- 1, Introduction to PlantUml
- 2, Summarize and sort out the relationship between classes
- 3, Introduction to PlantUml class diagram syntax
- 4, Class diagram
- 5, Class diagram PlantUml code
This article describes how to use the PlantUml plug-in to draw Uml diagrams
1, Introduction to PlantUml
PlantUML is a tool that can quickly write various diagrams. You can draw diagrams by installing Intellij Idea or Vs Code plug-in, or edit them online. The link is:
https://www.plantuml.com/plantuml/uml/SyfFKj2rKt3CoKnELR1Io4ZDoSa70000
The link to the class diagram example document is:
https://plantuml.com/zh/class-diagram
Make a fortune, pay attention + like + collect, don't get lost.
2, Summarize and sort out the relationship between classes
- Dependency
Unidirectional means that one class depends on the definition of another class, and the change of one class will affect another class. It is a "use a" relationship
If A depends on B, B is represented by A's local variables, method parameters, static method calls, etc
local variable
public class Animal {
public void drink() {
Water water = new Water();//local variable
....
}
}
Method parameters
public class Animal {
public void drink(Water water) {//Method parameters
....
}
}
Static method call
public class Animal {
public void drink() {
Water.drink();//Static method call
....
}
}
- Association
One way or two-way (usually we need to avoid using two-way association relationship) is A "has a" relationship. If A is one-way associated with B, it can be said that A has a B, which is usually expressed as A global variable.
One way Association:
public class Person {
public Phone phone;
public void setPhone(Phone phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
public Phone getPhone() {
return phone;
}
}
Bidirectional association:
public class Man {
public Women women;
public void setWomen(Women women) {
this.women = women;
}
public Women getWomen() {
return women;
}
}
public class Women {
public Man man;
public void setMan(Man man) {
this.man = man;
}
public Man getMan() {
return man;
}
}
- Aggregation and composition
They seem to be very different, but they are put together.
polymerization
Different types of work come together and become constructors. Constructors include engineers, electricians, carpenters, etc. they are the relationship between the whole and the individual, that is, the relationship of has-a. at this time, the whole and parts are separable, and they can have their own life cycle. That is, the construction personnel may not exist, but the engineer still exists.
public class Builders {
public Engineer engineer;
public void setEngineer(Engineer engineer) {
this.engineer = engineer;
}
public Engineer getEngineer() {
return engineer;
}
}
combination
The computer is composed of cpu, memory and hard disk. Although we all say "yes" in combination and aggregation, this "yes" is different. It embodies a relationship of contains-a, which is stronger than aggregation, also known as strong aggregation; It also reflects the relationship between the whole and the part, but at this time, the whole and the part are inseparable. The end of the whole life cycle means the end of the part life cycle. For example, if the cpu is broken, the computer will not be able to use.
public class Computer {
public Cpu cpu;
public void setCpu(Cpu cpu) {
this.cpu = cpu;
}
public Cpu getCpu() {
return cpu;
}
}
- Inheritance relationships (extensions)
Class inherits from abstract class, and subclass inherits from parent class
public class Child extends Father {
}
- Implementation relationships
Class implementation interface
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
}
}
3, Introduction to PlantUml class diagram syntax
- Class attribute field and method access permission mapping relationship**
| Symbol | Access rights |
|---|---|
| - | private |
| # | protected |
| ~ | package private |
| + | public |
- rely on
Water <... Animal: dependency
- relation
Phone < -- person: Association
- Bidirectional association
Man < – > women: bidirectional association
- polymerization
Engineer < – o Builders: aggregation
- combination
CPU < – * Computer: combination
- inherit
Father < | -- child: Inheritance
- realization
Runnable <|... MyRunnable : implements
- other
The arrow direction can be on the left or right.
– indicates a vertical solid line, - indicates a horizontal solid line.
... indicates the vertical dotted line, - indicates the horizontal dotted line.
You can use "" on both sides of the symbol to add a description of the element.
At the end of the relationship, you can use: to add a description of the relationship.
4, Class diagram
The class diagram is as follows:
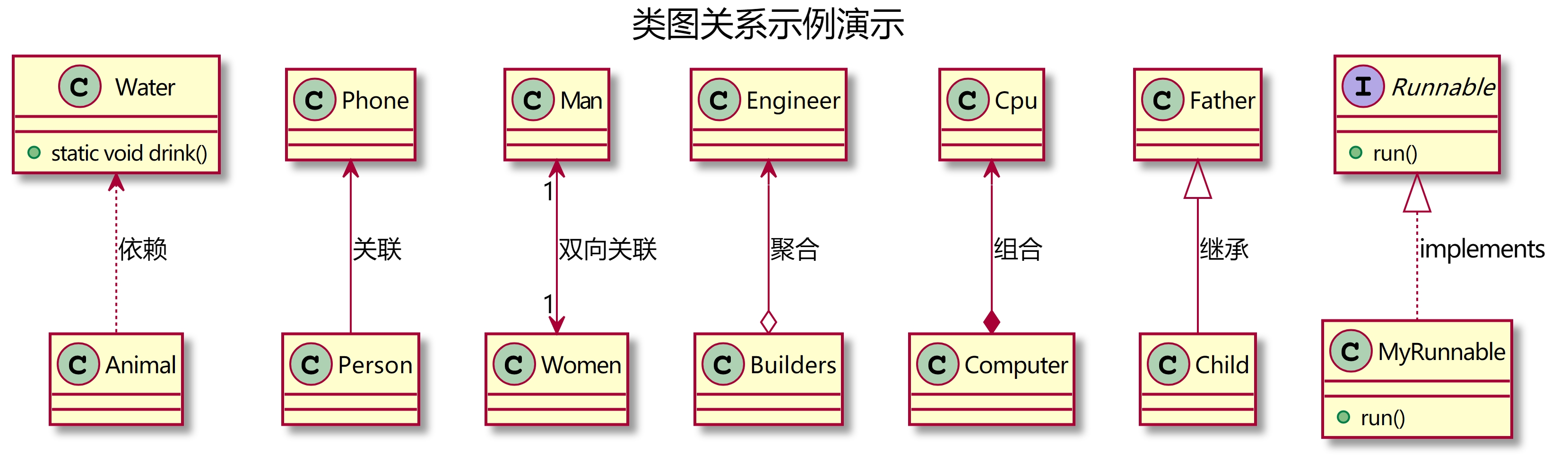
5, Class diagram PlantUml code
The plantuml code is as follows:
@startuml
scale 300 width
title Class diagram relationship example demonstration
class Water {
+static void drink()
}
class Animal {
}
class Phone {
}
class Person {
}
class Man {
}
class Women {
}
class Engineer {
}
class Builders {
}
class Cpu {
}
class Computer {
}
class Father {
}
class Child {
}
interface Runnable {
+run()
}
class MyRunnable {
+run()
}
Water <.. Animal : rely on
Phone <-- Person : relation
Man "1" <--> "1" Women : Bidirectional association
Engineer <--o Builders : polymerization
Cpu <--* Computer : combination
Father <|-- Child : inherit
Runnable <|.. MyRunnable : implements
@enduml
quote:
1.https://blog.csdn.net/qq_28379809/article/details/79499577
2.https://www.cnblogs.com/jisijie/p/5062109.html
3.https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1932863