Definition of Dictionary:
Dictionary is the most flexible data type in python besides list. Dictionaries can also be used to store multiple data, usually used to store information about an object. #The dictionary is an unordered data set and, when using the print function to output the dictionary, #In general, the order of output is inconsistent with that of definition
Difference between dictionary and list:
Lists are ordered sets of objects and
Dictionaries are unordered sets of objects and
Dictionary defined with {}
Dictionaries use key value pairs to store data. Key value pairs are used to separate data
Key key is index
Value value is data
Use between keys and values; separate
The key must be unique (because we have to find the data through the key)
Value can take any data type, but key can only use string, number or tupleView dictionary usage:
In [2]: xfl = {'name':'xuefeilong','age':18}
In [3]: type(xfl) View type is dictionary type
Out[3]: dict
In [4]: xfl. Many functions of dictionary are not commonly used
xfl.clear xfl.items xfl.pop xfl.viewitems
xfl.copy xfl.iteritems xfl.popitem xfl.viewkeys
xfl.fromkeys xfl.iterkeys xfl.setdefault xfl.viewvalues
xfl.get xfl.itervalues xfl.update
xfl.has_key xfl.keys xfl.values 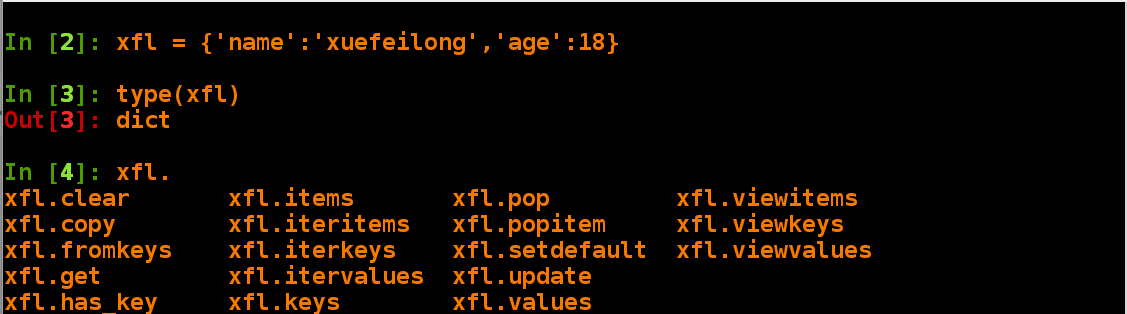
Define a dictionary:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
file: dict_01.py
date:2018-07-15 10:53 AM
author: xfl
desc:
"""
# Define a dictionary
# A dictionary is an unordered collection of data. When print ing out a dictionary
# Usually not in the same order as the definition
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
print xfl
Value from Dictionary:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
file: dict_01.py
date:2018-07-15 10:53 AM
author: xfl
desc:
"""
# Define a dictionary
# A dictionary is an unordered collection of data. When print ing out a dictionary
# Usually not in the same order as the definition
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
# print xfl
# 1. value
print xfl['height']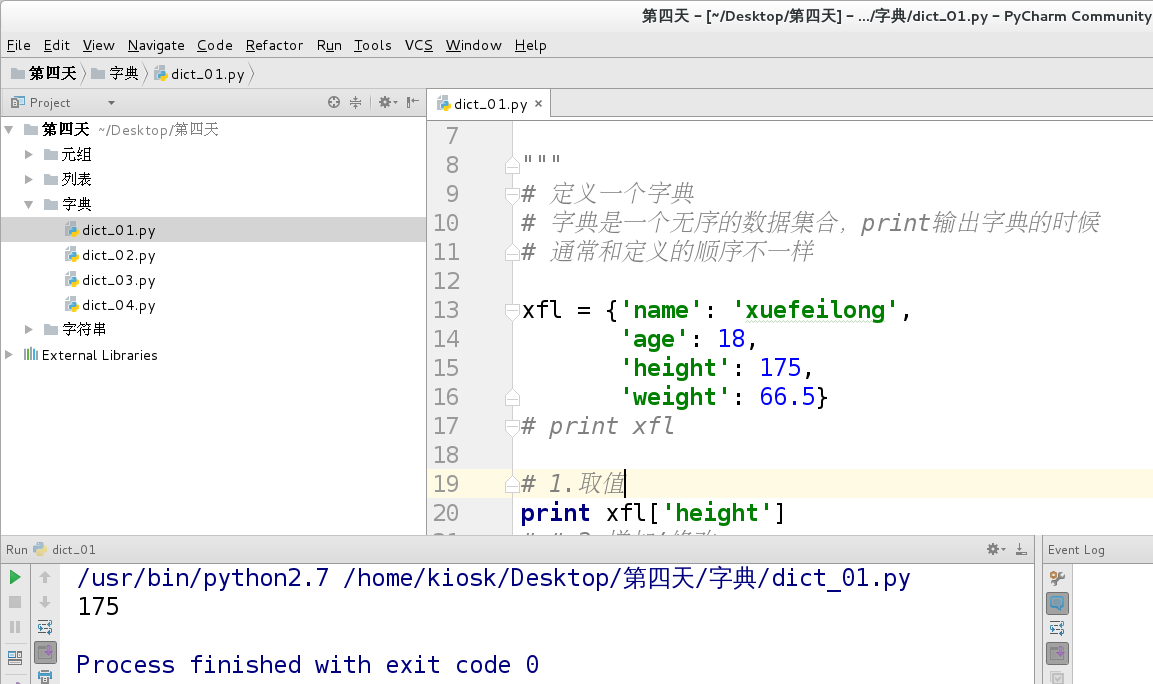
Modify the dictionary value:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
file: dict_01.py
date:2018-07-15 10:53 AM
author: xfl
desc:
"""
# Define a dictionary
# A dictionary is an unordered collection of data. When print ing out a dictionary
# Usually not in the same order as the definition
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
# print xfl
# 2. Add / modify
xfl['age'] = 21 # Replace key directly when it exists
print xfl
xfl['sex'] = 'man' # Add directly when the key does not exist
print xfl
To delete a dictionary element:
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
# 3. delete
xfl.pop('name')
print xfl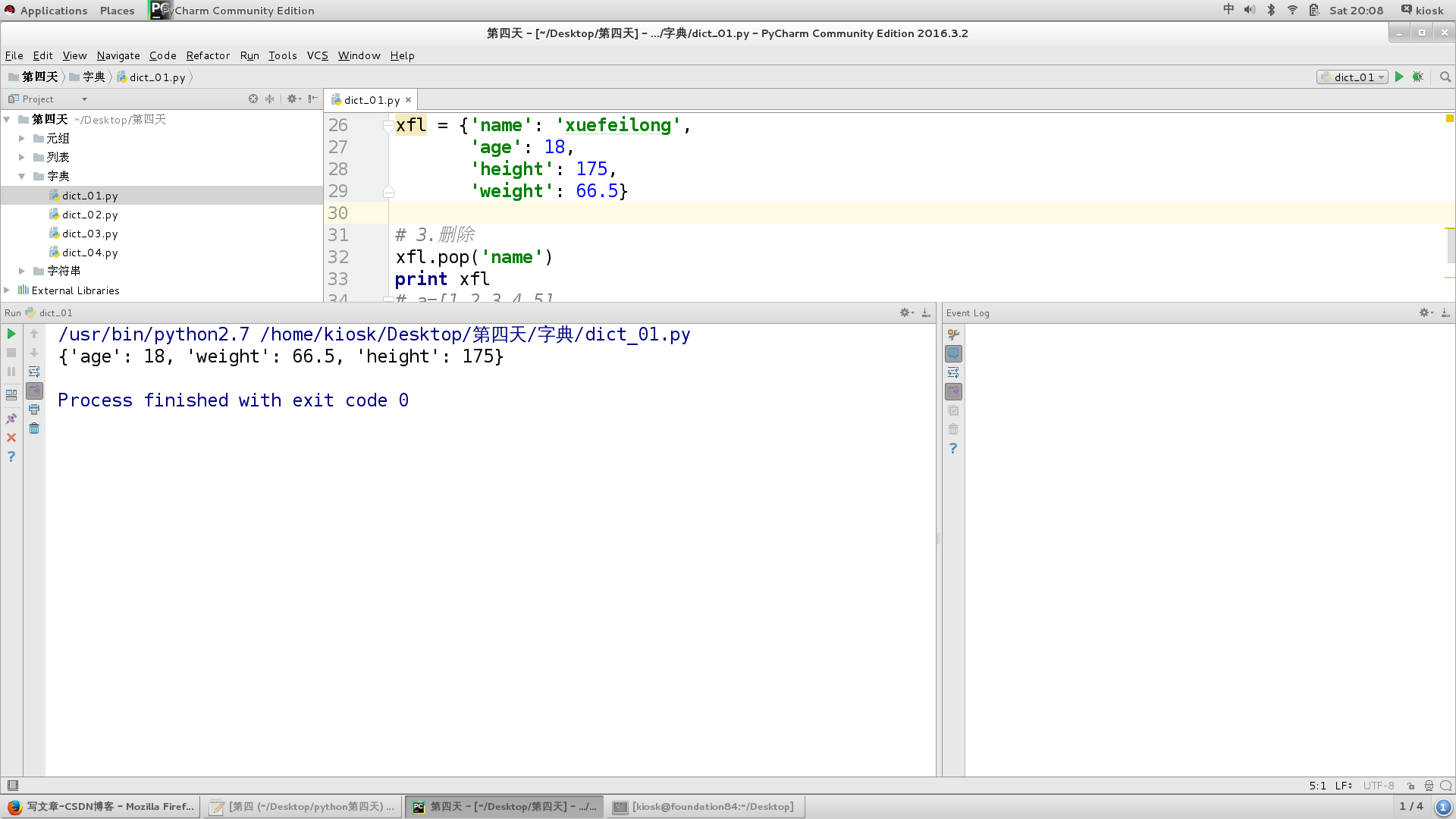
There is no extend in the dictionary usage, and errors will be reported when using. Don't confuse the concept:
a=[1,2,3,4,5]
b=[6,7,8]
print a.extend(b)
len count the number of key value pairs:
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
print xfl
# 1. Count the number of key value pairs
print len(xfl)
update merge Dictionary:
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
print xfl
# 2. Merge dictionary
# The dictionary's custom key is variable and unique
xyy = {'name': 'xiangyuanyuan',
# Existing key direct substitution
'sex': 'girl'}
# Non existent key added directly
xfl.update(xyy)
print xfl
Cycle key value:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
file: dict_03.py
date:2018-07-15 11:35 AM
author: xfl
desc:
"""
# Simply loop a key value
xfl = {'name': 'xuefeilong',
'age': 18,
'height': 175,
'weight': 66.5}
for k in xfl:
print '%s ----> %s' % (k, xfl[k])
# xfl[k] is output by K to index the corresponding value
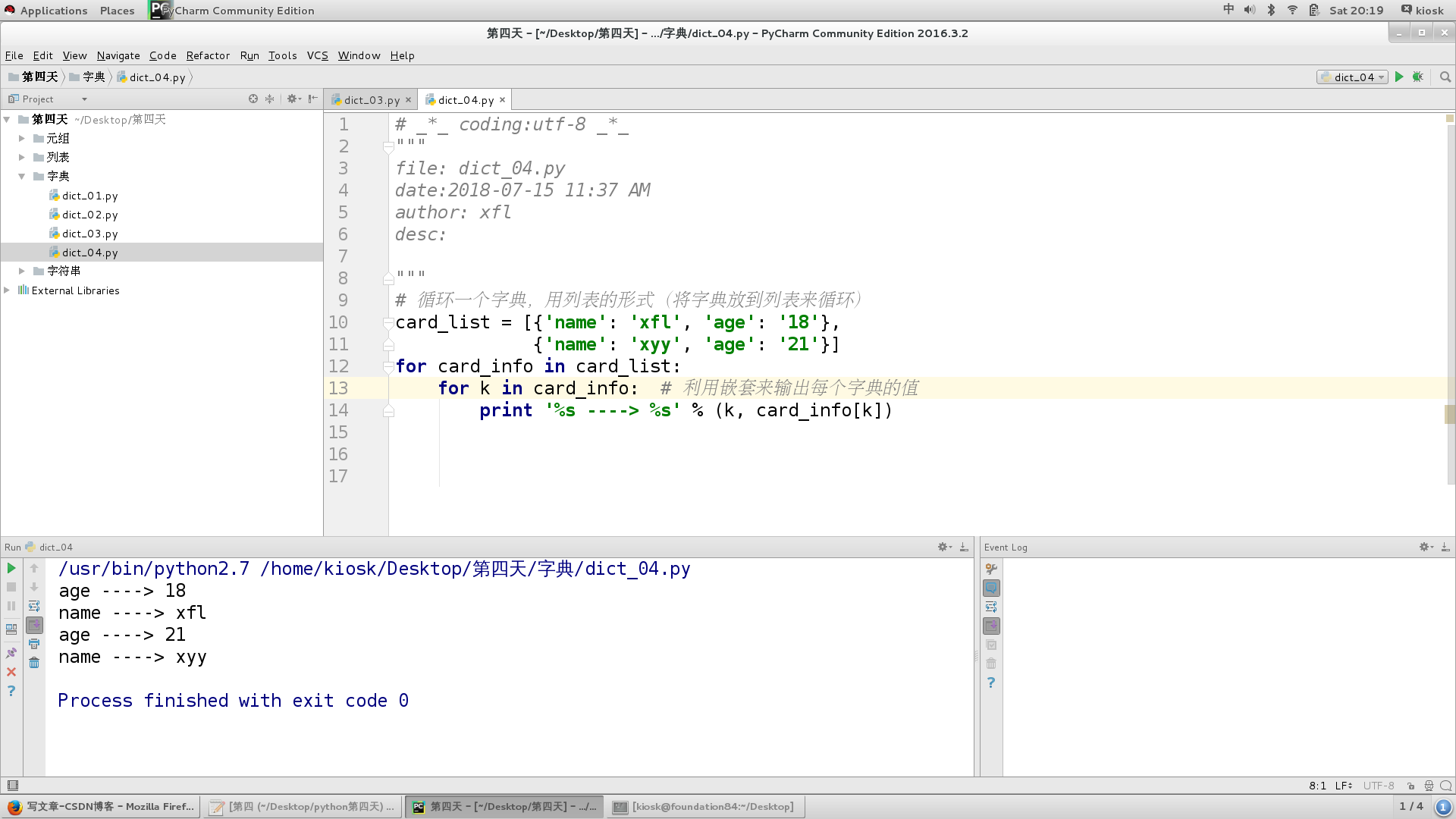
Circular Dictionary:
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
file: dict_04.py
date:2018-07-15 11:37 AM
author: xfl
desc:
"""
# Loop a dictionary in the form of a list (loop the dictionary by putting it in the list)
card_list = [{'name': 'xfl', 'age': '18'},
{'name': 'xyy', 'age': '21'}]
for card_info in card_list:
for k in card_info: # Using nesting to output the value of each dictionary
print '%s ----> %s' % (k, card_info[k])