0x00 introduction
In case of hacker intrusion, system crash or other security events affecting the normal operation of business, it is urgent to deal with them at the first time, so that the enterprise's network information system can resume normal operation in the shortest time, further find the source of intrusion, restore the process of intrusion accident, and give solutions and preventive measures to recover or reduce economic losses for the enterprise.
0x01 intrusion troubleshooting ideas
1.1 account security
Common query commands
Step 1 user information file
cat /etc/passwd ----------------------------------------- root:x:0:0:root:/root:/bin/bash account:password:UID:GID:GECOS:directory:shell ----------------------------------------------- User name: Password: user ID: group ID: User description: Home Directory: after login shell Note: only local login is allowed without password, and remote login is not allowed
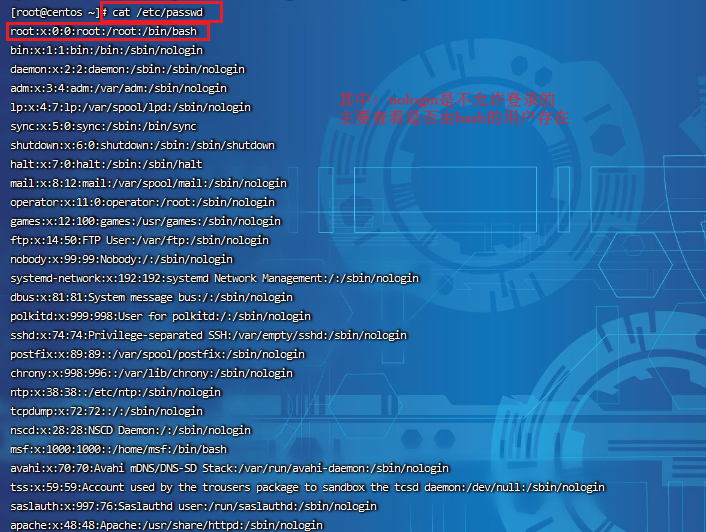
Step 2: view the shadow file
cat /etc/shadow ---------------------------------------------------------- root:$6$oGs1PqhL2p3ZetrE$X7o7bzoouHQVSEmSgsYN5UD4.kMHx6qgbTqwNVC5oOAouXvcjQSt.Ft7ql1WpkopY0UV9ajBwUt1DpYxTCVvI/:16809:0:99999:7::: User name: encryption password: date of last password modification: time interval between two password modifications: password validity: warning days after password modification expires: Grace days after password Expiration: account expiration time: reserved ----------------------------------------------

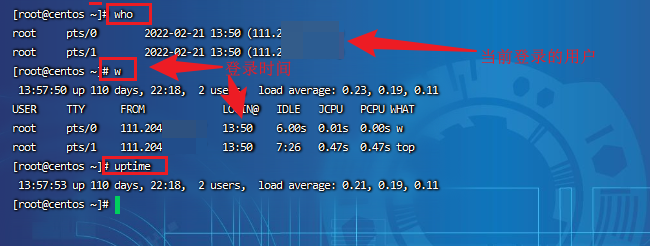
Step 3: check user login
who View current login user( tty Local login pts (remote login) w Check the system information and want to know the user's behavior at a certain time uptime Check the login time, number of users and load status
Intrusion troubleshooting ideas
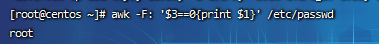
Step 1: query the privileged user (uid is 0)
awk -F: '$3==0{print $1}' /etc/passwd
The third column is uid Values, filtering uid=0 Yes, output
The second step is to query the account information that can be logged in remotely
awk '/\$1|\$6/{print $1}' /etc/shadow
Filter out the user information with password

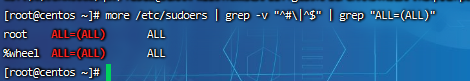
Step 3: check whether other accounts except root account have sudo permission.
If it is not necessary for management, sudo permission should be deleted for ordinary account
more /etc/sudoers | grep -v "^#\|^$" | grep "ALL=(ALL)"
Step 4 disable or delete redundant and suspicious accounts
usermod -L user Disable account, account cannot log in,/etc/shadow The second column is ! start userdel user delete user user userdel -r user Will delete user User, and will /home Directory user Delete the directory together
1.2 historical orders
Common query commands
Pass bash_history file to view the system commands executed by the account
1,root User's historical commands
histroy
2,open /home Under each account directory .bash_history,View the historical commands executed by ordinary accounts.
Add login for historical commands IP Address, execution time and other information:
1)Save 10000 commands
sed -i 's/^HISTSIZE=1000/HISTSIZE=10000/g' /etc/profile
2)stay/etc/profile Add the following line number configuration information at the end of the file:
######jiagu history xianshi#########
USER_IP=`who -u am i 2>/dev/null | awk '{print $NF}' | sed -e 's/[()]//g'`
if [ "$USER_IP" = "" ]
then
USER_IP=`hostname`
fi
export HISTTIMEFORMAT="%F %T $USER_IP `whoami` "
shopt -s histappend
export PROMPT_COMMAND="history -a"
######### jiagu history xianshi ##########
3)source /etc/profile Make configuration effective
Generation effect: 1 2018-07-10 19:45:39 192.168.204.1 root source /etc/profile
3,Clear history operation command: history -c
However, this command does not clear the records saved in the file, so it needs to be deleted manually .bash_profile Records in the file.
Intrusion troubleshooting ideas
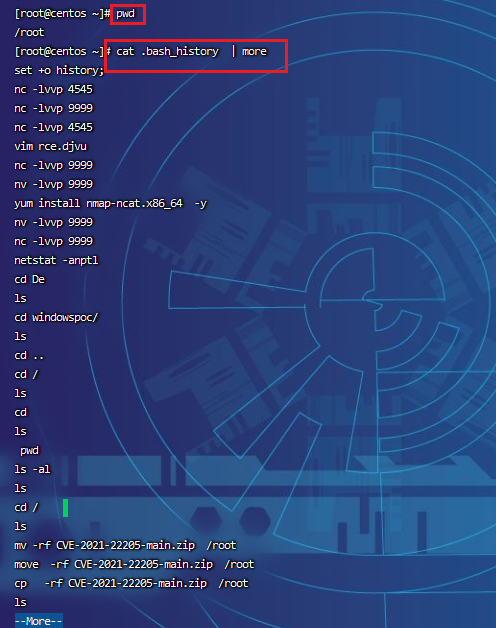
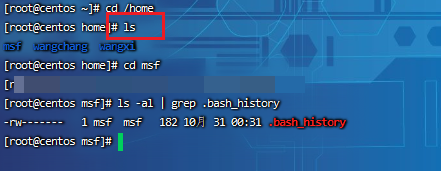
Enter the user directory and export the history command.
cd /home or root directory
cat .bash_history >> history.txt
1.3 check the abnormal port
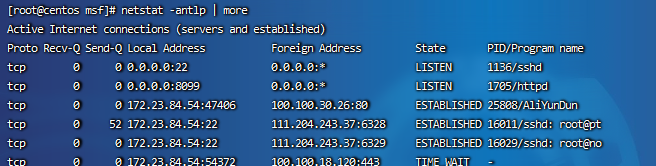
The first step is to use the netstat network connection command to analyze the suspicious port, IP and PID
netstat -antlp | more
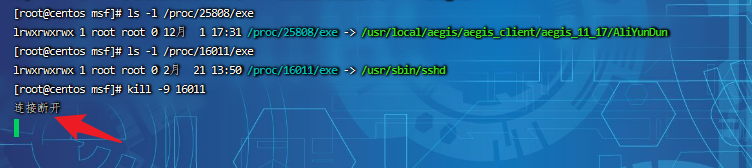
Step 2: check the process file path corresponding to the next pid,
function ls -l /proc/$PID/exe or file /proc/$PID/exe($PID Is the corresponding pid No.)
1.4 check the abnormal process
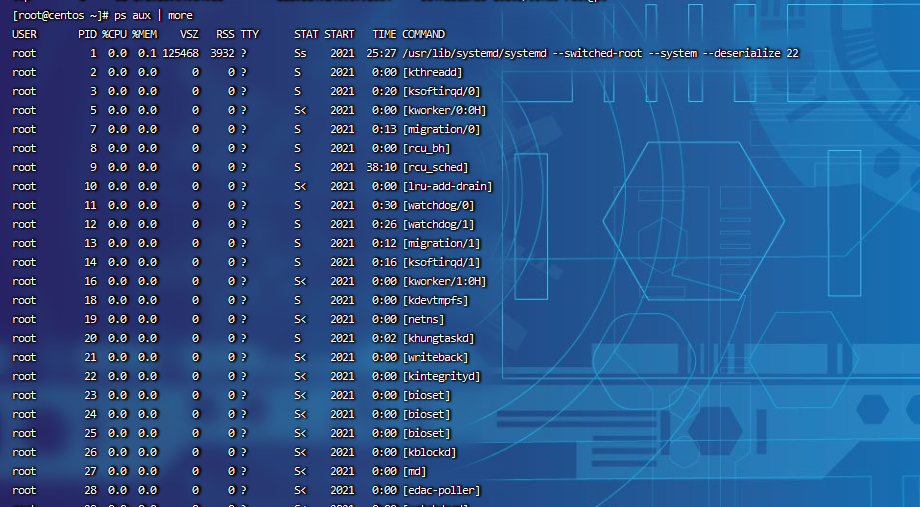
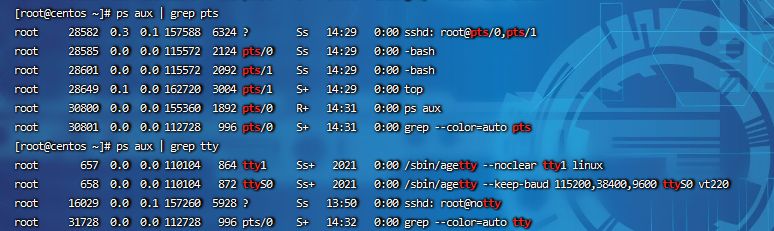
Use the ps command to analyze the process
ps aux | grep pid ps aux | grep pts ps aux | grep tty
1.5 check startup items
Common query commands
The first step is to understand the schematic diagram of system operation level:
| Run level | meaning |
|---|---|
| 0 | Shut down |
| 1 | Single user mode, which can be imagined as the security mode of windows, is mainly used for system repair |
| 2 | Incomplete command line mode without NFS service |
| 3 | The complete command line mode is the standard character interface |
| 4 | System retention |
| 5 | Graphic mode |
| 6 | Restart |
Step 2: check the run level command runlevel
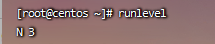
Step 3: view the configuration file
https://moments.blog.csdn.net/article/details/100107530
Intrusion troubleshooting ideas
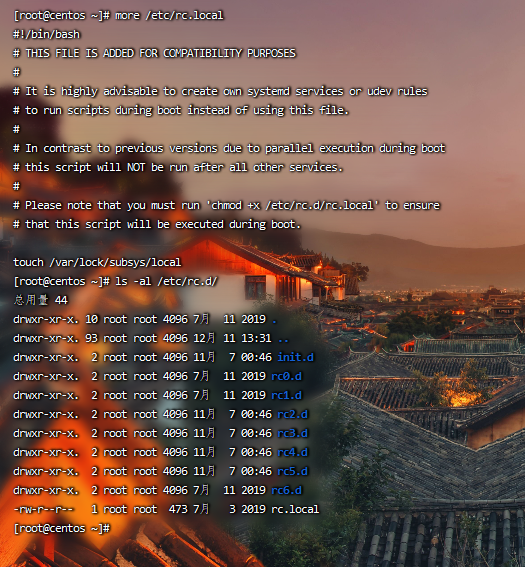
Startup item file:
more /etc/rc.local /etc/rc.d/rc[0~6].d ls -l /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/
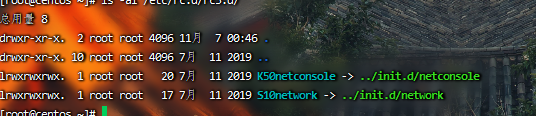
1.6 check scheduled tasks
Common query commands
Method 1: create a scheduled task through crontab
Basic command
crontab -l List a user cron Service details Tips: Written by default crontab The file is saved in (/var/spool/cron/User name e.g: /var/spool/cron/root crontab -r Delete each user cront task(Caution: delete all scheduled tasks) crontab -e Use the editor to edit the current crontab file For example:*/1 * * * * echo "hello world" >> /tmp/test.txt Write files every minute
Method 2: use anacron command to realize asynchronous scheduled task scheduling
Use case: run / home / backup.exe every day SH script:
vi /etc/anacrontab ----------------- @daily 10 example.daily /bin/bash /home/backup.sh ------------------
When the machine is in backup SH is expected to be turned off when it is running. anacron will run it ten minutes after the machine is turned on, instead of waiting for another seven days.
Intrusion troubleshooting ideas
Focus on whether there are malicious scripts in the following directories
/var/spool/cron/* /etc/crontab /etc/cron.d/* /etc/cron.daily/* /etc/cron.hourly/* /etc/cron.monthly/* /etc/cron.weekly/ /etc/anacrontab /var/spool/anacron/*
Tips:
more /etc/cron.daily/* View all files in the directory
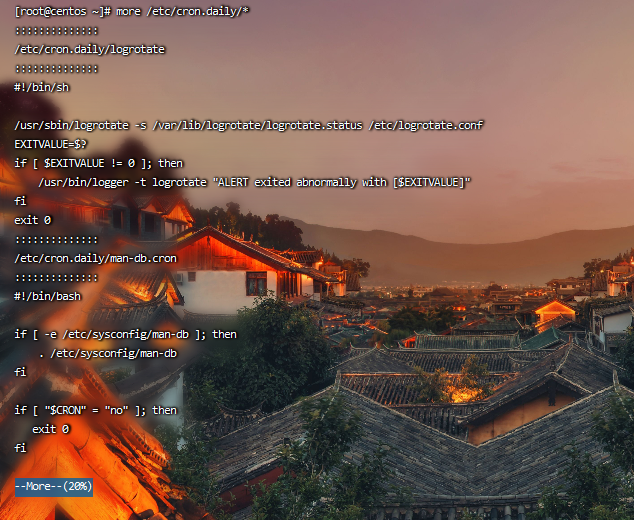
1.7 check the system log
Default log storage location: / var/log/
Check the log configuration: more / etc / rsyslog conf
| log file | explain |
|---|---|
| /var/log/cron | Logs related to system scheduled tasks are recorded |
| /var/log/cups | Log of printing information |
| /var/log/dmesg | It records the information of the kernel self-test when the system is powered on. You can also use the dmesg command to directly view the kernel self-test information |
| /var/log/mailog | Mail record information |
| /var/log/message | A log recording important information of the system. This log file will record most important information of the Linux system. If there is a problem with the system, the first thing to check should be this log file |
| /var/log/btmp | Log the error login log. This file is a binary file and cannot be viewed directly by vi. instead, use the lastb command to view it |
| /var/log/lastlog | Record the log of the last login time of all users in the system. This file is a binary file and cannot be viewed directly by vi. instead, use the lastlog command to view it |
| /var/log/wtmp | Permanently record the login and logout information of all users, and record the startup, restart and shutdown events of the system. Similarly, this file is also a binary file, which cannot be viewed directly by vi, but needs to be viewed by using the last command |
| /var/log/utmp | Record the information of the currently logged in user. This file will change with the login and logout of the user, and only record the information of the currently logged in user. Similarly, this file can't be queried directly by vi, but by using w,who,users and other commands |
| /var/log/secure | Record the authentication and authorization information. Any program involving account and password will be recorded, such as SSH login, su switching users, sudo authorization, and even adding users and modifying user passwords will be recorded in this log file |
Log analysis skills:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41901122/article/details/121729999?spm=1001.2014.3001.5501
Extract
In the years of struggle,
Worthy of every inch of time.
At the top of the mountain,
The river surged above the peaks,
Feel the long wind more mighty.