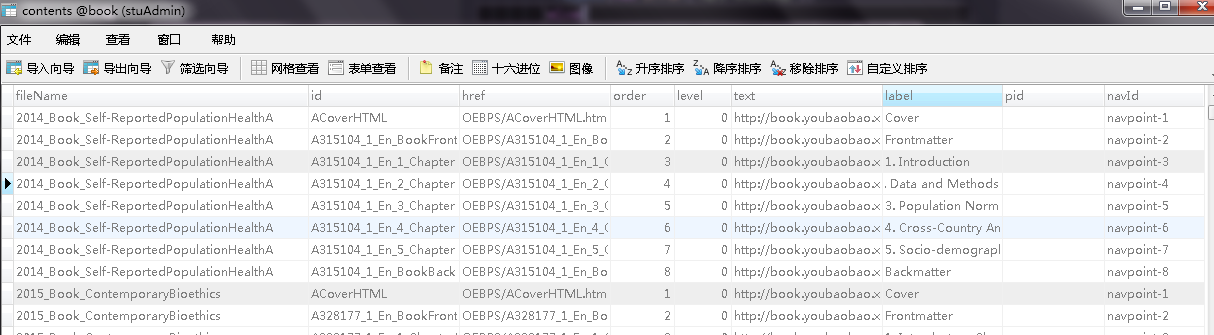
EBook list
E-book analysis data display
EbookUpload component
this.emit('onSuccess',response.data)
book/components/detail.vue
handleSuccess(data){
console.log(data);
},

After getting the data
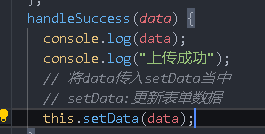
Then write a setData method
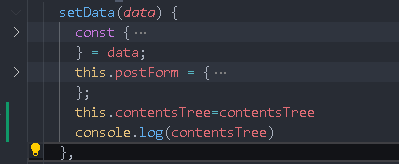
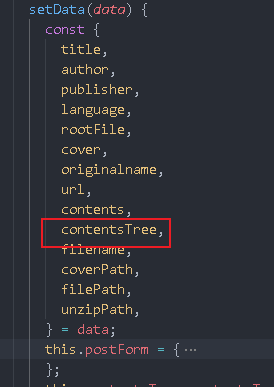
setData(data) {
const {
title,
author,
publisher,
language,
rootFile,
cover,
originalName,
url,
contents,
contentsTree,
fileName,
coverPath,
filePath,
unzipPath,
} = data;
this.postForm = {
title,
author,
publisher,
language,
rootFile,
cover,
url,
originalName,
contents,
fileName,
coverPath,
filePath,
unzipPath,
};
},
Re execute
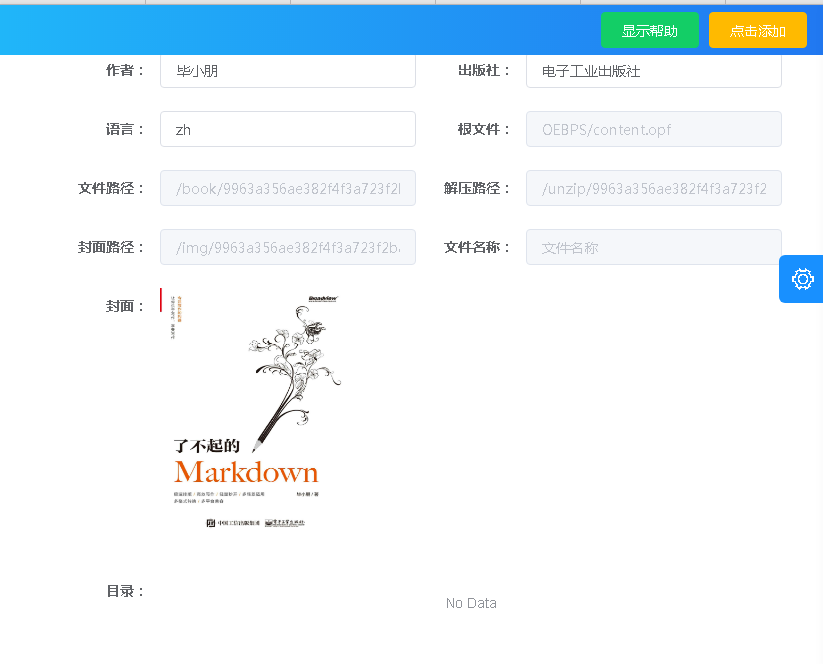
The case of filename here is wrong, but it is better to change the filename to originalName
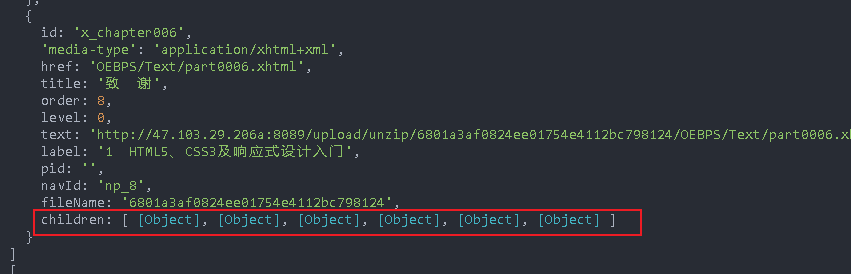
Tree expansion
El tree problem solving
Pass in the data attribute, which is an array. The array contains several objects. Each object corresponds to a level of tree, which contains label and children
https://element.eleme.io/#/zh-CN/component/tree#tree-shu-xing-kong-jian

E-book directories are different. We only use one-dimensional arrays for easy parsing, while the example is a nested array
We go to the server to transform it into nested. Of course, we can also do processing at the front end
If pid is not recognized, it indicates that it is a primary directory

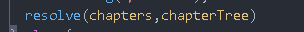
const chapterTree=[]
chapters.forEach(c=>{
c.children=[]
//If pid is not recognized, it indicates that it is a primary directory
if(c.pid===''){
chapterTree.push(c)
}
})
const chapterTree = []
chapters.forEach(c => {
// We have defined and assigned the label attribute earlier
c.children = []
//If pid is not recognized, it indicates that it is a primary directory
if (c.pid === '') {
chapterTree.push(c)
} else {
// If pid is not empty, it means that if there is a parent, find the parent first
const parent = chapters.find(_ =>
// If it's the same, you'll find the parent
_.navId === c.pid
)
parent.children.push(c)
}
})
console.log(chapterTree);

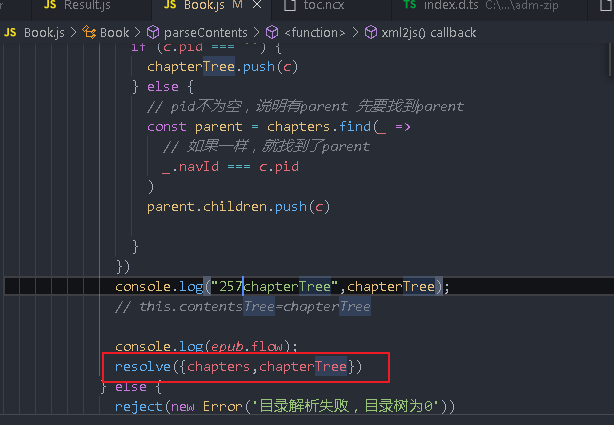

How to view the chapter content after clicking
https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/tree#events

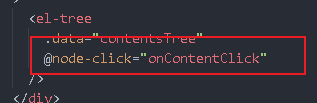
Look what's in the data
onContentClick(data){
console.log(data)
},
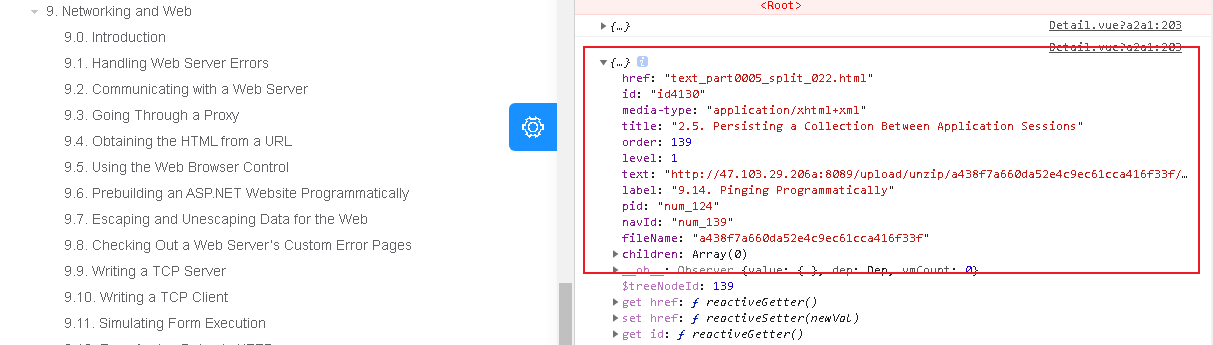
The most important is the text parameter
onContentClick(data){
// console.log(data)
if(data.text){
window.open(data.text)
}
},
Click into a chapter

But there are still problems with some books. For example, this one is different from the directory. 15-3 is optimized, so it is not optimized here

Development of e-book form verification function
Click the cross to clear
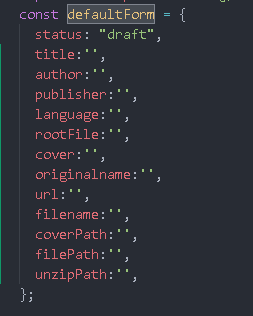
Supplement defaultForm
Check function
Looking at the element UI source code, you can see that two parameters will be returned
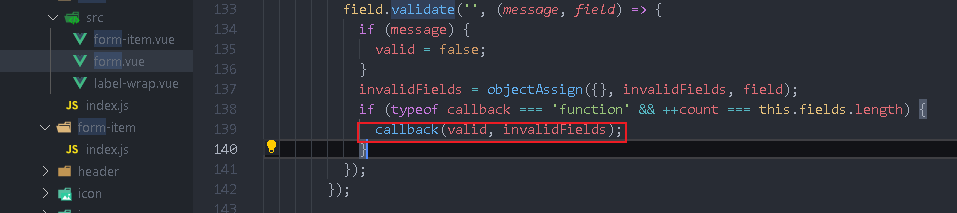
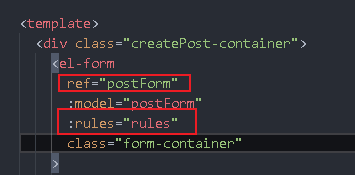
submitForm(){
this.$refs.postForm.validate((valid,fileds)=>{
console.log(valid,fileds);
// Pass verification
if(valid){
}else{
}
})
},
Write a rules object whose key is the prop attribute written in El form item
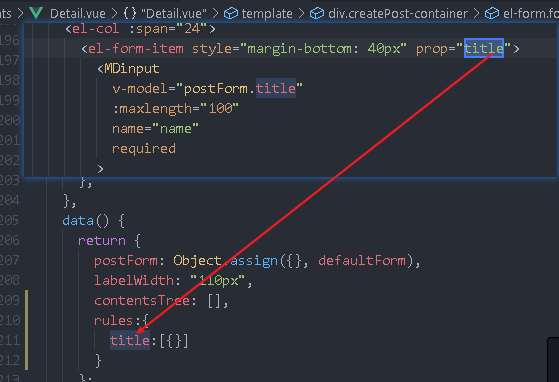
You can directly write required in the title. The custom verification rules used here (pass in function)
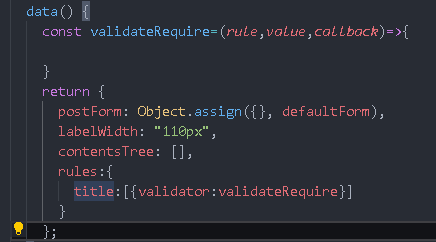
const validateRequire=(rule,value,callback)=>{
if(value===''||value.length==0){
callback(new Error('title Cannot be empty'))
}else{
callback()
}
}
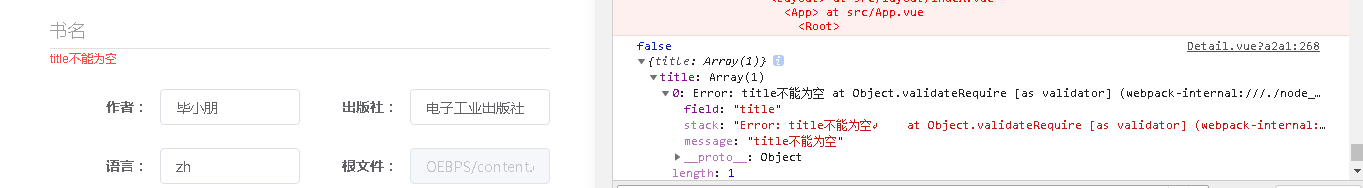
You can print the rule

reform
callback(new Error(rule.field + 'must be filled in'))
Here's a trick to do a field mapping
Write an object
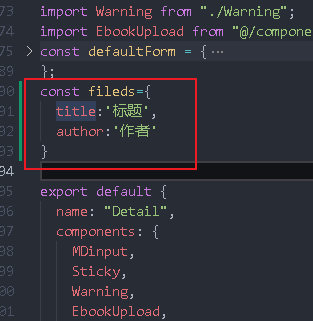
callback(new Error(fields[rule.field] + 'required'))

Now I want to get this sentence and show it on the page
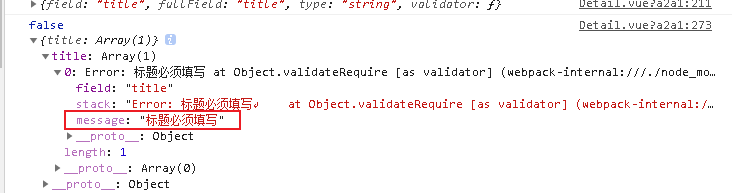
fields[Object.keys(fields)[0]][0].message
submitForm(){
this.$refs.postForm.validate((valid,fields)=>{
console.log(valid,fields);
if(valid){
}else{
// This is a general exception handling method
console.log(fields[Object.keys(fields)[0]][0].message)
const message=fields[Object.keys(fields)[0]][0].message
this.$message({
message,type:'error'
})
}
})
},
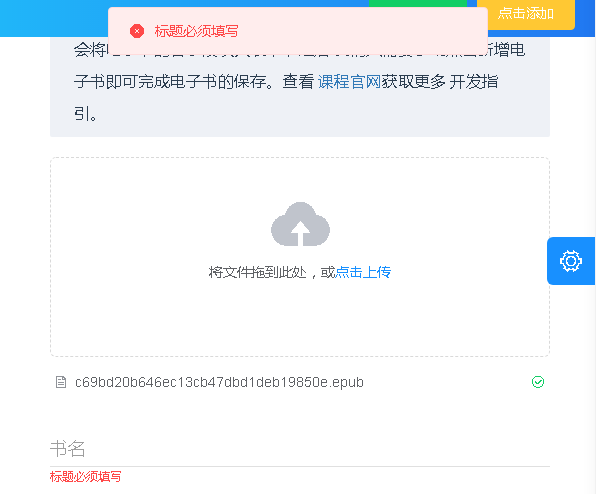
Add a prop author publisher language to the author publisher language
Add mapping
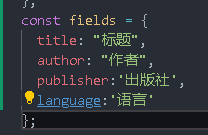
Then add rules in rules
rules: {
title: [{ validator: validateRequire }],
author: [{ validator: validateRequire }],
language: [{ validator: validateRequire }],
publisher: [{ validator: validateRequire }],
},
New e-book front-end logic
There are two methods for shallow copy: extension operator / object assign
Request interface
src/api/book.js
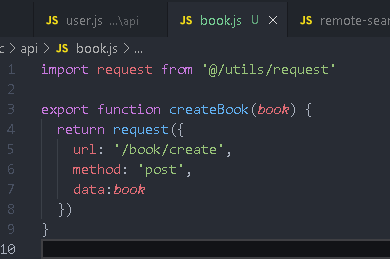
Detail.vue introduction
Interface development
utils/index.js uses the decode here
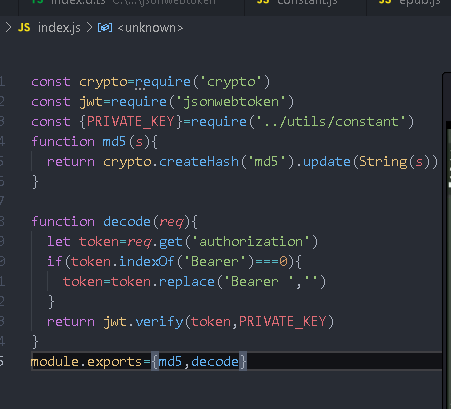
book.js
router.post('/create', (req, res, next) => {
const decoded=decode(req)
// Solve jwt
console.log(decoded);
})

Write a Book object. The logic generated by this book object can be from model / book JS
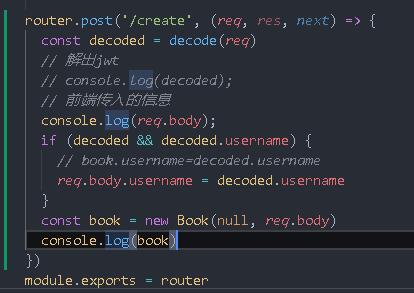
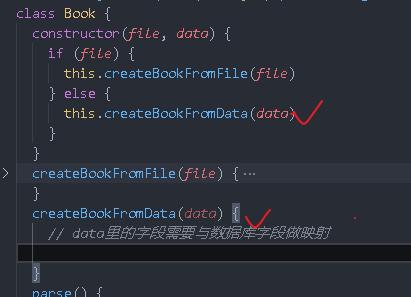
Database data
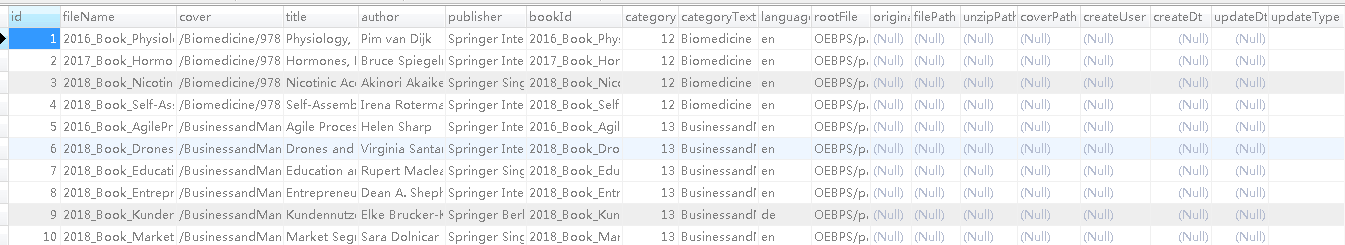
When printing data, you must pay attention to the code specification. The hump is the hump. Several useless humps regret it

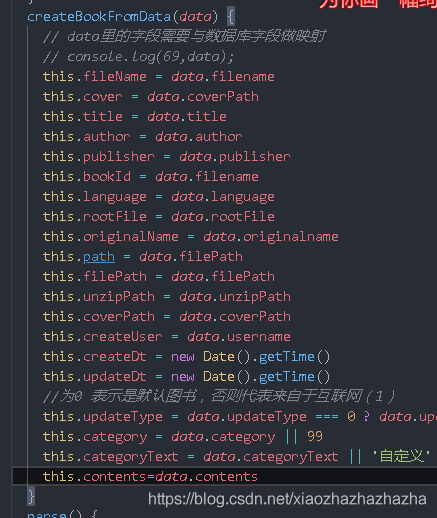
createBookFromData(data) {
// The fields in data need to be mapped with the database fields
// console.log(69,data);
this.fileName=data.filename
this.cover=data.coverPath
this.title=data.title
this.author=data.author
this.publisher=data.publisher
this.bookId=data.filename
this.language=data.language
this.rootFile=data.rootFile
this.originalName=data.originalname
this.path=data.filePath
this.filePath=data.filePath
this.unzipPath=data.unzipPath
this.coverPath=data.coverPath
this.createUser=data.username
this.createDt=new Date().getTime()
this.updateDt=new Date().getTime()
//0 means it is the default book, otherwise it means it comes from the Internet (1)
this.updateType=data.updateType===0?data.updateType:1
this.category=data.category||99
this.categoryText=data.categoryText||'custom'
}
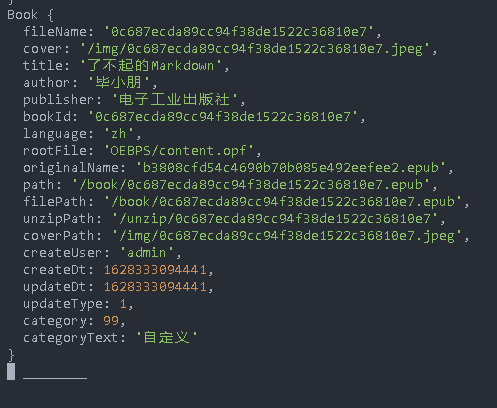
The book object is generated so that sql statements can be generated through the object
New e-book core logic ideas
Create a new service / book JS database operations
const Book=require('../model/Book')
function insertBook(book){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
try {
// Book must be an instance of the book object to avoid the absence of some parameters
// If it is an instance, it has the advantage of ensuring that those parameters are complete,
// Otherwise, an error may occur if a book object is arbitrarily passed in for insert ion
if(book instanceof Book) {
}else{
reject(new Error('The added Book object is illegal'))
}
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
})
}
module.exports={insertBook}
router/book.js
router.post('/create', (req, res, next) => {
const decoded = decode(req)
// Solve jwt
// console.log(decoded);
// Front end incoming information
console.log(req.body);
if (decoded && decoded.username) {
// book.username=decoded.username
req.body.username = decoded.username
}
// const book = new Book(null, req.body)
const book={}
bookService.insertBook(book).then((res)=>{
console.log(res);
}).catch((err)=>{
// console.log(err);
// Error and front end linkage
next(boom.badImplementation(err))
})
console.log(book)
})
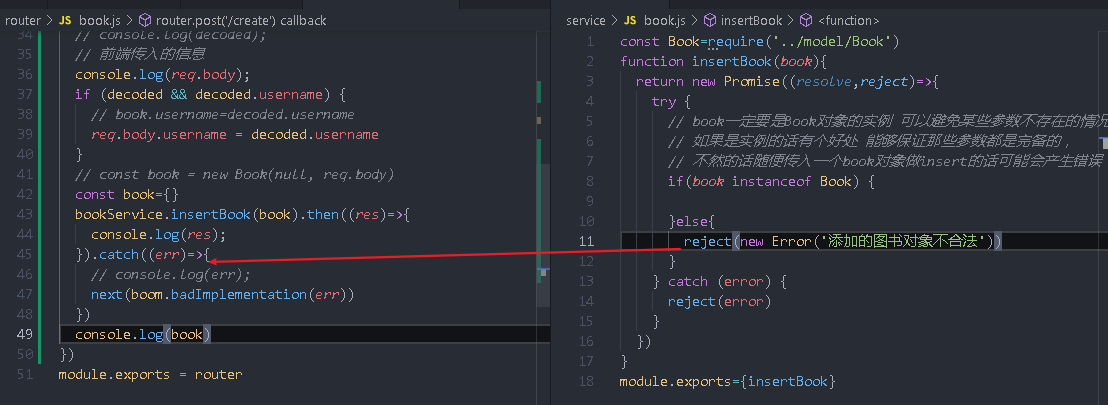
This is the general framework
Judge whether the e-book exists. If it already exists, remove the information in the database and the file
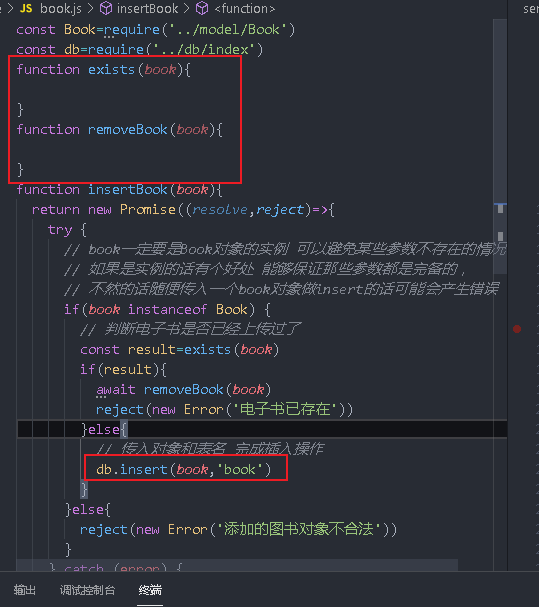
After insert, insert the directory into the directory table

There will be a large number of asynchronous operations in the operation database. Use async await to turn it into a synchronous method to reduce the number of callbacks. If promise is used, there will be a lot of nesting
That's the logic. Next, write a specific method
Database operation
The insert method determines whether the first parameter passed in is an object
Method to determine whether it is an object: utils / index js
function isObject(o){
return Object.prototype.toString.call(o)==='[object Object]'
}
It's very accurate to judge with this

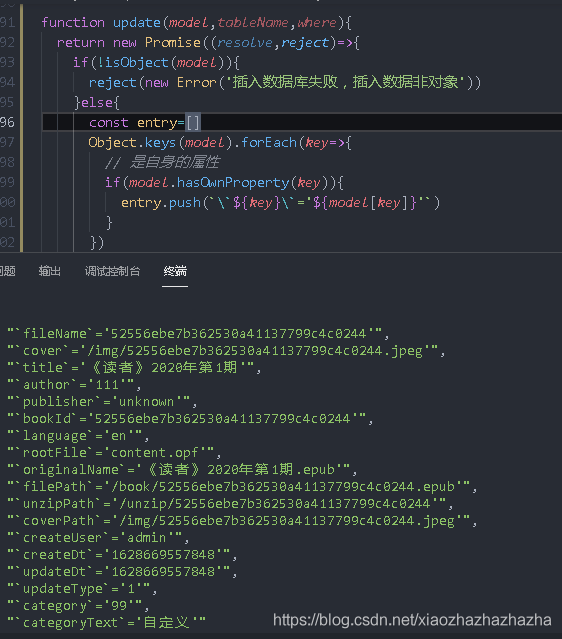
function insert(model,tableName){
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=>{
if(!isObject(model)){
reject(new Error('Failed to insert database, inserting data is not an object'))
}
})
}
Let's experiment
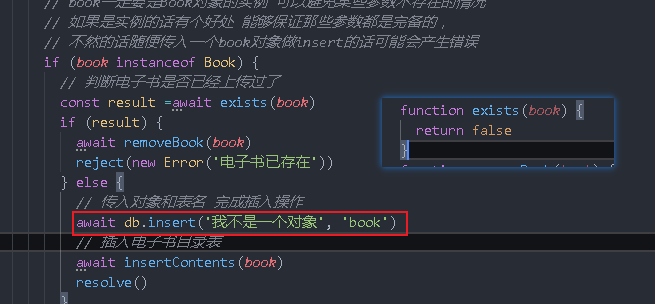
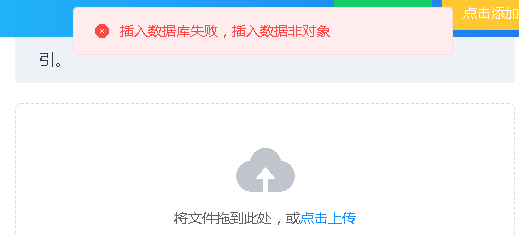
Back to the insert method

There is a skill in database operation
keys.push(`\`${key}\``)
Why? For example, in select from from book, the first from is not a keyword but a key, but the database will automatically recognize that it is a keyword and report an error. After adding backquotes, there is no problem
// Spell sql statement
if(keys.length>0&&values.length>0){
let sql=`insert into \`${tableName}\`(`
const keysString=keys.join(',')
const valuesString=values.join(',')
sql=`${sql}${keysString}) values (${valuesString})`
console.log(sql)
}
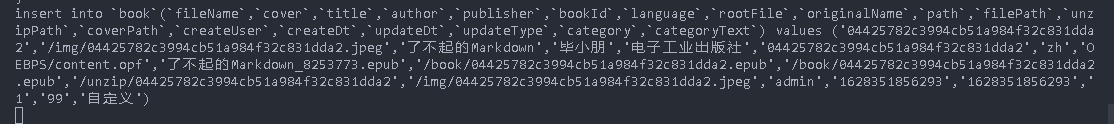
Then try to execute the sql statement successfully
// Spell sql statement
if(keys.length>0&&values.length>0){
let sql=`insert into \`${tableName}\`(`
const keysString=keys.join(',')
const valuesString=values.join(',')
sql=`${sql}${keysString}) values (${valuesString})`
console.log(sql)
const conn=connect()
try {
conn.query(sql,(err,result)=>{
if(err){
reject(err)
}else{
resolve(result)
}
})
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}finally{
conn.end()
}
}else{
reject(new Error('There are no properties in the object'))
}
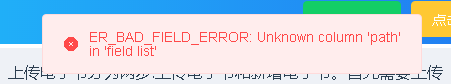
Prompt: there is no path field in the database
Here is a recommended practice
Book.js adds a new method toDb to filter the book object instead of using it as a whole
Remove the path
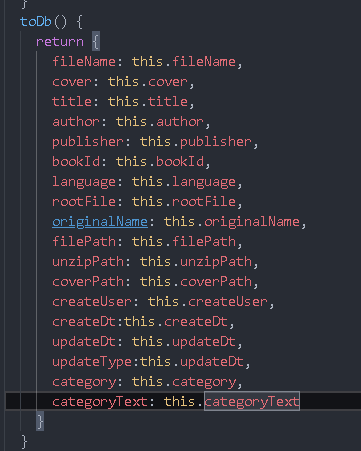
toDb() {
return {
fileName: this.fileName,
cover: this.cover,
title: this.title,
author: this.author,
publisher: this.publisher,
bookId: this.bookId,
language: this.language,
rootFile: this.rootFile,
originalName: this.originalName,
filePath: this.filePath,
unzipPath: this.unzipPath,
coverPath: this.coverPath,
createUser: this.createUser,
createDt:this.createDt,
updateDt: this.updateDt,
updateType:this.updateType,
category: this.category,
categoryText: this.categoryText
}
}
This book will be changed to book Todd () passes the result returned by toDb to insertBook, which will report an error, because insertBook will judge whether the incoming object is an instance of book
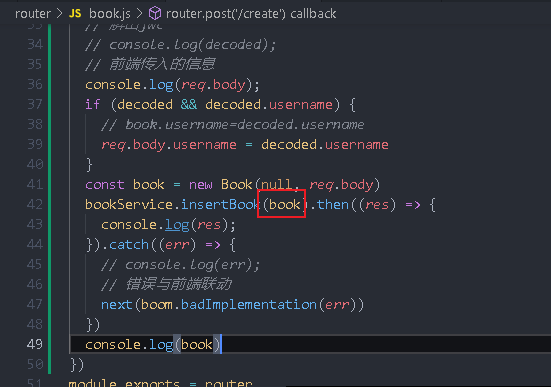
It's appropriate to write here
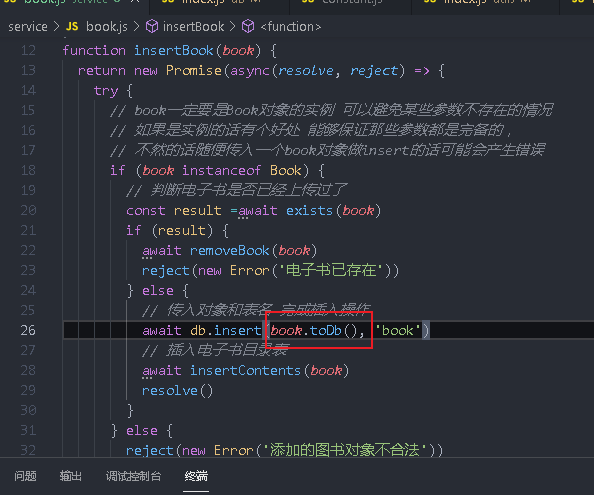
In this way, click Add to find more data in the database

Front end interaction optimization
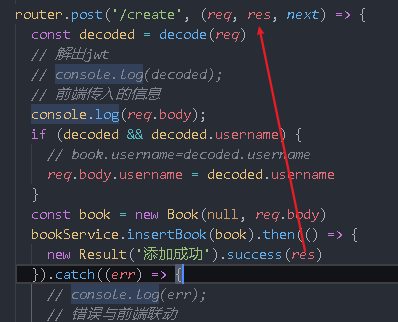
insertBook (book). Then ((RES) = > {}) res cannot be written here because the success method will automatically pass in res here, but in fact, res indicated by the red arrow above should be passed in
front end:
Get the back-end return value and display it on the front-end page
Don't use $message this time
https://element.eleme.cn/#/zh-CN/component/notification#notification-tong-zhi
Use a $notify that looks like him
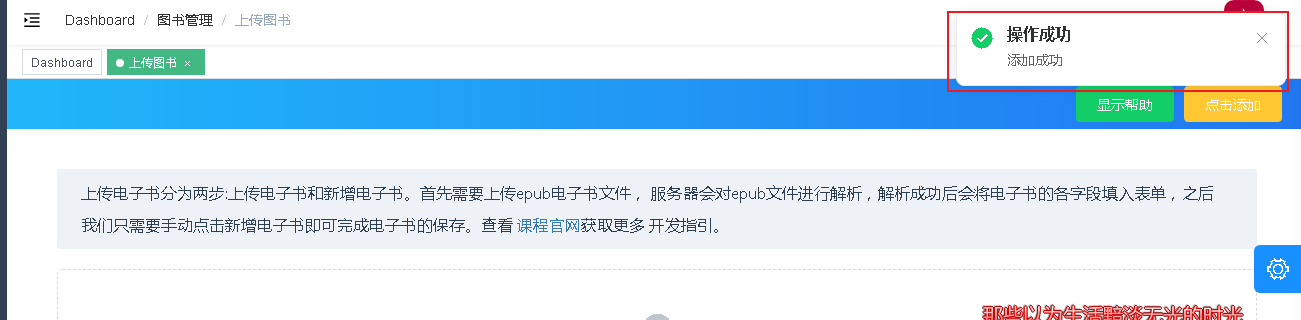
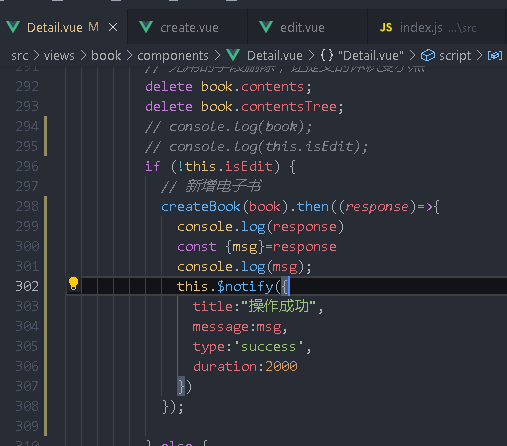
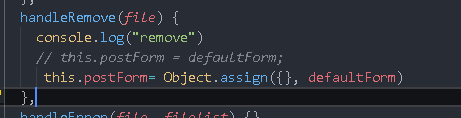
Another detail is that after the upload is successful, the list data can be removed, which has been used in the remove method
this.postForm = Object.assign({}, defaultForm);
The list is removed, but there are still bug s
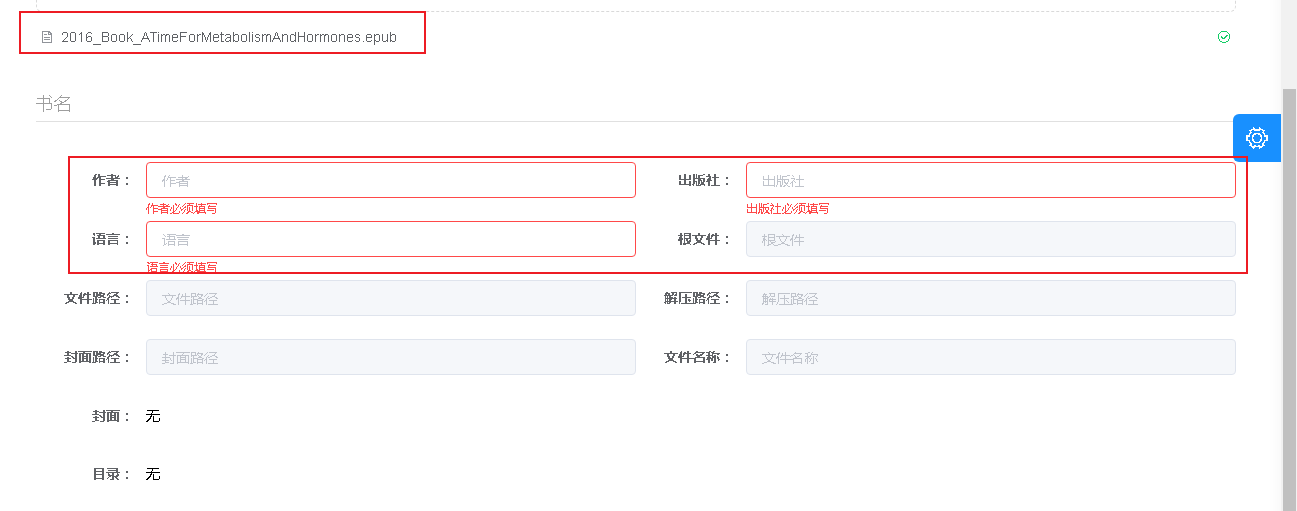
Here is a setDefault method to solve these problems
Leave this blank and the title is gone
setDefault(){
this.postForm = Object.assign({}, defaultForm);
this.fileList=[]
},
Next, eliminate the verification result
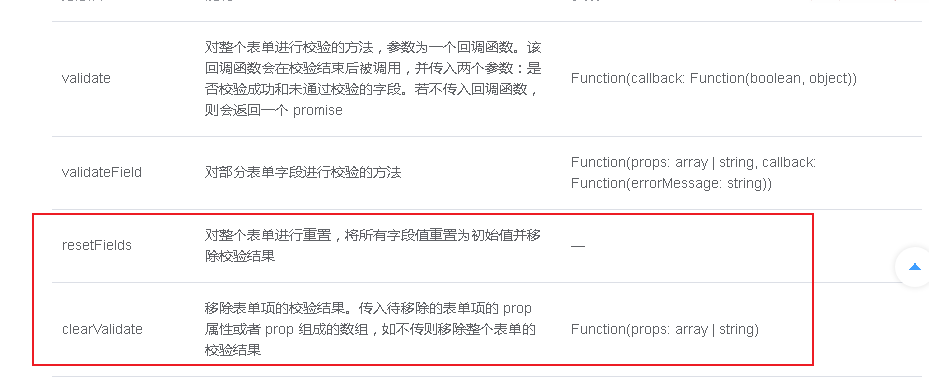
setDefault(){
// this.postForm = Object.assign({}, defaultForm);
this.fileList=[]
this.$refs.postForm.resetFields()
},
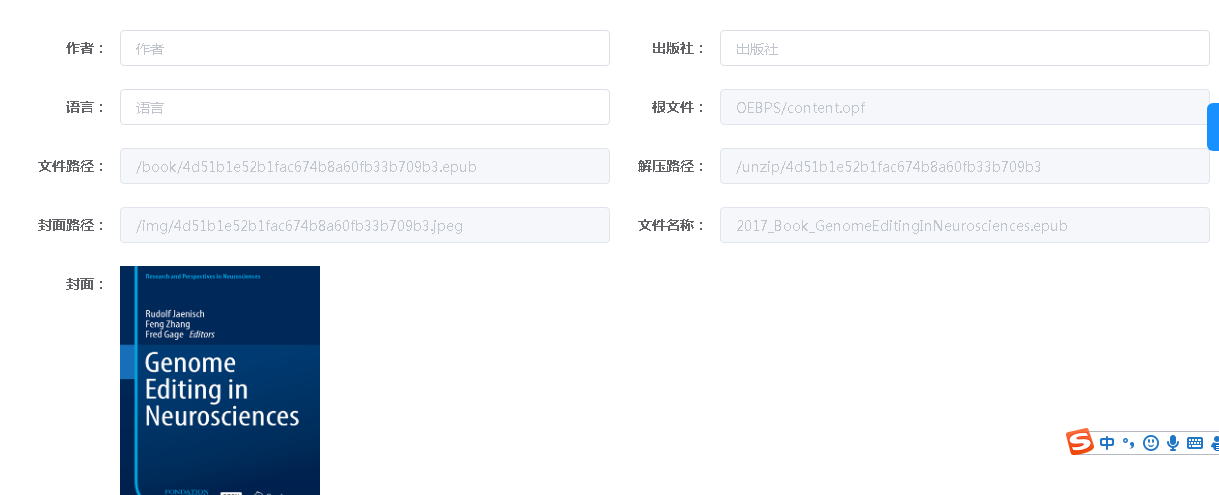
This is because no prop is passed in. If no prop is passed in, it will not be considered as a form option
The directory has not been eliminated
setDefault() {
// this.postForm = Object.assign({}, defaultForm);
this.contentsTree = []; // Eliminate directory
this.fileList = []; // title
this.$refs.postForm.resetFields();
},
Removing is also a call to this method
Add catalog to database function
Next, write the insertContents method
You need to get the contents under book
But the contents was deleted earlier, so there was no directory passed in
front end:
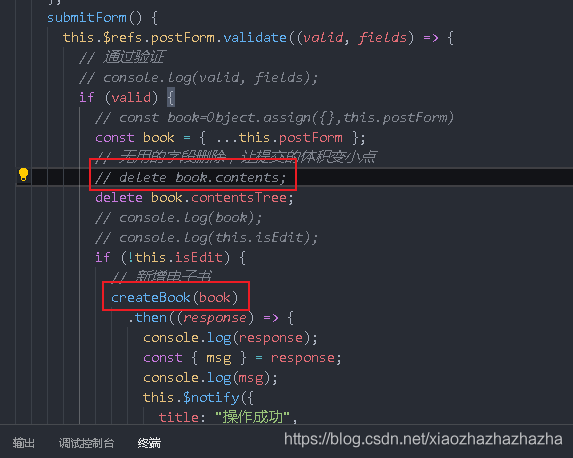
Back end reception:
You can write a getContents
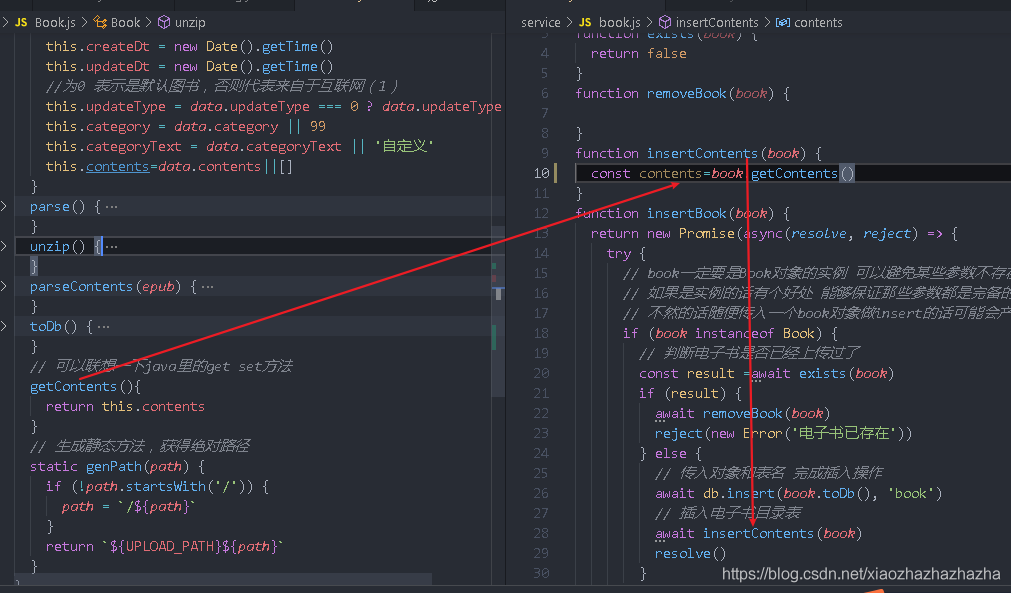
Ensure that you can insert the database after you get the contents
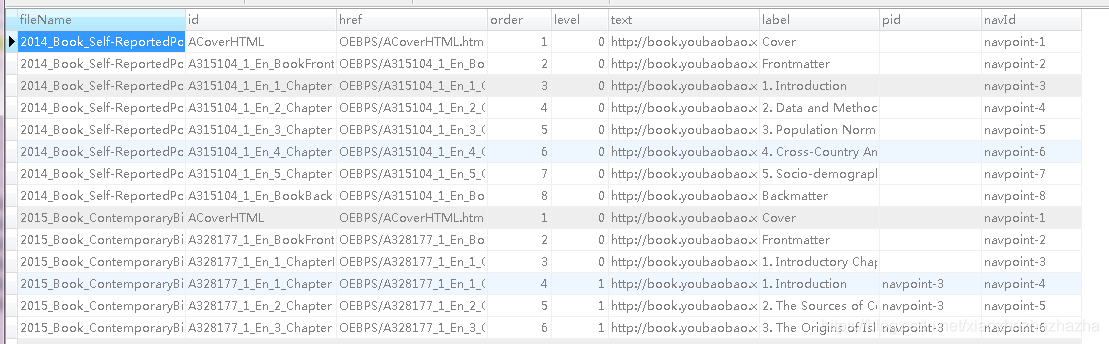
In contrast, there are still many redundant fields
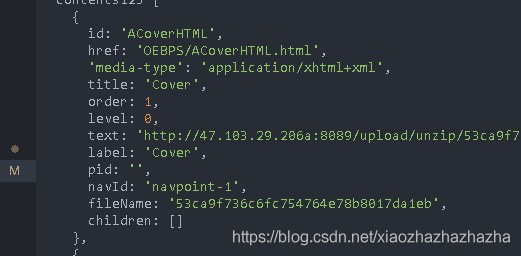
You can create an object and assign values once. Here's a trick - it's implemented through lodash
Through lodash, we can use its methods to achieve the functions we want
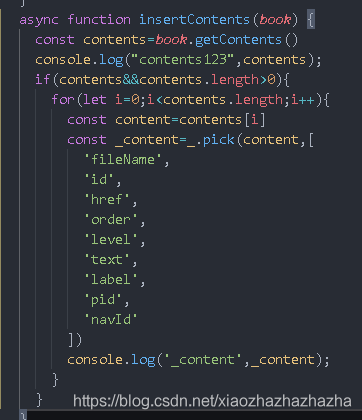
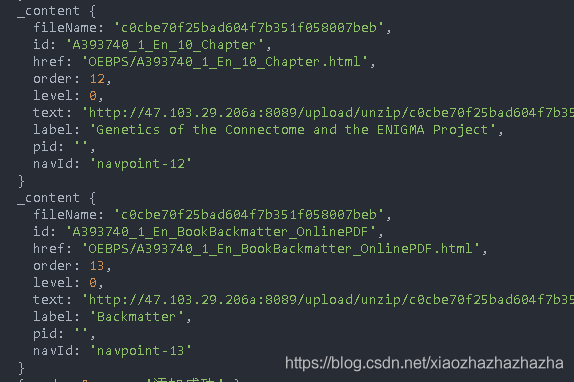
Call the insert method
await db.insert(_content,'contents')
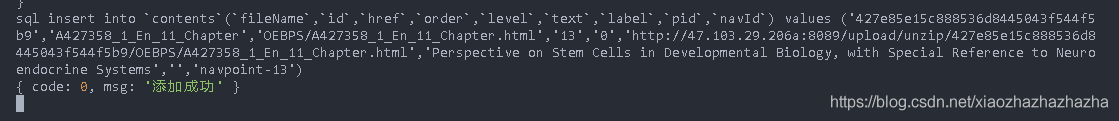
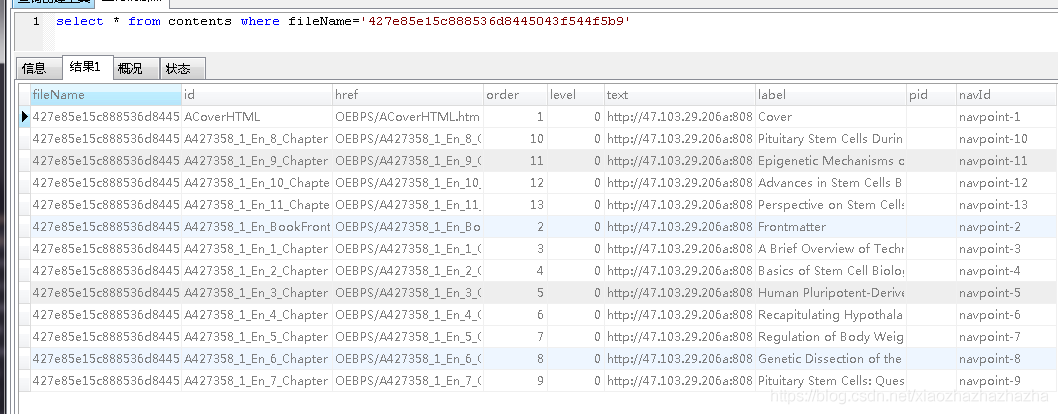
E-book deletion function
The following two logics have been written and the logic to be removed has been written
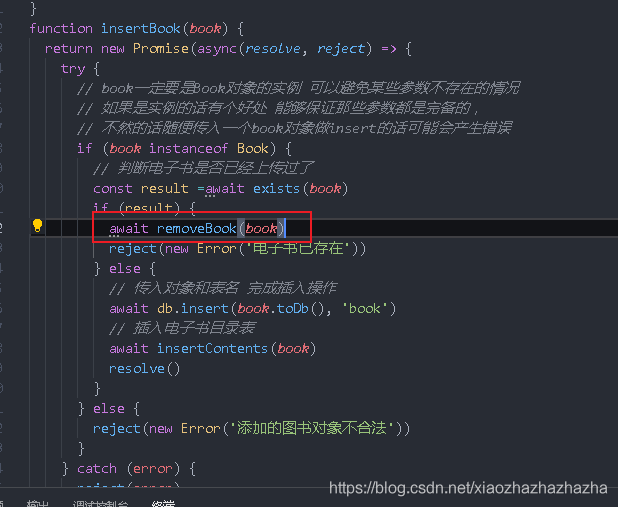
First, write the exists function to judge whether the e-book exists
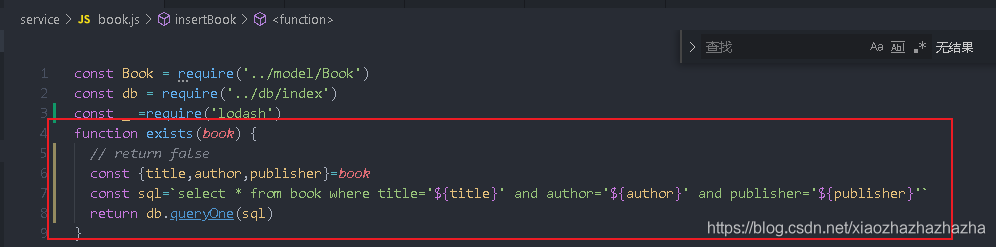
In order to facilitate the test, put the front-end this setDefault(); Comment out

In this case, you need to remove the currently uploaded e-book
function removeBook(book) {
if(book){
// Delete relevant files (e-book files, cover pages, unzipped files)
book.reset()
}
}
Enter book js
// Determine whether there is a static method for the path
static pathExists(path){
if(path.startsWith(UPLOAD_PATH)){
return fs.existsSync(path)
}else{
return fs.existsSync(Book.genPath(path))
}
}
Let's simulate it
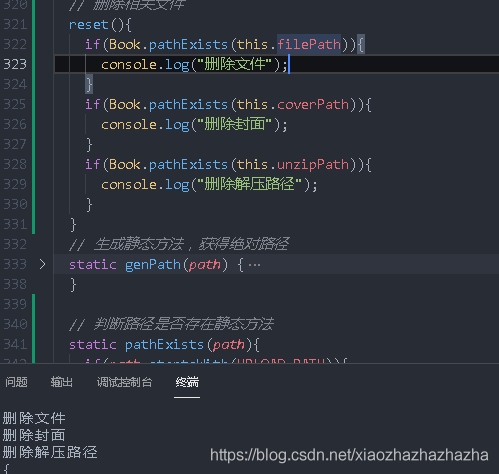
Single file deletion: unlinkSync
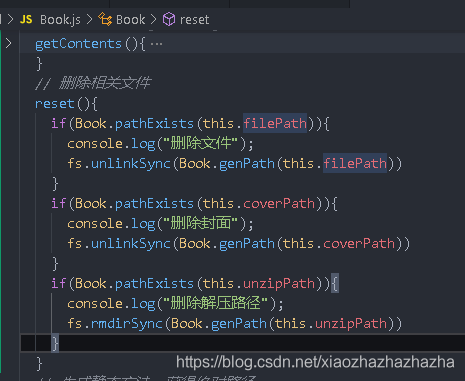
When deleting the decompression path, remember to add recursive: true FS rmdirSync(Book.genPath(this.unzipPath),{recursive:true})
This keeps only one file
The teacher added another operation to delete the database. I don't know why to add this step. It should not be written to the database, so I don't think I need to add this logic to delete the database
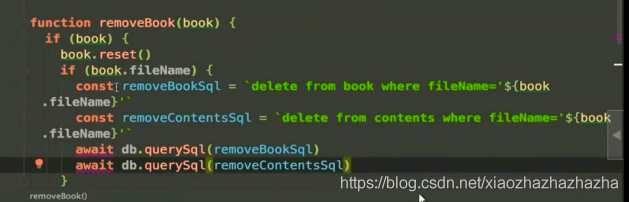
E-book query api
To realize the editing function, first get the filename and query the directory and content in the database according to the filename
It is returned to the front end after finding it, so you need to receive a parameter in the route
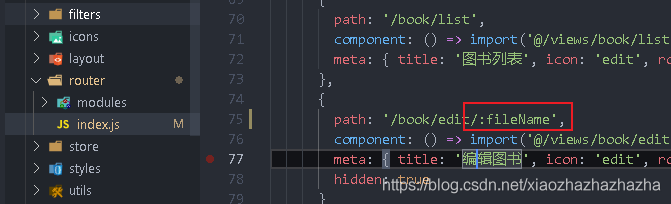
After that, you can click detail Get dynamic routing parameters from Vue
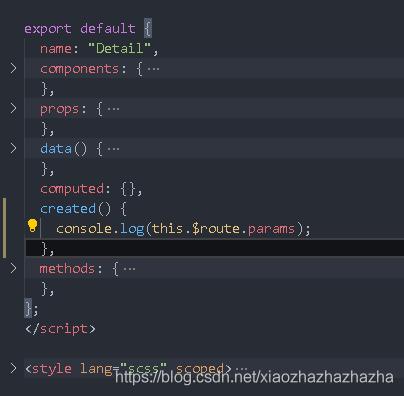
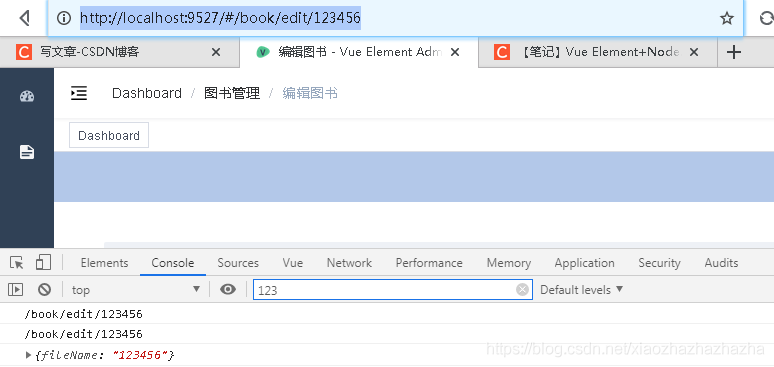
thinking
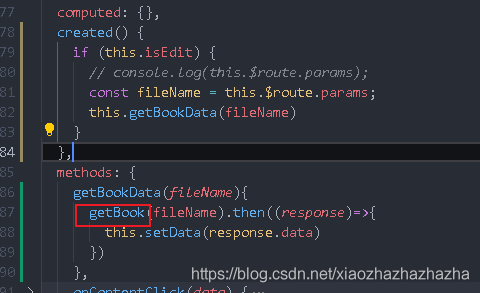
Now we need to implement the api of getBook
src/api/book.js
Note that the get method uses params. If it is post, it uses data
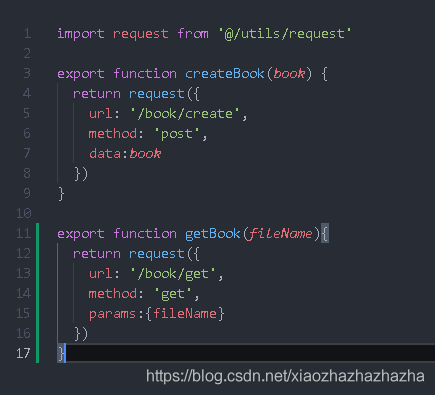

Server:
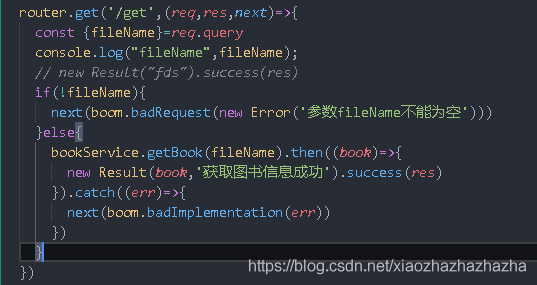
router.book.js
Rough frame
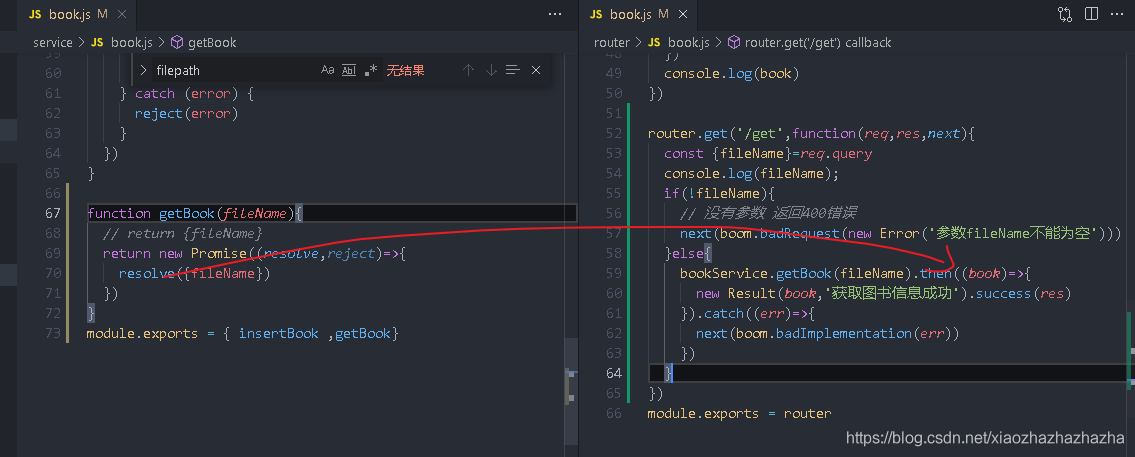
The getBook method is in service / book JS
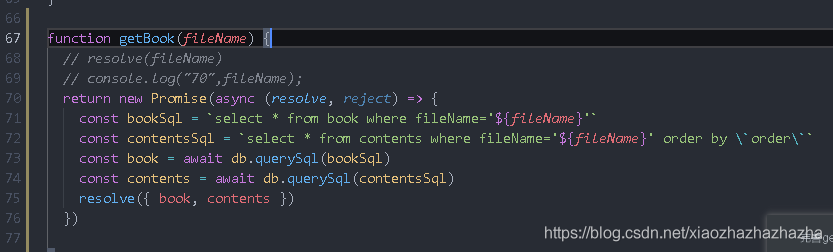
Improve getBook logic
You need to query the book table and contents table
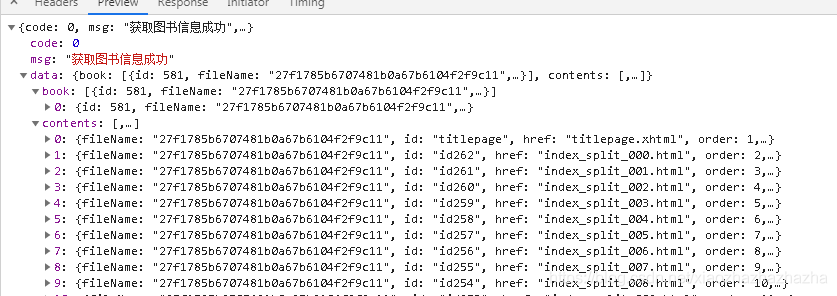
Further processing to show the data
resolve(book[0])
But there is no title, cover or catalogue
Solve the problem of the cover first
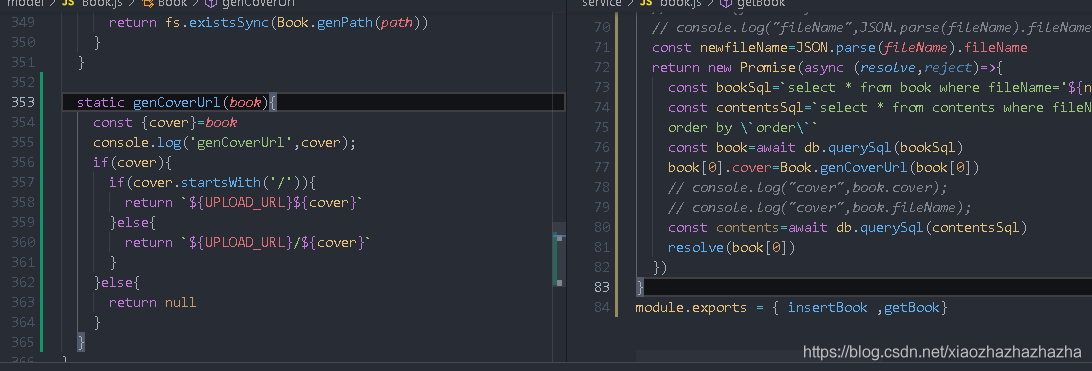
To solve the problem of directory display
Now the contents is an array structure. You need to convert the array into a contenttree
In fact, we have done this logic before,
const chapterTree = []
chapters.forEach(c => {
// We have defined and assigned the label attribute earlier
c.children = []
//If pid is not recognized, it indicates that it is a primary directory
if (c.pid === '') {
chapterTree.push(c)
} else {
// If pid is not empty, it means that if there is a parent, find the parent first
const parent = chapters.find(_ =>
// If it's the same, you'll find the parent
_.navId === c.pid
)
parent.children.push(c)
}
})
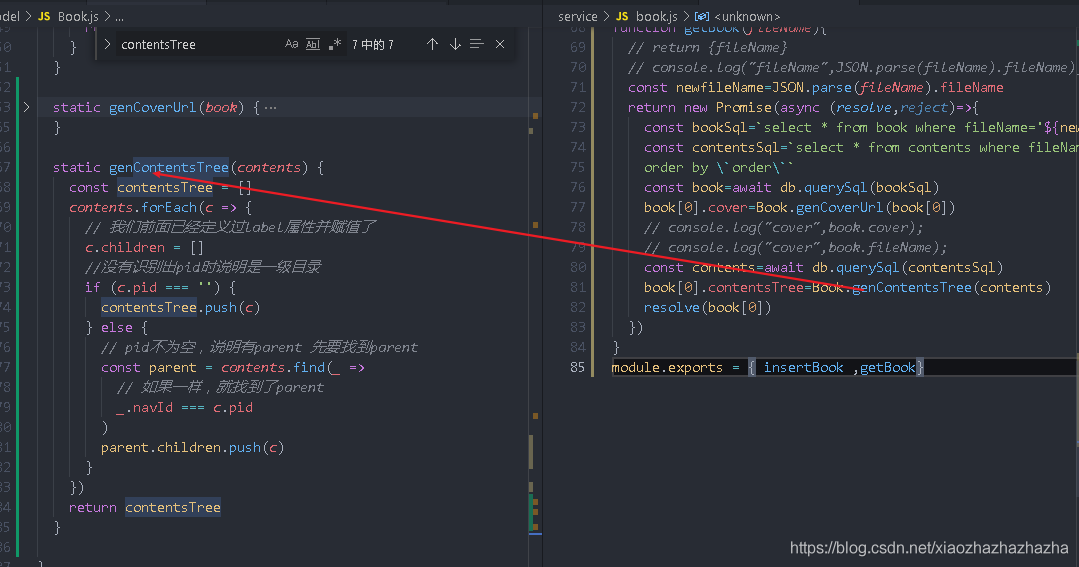
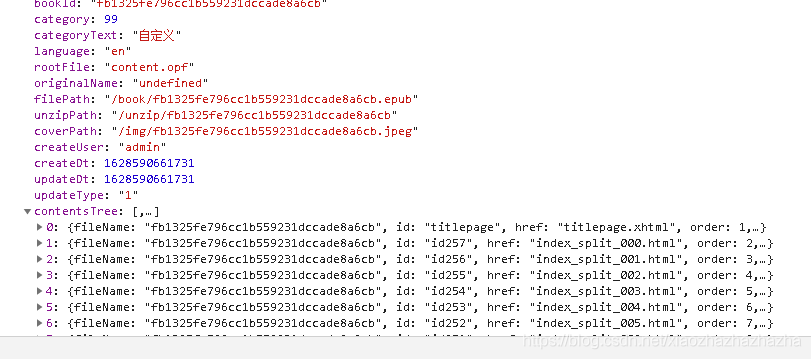
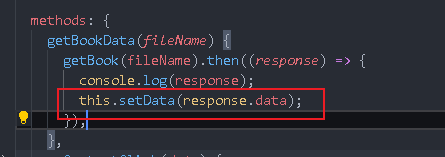
At this time, the directory still can't come out. Change the front-end code
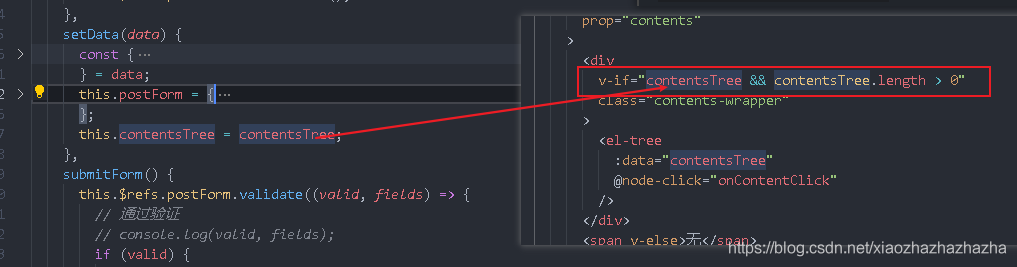
The next unsolved problem is the file information
Just assign a value to fileList
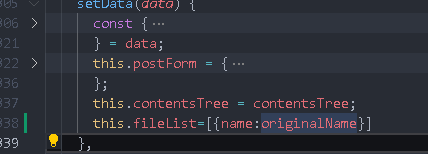
Edit eBook
Next, write the logic here
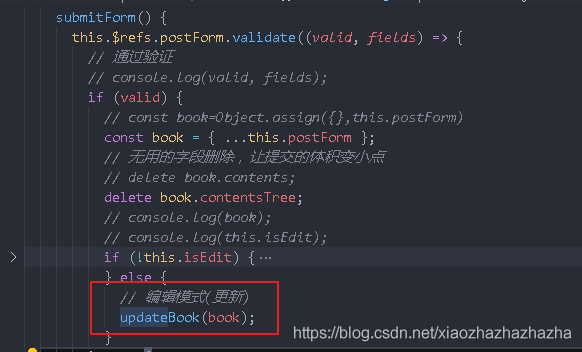
An interface is added to the front end
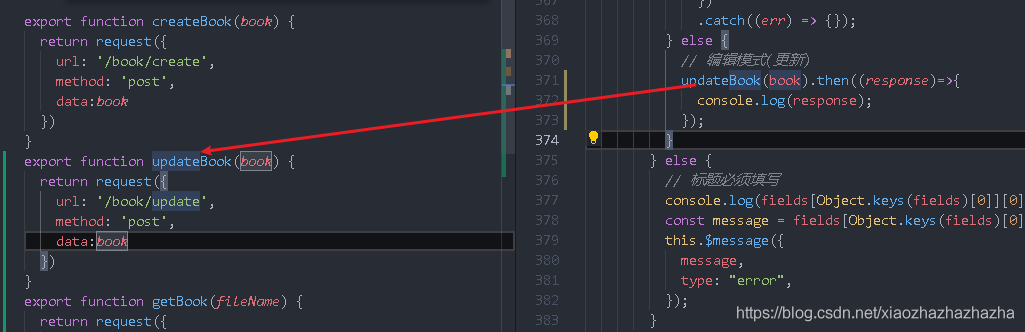
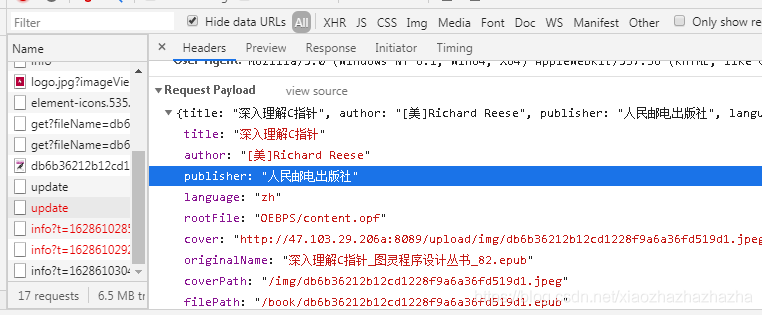
Although the interface has not been developed yet, you can still go to the network to have a look. You can find that the interface and parameters can be sent correctly
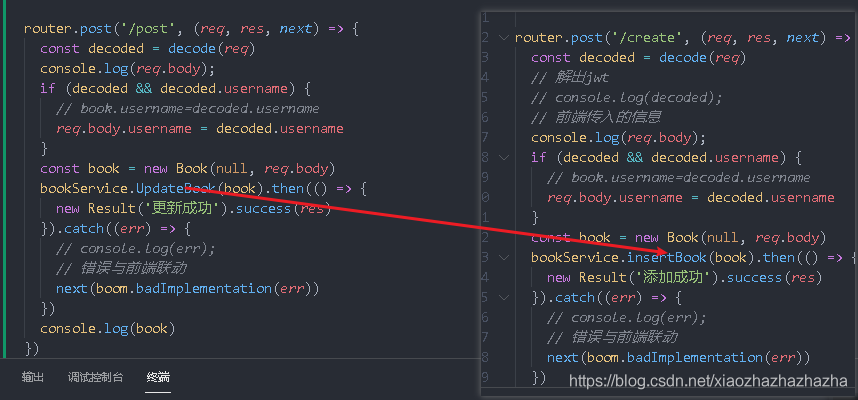
Now the server adds an interface
It is very similar to the previous create interface (it should be update if written incorrectly)
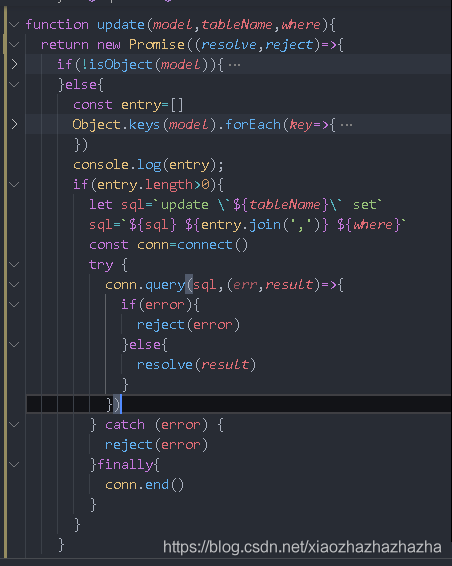
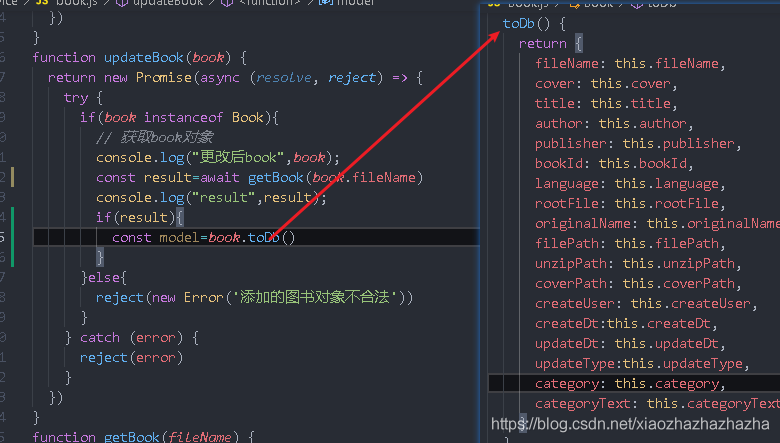
Now go to service / book JS to write the logic of updateBook
front end
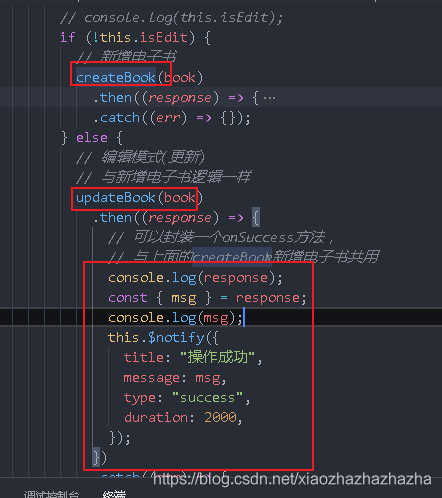
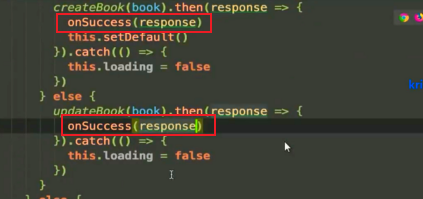
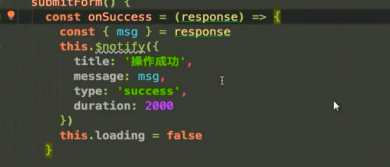
Book here Filename should be quoted
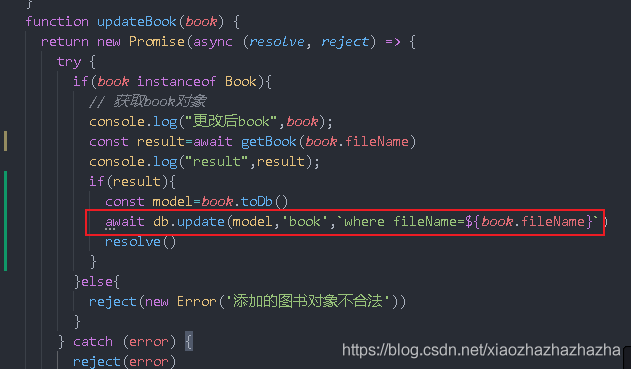
Write an update method to the database operation file