docker-compose
Docker compose project is the official open source project of docker, which is responsible for the rapid arrangement of docker container clusters
By writing a docker compose file, you can start / stop / update multiple services at the same time (you can define dependencies and start services in order)
Docker compose divides the managed containers into three layers:
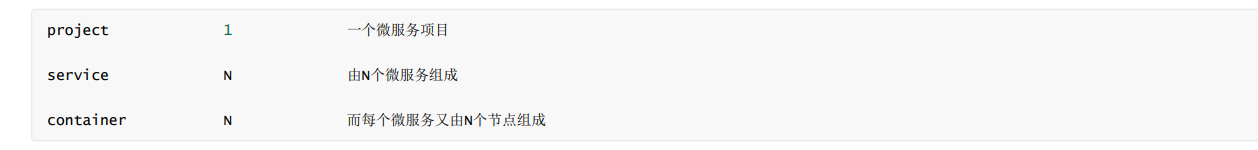
docker-compose.yml forms a project, which includes multiple services. Each service defines the image (or build image) of the container
The default project configuration file of docker compose is docker compose yml
Earlier, when we used Docker, we defined the Dockerfile file, and then used docker build, docker run and other commands to operate the container However, the application system of microservice architecture generally includes several microservices, and each microservice will generally deploy multiple instances. If each microservice needs to be started and stopped manually
Then the low efficiency and the large amount of maintenance can be imagined Docker Compose can easily and efficiently manage containers. It is an application tool for defining and running multi container dockers
Three step process
1) Use dockerfile or image to define the environment of the application so that it can be copied anywhere
2) At docker compose The services that make up the application are defined in YML so that they can run together in a separate environment
3) Run docker compose up to start and run the entire application
Docker compose installation and configuration
1. Upload files
Docker compose Linux x86_ 64 renamed docker compose
Upload the docker compose file just downloaded to the / usr/local/bin / directory of centos7
cd /usr/local/bin
2. Add executable permissions
chmod +x /usr/local/bin/docker-compose
docker-compose. Basic introduction to YML configuration file
version: specify docker compose Writing format of YML file
At present, compose has three versions: Version 1, version 2 and version 3. Compose distinguishes between version 1 and version 2 (Compose 1.6.0+,Docker Engine 1.10.0 +) Version 2 supports more instructions Version 1 will be deprecated in the future
services: multiple container collections
services: Container 1: Container 2:
Image: image name or image ID. if the image does not exist locally, Compose will try to pull the image
Build: in addition to the specified image, the service can also be based on a Dockerfile. The build task can be executed when starting with up. The build tag is build, and the path of the folder where the Dockerfile is located can be specified Compose will use
Dockerfile: automatically build the image, and then use the image to start the service container
hostname: when starting the highly available (cluster) microservice, it must be consistent with spring.com in the code configuration The profiles attribute is consistent
network_mode: configure the network mode of the service container
Environment: environment variable configuration. You can use array or dictionary
environment: RACK_ENV: development SHOW: 'ture' ------------------------- environment: - RACK_ENV=development - SHOW=ture
Docker compose basic instruction
View version information
docker-compose -v
Build and start the container
docker-compose up
Start a single service
docker-compose up Service name
Background startup service
docker-compose up -d
Stop and delete containers, networks, volumes, mirrors
docker-compose down
Start the specified service or start all services
docker-compose start [Service name]
Stop the specified service or stop all services
docker-compose stop [Service name]
List all running containers
docker-compose ps
Enter the specified container
docker-compose exec
Delete all (stopped) service containers
docker-compose rm
Parameters: - f: force direct deletion, including non stopped containers - v: delete the data volume mounted by the container
Docker compose network
Specify network mode
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
container_name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- 9999:80
volumes:
- /home/nginx/html:/etc/nginx/html
- /home/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d
- /home/nginx/log:/var/log/nginx
restart: alwaysWriting method
network_mode : "bridge" network_mode : "host" network_mode : "none" network_mode : "service:[service_name]" network_mode : "container:[container name/id]"
Reference an external network that already exists
1. Create a network to simulate the external network
docker network create --subnet 10.0.10.0/24 name
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
container_name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- 9999:80
volumes:
- /home/nginx/html:/etc/nginx/html
- /home/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d
- /home/nginx/log:/var/log/nginx
restart: always
networks:
- mm-net
networks:
mm-net:
external:
name: mmCustom network
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
container_name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- 9999:80
volumes:
- /home/nginx/html:/etc/nginx/html
- /home/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d
- /home/nginx/log:/var/log/nginx
restart: always
networks:
mm-net:
ipv4_address: 192.168.101.110
networks:
mm-net:
driver: bridge
ipam:
config:
- subnet: 192.168.101.0/24
gateway: 192.168.101.1Connect to mysql
version: '3'
services:
nginx:
container_name: my-nginx
image: nginx
ports:
- 9999:80
volumes:
- /home/nginx/html:/etc/nginx/html
- /home/nginx/conf.d:/etc/nginx/conf.d
- /home/nginx/log:/var/log/nginx
restart: always
mysql:
container_name: my-mysql
image: mysql:8.0.27
security_opt:
- seccomp:unconfined
ports:
- 2333:3306
volumes:
- /home/mysql/conf/my.cnf:/etc/my.cnf
- /home/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql
restart: always
environment:
- MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=root123
OK! It's over now. I hope I can help you!!!