http://blog.csdn.net/jasonliuvip/article/details/23888851
As we mentioned earlier, there is a problem with sorted list-based timers: adding timers is inefficient.The time frame we discuss below solves this problem.
In the figure, this is a simple time wheel:
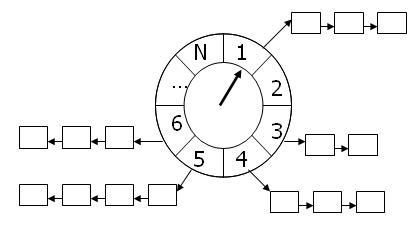
The solid pointer in the wheel points to a slot on the wheel, which rotates clockwise at a constant speed. Each step of rotation points to the next slot, and each turn is called a tick.
The time of a tick is called slot interval, which is actually the heart beat time.
The wheel has N slots, so it runs for one week at N x si.Each slot points to a timer list, and the timers on each list have the same characteristics: their timing times differ by an integer multiple of N*si.The time wheel uses this relationship to hash timers into different chains.
If the pointer now points to the slot CS and we want to add a timer with a time of ti, the timer will be inserted into the chain table corresponding to ts (timer slot): ts = (cs + (ti / si))%N
A timer based on a sorted list uses a unique list of chains to manage all timers, so the efficiency of insertion decreases as the number of timers increases.The time wheel uses the idea of a hash table to hash timers across different chains.
In this way, the number of timers on each chain table will be significantly reduced, and the efficiency of insertion operation will be less affected by the number of timers.
Obviously, for the time wheel, to improve the timing accuracy, the si value must be small enough; to improve the efficiency of execution, the N value must be large enough.
Let's implement a simple time wheel, just one wheel.Complex time wheels can have multiple, different wheels have different granularities.The two adjacent wheels make a high-precision turn, and the low-precision ones only move forward one slot, just like a water meter.
For a time wheel, the time complexity to add a timer is O(1), to delete a timer is O(1), and to execute a timer is O(n).
However, it is actually much more efficient to execute a timer than O(n), because the time wheel spreads all timers across different chains, the more slots the time wheel has, the more entries the Hash list has, and the fewer timers on each chain.Furthermore, our code only uses one time wheel, and when implemented with multiple wheels, its time complexity will approach O(1).
For the comparison of timer implementation under linux, you can see this article, which is very good: http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-cn-timers/
1. Code:
- //tw_timer.h
- #ifndef __TIME_WHEEL__
- #define __TIME_WHEEL__
- #include <time.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #define BUFFER_SIZE 64
- class tw_timer;
- //Client Data
- struct client_data
- {
- sockaddr_in address;
- int sockfd;
- char buf[BUFFER_SIZE];
- tw_timer *timer;
- };
- //timer
- class tw_timer
- {
- public:
- tw_timer(int rot, int ts)
- :next(NULL), prev(NULL), rotation(rot), time_slot(ts) {}
- public:
- int rotation; //The timer takes effect after how many turns on the timewheel
- int time_slot; //Which slot on the time wheel does the timer belong to
- void (*cb_func)(client_data*); //Callback function of timer
- client_data *user_data; //Client Data
- tw_timer *prev; //Point to the last timer
- tw_timer *next; //Point to Next Timer
- };
- //Time Wheel
- class time_wheel
- {
- public:
- time_wheel();
- ~time_wheel();
- tw_timer* add_timer(int timeout); //Create a timer based on the timer value and insert it in the right place
- void del_timer(tw_timer *timer); //Delete Target Timer
- void tick(); //Call this function after time has elapsed, and the time wheel rolls forward one slot interval
- private:
- static const int N = 60; //Number of slots on the time wheel
- static const int TI = 1; //Slot interval time, i.e. one turn per second
- int cur_slot; //Current groove of time wheel
- tw_timer *slots[N]; //Slots in the timewheel, where each element points to a timer chain
- };
- #endif
- //tw_timer.cpp
- #include "tw_timer.h"
- time_wheel::time_wheel():cur_slot(0)
- {
- //Initialize the head nodes of each slot
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
- slots[i] = NULL;
- }
- time_wheel::~time_wheel()
- {
- //Traverse through each slot and destroy the timer
- for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i) {
- tw_timer *tmp = slots[i];
- while (tmp) {
- slots[i] = tmp->next;
- delete tmp;
- tmp = slots[i];
- }
- }
- }
- tw_timer* time_wheel::add_timer(int timeout)
- {
- if (timeout < 0)
- return NULL;
- int ticks = 0; //Total ticks required to insert timer
- if (timeout < TI)
- ticks = 1;
- else
- ticks = timeout / TI;
- int rotation = ticks / N; //Calculate how many turns the timer to insert will turn on the timewheel before triggering
- int ts = (cur_slot + ticks) % N; //Calculate where the timer to hold should be inserted
- //int ts = (cur_slot + (ticks %N)) % N;
- //Create a timer that is triggered after the rotation circle is rotated by the time wheel and is located in slot ts
- tw_timer *timer = new tw_timer(rotation, ts);
- //If the slot is empty, it has a new timer inserted and set to the head node of the slot
- if (!slots[ts]) {
- printf("add timer, rotation is %d, ts is %d, cur_slot is %d\n",
- rotation, ts, cur_slot);
- slots[ts] = timer;
- }
- else {
- timer->next = slots[ts];
- slots[ts]->prev = timer;
- slots[ts] = timer;
- }
- return timer;
- }
- void time_wheel::del_timer(tw_timer *timer)
- {
- if (!timer)
- return;
- int ts = timer->time_slot;
- if (timer == slots[ts]) { //If it is a header node
- slots[ts] = slots[ts]->next;
- if (slots[ts])
- slots[ts]->prev = NULL;
- delete timer;
- }
- else {
- timer->prev->next = timer->next;
- if (timer->next)
- timer->next->prev = timer->prev;
- delete timer;
- }
- }
- void time_wheel::tick()
- {
- //Get the head node of the current slot on the timewheel
- tw_timer *tmp = slots[cur_slot];
- printf("current slot is %d\n", cur_slot);
- while (tmp) {
- printf("tick the timer once\n");
- //If the rotation value of the timer is greater than 0, it is not processed
- if (tmp->rotation > 0) {
- tmp->rotation--;
- tmp = tmp->next;
- }
- else {
- tmp->cb_func(tmp->user_data);
- if (tmp == slots[cur_slot]) {
- printf("delete header in cur_slot\n");
- slots[cur_slot] = tmp->next;
- delete tmp;
- if (slots[cur_slot])
- slots[cur_slot]->prev = NULL;
- tmp = slots[cur_slot];
- }
- else {
- tmp->prev->next = tmp->next;
- if (tmp->next)
- tmp->next->prev = tmp->prev;
- tw_timer *tmp2 = tmp->next;
- delete tmp;
- tmp = tmp2;
- }
- }
- }
- //Update the current slot of the time wheel to reflect the rotation of the time wheel
- cur_slot = ++cur_slot % N;
- }
- //nonactive_conn.cpp
- //Close inactive connections
- #include <sys/types.h>
- #include <sys/socket.h>
- #include <netinet/in.h>
- #include <arpa/inet.h>
- #include <stdio.h>
- #include <stdlib.h>
- #include <unistd.h>
- #include <string.h>
- #include <errno.h>
- #include <fcntl.h>
- #include <sys/epoll.h>
- #include <assert.h>
- #include <signal.h>
- #include <pthread.h>
- #include "tw_timer.h"
- #define FD_LIMIT 65535
- #define MAX_EVENT_NUMBER 1024
- #define TIMESLOT 100
- static int pipefd[2];
- static time_wheel client_conn_time_wheel;
- static int epollfd = 0;
- int setnonblocking(int fd); //Set up non-blocking
- int addfd(int epollfd, int fd); //Add Descriptor Event
- void sig_handler(int sig); //Signal processing function
- void addsig(int sig); //Add Signal Processing Function
- void timer_handler(); //TimerTask
- void cb_func(client_data *user_data); //Timer callback function
- int main(int argc, char *argv[])
- {
- if (argc != 2) {
- fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s port\n", argv[0]);
- return 1;
- }
- int port = atoi(argv[1]);
- int ret = 0;
- int error;
- struct sockaddr_in address;
- bzero(&address, sizeof(address));
- address.sin_family = AF_INET;
- address.sin_port = htons(port);
- address.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
- int sockfd = socket(PF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
- if (sockfd == -1) {
- fprintf(stderr, "create socket failed\n");
- return 1;
- }
- int reuse = 1;
- ret = setsockopt(sockfd, SOL_SOCKET, SO_REUSEADDR, &reuse, sizeof(reuse));
- if (ret == -1) {
- error = errno;
- while ((close(sockfd) == -1) && (errno == EINTR));
- errno = error;
- return 1;
- }
- if ( (bind(sockfd, (struct sockaddr*)&address, sizeof(address)) == -1) ||
- (listen(sockfd, 5) == -1)) {
- error = errno;
- while ((close(sockfd) == -1) && (errno == EINTR));
- errno = error;
- return 1;
- }
- int epollfd = epoll_create(5);
- if (epollfd == -1) {
- error = errno;
- while ((close(sockfd)) && (errno == EINTR));
- errno = error;
- return 1;
- }
- ret = socketpair(PF_UNIX, SOCK_STREAM, 0, pipefd);
- if (ret == -1) {
- error = errno;
- while ((close(sockfd) == -1) && (errno == EINTR));
- errno = error;
- return 1;
- }
- epoll_event events[MAX_EVENT_NUMBER];
- setnonblocking(pipefd[1]);
- addfd(epollfd, pipefd[0]);
- addfd(epollfd, sockfd);
- //Add Signal Processing
- addsig(SIGALRM);
- addsig(SIGTERM);
- bool stop_server = false;
- client_data *users = new client_data[FD_LIMIT];
- bool timeout = false;
- alarm(1);
- printf("server start...\n");
- while (!stop_server) {
- int number = epoll_wait(epollfd, events, MAX_EVENT_NUMBER, -1);
- if (number < 0 && errno != EINTR) {
- fprintf(stderr, "epoll_wait failed\n");
- break;
- }
- for (int i = 0; i < number; i++) {
- int listenfd = events[i].data.fd;
- if (listenfd == sockfd) {
- struct sockaddr_in client_address;
- socklen_t client_addrlength = sizeof(client_address);
- int connfd;
- while ( ((connfd = accept(listenfd, (struct sockaddr*)&client_address, &client_addrlength)) == -1) &&
- (errno == EINTR));
- addfd(epollfd, connfd);
- users[connfd].address = client_address;
- users[connfd].sockfd = connfd;
- tw_timer *timer = NULL;
- timer = client_conn_time_wheel.add_timer(TIMESLOT);
- if (timer) {
- timer->user_data = &users[connfd];
- timer->cb_func = cb_func;
- users[connfd].timer = timer;
- fprintf(stderr, "client: %d add tw_timer successed\n", connfd);
- }
- else {
- fprintf(stderr, "client: %d add tw_timer failed\n", connfd);
- }
- }
- else if((listenfd == pipefd[0]) && (events[i].events & EPOLLIN)) {
- int sig;
- char signals[1024];
- ret = recv(pipefd[0], signals, sizeof(signals), 0);
- if (ret == -1) {
- continue;
- }
- else if (ret == 0) {
- continue;
- }
- else {
- for (int i = 0; i < ret; i++) {
- switch (signals[i]) {
- case SIGALRM:
- {
- timeout = true;
- break;
- }
- case SIGTERM:
- {
- stop_server = true;
- break;
- }
- default:
- break;
- }
- }
- }
- }
- else if (events[i].events & EPOLLIN) {
- memset(users[listenfd].buf, '\0', BUFFER_SIZE);
- ret = recv(listenfd, users[listenfd].buf, BUFFER_SIZE-1, 0);
- printf("get %d bytes of client data: %s from %d\n",
- ret, users[listenfd].buf, listenfd);
- tw_timer *timer = users[listenfd].timer;
- if (ret < 0) {
- if (errno != EAGAIN) {
- cb_func(&users[listenfd]);
- if (timer)
- client_conn_time_wheel.del_timer(timer);
- }
- }
- else if (ret == 0) {
- cb_func(&users[listenfd]);
- if (timer)
- client_conn_time_wheel.del_timer(timer);
- }
- else {
- if (timer) {
- printf("conntioned..to do adjuest timer\n");
- }
- }
- }
- else {
- }
- }
- if (timeout) {
- timer_handler();
- timeout = false;
- }
- }
- close(sockfd);
- close(pipefd[1]);
- close(pipefd[0]);
- delete[] users;
- return 0;
- }
- int setnonblocking(int fd)
- {
- int old_option = fcntl(fd, F_GETFL);
- int new_option = old_option | O_NONBLOCK;
- fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, new_option);
- return old_option;
- }
- int addfd(int epollfd, int fd)
- {
- epoll_event event;
- event.data.fd = fd;
- event.events = EPOLLIN | EPOLLET;
- epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_ADD, fd, &event);
- setnonblocking(fd);
- }
- void sig_handler(int sig)
- {
- int save_error = errno;
- int msg = sig;
- send(pipefd[1], (char*)&msg, 1, 0);
- errno = save_error;
- }
- void addsig(int sig)
- {
- struct sigaction sa;
- memset(&sa, '\0', sizeof(sa));
- sa.sa_handler = sig_handler;
- sa.sa_flags |= SA_RESTART;
- sigfillset(&sa.sa_mask);
- assert(sigaction(sig, &sa, NULL) != -1);
- }
- void timer_handler()
- {
- client_conn_time_wheel.tick();
- alarm(1);
- }
- void cb_func(client_data *user_data)
- {
- epoll_ctl(epollfd, EPOLL_CTL_DEL, user_data->sockfd, 0);
- assert(user_data);
- close(user_data->sockfd);
- printf("close fd %d\n", user_data->sockfd);
- }
Reference: linux High Performance Server Programming