1, Docker overview
1. Why does docker appear?
One product: development – online two sets of environments! Application environment, application configuration! Development - operation and maintenance. Question: I can allow it on my computer! Service unavailable due to version update! Is it a big test for operation and maintenance? The environment configuration is very troublesome. Every machine needs to deploy the environment (cluster Redis, ES, Hadoop...)! It takes a lot of trouble. Publish a project (jar + (Redis MySQL JDK ES)). Can the project be installed and packaged with the environment! Previously, configuring an application environment Redis MySQL JDK ES Hadoop on the server was too cumbersome to cross platform. Development environment Windows, finally released to Linux! Tradition: development jar, operation and maintenance to do! Now: development, packaging, deployment and launch, and a set of processes are completed! Android process: java - apk - publish (app store) one three, use apk and install it! Docker process: java jar (environment) - package project with environment (image) - (docker warehouse: store) --- docker puts forward solutions to the above problems!
2, Docker installation
1. Basic composition of docker
2. Install Docker
Environmental preparation
1. You need to know a little about Linux
2.CentOS 7
3. We use Xshell to connect to the remote server for operation
Environment view
# The system kernel is above 3.10 [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# uname -r 3.10.0-1160.11.1.el7.x86_64
# System version [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
install
Help documentation
# 1. Uninstall old version
yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
# 2. Required installation package
yum install -y yum-utils
# 3. Set up a mirrored warehouse
# The default is from abroad (not recommended)
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# It is recommended to use Alibaba cloud's, very fast (recommended)
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
#Update yum package index
yum makecache fast
#4. Install docker CE community version related to docker, while ee is enterprise version
yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io
# 5. Start docker
systemctl start docker
#6. Use docker version to check whether the operation is successful
docker version
#7. Testing
docker run hello-world
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker run hello-world
Unable to find image 'hello-world:latest' locally
latest: Pulling from library/hello-world
b8dfde127a29: Pull complete
Digest: sha256:7d91b69e04a9029b99f3585aaaccae2baa80bcf318f4a5d2165a9898cd2dc0a1
Status: Downloaded newer image for hello-world:latest
Hello from Docker!
This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
To generate this message, Docker took the following steps:
1. The Docker client contacted the Docker daemon.
2. The Docker daemon pulled the "hello-world" image from the Docker Hub.
(amd64)
3. The Docker daemon created a new container from that image which runs the
executable that produces the output you are currently reading.
4. The Docker daemon streamed that output to the Docker client, which sent it
to your terminal.
To try something more ambitious, you can run an Ubuntu container with:
$ docker run -it ubuntu bash
Share images, automate workflows, and more with a free Docker ID:
https://hub.docker.com/
For more examples and ideas, visit:
https://docs.docker.com/get-started/
# 8. Check the downloaded image [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest d1165f221234 5 months ago 13.3kB
Understanding: uninstalling docker
#1. Uninstall dependency yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io #2. Delete resources rm -rf /var/lib/docker # /var/lib/docker is the default working path of docker!
3. Alibaba cloud image acceleration
1. Log in to alicloud and find the container service
2. Image accelerator
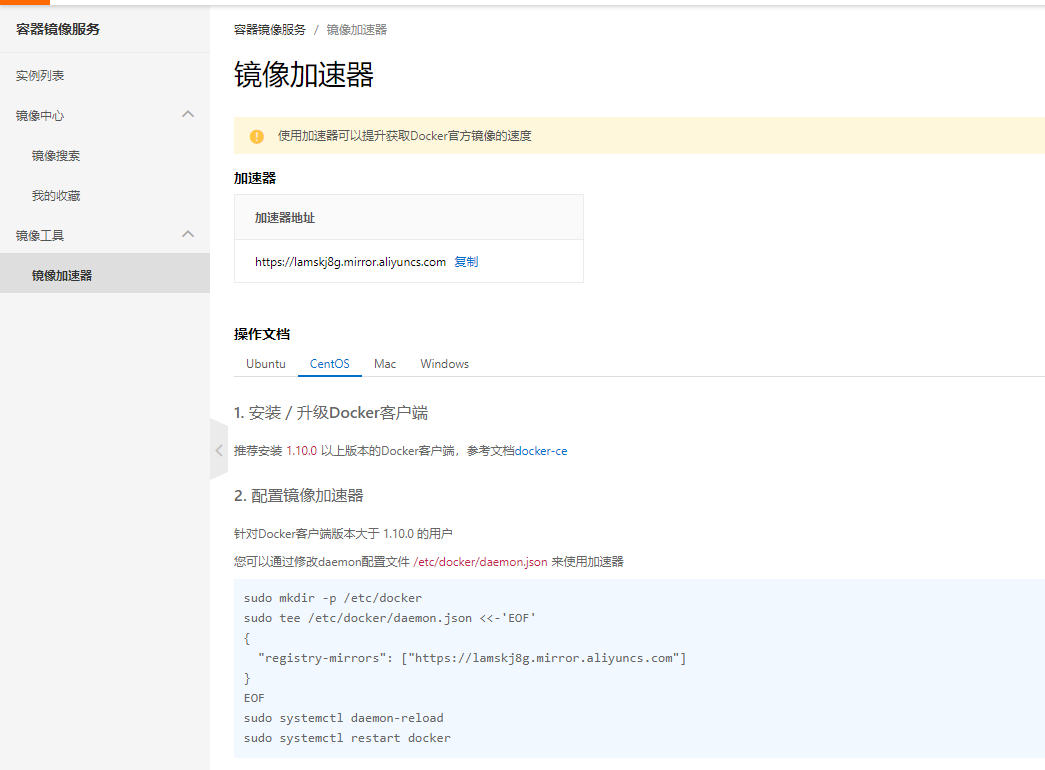
2. Configuration and use
sudo mkdir -p /etc/docker
sudo tee /etc/docker/daemon.json <<-'EOF'
{
"registry-mirrors": ["https://lamskj8g.mirror.aliyuncs.com"]
}
EOF
sudo systemctl daemon-reload
sudo systemctl restart docker
4.docker operation flow chart
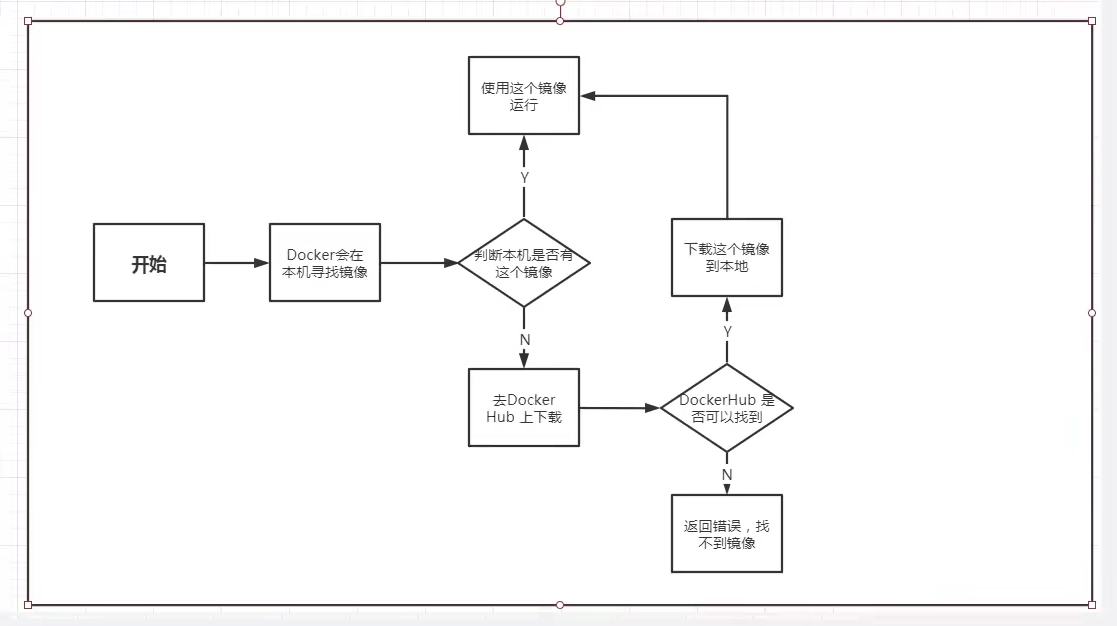
5. Bottom layer principle
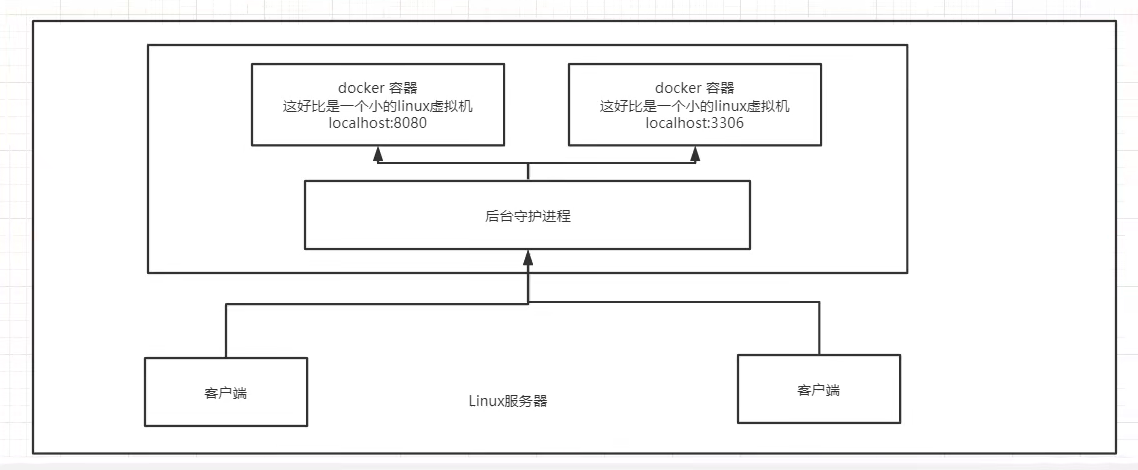
How does Docker work?
Docker is a client server system. The daemon of docker runs on the host. Access from the client through Socket!
When docker server receives the docker client instruction, it will execute this command!
Why is Docker faster than VM
1.Docker has fewer abstraction layers than virtual machines.
2.docker uses the kernel of the host, and the VM needs to be a Guest OS.

Therefore, when creating a new container, docker does not need to reload an operating system kernel like a virtual machine to avoid booting. The virtual machine loads the Guest OS at the minute level, while docker uses the operating system of the host, omitting this complex process at the second level!
3, Common commands of Docker
Help command
docker version #Displays the version information of docker. docker info #Displays the system information of docker, including the number of images and containers docker command --help #Help command #Address of help document: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/build/
Address of help document: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/build/
Mirror command
docker images view images on all local hosts
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker images
REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE
hello-world latest d1165f221234 5 months ago 13.3kB
# explain
REPOSITORY # Mirrored warehouse source
TAG # Mirrored label
IMAGE ID # id of the mirror
CREATED # Creation time of the image
SIZE # Mirror size
# Optional
-a, --all Show all images (default hides intermediate images) #List all mirrors
-q, --quiet Only show numeric IDs # Only the id of the mirror is displayed
# results of enforcement
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker images -aq displays the IDs of all images
d1165f221234
docker search search image
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker search mysql
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11332 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4307 [OK]
mysql/mysql-server Optimized MySQL Server Docker images. Create... 841 [OK]
# Optional, filter by collection (stara)
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker search --help
Usage: docker search [OPTIONS] TERM
Search the Docker Hub for images
Options:
-f, --filter filter Filter output based on conditions provided
--format string Pretty-print search using a Go template
--limit int Max number of search results (default 25)
--no-trunc Don't truncate output
# Example: search for collections greater than 3000
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker search mysql --filter=STARS=3000
NAME DESCRIPTION STARS OFFICIAL AUTOMATED
mysql MySQL is a widely used, open-source relation... 11332 [OK]
mariadb MariaDB Server is a high performing open sou... 4307 [OK]
docker pull Download Image
# Download Image docker pull image name [: tag] [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest #If you do not write tag, the default is latest latest: Pulling from library/mysql e1acddbe380c: Pull complete #Layered Download: the core federated file system of docker image bed879327370: Pull complete 03285f80bafd: Pull complete ccc17412a00a: Pull complete 1f556ecc09d1: Pull complete adc5528e468d: Pull complete 1afc286d5d53: Pull complete 6c724a59adff: Pull complete 0f2345f8b0a3: Pull complete c8461a25b23b: Pull complete 3adb49279bed: Pull complete 77f22cd6c363: Pull complete Digest: sha256:d45561a65aba6edac77be36e0a53f0c1fba67b951cb728348522b671ad63f926 # Signature anti-counterfeiting Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Real address # Equivalent to it docker pull mysql docker pull docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Specified version download [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker pull mysql:5.7 5.7: Pulling from library/mysql e1acddbe380c: Already exists bed879327370: Already exists 03285f80bafd: Already exists ccc17412a00a: Already exists 1f556ecc09d1: Already exists adc5528e468d: Already exists 1afc286d5d53: Already exists 4d2d9261e3ad: Pull complete ac609d7b31f8: Pull complete 53ee1339bc3a: Pull complete b0c0a831a707: Pull complete Digest: sha256:7cf2e7d7ff876f93c8601406a5aa17484e6623875e64e7acc71432ad8e0a3d7e Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.7 docker.io/library/mysql:5.7
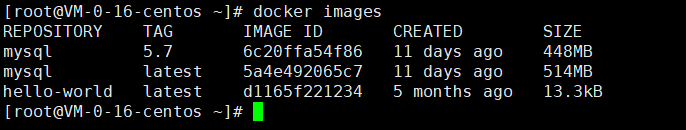
docker rmi delete image
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker rmi -f image id #Deletes the specified mirror [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker rmi -f image id image id image id image id#Deletes the specified mirror [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) #Delete all mirrors 2
Container command
docker run # Image id creates a new container and starts docker ps # List all running containers docker container list docker rm container id # Delete specified container docker start container id #Start container docker restart container id #Restart container docker stop container id #Stop the currently running container docker kill container id #Force stop of current container
Note: only when we have an image can we create a container. For linux, download a centos image to test and learn
docker pull centos
Create a new container and start
docker run [Optional parameters] image
# Parameter description
--name="name" the second name Name the container tomcat01 tomcat02 ,Used to distinguish containers
-d Run in background mode
-it Run interactively and enter the container to view the content
-p (Lowercase) specifies the port of the container -p 8080:8080
-p ip: Container port (common)
-p Host port: container port (common)
-p Container port
-P ((uppercase) randomly specify the port
# test
# Enter container
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash
[root@a34f38728486 /]# ls # Check the centos basic version in the container. Many commands are imperfect
bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var
# Return host from container
[root@a34f38728486 /]# exit
exit
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]#
List all running containers
# docker ps command
# Lists currently running containers
-a # List all running containers + bring out historically running containers
-n=? # Displays recently created containers
-q # Displays only the number of the container
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker ps -a
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
a34f38728486 centos "/bin/bash" 5 minutes ago Exited (0) About a minute ago infallible_davinci
5f9e8f36db41 d1165f221234 "/hello" 5 hours ago Exited (0) 5 hours ago magical_wu
Exit container
exit # Direct container stop and exit ctrl + P+Q # The container does not stop exiting
Delete container
docker rm container id #Delete the specified container (you cannot delete a running container). If you want to forcibly delete rm -f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) #Delete all containers docker ps -a -q|xargs docker rm #Delete all containers
Start and stop containers
docker start container id #Start container docker restart container id #Restart container docker stop container id #Stop the currently running container docker kill container id #Force stop of current container
Common other commands
Background start command
# Command docker run -d image name [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker run -d centos 6ad949d5bb619381d2e139608529d9a31f856134d7d22c9f96f5feb82bdbeede [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES # Problem: docker ps found centos stopped # In the common pit, when the docker container runs in the background, there must be a foreground process. When docker finds that there is no application, it will automatically stop # nginx, when the container starts and finds that it does not provide services, it will stop immediately, that is, there is no program
view log
docker logs --help
# results of enforcement
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker logs --help
Usage: docker logs [OPTIONS] CONTAINER
Fetch the logs of a container
Options:
--details Show extra details provided to logs
-f, --follow Follow log output
--since string Show logs since timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
-n, --tail string Number of lines to show from the end of the logs (default "all")
-t, --timestamps Show timestamps
--until string Show logs before a timestamp (e.g. 2013-01-02T13:23:37Z) or relative (e.g. 42m for 42 minutes)
# Simulation log
docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo hzl-log-a;sleep 1;done"
# results of enforcement
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker run -d centos /bin/sh -c "while true;do echo hzl-log-a;sleep 1;done"
f9cb42705132e7b6db4e9bd099f3fb56f306e10334565c11025ed54de61e8f25
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker ps
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
f9cb42705132 centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 7 seconds ago Up 7 seconds serene_pascal
#Show log
-tf #Display log information (always updated)
--tail number #Number of logs to be displayed
docker logs -t --tail n container id #View n line logs
docker logs -tf container id #Follow the log
[root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker logs -tf --tail 10 f9cb42705132
View the process information in the container ps
# Command docker top container id root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker top f9cb42705132 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 28999 28979 0 17:24 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c while true;do echo hzl-log-a;sleep 1;done root 30912 28999 0 17:30 ? 00:00:00 /usr/bin/coreutils --coreutils-prog-shebang=sleep /usr/bin/sleep 1
View the metadata of the image
docker inspect container id
Enter the currently running container
# We usually run the container in the background mode. We need to enter the container and modify some configurations # Mode 1 # command docker exec -it container id bashshell # test [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES f9cb42705132 centos "/bin/sh -c 'while t..." 14 minutes ago Up 14 minutes serene_pascal f7c2c7f3b2a8 centos "/bin/bash" 18 minutes ago Up 18 minutes jovial_meninsky [root@VM-0-16-centos ~]# docker exec -it f9cb42705132 /bin/bash [root@f9cb42705132 /]# # Mode II docker attach container id # docker exec # After entering the container, open a new terminal, which can be operated inside (commonly used) # docker attach # Entering the terminal where the container is executing will not start a new process
Copy from container to host
docker cp container id:In container path host destination path # test # Enter the inside of the container [root@VM-0-16-centos home]# docker attach a5e3ff1352f3 [root@a5e3ff1352f3 /]# cd home/ [root@a5e3ff1352f3 home]# ls [root@a5e3ff1352f3 home]# touch test-hzl.java [root@a5e3ff1352f3 home]# ls test-hzl.java # Exit container [root@a5e3ff1352f3 home]# exit exit [root@VM-0-16-centos home]# docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES [root@VM-0-16-centos home]# docker ps -a CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES a5e3ff1352f3 centos "/bin/bash" 3 minutes ago Exited (0) 7 seconds ago blissful_williamson # Copy the file to the host (the container stops and the data can be copied) [root@VM-0-16-centos home]# docker cp a5e3ff1352f3:/home/test-hzl.java /home/ [root@VM-0-16-centos home]# ls kuangshen.java memcached redis test-hzl.java www # Copying is a manual process, which can be realized by using -v volume technology in the future
Summary
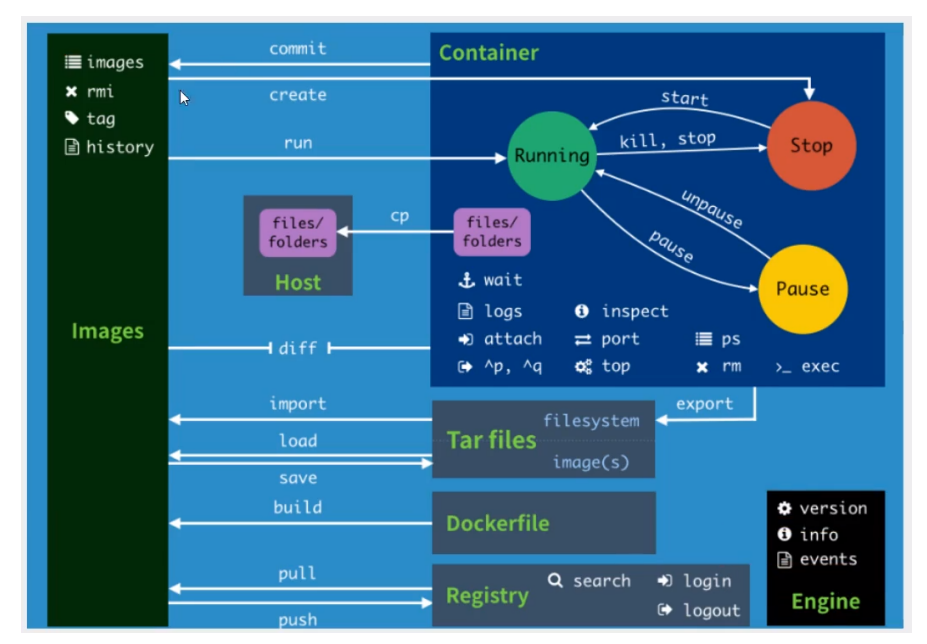
Docker command help document (important)
attach Attach local standard input, output, and error streams to a running container #The image of the specified operation of the attach connection under the current shell build Build an image from a Dockerfile # Customized image through Dockerfile commit Create a new image from a container's changes #Commit the current container as a new image cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem # Copy file create Create a new container #Create a new container diff Inspect changes to files or directories on a container's filesystem #View the changes of docker container events Get real time events from the server # Get container real time from service exec Run a command in a running container # Running commands on a running container export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive #Export container file system as For one tar Archive file[corresponding import] history Show the history of an image # Show a mirror formation history images List images #Lists the current mirrors of the system import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image # from tar Create a file system image of the imported content in the package info Display system-wide information # Display system wide information inspect Return low-level information on Docker objects #View container details kill Kill one or more running containers # kill specifies the docker container load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN #Load from a tar package or standard input A mirror[corresponding save] login Log in to a Docker registry # logout Log out from a Docker registry logs Fetch the logs of a container pause Pause all processes within one or more containers port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container ps List containers pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rename Rename a container restart Restart one or more containers rm Remove one or more containers rmi Remove one or more images run Run a command in a new container save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) search Search the Docker Hub for images start Start one or more stopped containers stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics stop Stop one or more running containers tag Create a tag TARGET_IMAGE that refers to SOURCE_IMAGE top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers version Show the Docker version information wait Block until one or more containers stop, then print their exit
This article is used as a note. If there is any infringement, please; Contact to delete now!