Overview of Docker
Why does Docker appear?
One product: development-online environment! Application Environment, Application Configuration!
Development - Operations and Maintenance. Question: I can run on my computer! Version update, rendering the service unavailable! For operations and maintenance, the test is very big?
Environment configuration is cumbersome, and every machine has to deploy the environment (cluster Redis, ES, Hadoo...! Time consuming and laborious).
Publish a project ** (jar+ (Redis MySQL JDK ES)**, can all projects be packaged with environment installation?
Previously, configuring an application environment on the server, Redis MySQL jdk ES Hadoop, was too cumbersome to be cross-platform.
Windows, and finally to Linux!
Traditionally: Develop jar, run and maintain it!
Now: Develop packaged deployment online, a set of processes completed!.
java-apk-publish (app store) - Zhang San uses apk-install is available!
java - jar - Package project with environment (mirror) -- -- (Docker repository: store) -- Download our published mirror - run it directly!
Docker offers solutions to the above problems!
Docker's ideas come from containers!
JRE - Multiple Applications (Port Conflict) - Originally Crossed!
Isolation: Docker's core idea! Pack and pack! Each box is isolated from each other.
Docker makes the most of your server through isolation!
Docker History
In 2013, Docker Open Source!
More and more people are discovering the benefits of Docker! It's on fire, Docker updates every month!
On April 9, 2014, Docker 1.0 was released!
Why is Docker so hot? Very light!
We used virtual machine technology before container technology came out!.
Virtual Machine: Install a Vmware in Windows, through which we can virtual out one or more computers! Heavy!
Virtual machine is also a virtualization technology, Docker container technology, is also a virtualization technology!
vm : 1inux centos Native Mirror(A computer! )Isolation, multiple virtual machines need to be turned on!How many? G A few minutes docker:Isolation, mirroring(Core Environment 4 m + jdk + mysq1) Very compact, just run the mirror !Compact!How many? M KB Seconds start
Talk about Docker
Docker is based on Go Language! Open Source Project!
Official website: https://www.docker.com/
Document address: https://docs.docker.com/ Docker's documentation is super detailed!
Warehouse address: https://hub.docker.com/
What can Docker do?
Disadvantages of virtual machine technology:
-
High resource usage
-
Too many redundant steps
-
Start very slowly!
Containerization Technology
Containerized technology is not a complete operating system for simulation
[External chain picture transfer failed, source station may have anti-theft chain mechanism, suggest saving pictures and uploading them directly (img-5Xe3PmUi-1638817) (C:UsersTang SanAppDataRoamingTyporatypora-user-imagesdocker)]Containerization technology.png)
Compare Docker with virtual machine technology:
- A traditional virtual machine that virtualizes a piece of hardware, runs a complete operating system, and then installs and runs software on it
- Applications inside containers run directly on the host's content. Containers do not have their own cores or virtual hardware, so they are lightweight
- Each container is isolated from each other, and each container has its own file system that does not affect each other. |
DevOps (Development, Operations)
Apply faster delivery and deployment
Tradition: a bunch of help documents, Installers
Docker: Package Mirror Publish Test, run at one click
Easier upgrade and expansion
After using Docker, we deploy the app just like building blocks!
Package the project as a mirror to extend Server A! Server B
Simpler System Operations
After containerization, our development and testing environments are highly consistent.
More efficient use of computing resources
Docker is a kernel-level virtualization that can run many container instances on another physical machine! Server performance can be squeezed to the extreme.
Docker Installation
Basic composition of Docker
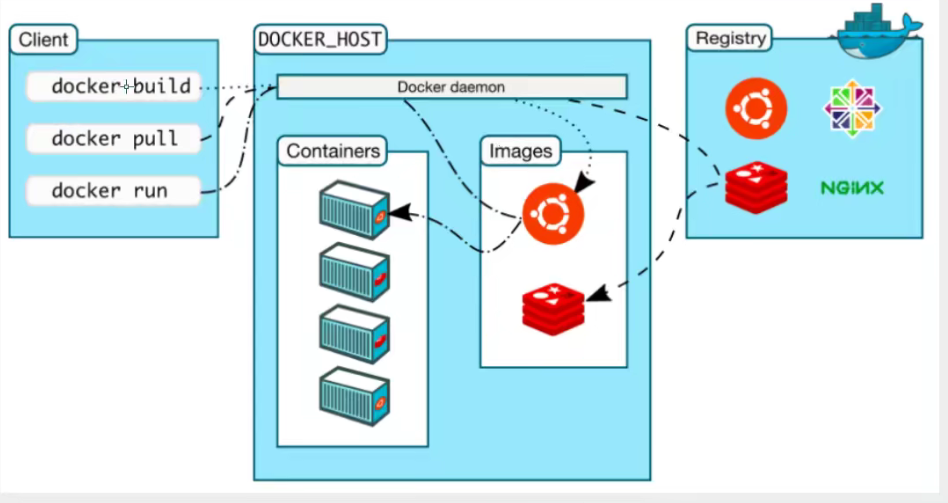
Image:
The docker image is like a template through which container services can be created. The Tomcat image ==> run ==> tomcat01 container (provider server),
This mirror allows you to create multiple containers (where the final service runs or the project runs).
Containers:
Docker uses container technology to run one or a group of applications independently, created by mirroring.
Start, stop, delete, basic commands!
You can now think of this container as a simple linux system
Repository:
The warehouse is where the mirror is stored!
Warehouses are divided into public warehouses and private warehouses!
Docker Hub (default is foreign)
Ali...all have container servers (Configure Mirror Acceleration!)
Install Docker
# View the version of the system [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# cat /etc/os-release NAME="CentOS Linux" VERSION="7 (Core)" ID="centos" ID_LIKE="rhel fedora" VERSION_ID="7" PRETTY_NAME="CentOS Linux 7 (Core)" ANSI_COLOR="0;31" CPE_NAME="cpe:/o:centos:centos:7" HOME_URL="https://www.centos.org/" BUG_REPORT_URL="https://bugs.centos.org/" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT="CentOS-7" CENTOS_MANTISBT_PROJECT_VERSION="7" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT="centos" REDHAT_SUPPORT_PRODUCT_VERSION="7"
install
Help Documentation:
# 1. Uninstall old versions
yum remove docker \
docker-client \
docker-client-latest \
docker-common \
docker-latest \
docker-latest-logrotate \
docker-logrotate \
docker-engine
# 2. Installation packages required
yum install -y yum-utils
# 3. Set up mirrored warehouses
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #Default is foreign
yum-config-manager \
--add-repo \
http://mirrors.aliyun.com/docker-ce/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo #Domestic mirroring recommended, faster
# Update yum package index
yum makecache fast
# 4. Install Docker Engine docker-ce Community ee Enterprise Edition
yum install docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # This is the latest version installed by default
sudo yum install docker-ce-19.03.8 docker-ce-cli-19.03.8 containerd.io # Install the corresponding version, centos7, I'm using 19.03.8
# 5. Start Docker
systemctl start docker
# 6. Check the version to see if the installation was successful
docker version
# 7. Hello-word uses hello-world to test, if timed out, to change to a domestic mirror
docker run hello-world
# 8. View all mirrors
docker images
Uninstall Docker
# 1. Uninstall dependency yum remove docker-ce docker-ce-cli containerd.io # 2. Delete resources rm -rf /var/lib/docker # Default working path for/var/lib/docker docker
HelloWorld process
Run's flow analysis diagram (docker run image)
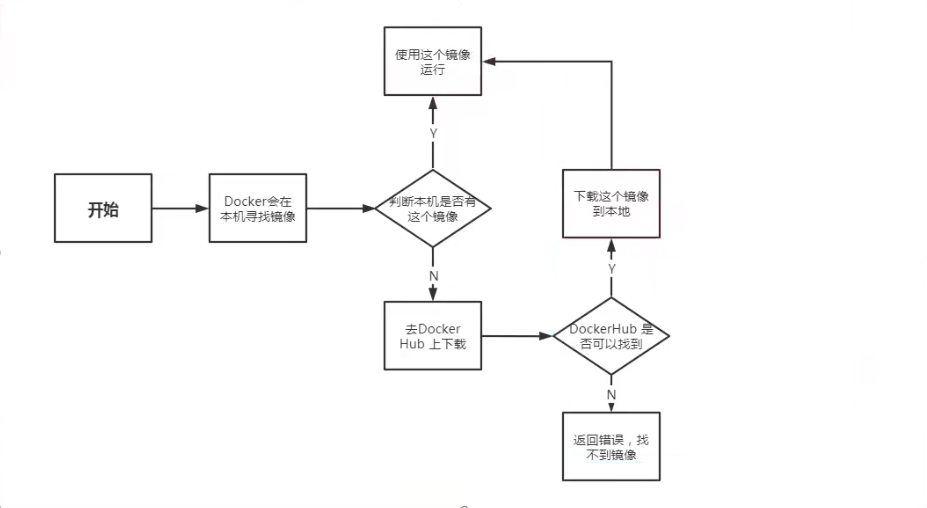
Underlying principle
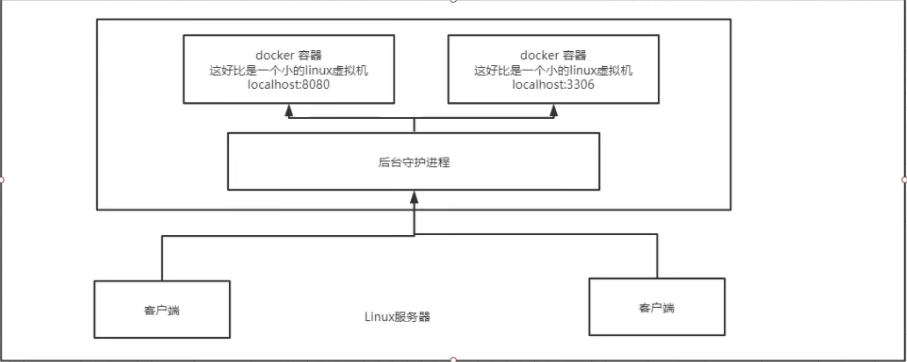
What does Docker do?
Docker is a Client-Server architecture with a daemon running on the host. Access from client via Socket!
DockerServer receives instructions from Docker-Client and executes them!
Why is Docker faster than VM?
- Docker has fewer abstraction layers than virtual machines.
- The docker utilizes the host's kernel, and the vm needs to be Guest OS.
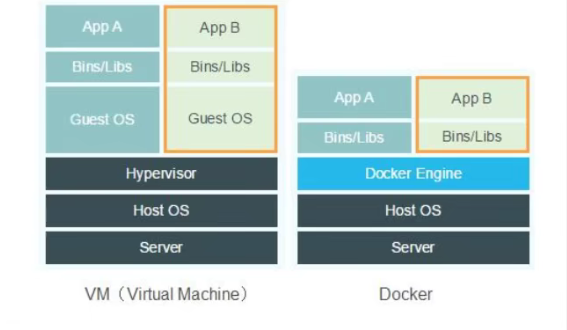
So when you create a new container, docker does not need to reload an OS kernel like a virtual machine to avoid booting. The virtual machine is loading GuestOS, minute
Clock level, and docker is using the host's operating system, omitting this complex process, second level! |
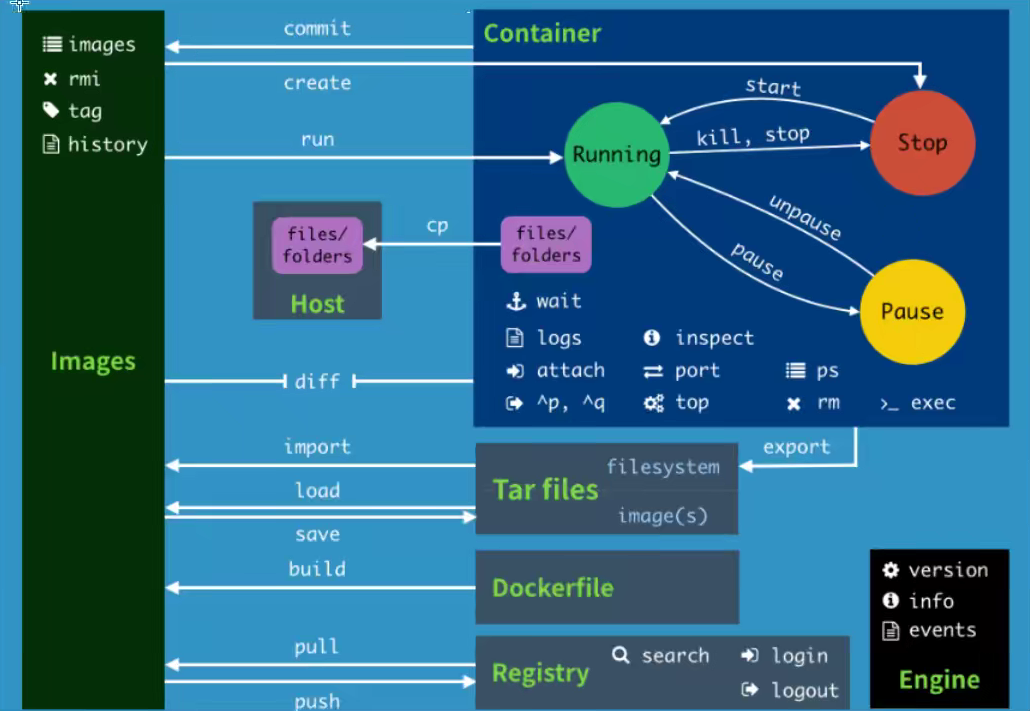
Common Docker Commands
Help Command
docker version # Version information for docker docker info # Displays docker system information, including the number of mirrors and containers docker (command) --help # Help Command
Address of the help document: https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/
Mirror Command
docker images: view all mirrors on this machine
[root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE hello-world latest feb5d9fea6a5 8 weeks ago 13.3kB #explain REPOSITORY Mirrored warehouse source(Mirror Name) TAG Mirror Label IMAGE ID mirrored id CREATED Creation time of mirror SIZE The size of the mirror # Optional -a , --all # List all mirrors -q , --quiet # Show only the id of the mirror
docker search mirror name: the search mirror corresponds to the mirror of the official website
[root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker search mysql [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker search mysql --filter=STARS=3000 # Mirror of stars>3000
docker pull mirror name: download mirror
[root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker pull mysql Using default tag: latest # If you don't write tag s, the default is latest's latest version latest: Pulling from library/mysql a10c77af2613: Pull complete # Hierarchical download, docker image's core federated file system b76a7eb51ffd: Pull complete 258223f927e4: Pull complete 2d2c75386df9: Pull complete 63e92e4046c9: Pull complete f5845c731544: Pull complete bd0401123a9b: Pull complete 3ef07ec35f1a: Pull complete c93a31315089: Pull complete 3349ed800d44: Pull complete 6d01857ca4c1: Pull complete 4cc13890eda8: Pull complete Digest: sha256:aeecae58035f3868bf4f00e5fc623630d8b438db9d05f4d8c6538deb14d4c31b # autograph Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:latest docker.io/library/mysql:latest # Real Address #Equivalent to it docker pu11 mysq1 docker pu11 docker.io/1ibrary/mysq1:latest # Specified version download [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker pull mysql:5.7 guarantees a corresponding version in the repository 5.7: Pulling from library/mysql a10c77af2613: Already exists b76a7eb51ffd: Already exists 258223f927e4: Already exists 2d2c75386df9: Already exists 63e92e4046c9: Already exists f5845c731544: Already exists bd0401123a9b: Already exists 2724b2da64fd: Pull complete d10a7e9e325c: Pull complete 1c5fd9c3683d: Pull complete 2e35f83a12e9: Pull complete Digest: sha256:7a3a7b7a29e6fbff433c339fc52245435fa2c308586481f2f92ab1df239d6a29 Status: Downloaded newer image for mysql:5.7 docker.io/library/mysql:5.7
**docker rmi mirror name/ID: delete mirror**
# Generally deleted by id, because the mirror name may be the same (version is different) docker rmi -f 8b43c6af2ad0 # -f Forced Delete docker rmi -f container id container id # Delete Multiple Mirrors docker rmi -f $(docker images -aq) # Delete all containers
Container commands
Description: Create a container with a mirror to download a centos for testing
docker pull centos # Download centos image
New Container and Start
docker run [Optional parameters] image #Parameter Description --name="Name'Container name tomcat01 tomcat02, Used to distinguish containers -d Run in background mode -it Run interactively, enter the container to view the contents -P Specify the port of the container-p8080: 8080 -p ip:Host Port:Container Port -p Host Port:Container Port (Common) -p Container Port Container Port -P Randomly specified port # Test, start and enter container [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker run -it centos /bin/bash [root@74629498e41d /]# [root@74629498e41d /]# ls # Looking at centos inside the container, the base version, many commands are imperfect! bin dev etc home lib lib64 lost+found media mnt opt proc root run sbin srv sys tmp usr var [root@74629498e41d /]# exit # Exit Container Command Exit to Host
List all running containers
# docker ps List running containers # Docker PS-A List all containers that have been run (running + closed containers) # Docker ps-a-n=1 Lists recently run containers-n=1 indicates a recently run container-n=2 indicates two recently run containers # Docker ps-aq Lists all running containers-q to show only the number of the container
Exit Container
exit # Container stops directly and exits Ctrl + P + Q # Container does not stop exiting
Delete Container
docker rm container id # Deleting the specified container does not delete the running container, forcing deletion-f docker rm -f $(docker ps -aq) # Delete all containers docker ps -a -q |xargs docker rm # Delete all containers
Start and Stop Containers
docker start container id # Start Container docker restart container id # Restart Container docker stop container id # Stop the currently running container docker kill container id # Force stop of currently running container
Other Commands in Common Use
Background Launch Command
# Docker run-d mirror name [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker run -d centos # Background boot centos 34bcd5c841bbf930aeb47d047e1fcc2713f72754deb2c6fac36ffc87e1c4dd82 #Problem docker ps, centos stopped #Common pits. The docker container runs in the background and must have a foreground process. When docker finds no application, it stops automatically # nginx, when the container starts up and finds itself not servicing, it stops immediately, or there is no program
view log
# Docker logs-tf container id view all logs--tail n stands for n logs only docker logs -tf --tail 5 bcb03d79aee3
View the container's entry information
# docker top container id [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker top bcb03d79aee3 UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD root 27904 27889 0 20:09 ? 00:00:00 /bin/bash
View container metadata
# docker inspect container id
Enter the currently running container
# This is when exit exits the container, for example, after exit centos, enters the container again or when running in the background docker exec -it container id /bin/bash # Open a new terminal after entering the container to operate inside docker attach container id # Enter the terminal that the container is executing and will not start a new process
Copy files from container to host
docker cp container id:In-Container Path Destination Host Path Copying is a manual process, You can use it later-v Volume Technology,Implementable,Automatic Synchronization
Homework exercises
Docker Install Ngnix
# 1. Search Mirror # 2. Download Mirror # 3. Run tests # -d Background running #--name Name the container # -p host port: container internal port [root@kuangshen home]# docker run -d --name nginx01 -p 3344:80 nginx # Enter Container [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ docker]# docker exec -it nginx01 /bin/bash root@7fd1a7dbb5b5:/# whereis nginx nginx: /usr/sbin/nginx /usr/lib/nginx /etc/nginx /usr/share/nginx root@7fd1a7dbb5b5:/# cd /etc/nginx root@7fd1a7dbb5b5:/etc/nginx# ls conf.d fastcgi_params mime.types modules nginx.conf scgi_params uwsgi_params root@7fd1a7dbb5b5:/etc/nginx#
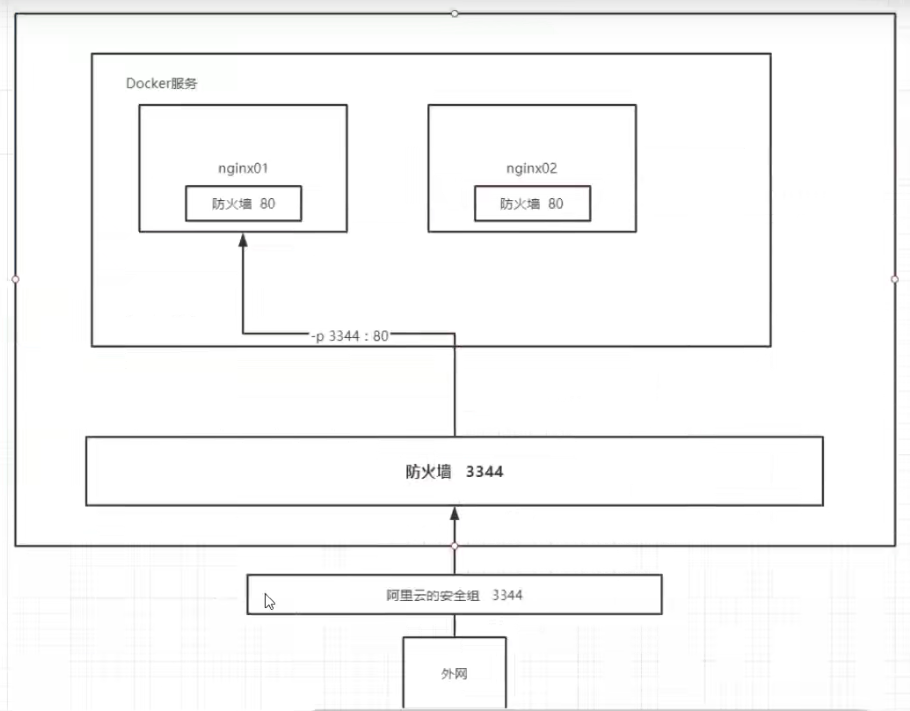
Think about it: Do we need to go inside the container every time we change the nginx configuration file? Very cumbersome, if I could provide a mapping path outside the container to get there
Does the container modify the file name so that it can be automatically modified inside the container? - v Data Volume
Docker installs a Tomcat
#Official Use docker run -it --rm tomcat:9.0 #Our previous startups were all in the background, after stopping the container, the container can still be found docker run -it --rm # Usually for testing purposes, delete when used # Download Start docker pull tomcat:9.0 # Start Run docker run -d -p 3355:8080 --name tomcat01 tomcat # Enter Container [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker exec -it tomcat01 /bin/bash #Problem found: 1, 1inux commands are fewer, 2. The webapps file is empty. Reasons for Ali cloud mirroring. The default is the smallest mirror, eliminating all unnecessary images. #Ensure minimum runnable environment!
Think about it: We'll deploy the project in the future. Is it very troublesome to enter the container every time? If I could provide a mapping path outside the container, webapps,
We place items outside and synchronize to inside automatically.
Deploy es + kibana
# es exposes many ports! # es10 consumes memory # es data generally needs to be placed in a secure directory! mount # --net somenetwork? Network Configuration #Start elasticsearch docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" elasticsearch:7.6.2 #Start inux and stuck docker stats to check cpu status # es is memory intensive, 1.xG 1core 2G! #View docker stats #Testing es was successful enough
#Close now, increase memory limit, modify profile-e environment configuration modification docker run -d --name elasticsearch02 -p 9200:9200 -p 9300:9300 -e "discovery.type=single-node" -e ES_JAVA_OPTS="Xms256m -Xmx512m" elasticsearch:7.6.2
visualization
portainer (use this first)
docker run -d -p 8088:9000 \ --restart=always -V /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock --privileged-true portainer/portainer
Access External/Intranet 8088
Docker Mirror
What is the mirror image?
Mirror is a lightweight, executable, stand-alone package that packages software running environments and software developed based on them and contains all the necessary components to run a software
Contains, including code, runtime libraries, environment variables, and configuration files.
All applications, just pack a docker image and run!
How to get a mirror:
- Download from remote repository
- Friend's copy for you
- Make your own mirror DockerFile
Docker mirror loading principle
UnionFS (Federated File System)
This is the layer we see when we download it!
UnionFS: The Union File System (UnionFS) is a hierarchical, lightweight, and high performance file system that supports modifications to the file system
As a layer-by-layer overlay of submissions, different directories can also be mounted under the same virtual file system (unite several directories into a single virtual file system)
filesystem). The Union file system is the basis of Docker mirroring. Mirrors can be inherited by layers, and each can be made based on the underlying mirror (without a parent).
Specific application mirrors.
Features: Load multiple file systems at once, but from the outside, you can only see one file system. Joint loading will overlay each layer of file systems, so that the end result is
The file system will contain all the underlying files and directories
Docker mirror loading principle
The docker's mirror actually consists of a layer-by-layer file system, UnionFS.
bootfs(boot file system) mainly contains bootloader and kernel. bootloader is mainly to boot the kernel. Linux will load bootfs file system when it is just started
Generally, at the bottom of the Docker image is bootfs. This layer is the same as our typical Linux/Unix system, with boot loaders and cores. When boo loading is complete
After that, the entire kernel is in memory, and the use of memory has been transferred from bootfs to the kernel, and bootfs will be uninstalled by the system.
rootfs (root file system), on top of bootfs. These include standard directories and files such as /dev, /proc, /bin, /etc on typical Linux systems. rootfs is
Various operating system distributions, such as Ubuntu, Centos, and so on.
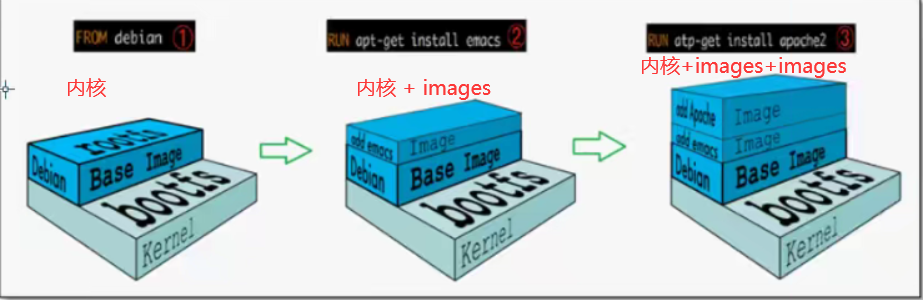
For a compact OS, rootfs can be very small and contain only the most basic commands, tools, and libraries, since the underlying layer uses Host's kernel directly, and only its own
You need to provide rootfs. So bootfs are basically the same for different linux distributions, rootfs are different, so different distributions can be public
bootfs.
Layered Mirror
You can see that downloads are one tier at a time
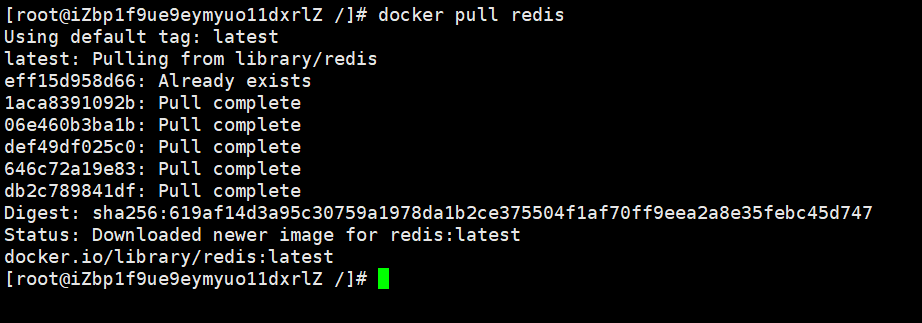
Once installed, layers will not be installed, such as Already exists above
Commit mirror
How to submit a mirror of yourself
docker commit Submit Container to a New Copy # Commands work like GITS docker commit -m="Information submitted" -a="author" container id Target Mirror Name:[tag]
Field Test
#1. Start a default Tomcat #2. Discover that this default tomcat is not a webapps application. The reason for mirroring is that there are no files underneath the official mirror default webapps! #3.Copy in the basic files yourself! #4. Submit containers that we have operated on to a mirror via commit! We can use the mirror we modified later. This is one of our own modified images
Container data volume
What is a container data volume?
docker's concept review
Package applications and environments into a single image!
Data? If the data is all in containers, our containers will delete and the data will be lost! Requirement: Data can be persisted
MySQL, container deleted, library deleted run! Requirement: MySQL data can be stored locally!
There can be a technology for data sharing between containers! Data generated in Docker container, sync to local!
This is volume technology! Mount directories, mount directories inside our containers onto Linux!
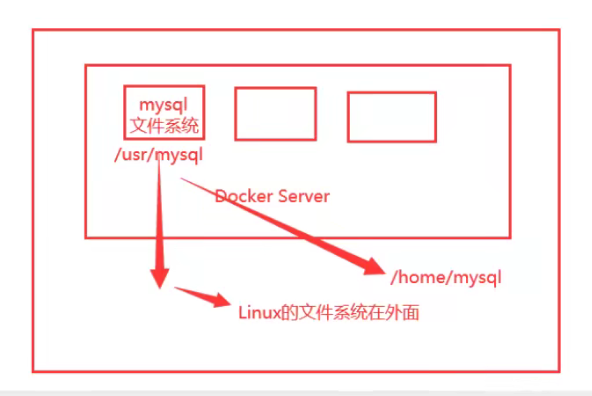
In a word: container persistence and synchronization! Containers can also share data!
Using data volumes
Mode 1: mount-v directly using the command
docker run -it -v Host Directory:Container contents
# test [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ home]# docker run -it -v /home/ceshi:/home centos /bin/bash # We can use docker inspect container id when starting up
"Mounts": [
{
"Type": "bind",
"Source": "/home/ceshi",
"Destination": "/home",
"Mode": "",
"RW": true,
"Propagation": "rprivate"
}
],
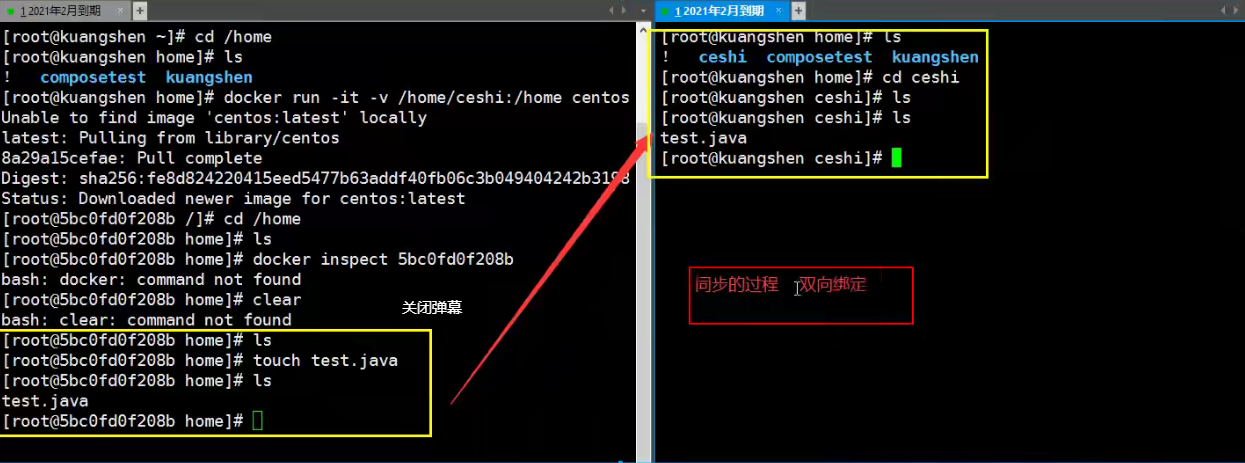
Test discovery again
- Stop Container
- Modify Files on Host
- Start Container
- The data in the container is still synchronized!
Benefit: We only need local modifications for future modifications, and the container will synchronize automatically!
Install Mysql
# Get Mirror [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker pull mysql:5.7 #Run container, data mount is required! #Install Start mysq1 You need to configure the password, this is a point of attention! #Official test: docker run--name mysq101-e MYSQL_ ROOT_ PASSWORD=my-secret-pw-d mysq1:tag # Multiple directories can be mounted at the same time, bi-directional binding # -d:Background running - p:Port Mapping - v: Data volume mount - e:Environment Configuration -- Name:Container name # Start your own [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ /]# docker run -d -p 3310:3306 -v /home/mysql/conf:/etc/mysql/conf.d -v /home/mysql/data:/var/lib/mysql -e MYSQL_ROOT-PASSWORD=123456 --name mysql01 mysql:5.7 # After successful startup, you can use sqlyog tests locally # sqlyog-3310 connected to server and 3306 mapping inside container, then we can connect!
Suppose container is deleted
We found that the volume we mounted locally is still not lost, which enables container data persistence!
Anonymous and Anonymous Mounts
# Usually mounted with a name -V Path inside container #Anonymous mount -V Volume Name:Path inside container #Named Mount -V /Host Path:Path inside container #Specify the path to mount!
extend
#Change read and write permissions ro through -V container path: ro rw readonly # Read-only rW readwrite #Read-write #Once this setting sets container permissions, containers limit what we can mount! docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -V juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:ro nginx docker run -d -P --name nginx02 -V juming-nginx:/etc/nginx:rw nginx
First Identity Dockerfile
A modified container was originally submitted through commit and then mirrored
Dockerfile is the build file used to build the docker image! Command script! Experience it first!
Through this script, mirrors can be generated one layer at a time, scripts commands one by one, each command is one layer!
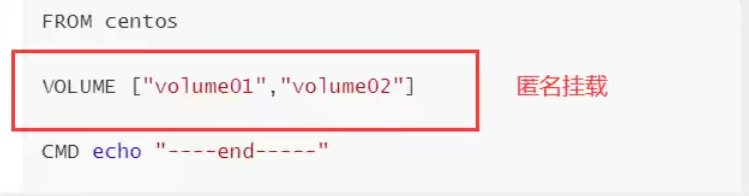
#Create a dockerfile with a name that randomly suggests a Dockerfile #Content directive (uppercase) parameters in file FROM centos VOLUME ["volume01" ,"volume02"] CMD echo "----end-----" CMD /bin/bash #Every command here is the mirror floor!
# -f is built from which file [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ docker-test-volume]# docker build -f dockerfile -t kuangshen/centos:1.0 . # image after successful build [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ docker-test-volume]# docker images REPOSITORY TAG IMAGE ID CREATED SIZE kuangshen/centos 1.0 710cd474d3b2 4 seconds ago 231MB
# Start Container docker run -it image id
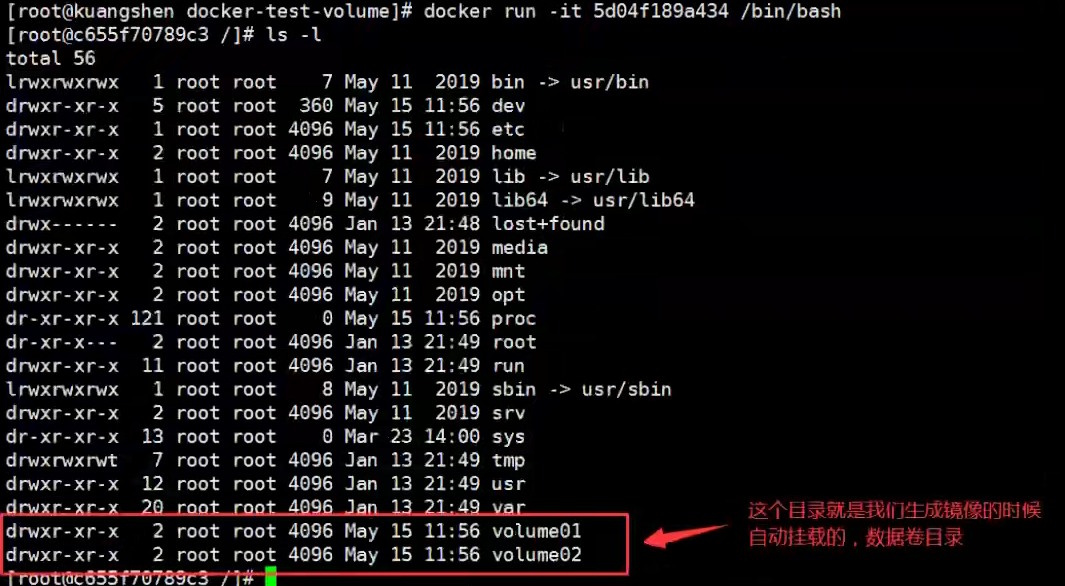
There must be a synchronized directory outside this volume!
Data Volume Container
Synchronize data with multiple mysql s!

# --Mount between volumes-front containers [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ docker-test-volume]# docker run -it --name docker02 --volumes-from docker01 kuangshen/centos:1.0
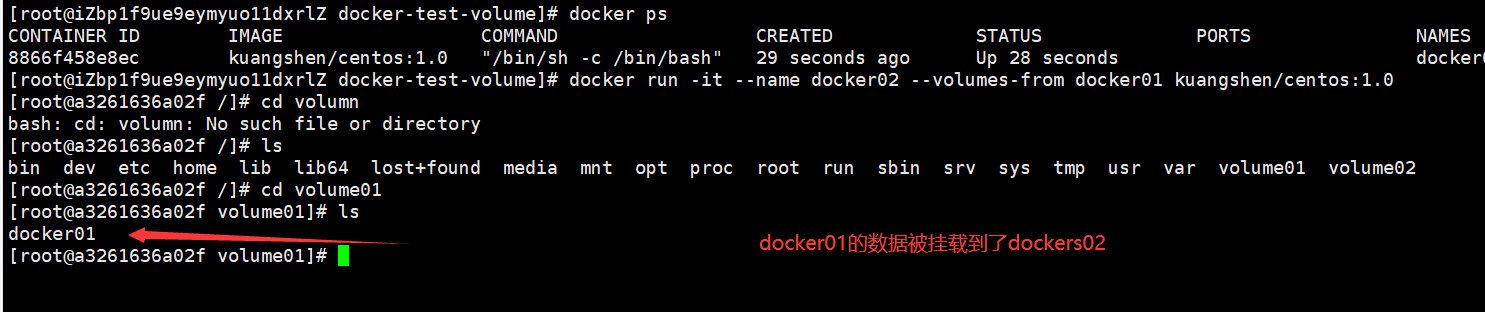
Essentially, docker01 and 02 point to the address of the host, so delete docker01 and docker02 will have data.
Dockerfile
Introduction to Dockerfile
The dockerfile is the file used to build the docker image! Command parameter script
Construction steps:
- Write a dockerfile
- Docker builds into a mirror
- docker run run mirror
- docker push releases mirror (DockerHub, Ali Cloud Mirror Warehouse)
Many of the official mirrors are basic packages and many of the functions are not available. We usually set up our own mirrors!
Dockerfile build process
Fundamentals:
- Each reserved keyword (instruction) must be an uppercase letter
- Execute from top to bottom
- #indicates a comment
- Each instruction creates and submits a new mirror layer!
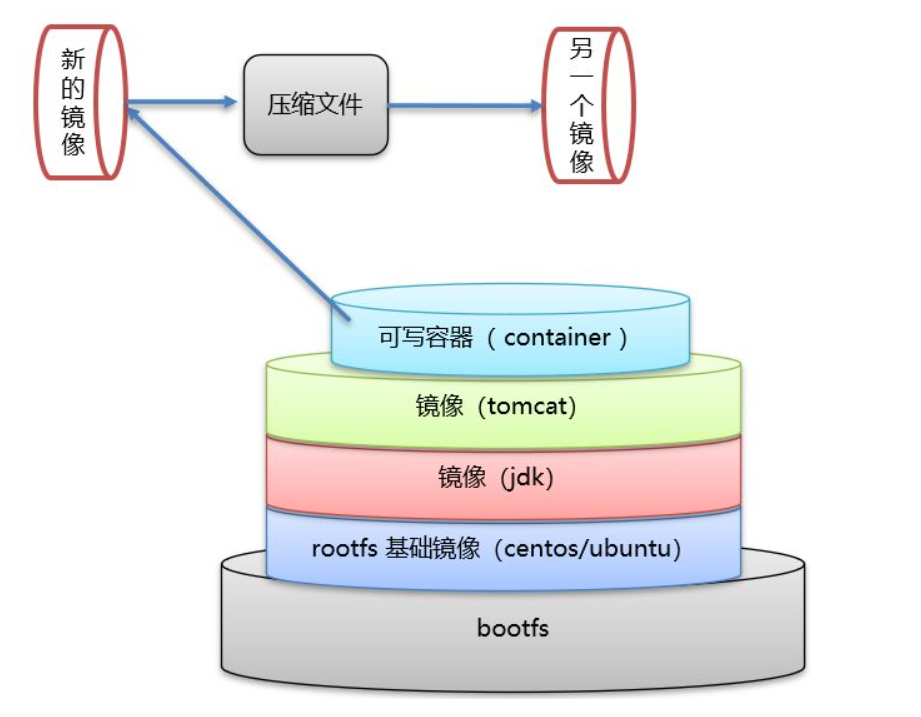
Dockerfile is for development, publishing projects, mirroring, dockerfile needs to be written
Step: Develop, deploy, operate and maintain...
DockerFile: Build a file, define all the steps, source code
Dockerlmages: Build a generated image through DackerFile, and ultimately publish and run the product!
Docker container: A container is a mirror that runs to provide a server
Dockerfile directive
FROM #Basic Mirror, everything built from here MAINTAINER #Who wrote the mirror, name + mailbox RUN #Commands to run when building a mirror ADD #Step: tomcat mirror, this tomcat compressed package! Add Content WORKDIR #Mirrored Working Directory VOLUME #Mounted Directory EXPOSE #Keep Port Configuration CMD #Specifies the command to run when this container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT #You can append commands by specifying which commands to run when this container starts ONBUILD #When an inherited DockerFile is built, the ONBUILD directive is run. Trigger command. COPY #Like ADD, copy our files into a mirror ENV #Set environment variables when building

Field Test
Create your own centos
# 1. Write dockerfile [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ dockerfile]# cat mydockerfile-centos FROM centos LABEL "author"="zhangchuan" LABEL "email"="1581546384@qq.com" ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH RUN yum -y install vim RUN yum -y install net-tools EXPOSE 80 CMD echo &MYPATH CMD echo "----end----" CMD /bin/bash # 2. Build a mirror from this file #Command docker build-f dockerfile file file path-t mirror name: [tag] [root@iZbp1f9ue9eymyuo11dxrlZ dockerfile]# docker build -f mydockerfile-centos -t mycentos:1.0 . Successfu1ly built e2bd75cfe070 Successfu1ly tagged mycentos :0.1 # 3. Test Run Native centos No, pwd,vim These commands,Self-built centos These commands were added
docker history image id # View the construction of the mirror
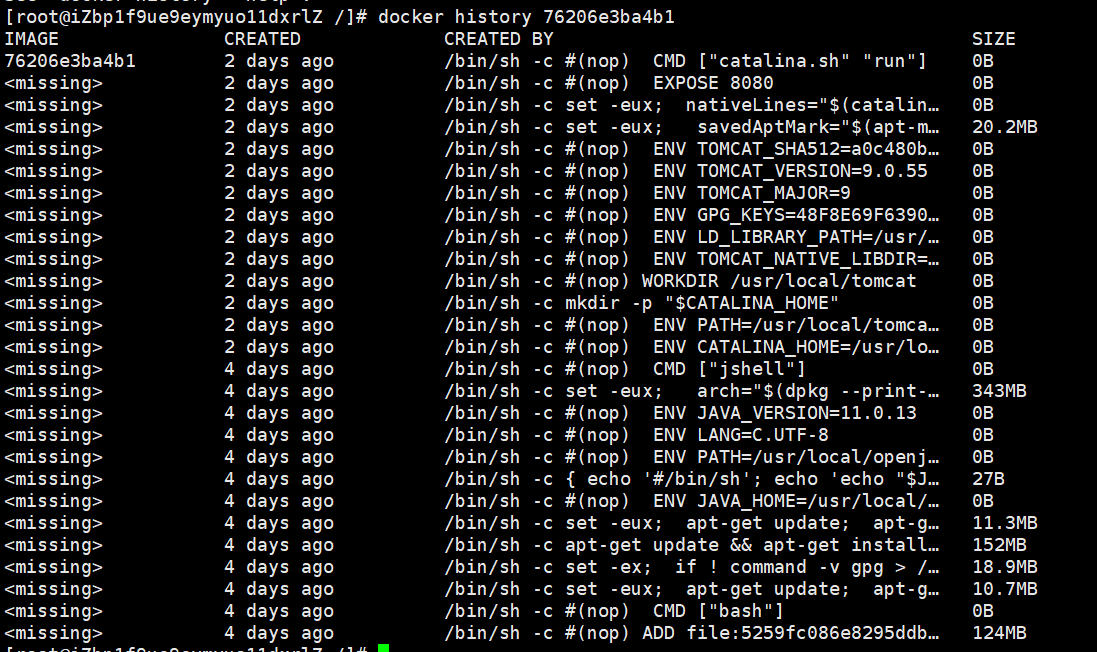
Get a mirror and you can study the whole process of building it!
Difference between CMD and ENTRYPOINT
CMD #Specifies the command to run when this container starts. Only the last one will take effect and can be replaced ENTRYPOINT #You can append commands by specifying which commands to run when this container starts
Actual Warfare: Tomcat Mirror
- Prepare a tomcat zip package for the mirror file, a jdk zip package!
- Write a dockerfile in uppercase Dockerfile (official command: recommendation). build will automatically look for this file without specifying -f!
FROM centos LABEL "author"="zhangchuan" LABEL "email"="1581546384@qq.com" COPY readme.txt /usr/local/readme.txt ADD jdk-8u311-linux-x64.tar.gz /usr/local/ ADD apache-tomcat-8.5.72.tar.gz /usr/local/ RUN yum -y install vim ENV MYPATH /usr/local WORKDIR $MYPATH ENV JAVA_HOME /usr/local/jdk1.8.0_311 ENV CLASSPATH $JAVA_HOME/lib/dt.jar:$JAVA_HOME/lib/tools.jar ENV CATALINA_HOME /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.72 ENV CATALINA_BASH /usr/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.72 ENV PATH $PATH:$JAVA_HOME/bin:$CATALINAHOME/1ib:$CATALINA_HOME/bin EXPOSE 8080 CMD /usr/Local/ apache- tomcat-8.5.72/bin/startup.sh && tail -F /url/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.72/bin/logs/catalina.out
# 3. Start your own mirror docker run -d -p:9090:8080 --name kuangshentomcat -v /home/kuangshen/build/tomcat/test:/url/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.72/webapps/test -v /home/kuangshen/build/tomcat/tomcatlogs/:/url/local/apache-tomcat-8.5.72/logs diytomcat
Publish your own image
DockerHub
-
address https://hub.docker.com/ Register your own account!
-
Make sure this account is logged in
-
Submit your own image on our server
-
Once you've logged in, you can submit a mirror, which is a docker push
[root@kuangshen tomcat]# docker tag f8559daf1fc2 kuangshen/tomcat:1. 0
Can also be published to Ali Cloud Mirror
SpringBoot Micro Services Package Docker Mirrors
Technological process
- Architecture springboot project
- Packaging applications
- Write dockerfile
- Build Mirror
- Publish Run!
actual combat
- Package the project into a jar package
- Write Dockerfile
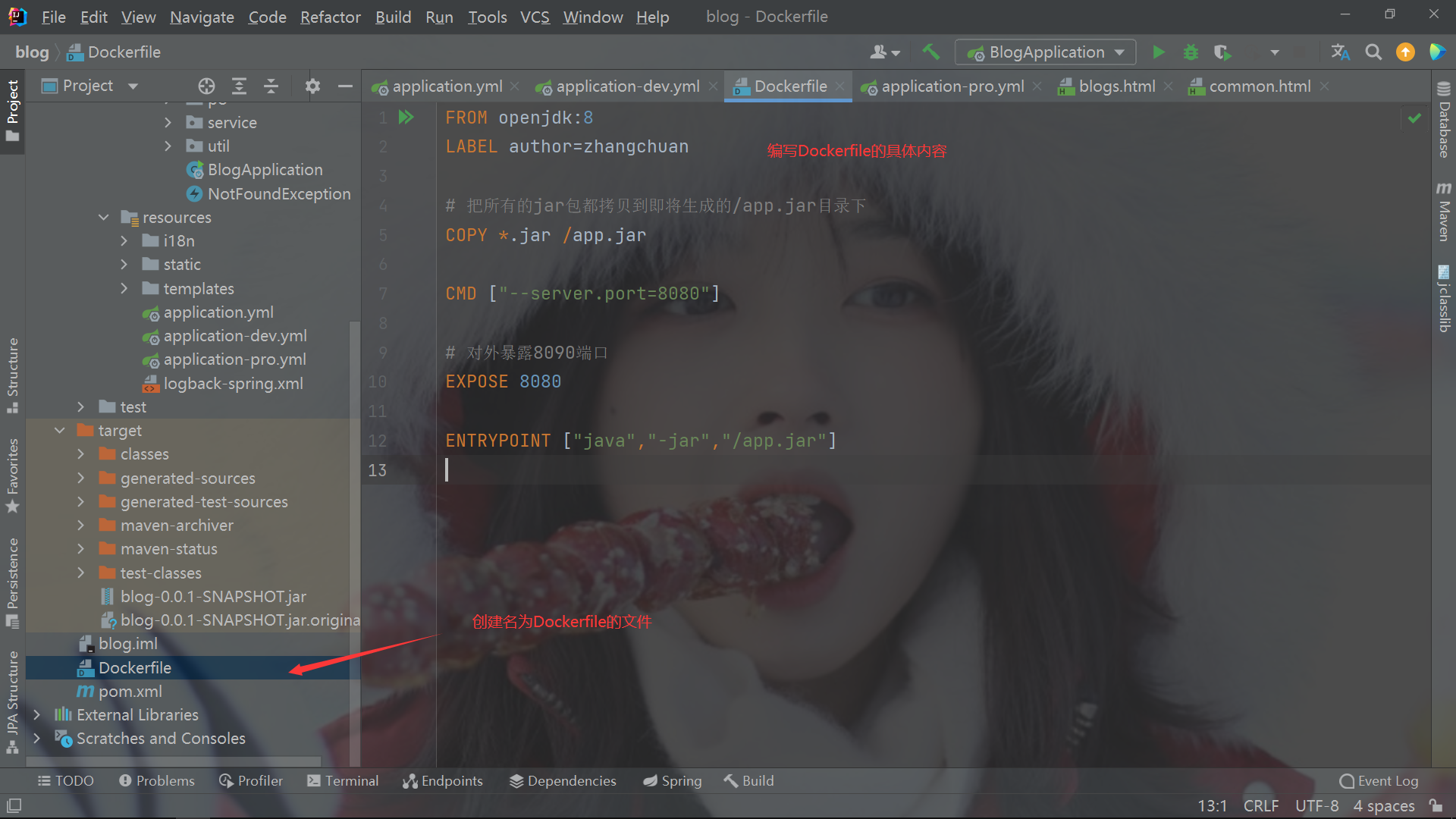
- Upload to remote server via Xftp
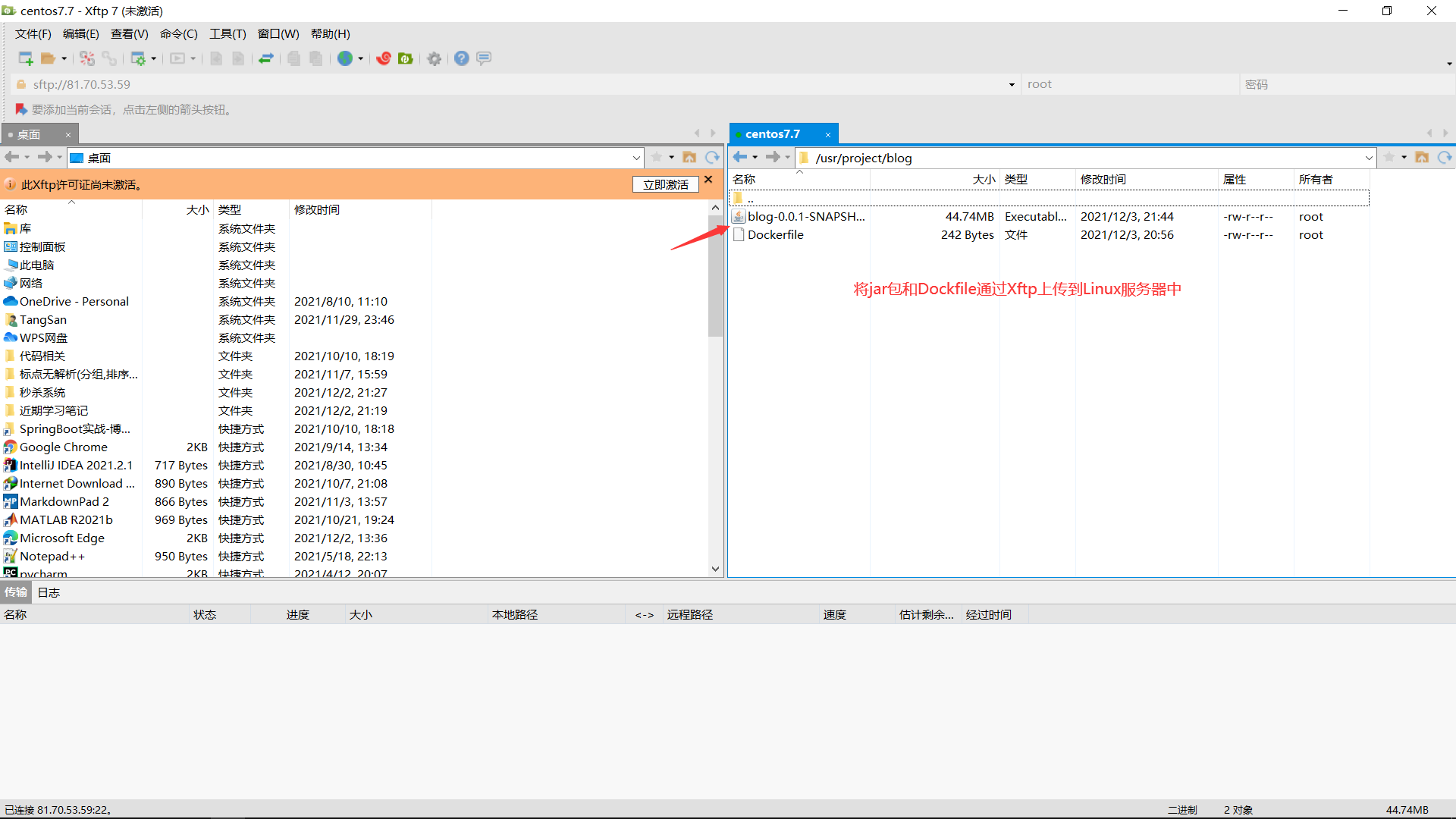
- Use Xshell to open to the file directory where the jar package was uploaded and build a mirror
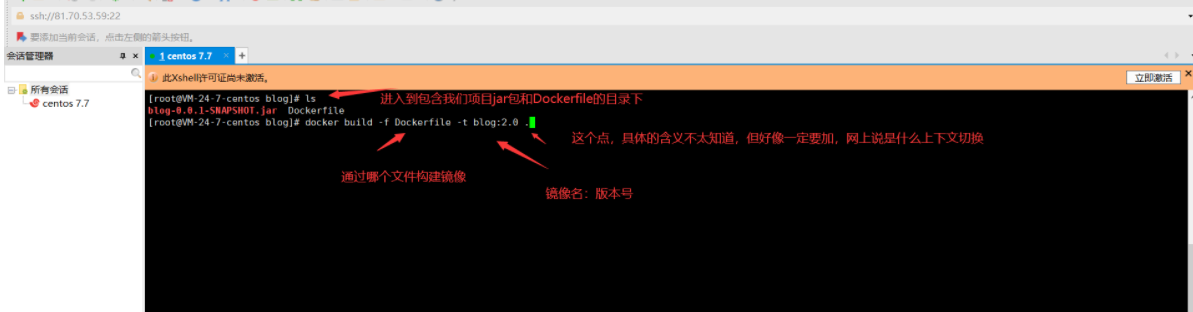
-
Running Project Mirror
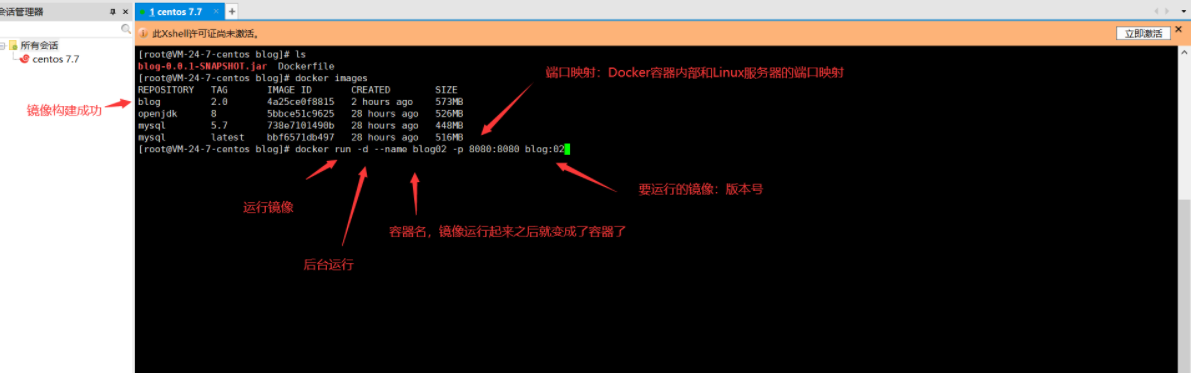
-
If you need MySQL in your project, you need to use Docker to pull the MySQL image and run it
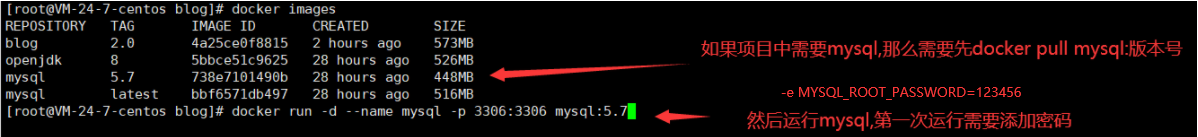
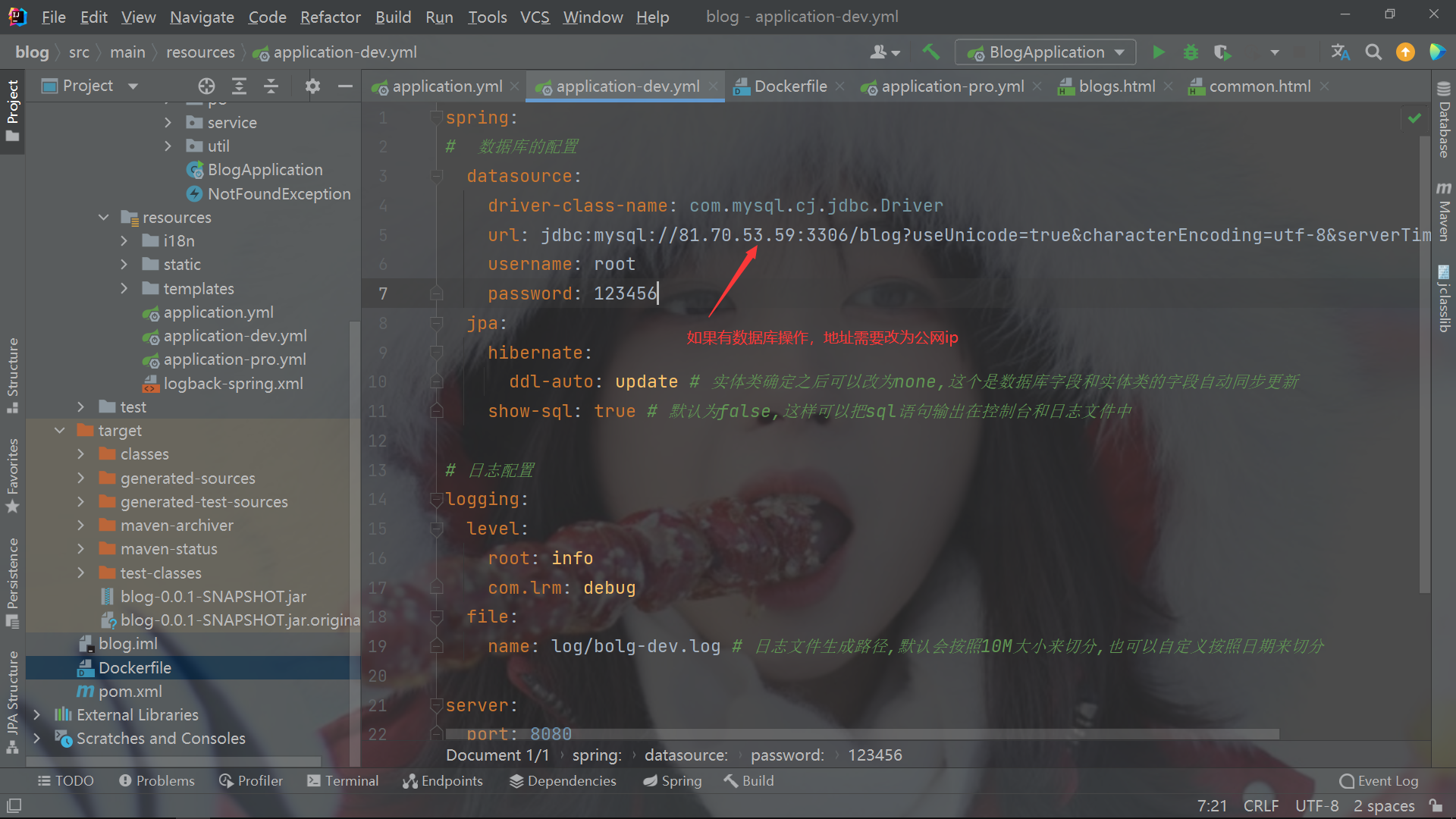
- Project database address also needs to be changed to remote address
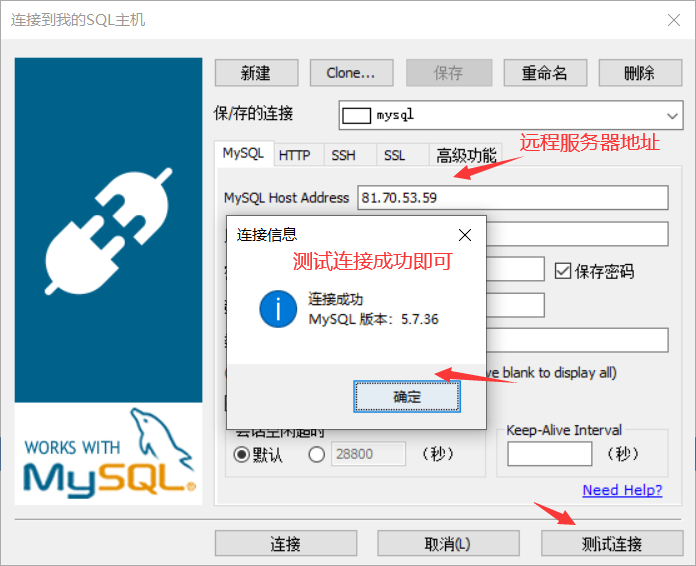
- Utilize local testing of remote MySQL services
-
Then add the database corresponding to the project and import the corresponding sql script!!
-
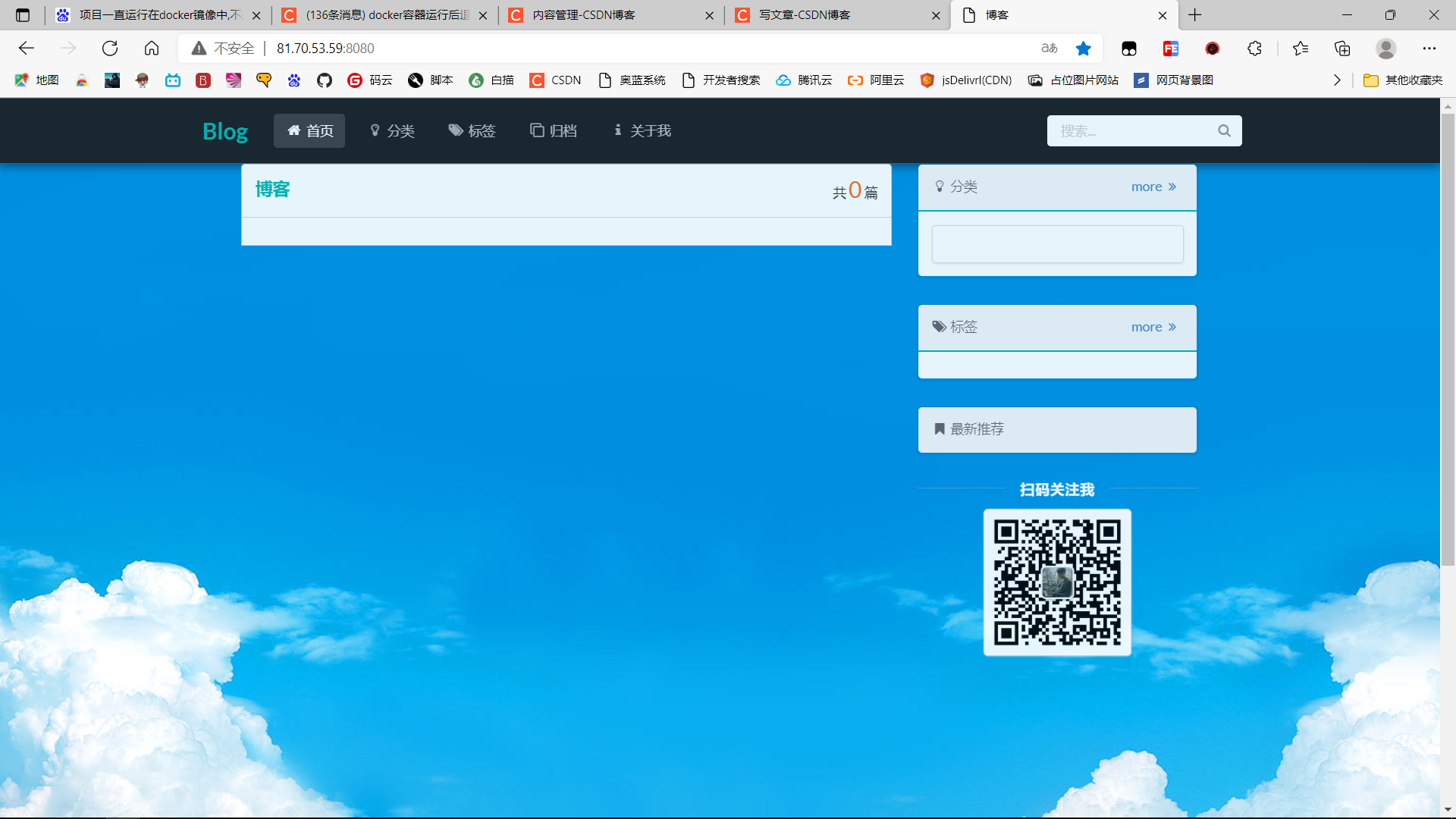
Successfully accessed the project, sql script has not been imported yet, so there is no data public network Ip+port number for now
Source: Meet the gods, Docker teaching video
Video link: Docker's latest ultra-detailed tutorial is easy to understand.