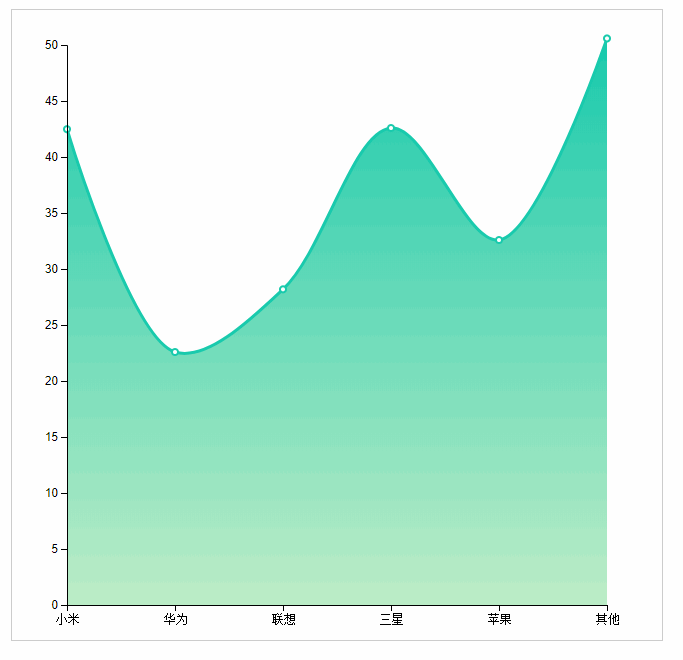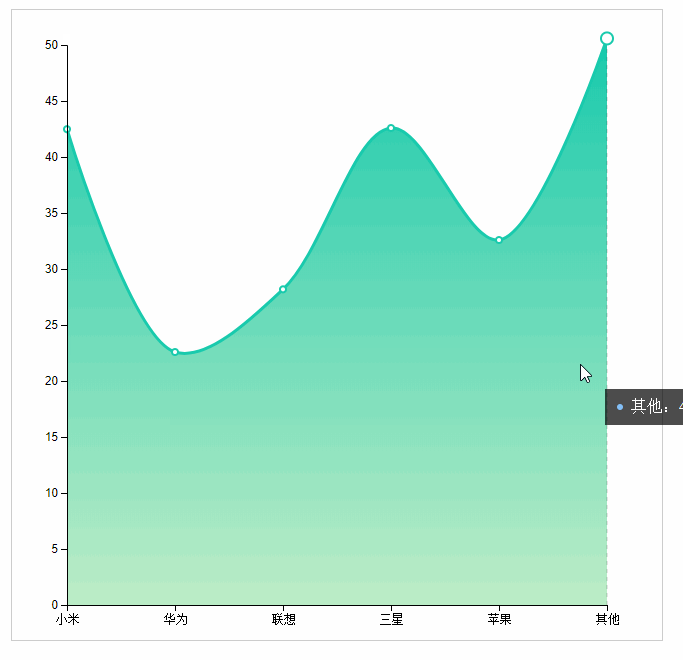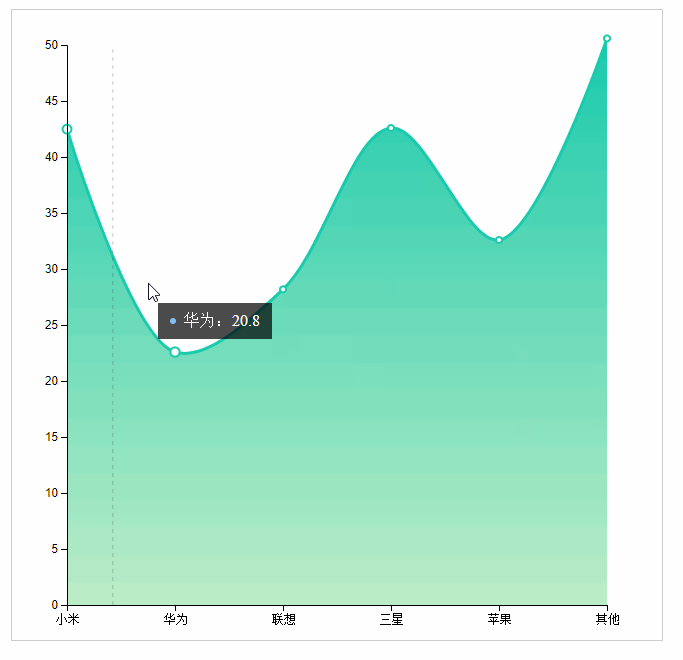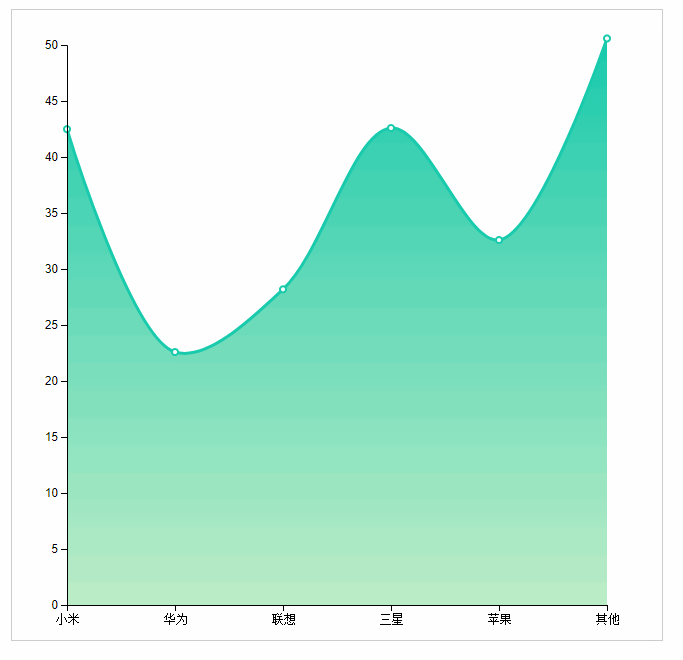
Area map reference ecrats address: http://echarts.baidu.com/examples/editor.html?c=area-stack
Area map github address: https://github.com/dkr380205984/myComponent/blob/master/src/page/d3/area.vue
There are almost no difficulties in the implementation of area map. If you have known how to write my broken line map.
Function point: mouse move in event is a little more complex, in fact, it is a calculation problem. See code Notes for details.
Special point: x-axis abscissa. The scale used is not conventional. In order to generate a better picture, it is necessary to select the scale with no blank on both sides.
//x-axis scale
//d3.scalePoint - creates an ordinal fixed-point scale. Leave no space on either side of the x-axis
//d3.scaleBand - creates an ordinal segmented scale. Leaves both sides of the x-axis blankThis series is an advanced series. If you don't understand the previous articles, you may need to look at the first article of each series. I don't take the trouble to write the general configuration items like the teacher over and over again, which also wastes my personal time. If you don't understand anything, you can leave a message and ask questions. I think the notes are clear.
Source code is as follows
<template>
<div id="area"></div>
</template>
<script>
import * as d3 from 'd3'
export default {
data: function () {
return {
data: [{
name: 'millet',
value: 40.7
}, {
name: 'HUAWEI',
value: 20.8
}, {
name: 'association',
value: 26.4
}, {
name: 'Samsung',
value: 40.8
}, {
name: 'Apple',
value: 30.8
}, {
name: 'Other',
value: 48.8
} ],
width: '',
heigth: '',
padding: {
left: '30px',
right: '30px',
top: '20px',
bottom: '20px'
}
}
},
methods: {
getStyle: function (obj, attr) {
if (obj.currentStyle) {
return obj.currentStyle[attr]
} else {
return document.defaultView.getComputedStyle(obj, null)[attr]
}
}
},
mounted () {
let _this = this
let dom = document.getElementById('area')
// dom container width and height, parameter padding
let width = parseFloat(this.width) || parseFloat(this.getStyle(dom, 'width'))
let height = parseFloat(this.height) || parseFloat(this.getStyle(dom, 'height'))
let padLeft = parseFloat(this.padding.left)
let padRight = parseFloat(this.padding.right)
let padTop = parseFloat(this.padding.top)
let padBottom = parseFloat(this.padding.bottom)
let minHeight = parseFloat(this.minHeight) || 0
if (isNaN(width) || isNaN(height)) {
console.error('width or height Parameter error')
return
}
// Check whether there is a problem with the padding parameter
if (isNaN(padLeft) || isNaN(padRight) || isNaN(padTop) || isNaN(padBottom)) {
console.error('padding Parameter error')
return
}
// Start drawing, create svg canvas
let svg = d3.select('#area')
.append('svg')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height)
// x-axis scale
// d3.scalePoint - creates an ordinal fixed-point scale. Leave no space on either side of the x-axis
// d3.scaleBand - creates an ordinal segmented scale. Leaves both sides of the x-axis blank
// It looks more beautiful without leaving blank here
let xData = _this.data.map((item) => item.name)
let xScale = d3.scalePoint().domain(xData).range([0, width - padLeft - padRight])
let xAxis = d3.axisBottom().scale(xScale)
// y scale
let yData = _this.data.map((item) => item.value)
let max = d3.max(yData)
let yScale = d3.scaleLinear().domain([0, max]).range([height - padTop - padBottom, minHeight]).nice()
max = yScale.domain()[1]
let yAxis = d3.axisLeft().scale(yScale)
// Create a color transition before creating the region generator
let defs = svg.append('defs')
let linearGradient = defs.append('linearGradient')
.attr('id', 'linearColor')
.attr('x1', '0%')
.attr('y1', '0%')
.attr('x2', '0%')
.attr('y2', '100%')
let a = '#19CAAD'
let b = '#BEEDC7'
linearGradient.append('stop')
.attr('offset', '0%')
.style('stop-color', 'white')
.style('stop-color', a.toString())
linearGradient.append('stop')
.style('stop-color', 'white')
.attr('offset', '100%')
.style('stop-color', b.toString())
// Create a region generator
let area = d3.area()
.x(function (d, i) {
return xScale(d.name) + padLeft
// Return padleft + (width - padleft - padright) / "this. Data. Length * (I + 0.5) / / set x0 and x1 accessors. Of course, you can set them separately. It's unnecessary
})
.y0(function (d, i) {
return height - padBottom // Set y0 to x-axis
})
.y1(function (d, i) {
return yScale(d.value)
})
.curve(d3.curveCatmullRom)
svg.append('path')
.attr('d', area(_this.data))
.style('fill', 'url(#' + linearGradient.attr('id') + ')')
// Add a line
let line = d3.line()
.x(function (d, i) {
// There's a problem with xScale
return padLeft + xScale(d.name)
})
.y(function (d, i) {
return yScale(d.value)
})
.curve(d3.curveCatmullRom)
svg.append('path')
.attr('stroke', '#19CAAD')
.attr('stroke-width', '3px')
.attr('fill', 'none')
.attr('class', 'line')
.attr('d', line(_this.data))
// Add circle description
let circle = svg.selectAll('.circle')
.data(_this.data)
.enter()
.append('circle')
.attr('class', 'circle')
.style('fill', 'white')
.style('stroke', '#19CAAD')
.style('stroke-width', '2')
.attr('r', 3)
.attr('cx', function (d, i) {
return padLeft + xScale(d.name)
})
.attr('cy', function (d) {
return yScale(d.value)
})
// Complete the animation by masking
// Design idea: add a mask, cover the area map, and then pan left to right, which looks like the animation effect of the area map itself
let shadow = svg.append('rect')
.attr('width', width)
.attr('height', height)
.style('fill', 'white')
.attr('x', 0)
// Move mask, complete animation
shadow.transition()
.delay(500)
.duration(2500)
.ease(d3.easeLinear)
.attr('x', width)
.attr('width', 0)
// Add toolbips
let toolTips = d3.select('body').append('div')
.attr('class', 'toolTips')
.style('opacity', 0)
.style('position', 'absolute')
// Add guides
let subline = svg.append('line')
.attr('class', 'subline')
.attr('stroke', 'rgba(0,0,0,0.2)')
.attr('stroke-width', '1')
// Set dashed line
.attr('stroke-dasharray', '4,4')
.attr('y1', height - padBottom)
.attr('y2', padTop)
.style('opacity', 0)
svg.on('mouseover', function () {
toolTips.style('opacity', 1)
subline.style('opacity', 1)
})
svg.on('mousemove', function () {
// By calculation, which node is closer to the current mouse
let count = (d3.event.offsetX - padLeft) / (width - padLeft - padRight) * (_this.data.length - 1)
count = Math.round(count) >= _this.data.length ? _this.data.length - 1 : count // Determine whether count is the value of > = data.length, and establish the boundary value
let node = _this.data[Math.round(count)]
let html = `<div class="clearfix"><div class="border" style="background:'#F4606C'"></div><span>${node.name}: ${node.value}</span></div>`
let mouseX = d3.event.clientX + 25
let mouseY = d3.event.clientY + 25
// If your style uses scoped, your style should be written to App.vue, otherwise the style of the inserted element will not take effect
toolTips.html(`<div class="tolTp">${html}</div>`)
.style('left', mouseX + 'px')
.style('top', mouseY + 'px')
// Animate the circle
circle
.transition()
.ease(d3.easeBounceOut)
.duration(100)
.attr('r', function (d, i) {
if (i === Math.round(count)) {
return 6
} else {
return 3
}
})
subline
.transition()
.duration(50)
.attr('x1', padLeft + xScale(node.name))
.attr('x2', padLeft + xScale(node.name))
})
svg.on('mouseout', function (d) {
subline.style('opacity', 0)
toolTips.style('opacity', 0)
toolTips.html('')
circle.transition()
.ease(d3.easeBounceOut)
.duration(100).attr('r', function (d, i) { return 3 })
})
// Last added due to the highest level of axis
// Add x axis
svg.append('g')
.attr('transform', 'translate(' + padLeft + ',' + (height - padBottom) + ')')
.call(xAxis)
.style('font-size', '12px')
// Draw y axis
svg.append('g')
.attr('transform', 'translate(' + padLeft + ',' + padTop + ')')
.call(yAxis)
.style('font-size', '12px')
}
}
</script>
<style lang="less">
#area{
width: 600px;
height: 600px;
margin: 20px 20px;
padding: 15px 25px;
border:1px solid #cccccc;
position: relative;
}
.tolTp{
padding:8px 12px;
background: rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.7);
color:white;
.border{
width: 6px;
height: 6px;
border-radius: 3px;
background: #83bff6;
float: left;
margin:7px 8px 7px 0;
}
span{
float: left;
line-height: 20px;
}
}
</style>