1, Shell Basics
Shell:Shell is a program written in C language. It is a bridge for users to use Linux. Shell is both a command language and a programming language.
Shell refers to an application that provides an interface through which users can access the services of the operating system kernel.
shell script: a script program written for the shell.
1.1 shell statement
1.1.1 shell output statement and shell comment statement
(1) Output statement echo
Display normal string
#!/bin/bash # From above #! Is a kind of convention tag, which can tell the system what kind of interpreter this script needs to execute; echo "Hello, world!"
Show wrap
echo -e "OK! \n" # -e open escape echo "It is a test"
Show no line breaks
echo -e "OK! \c" # -e enable escape \ c do not wrap echo "It is a test
Results directed to file
echo "It is a test" > myfile
(2) comment statement
For single line notes#
multiline comment
:<<EOF Note Content ... Note Content ... Note Content ... EOF
1.1.2 shell variables
(1) Define variables
When defining a variable, the variable name is not marked with a dollar sign
country="China" Number=100 country="America" #Redefine variable values
Note: 1. There must be no space between variable name and equal sign;
2. The first character must be a letter (A-Z, A-Z).
3. There can be no space in the middle. You can use underscore ().
4. Punctuation cannot be used.
5. The keyword in bash cannot be used
(2) Use variables
It is OK to add the dollar sign $in front of a defined variable. In addition, the {} of the variable is optional. Its purpose is to help the interpreter identify the boundary of the variable.
country="China"
echo $country
echo ${country}
echo "I love my ${country}abcd!" (3) Delete variable
unset variable_name
1.1.3 shell string
(1) Define string
String is the most commonly used and useful data type in shell programming (there are no other types to use except numbers and strings). String can use single quotation marks, double quotation marks or no quotation marks.
str='this is a string' #Single quote string #Double quotation mark definition string your_name="runoob" str="Hello, I know you are \"$your_name\"! \n" echo -e $str
- You can have variables in double quotes
- Escape characters can appear in double quotation marks
(2) Splice string
your_name="runoob"
# Use double quotation mark splicing
greeting="hello, "$your_name" !"
greeting_1="hello, ${your_name} !"
echo $greeting $greeting_1(3) Get string length, extract string, find string
#Get string length
string="abcd"
echo ${#string} #Output 4
#Extract substring
string="runoob is a great site" #Intercept 4 characters from the second character of the string:
echo ${string:1:4} # Output unoo
#Find string
string="runoob is a great site" #Find the position of the character i or o (calculate which letter appears first)
echo `expr index "$string" io` # Output 4
Note: in the above script, ` is a backquote, not a single quote '.
1.1.4 shell array
(1) Define array
array_name=(value0 value1 value2 value3)
Define arrays individually
array_name[0]=value0 array_name[1]=value1 array_name[n]=valuen
(2) Read array
The general format for reading array element values is:
${array name [subscript]}
valuen=${array_name[n]}Use the @ symbol to get all the elements in the array
echo ${array_name[@]}(3) get array length
# Gets the number of array elements
length=${#array_name[@]}1.1.5 shell operators
(1) Arithmetic operation
expr is an expression evaluation tool, which can be used to evaluate expressions.
a=10 b=20 expr $a + $b expr $a - $b expr $a \* $b expr $a / $b expr $a % $b a=$b
Or:
a=10 b=20 val=`expr $a + $b` echo "a + b : $val" val=`expr $a - $b` echo "a - b : $val" val=`expr $a \* $b` echo "a * b : $val" val=`expr $b / $a` echo "b / a : $val" val=`expr $b % $a` echo "b % a : $val" if [ $a == $b ] then echo "a be equal to b" fi if [ $a != $b ] then echo "a Not equal to b" fi
(2) Relational operator
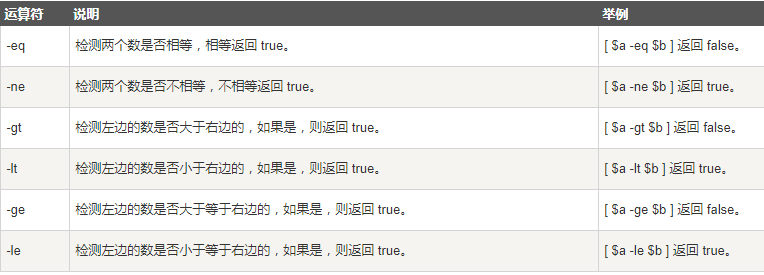
a=10 b=20 if [ $a -eq $b ] then echo "$a -eq $b : a be equal to b" else echo "$a -eq $b: a Not equal to b" fi if [ $a -ne $b ] then echo "$a -ne $b: a Not equal to b" else echo "$a -ne $b : a be equal to b" fi if [ $a -gt $b ] then echo "$a -gt $b: a greater than b" else echo "$a -gt $b: a Not greater than b" fi if [ $a -lt $b ] then echo "$a -lt $b: a less than b" else echo "$a -lt $b: a Not less than b" fi if [ $a -ge $b ] then echo "$a -ge $b: a Greater than or equal to b" else echo "$a -ge $b: a less than b" fi if [ $a -le $b ] then echo "$a -le $b: a Less than or equal to b" else echo "$a -le $b: a greater than b" fi
Output results:
10 -eq 20: a is not equal to b 10 -ne 20: a is not equal to b 10 -gt 20: a not greater than b 10 -lt 20: a less than b 10 -ge 20: a less than b 10 -le 20: a less than or equal to b
(3) Boolean operation
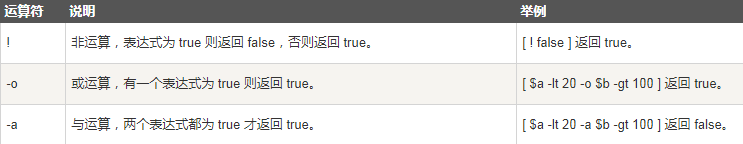
a=10 b=20 if [ $a != $b ] then echo "$a != $b : a Not equal to b" else echo "$a == $b: a be equal to b" fi if [ $a -lt 100 -a $b -gt 15 ] then echo "$a Less than 100 and $b Greater than 15 : return true" else echo "$a Less than 100 and $b Greater than 15 : return false" fi if [ $a -lt 100 -o $b -gt 100 ] then echo "$a Less than 100 or $b Greater than 100 : return true" else echo "$a Less than 100 or $b Greater than 100 : return false" fi if [ $a -lt 5 -o $b -gt 100 ] then echo "$a Less than 5 or $b Greater than 100 : return true" else echo "$a Less than 5 or $b Greater than 100 : return false" fi
Output results
10 != 20: A is not equal to b 10 less than 100 and 20 more than 15: return true 10 less than 100 or 20 greater than 100: returns true 10 less than 5 or 20 greater than 100: false is returned
(4) Logical operation
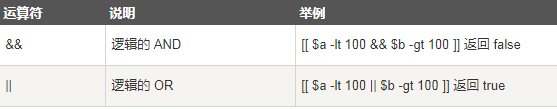
a=10 b=20 if [[ $a -lt 100 && $b -gt 100 ]] then echo "return true" else echo "return false" fi if [[ $a -lt 100 || $b -gt 100 ]] then echo "return true" else echo "return false" fi
1.1.6 shell judgment statement
Including: 1. if [expression] then # statement # fi
2. if [expression] then statement else statementfi
3. if [expression] then statement... Elif [expression] then statement elif [expression] then statement... fi
a=10 b=20 if [ $a == $b ] then echo "a is equal to b" else echo "a is not equal to b" fi
$in shell script? It refers to the successful or failed status of the last command execution. If success is 0, failure is 1. The statement if [$? - EQ 0] is the last command to judge the if statement. If the execution is successful, execute the statement in if, otherwise execute the content in else.
cd u-boot if [ $? -eq 0 ]; then echo "====Build uboot ok!====" else echo "====Build uboot failed!====" exit 1 fi
(1) if statement
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
fi(2) if else statement
if condition
then
command1
command2
...
commandN
else
command
fi(3) if else -if else statement
if condition1
then
command1
elif condition2
then
command2
else
commandN
fi(4) case statement
echo 'Enter a number between 1 and 4:'
echo 'The number you entered is:'
read aNum
case $aNum in
1) echo 'You chose 1'
;;
2) echo 'You chose 2'
;;
3) echo 'You chose 3'
;;
4) echo 'You chose 4'
;;
*) echo 'You didn't enter a number between 1 and 4'
;;
esac1.1.7 circular statements
(1) for loop statement
General format:
for variable in list
do
command1
command2
...
commandN
doneUsage:
for loop in 1 2 3 4 5
do
echo "The value is: $loop"
don(2) while loop statement
#!/bin/bash
int=1
while(( $int<=5 ))
do
echo $int
let "int++"
done1.1.8 shell transfer parameters
#!/bin/bash echo "Shell Pass parameter instance!"; echo "Executed file name: $0"; echo "The first parameter is: $1"; echo "The second parameter is: $2"; echo "The third parameter is: $3";
$ chmod +x test.sh $ ./test.sh 1 2 3 Shell pass parameter instance! Executed file name:/ test.sh The first parameter is: 1 The second parameter is: 2 The third parameter is: 3
1.1.9 shell functions
(1) Parameter function not found
demoFun(){
echo "This is my first shell function!"
}
echo "-----Function starts execution-----"
demoFun
echo "-----Function execution completed-----"(2) Function with parameters
funWithParam(){
echo "The first parameter is $1 !"
echo "The second parameter is $2 !"
echo "The tenth parameter is $10 !"
echo "The tenth parameter is ${10} !"
echo "The eleventh parameter is ${11} !"
echo "The total number of parameters is $# One! "
echo "Output all parameters as a string $* !"
}
funWithParam 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 34 732, docker statement
(1)docker load
docker load command to import image files * tar, which is generally exported by the docker save command.
docker load -i test.tar // Or the following code, equivalent effect docker load < test.tar
-- input, - I: Specifies the imported file
3, Container installation scripting
docker -v | grep "version" if [ $? -eq 0 ] ;then systemctl start docker #! Start docker service docker load -i test.tar #! Import mirror docker run -dit --name #! Start container systemctl daemon-reload docker logs -f -t test else echo " docker is not exist" fi
reference:
[1]shell script under linux (basic)
shell script under linux (basic) - great Xia Yin - blog Garden