect the command line of linux and upload files to linux through the xftp file transfer tool
6.1 xshell installation
As shown in the figure above, double-click xshell4 Exe to install
If the following prompt appears, click Yes, which is a prompt mechanism provided by win8, win10 and other operating systems for security.
Start installation
Click next as shown in the figure below
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Click Install as shown in the figure below
Click Finish to finish the installation
6.2 xftp installation
As shown below, double-click xftp4 Exe to install
Similarly, if the following figure appears, click Yes
Start installation
As shown below, click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Select as shown in the figure below and click next
Click Install as shown in the figure below
6.3 use of xshell and xftp
After installing xshell and xftp, generate shortcuts to xshell and xftp on the desktop
Double click the Xshell4 shortcut to run the xshell
As shown in the figure below, click open
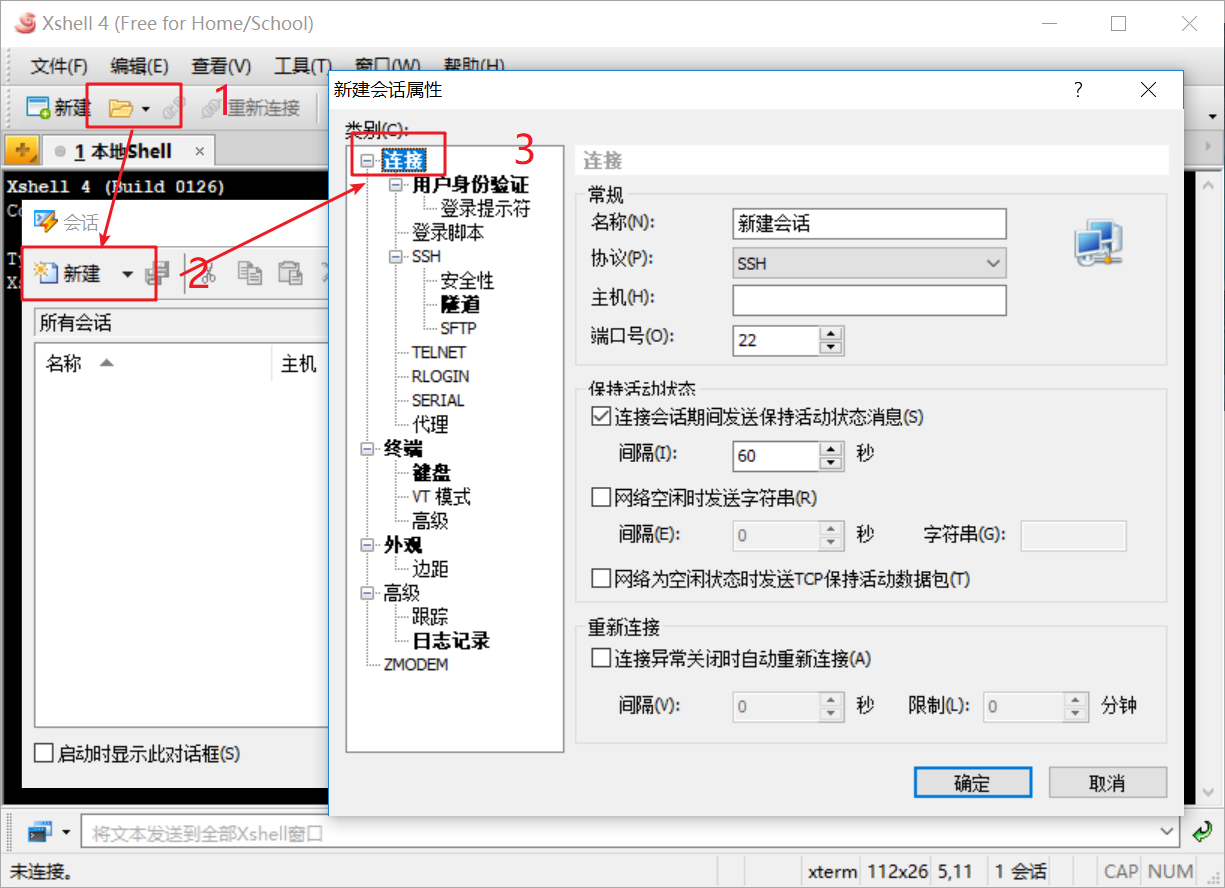
As shown in the following figure, enter the name basecentos (corresponding name for each virtual machine connection) and the ip address of the virtual machine to be connected
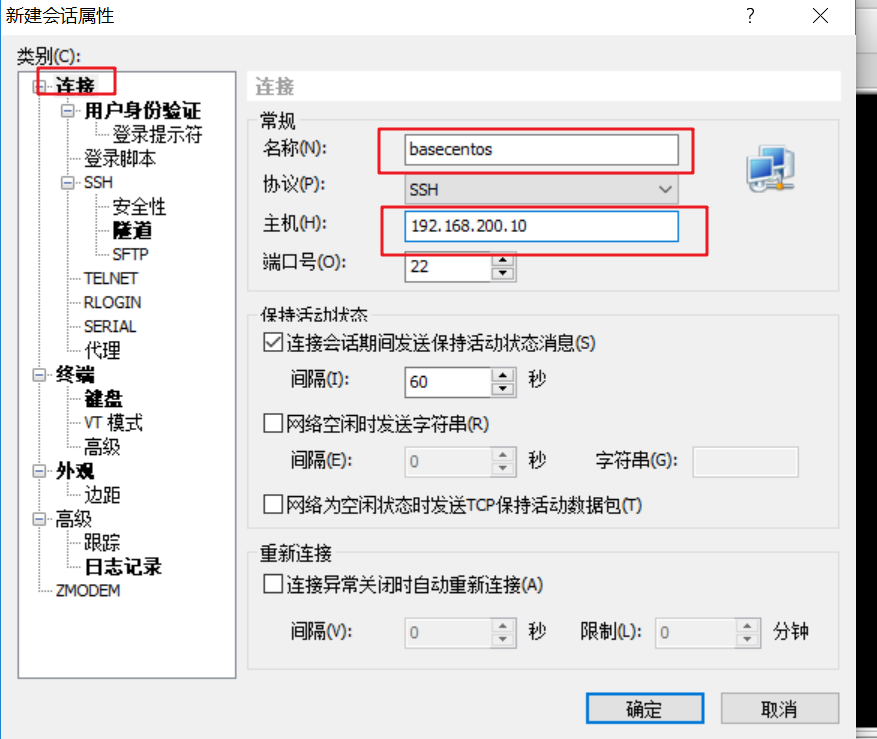
As shown in the figure below, click user authentication, enter the user name (root) and password (root), and click OK
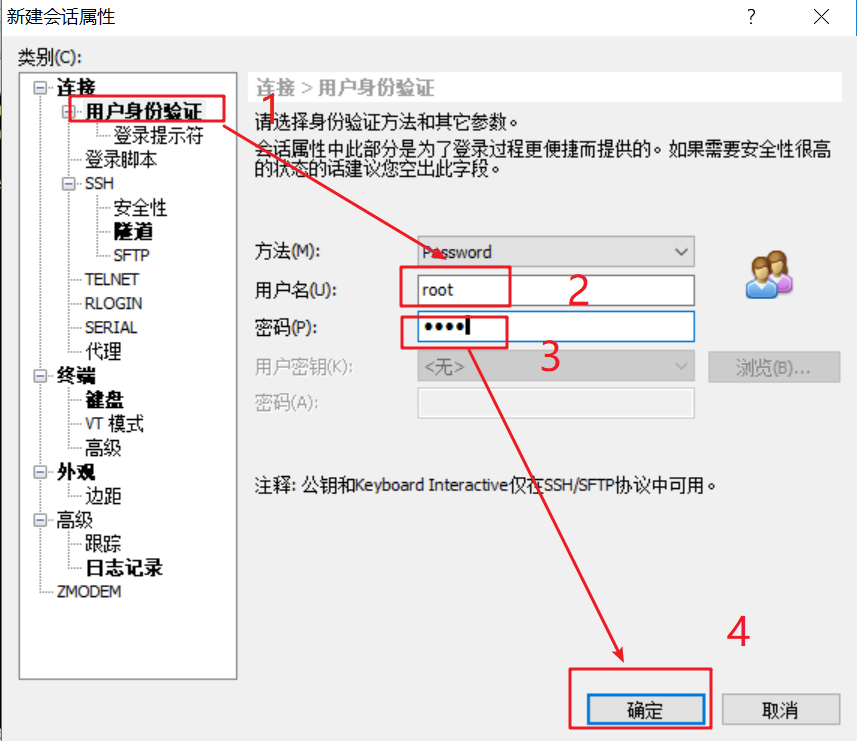
After confirmation, create the following session connection (basecentos), and click Connect
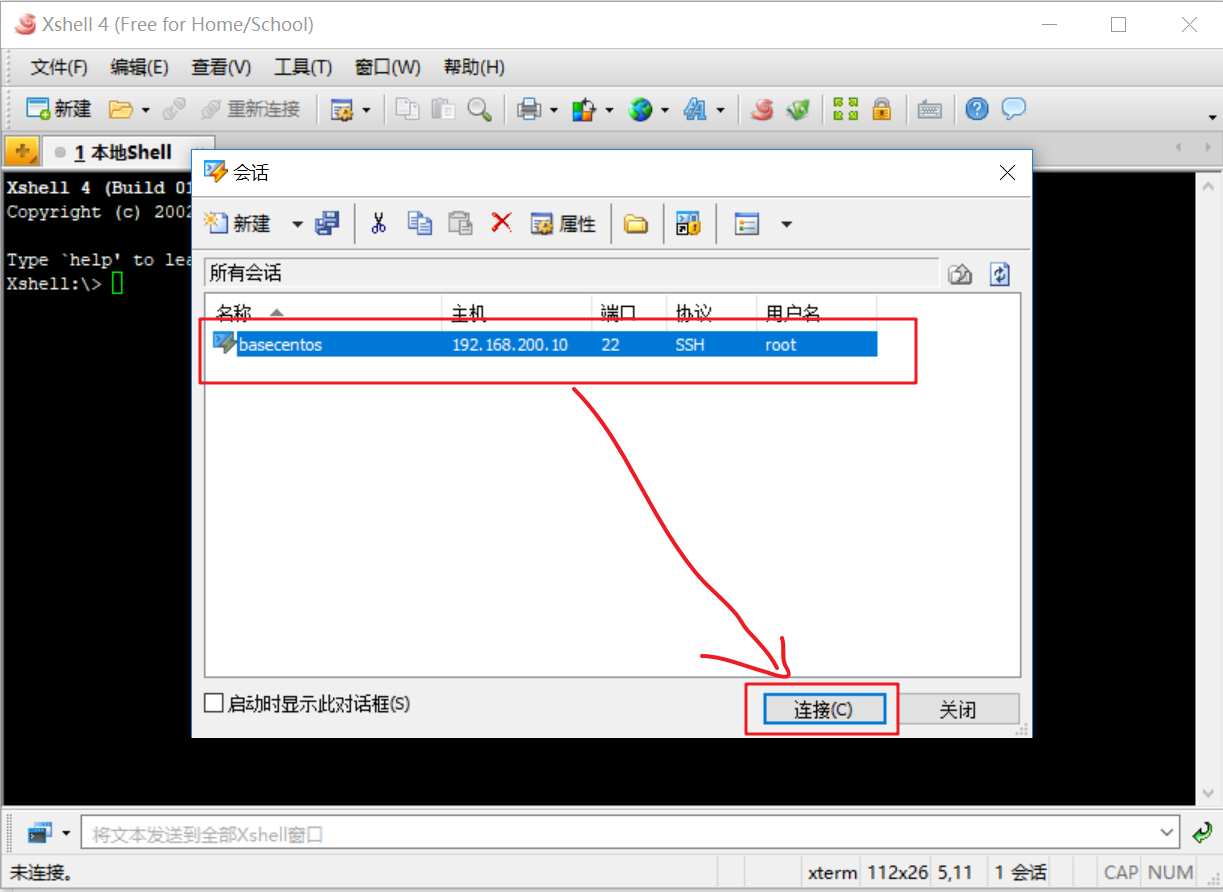
As shown in the figure below, when connecting to the virtual machine for the first time, xshell needs to save the user name and password of the connected user. It can not be entered during the next login to facilitate later login.
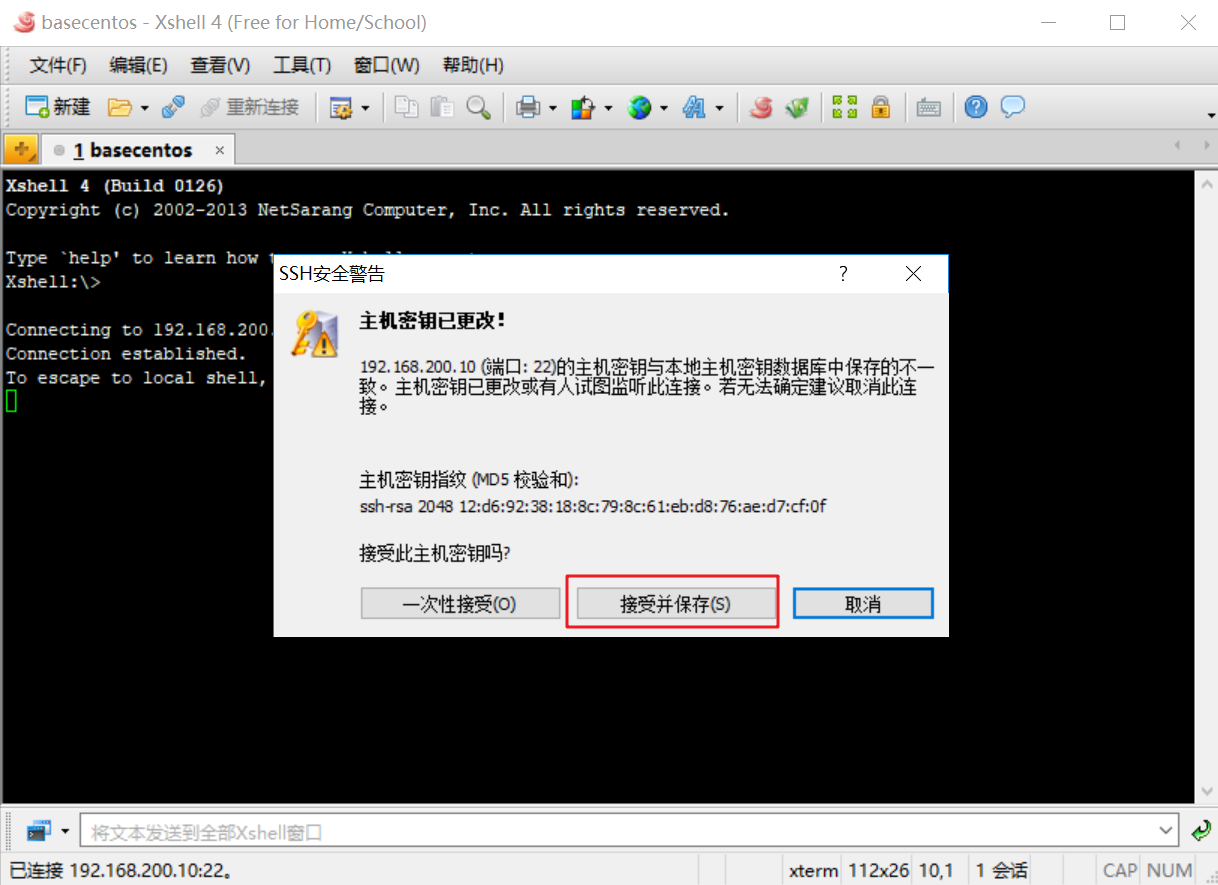
As shown in the figure below, we have successfully logged into the linux system of basecentos virtual machine
So far, we have finished connecting linux with xshell. We will find that the font is too small and uncomfortable. Next, we adjust the font, as shown in the following figure:
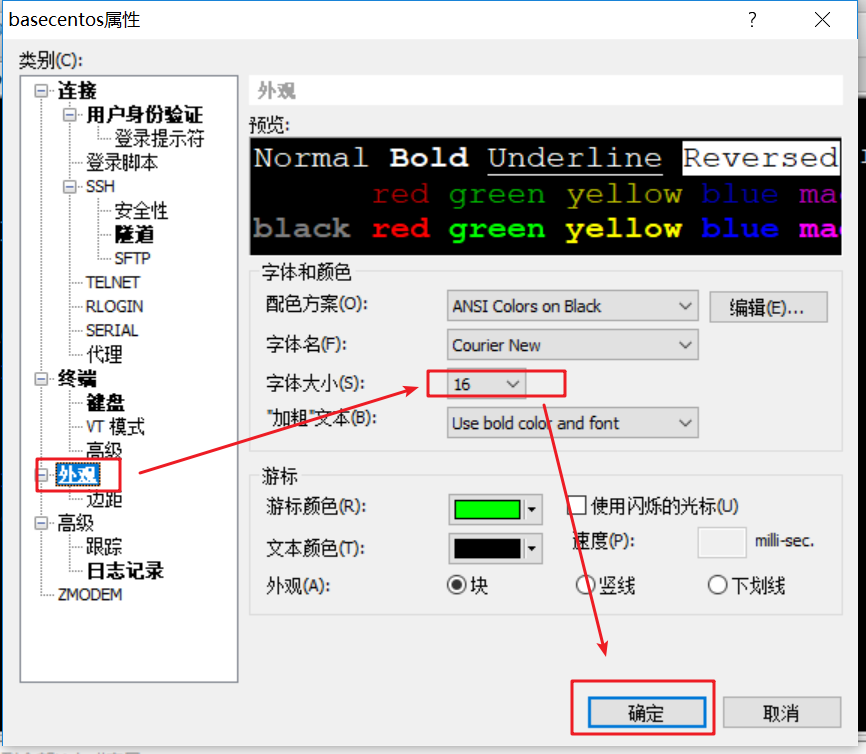
As shown in the figure below, click appearance, select font 16 on the right, and click OK to complete the setting
7. Upload jdk
Upload the downloaded jdk to our installed linux system. By default, we use root to install the jdk.
At this time, we need to use xftp to upload the jdk installation package
As shown in the figure below, click the xftp button to open the xftp tool
The xftp window is as follows:
Select the jdk installation package under linux environment on the left, hold down the left mouse button and drag it directly to the right, then release the mouse to see the following upload progress
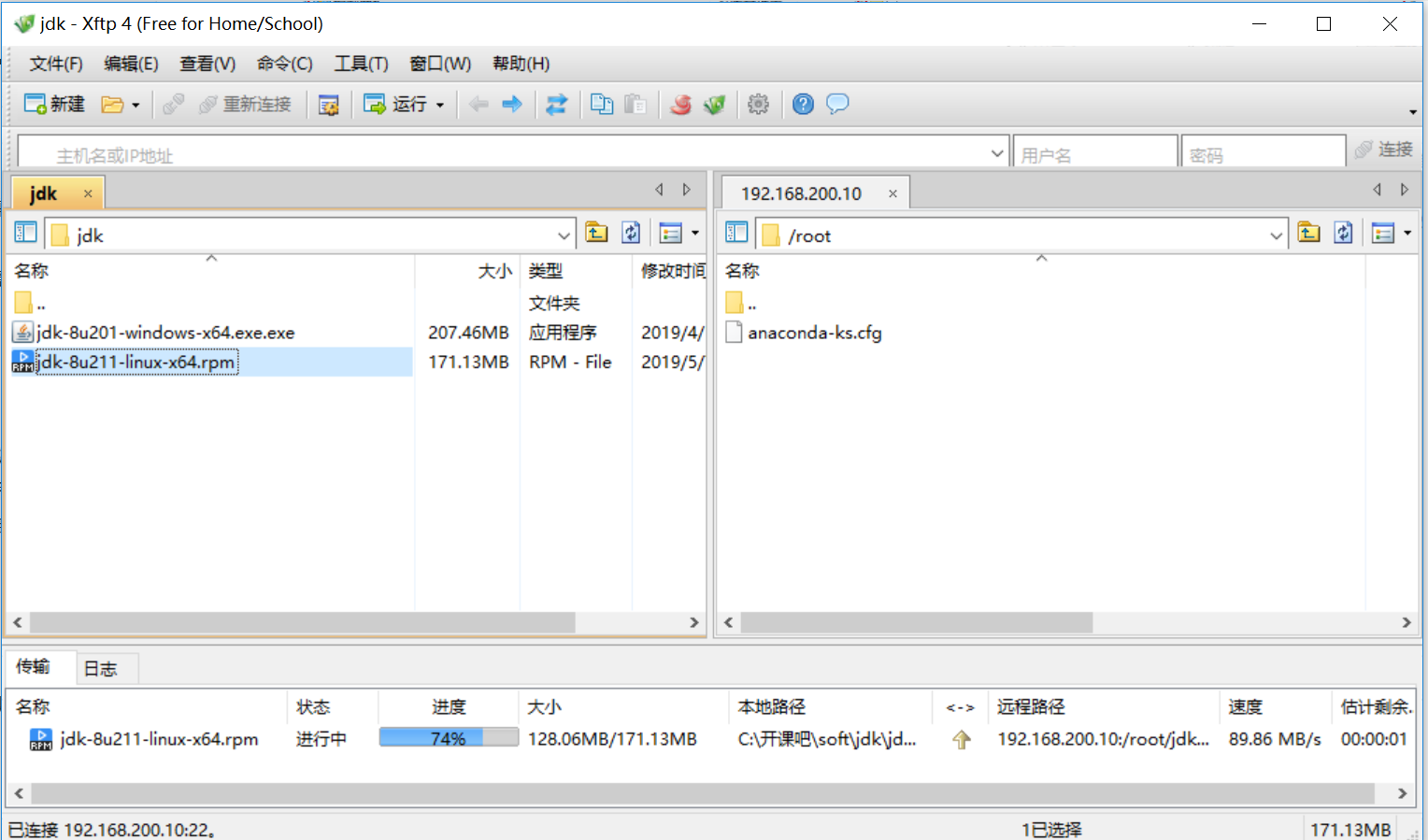
As shown in the figure below, the upload is completed
After uploading, we can close the xftp window and return to the xshell command window.
Enter the ll command in the xshell command window and press enter. As shown in the figure below, you can see the jdk installation file just uploaded
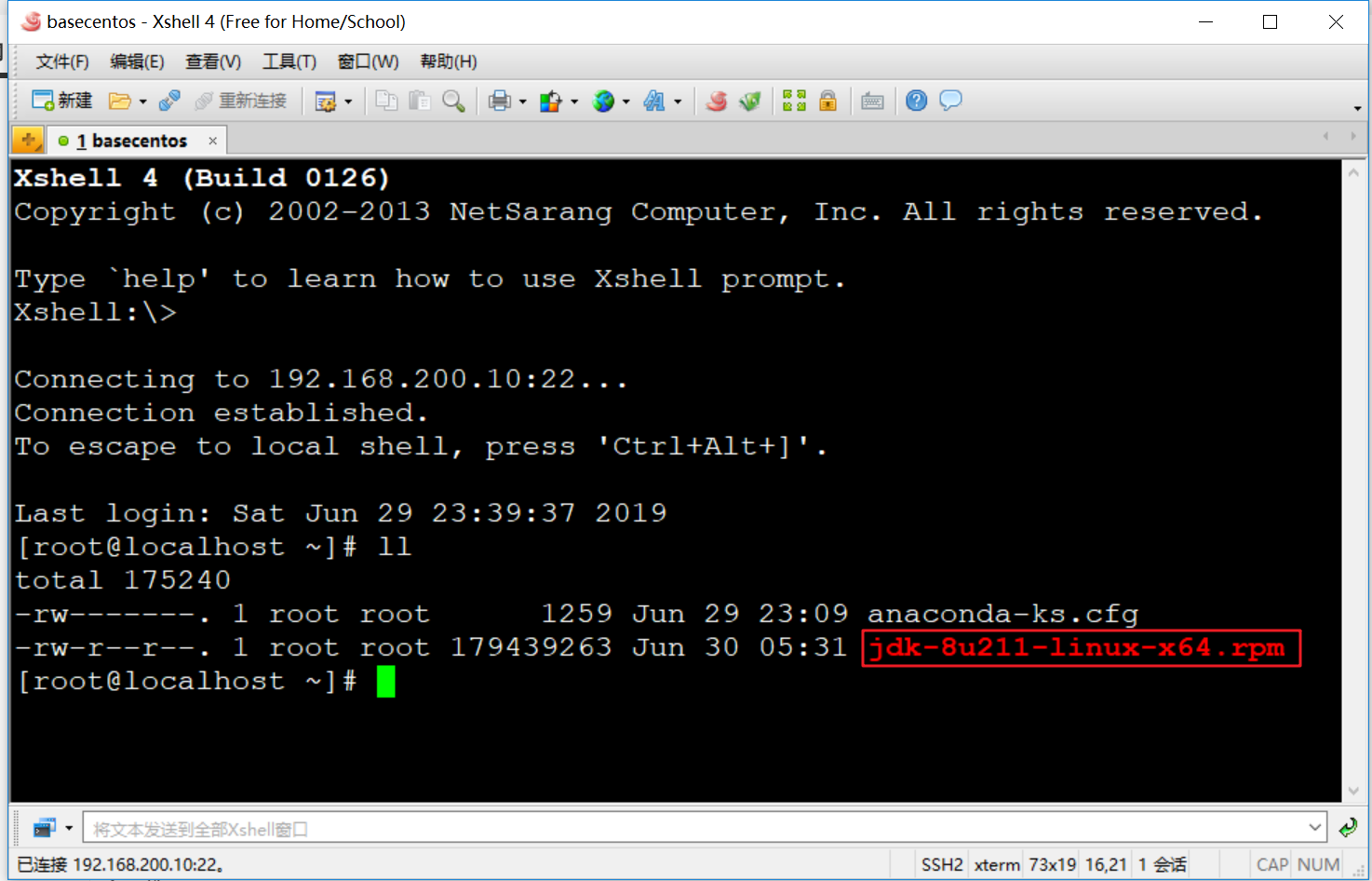
8. Install JDK
So far, we have uploaded the jdk installation package to the root working directory of linux through xftp tool, and then we will install it
8.1 installation jdk
[root@localhost ~]# rpm -ivh jdk-8u211-linux-x64.rpm
The following figure shows the jdk installation process

As shown in the figure below, jdk installation is completed

8.2 configuring java environment variables
1. Find the installation directory of jdk
#First, use the find command to find the java installation directory [root@localhost ~]# find / -name java /etc/alternatives/java /etc/pki/ca-trust/extracted/java /etc/pki/java /var/lib/alternatives/java /usr/bin/java /usr/java #Installation directory of java(jdk) /usr/java/jdk1.8.0_211-amd64/bin/java /usr/java/jdk1.8.0_211-amd64/jre/bin/java [root@localhost ~]#
2. Configure environment variables
Use the vi command to modify the under the root directory bash_profile file
[root@localhost ~]# vi .bash_profile
# .bash_profile
# Get the aliases and functions
if [ -f ~/.bashrc ]; then
. ~/.bashrc
fi
# User specific environment and startup programs
#java environment variables
JAVA_HOME=/usr/java/jdk1.8.0_211-amd64
#Add java environment variables to path
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/bin:$JAVA_HOME/bin
export JAVA_HOME
export PATH
~ #First press esc in the upper left corner of the keyboard, then press and hold shift to enter: (colon) and enter wq! (force save)
:wq!
[root@localhost ~]# vi .bash_profile
#Use the source command to validate the configured environment variables
[root@localhost ~]# source .bash_profile
#Use the java -version command to check whether the java environment variable configuration is successful
[root@localhost ~]# java -version
#Displaying java version "1.8.0_211" indicates that the Java environment variable (JAVA_HOME) has been configured successfully
java version "1.8.0_211"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_211-b12)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.211-b12, mixed mode)
[root@localhost ~]#
9. Configure time synchronization
In the later stage, when building a big data cluster, the time between nodes needs to be the same, so we need to synchronize the time between nodes and time center when building a cluster.
9.1 installing time synchronization software
Use the command: yum install -y ntpdate to install time synchronization software (yum is an online software installation tool under linux. Let's use it briefly first, which will be explained in subsequent courses)
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y ntpdate Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Determining fastest mirrors * base: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * extras: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn base | 3.6 kB 00:00:00 extras | 3.4 kB 00:00:00 . . . Complete!
9.2 configure timing and time synchronization
#Use the crontab - e command to add a timed time synchronization configuration [root@localhost ~]# crontab -e #After executing the crontab -e command, press the letter i on the keyboard to enter the editing mode, enter the content, then press esc in the upper left corner of the keyboard to enter the command mode, press the main shift to enter: (colon), and enter wq! Press enter to finish saving #The following configuration means that the time is synchronized every minute */1 * * * * /usr/sbin/ntpdate us.pool.ntp.org; ~ :wq! #Wait for about one minute and use the date command to check whether the system time is synchronized [root@localhost ~]# date Sun Jun 30 10:51:17 CST 2019 [root@localhost ~]#
10. Install the network tool net tools
Net tools is a network troubleshooting tool under the same linux system. We often use it to check the operation of the cluster network
[root@localhost ~]# yum install -y net-tools Loaded plugins: fastestmirror Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * extras: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn * updates: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn Resolving Dependencies --> Running transaction check ---> Package net-tools.x86_64 0:2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7 will be installed --> Finished Dependency Resolution Dependencies Resolved ================================================================================================ Package Arch Version Repository Size ================================================================================================ Installing: net-tools x86_64 2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7 base 306 k Transaction Summary ================================================================================================ Install 1 Package Total download size: 306 k Installed size: 918 k Downloading packages: net-tools-2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7.x86_64.rpm | 306 kB 00:00:00 Running transaction check Running transaction test Transaction test succeeded Running transaction Installing : net-tools-2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7.x86_64 1/1 Verifying : net-tools-2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7.x86_64 1/1 Installed: net-tools.x86_64 0:2.0-0.24.20131004git.el7 Complete! [root@localhost ~]#
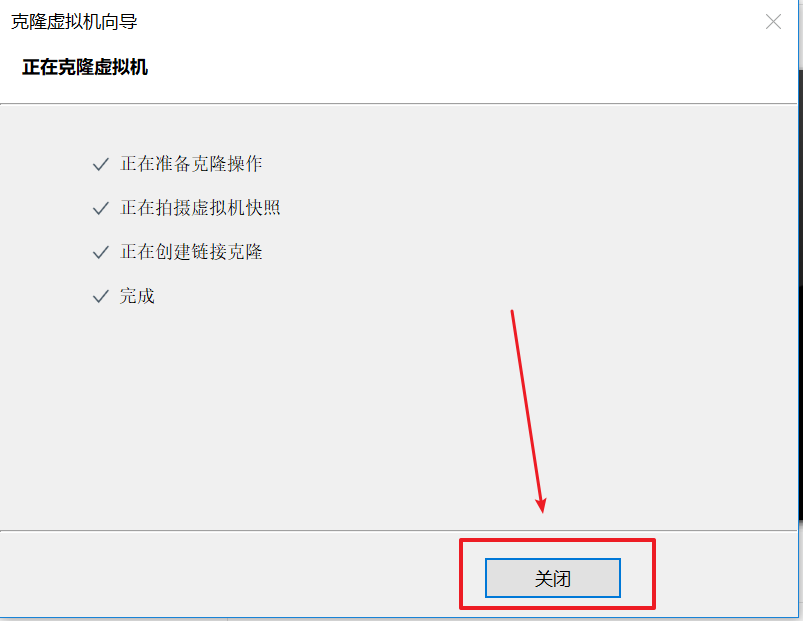
11. Clone virtual machine
In order to ensure that the configuration of all our machine environments is consistent, we need to clone the virtual machine. At the same time, we only need to install the linux operating system on one virtual machine, and the cloned machine also has the linux system installed, which saves us the time of repeatedly installing the linux system and reduces the errors of inconsistent configuration among our multiple host systems
So far, we need to build a cluster of three machines, so we need three machines. We cloned three from one machine.
11.1. Shut down the currently running virtual machine
When cloning a virtual machine, you need to shut down the currently running virtual machine
[root@localhost ~]# init 0 #Enter init 0 and press enter when finished
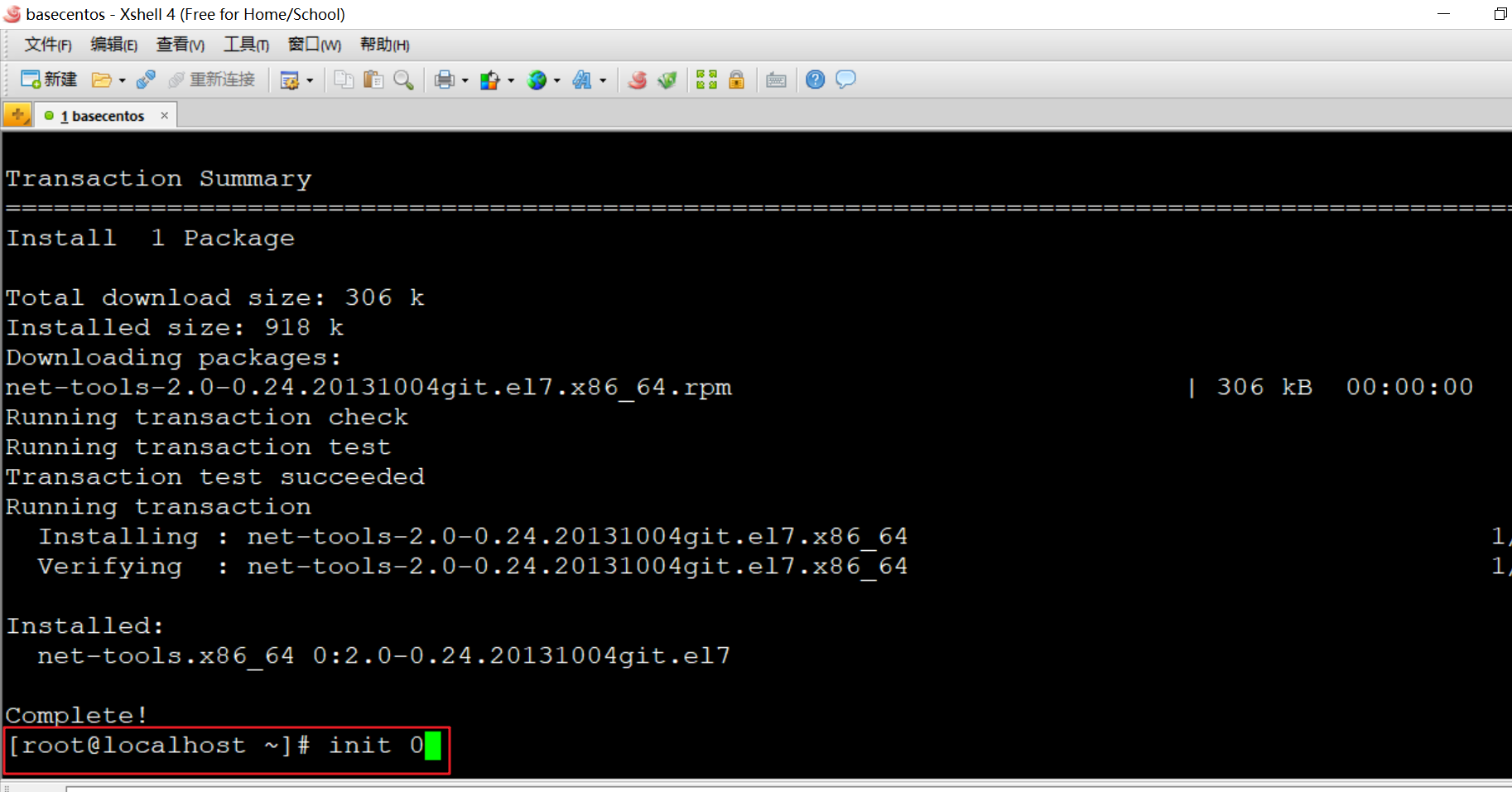
As shown in the figure below, we will find that the basecentos session of the xshell connection has been closed
11.2 cloning virtual machines
Switch to the main interface of VMware Workstation, our virtual machine management software, and continue with the following steps
1. As shown in the figure below, in BaseCentos7
Click next as shown below
Click next as shown below
Click next as shown below
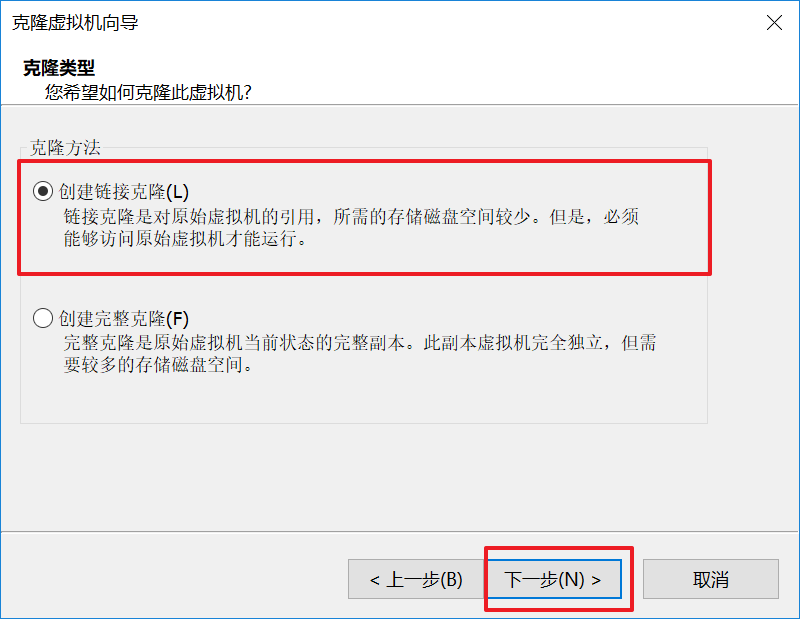
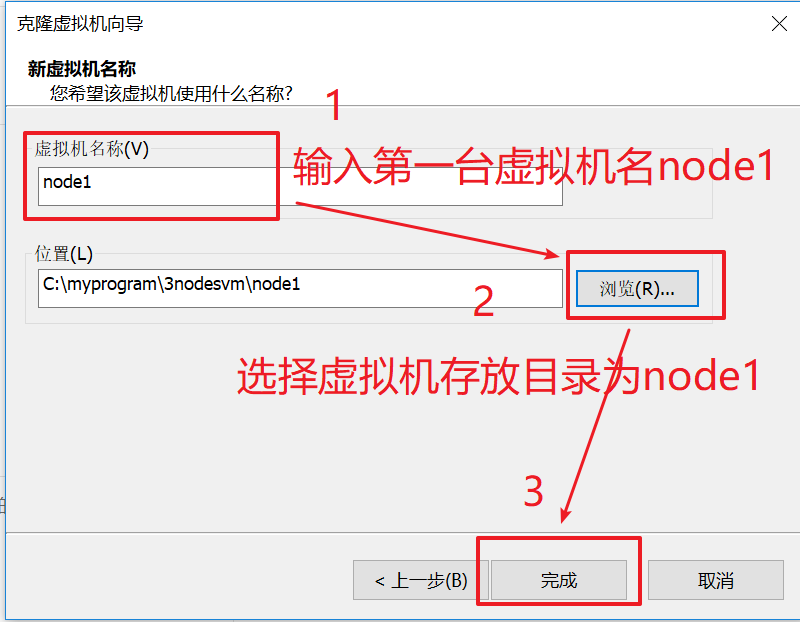
As shown in the figure below, enter the name of the virtual machine and select the storage path of the first virtual machine C: \ myprogram \ 3nodesvm \ node1 (if the path does not exist, please install such a path level to create it by yourself)
As shown in the figure below, click close to finish cloning
After the virtual machine cloning operation is completed, we use the same method above to clone two virtual machines node2 and node3. After the operation is completed, as shown in the figure below, we can find that three virtual machines have been completely created