Initialization of Transport module
The initialization of the transport module is mainly completed in the constructor when the node is started.
When the node is started, the communication module is initialized mainly in the build function.
protected Node(
final Environment environment, Collection<Class<? extends Plugin>> classpathPlugins, boolean forbidPrivateIndexSettings) {
logger = LogManager.getLogger(Node.class);
final List<Closeable> resourcesToClose = new ArrayList<>(); // register everything we need to release in the case of an error
boolean success = false;
try {
...
...
...
// Filter out the list of ActionPlugin plug-ins and pass them into the ActionModule constructor as parameters. The request and processing classes of TCP and HTTP will be registered and bound in the ActionModule.
ActionModule actionModule = new ActionModule(false, settings, clusterModule.getIndexNameExpressionResolver(), settingsModule.getIndexScopedSettings(), settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), settingsModule.getSettingsFilter(), threadPool, pluginsService.filterPlugins(ActionPlugin.class), client, circuitBreakerService, usageService);
...
final RestController restController = actionModule.getRestController();
// Filter out the list of NetworkPlugin plug-ins and pass them into the NetworkModule constructor as parameters
final NetworkModule networkModule = new NetworkModule(settings, false, pluginsService.filterPlugins(NetworkPlugin.class),
threadPool, bigArrays, pageCacheRecycler, circuitBreakerService, namedWriteableRegistry, xContentRegistry,
networkService, restController);
...
...
...
// Get the initialized Transport through the network module
final Transport transport = networkModule.getTransportSupplier().get();
Set<String> taskHeaders = Stream.concat(
pluginsService.filterPlugins(ActionPlugin.class).stream().flatMap(p -> p.getTaskHeaders().stream()),
Stream.of(Task.X_OPAQUE_ID)
).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// Building TransportService based on network module
final TransportService transportService = newTransportService(settings, transport, threadPool,
networkModule.getTransportInterceptor(), localNodeFactory, settingsModule.getClusterSettings(), taskHeaders);
final ResponseCollectorService responseCollectorService = new ResponseCollectorService(clusterService);
// Building searchTransportService service based on TransportService
final SearchTransportService searchTransportService = new SearchTransportService(transportService,
SearchExecutionStatsCollector.makeWrapper(responseCollectorService));
final Consumer<Binder> httpBind;
final HttpServerTransport httpServerTransport;
// Get the initialized Transport through the network module. Can HTTP also be closed?
if (networkModule.isHttpEnabled()) {
httpServerTransport = networkModule.getHttpServerTransportSupplier().get();
httpBind = b -> {
b.bind(HttpServerTransport.class).toInstance(httpServerTransport);
};
} else {
httpBind = b -> {
b.bind(HttpServerTransport.class).toProvider(Providers.of(null));
};
httpServerTransport = null;
}
...
...
...
if (NetworkModule.HTTP_ENABLED.get(settings)) {
logger.debug("initializing HTTP handlers ...");
// Initialize the mapping of REST request and processing classes
actionModule.initRestHandlers(() -> clusterService.state().nodes());
}
logger.info("initialized");
success = true;
...
...
...
}
Initialization of ActionModule
The internal initialization of ActionModule is loaded through plug-in, which mainly completes the mapping of registered Action and processing class and the creation of RestController.
public ActionModule(boolean transportClient, Settings settings, IndexNameExpressionResolver indexNameExpressionResolver,
IndexScopedSettings indexScopedSettings, ClusterSettings clusterSettings, SettingsFilter settingsFilter,
ThreadPool threadPool, List<ActionPlugin> actionPlugins, NodeClient nodeClient,
CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService, UsageService usageService) {
this.transportClient = transportClient;
this.settings = settings;
this.indexNameExpressionResolver = indexNameExpressionResolver;
this.indexScopedSettings = indexScopedSettings;
this.clusterSettings = clusterSettings;
this.settingsFilter = settingsFilter;
this.actionPlugins = actionPlugins;
// Set the action, register the action and bind the mapping of the corresponding handler
actions = setupActions(actionPlugins);
// Configure the action filter
actionFilters = setupActionFilters(actionPlugins);
autoCreateIndex = transportClient ? null : new AutoCreateIndex(settings, clusterSettings, indexNameExpressionResolver);
destructiveOperations = new DestructiveOperations(settings, clusterSettings);
Set<String> headers = Stream.concat(
actionPlugins.stream().flatMap(p -> p.getRestHeaders().stream()),
Stream.of(Task.X_OPAQUE_ID)
).collect(Collectors.toSet());
// rest wrapper
UnaryOperator<RestHandler> restWrapper = null;
for (ActionPlugin plugin : actionPlugins) {
UnaryOperator<RestHandler> newRestWrapper = plugin.getRestHandlerWrapper(threadPool.getThreadContext());
if (newRestWrapper != null) {
logger.debug("Using REST wrapper from plugin " + plugin.getClass().getName());
if (restWrapper != null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot have more than one plugin implementing a REST wrapper");
}
restWrapper = newRestWrapper;
}
}
mappingRequestValidators = new TransportPutMappingAction.RequestValidators(
actionPlugins.stream().flatMap(p -> p.mappingRequestValidators().stream()).collect(Collectors.toList())
);
if (transportClient) {
restController = null;
} else {
// Build the RestController object
restController = new RestController(headers, restWrapper, nodeClient, circuitBreakerService, usageService);
}
}
Initialization of NetworkModule
Construct the NetworkModule object, and load the three member objects through plug-ins when executing the constructor.
Primary data member object
Map<String, Supplier<Transport>> transportFactories Map<String, Supplier<HttpServerTransport>> transportHttpFactories List<TransportInterceptor> transportIntercetors
Transport: responsible for RPC requests from internal nodes
HttpServerTransport: responsible for the REST Service of the client
TransportInterceptor: transport layer interceptor
public NetworkModule(Settings settings, boolean transportClient, List<NetworkPlugin> plugins, ThreadPool threadPool,
BigArrays bigArrays,
PageCacheRecycler pageCacheRecycler,
CircuitBreakerService circuitBreakerService,
NamedWriteableRegistry namedWriteableRegistry,
NamedXContentRegistry xContentRegistry,
NetworkService networkService, HttpServerTransport.Dispatcher dispatcher) {
this.settings = settings;
this.transportClient = transportClient;
// Traverse the plug-ins and register httptransport, transport and transportinterceptor respectively
for (NetworkPlugin plugin : plugins) {
if (transportClient == false && HTTP_ENABLED.get(settings)) {
Map<String, Supplier<HttpServerTransport>> httpTransportFactory = plugin.getHttpTransports(settings, threadPool, bigArrays,
circuitBreakerService, namedWriteableRegistry, xContentRegistry, networkService, dispatcher);
for (Map.Entry<String, Supplier<HttpServerTransport>> entry : httpTransportFactory.entrySet()) {
// In fact, you can't use TransportClient to create HTTP communication transport, and you can't have HttpServerTransport with the same name
registerHttpTransport(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
}
Map<String, Supplier<Transport>> transportFactory = plugin.getTransports(settings, threadPool, pageCacheRecycler,
circuitBreakerService, namedWriteableRegistry, networkService);
for (Map.Entry<String, Supplier<Transport>> entry : transportFactory.entrySet()) {
// Check that there is no Transport with the same name
registerTransport(entry.getKey(), entry.getValue());
}
List<TransportInterceptor> transportInterceptors = plugin.getTransportInterceptors(namedWriteableRegistry,
threadPool.getThreadContext());
for (TransportInterceptor interceptor : transportInterceptors) {
// Register transport layer interceptor
registerTransportInterceptor(interceptor);
}
}
}
When the construction is completed, provide external services through getTransportSupplier, getHttpServerTransportSupplier and getTransportInterceptor.
NetworkPlugin
NetworkPlugin is an interface. Netty4Plugin implements it and inherits Plugin.
The getTransports and getHttpTransports methods of NetworkPlugin are implemented in Netty4Plugin, and Netty4Transport and Netty4HttpServerTransport are constructed respectively for Transport (TCP) transmission and HTTP transmission.
Netty4Transport
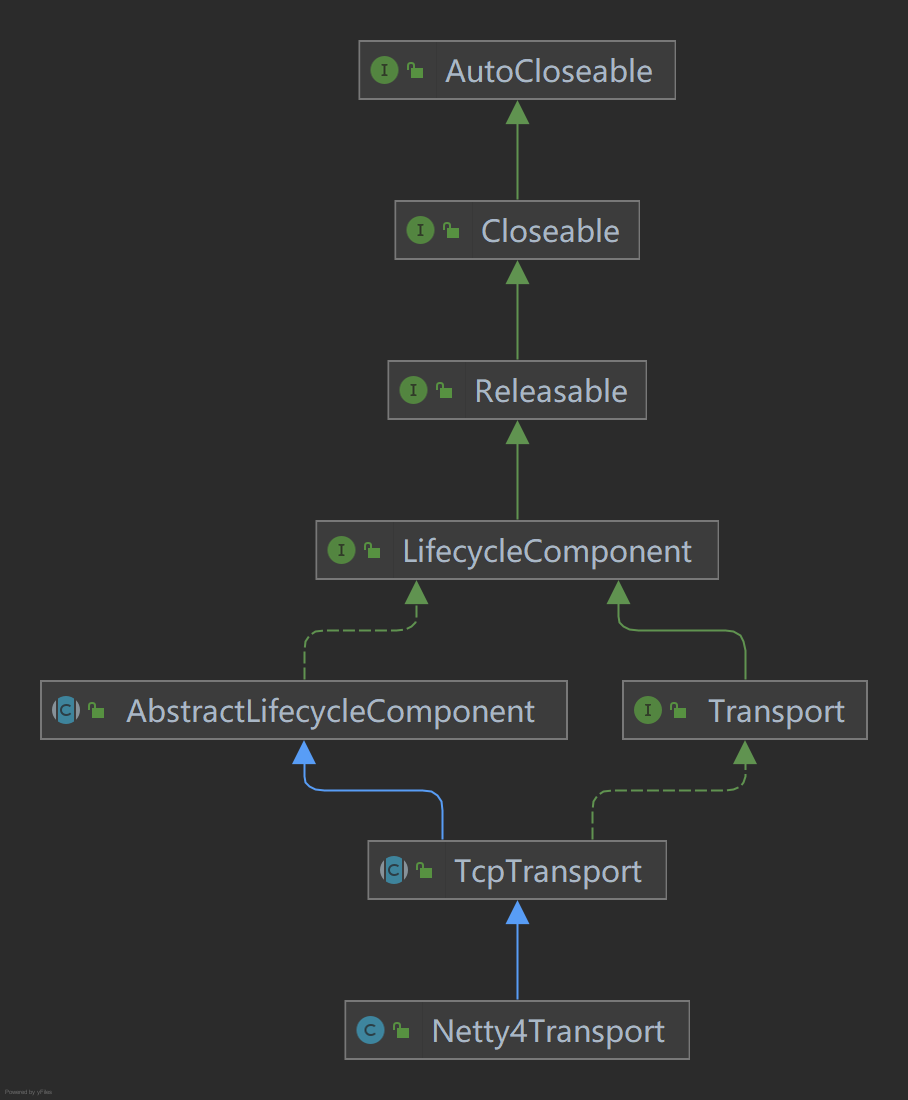
Through the class diagram, it can be found that Netty4Transport inherits TcpTransport, and TcpTransport implements the Transport interface, which should be in the implementation of the Transport layer and control the interaction of data in the Transport layer. The abstract method of doStart is implemented in Netty4Transport to start TCP services. At startup, by default, the Client side and Server side are built at the same time. The netty4 framework is mainly used to realize these functions.
@Override
protected void doStart() {
boolean success = false;
try {
ThreadFactory threadFactory = daemonThreadFactory(settings, TRANSPORT_WORKER_THREAD_NAME_PREFIX);
eventLoopGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup(workerCount, threadFactory);
// Initialize client
clientBootstrap = createClientBootstrap(eventLoopGroup);
// The default is to enable the Server-side configuration and initialize the Server-side
if (NetworkService.NETWORK_SERVER.get(settings)) {
for (ProfileSettings profileSettings : profileSettings) {
createServerBootstrap(profileSettings, eventLoopGroup);
bindServer(profileSettings);
}
}
super.doStart();
success = true;
} finally {
if (success == false) {
doStop();
}
}
}
Netty4HttpServerTransport
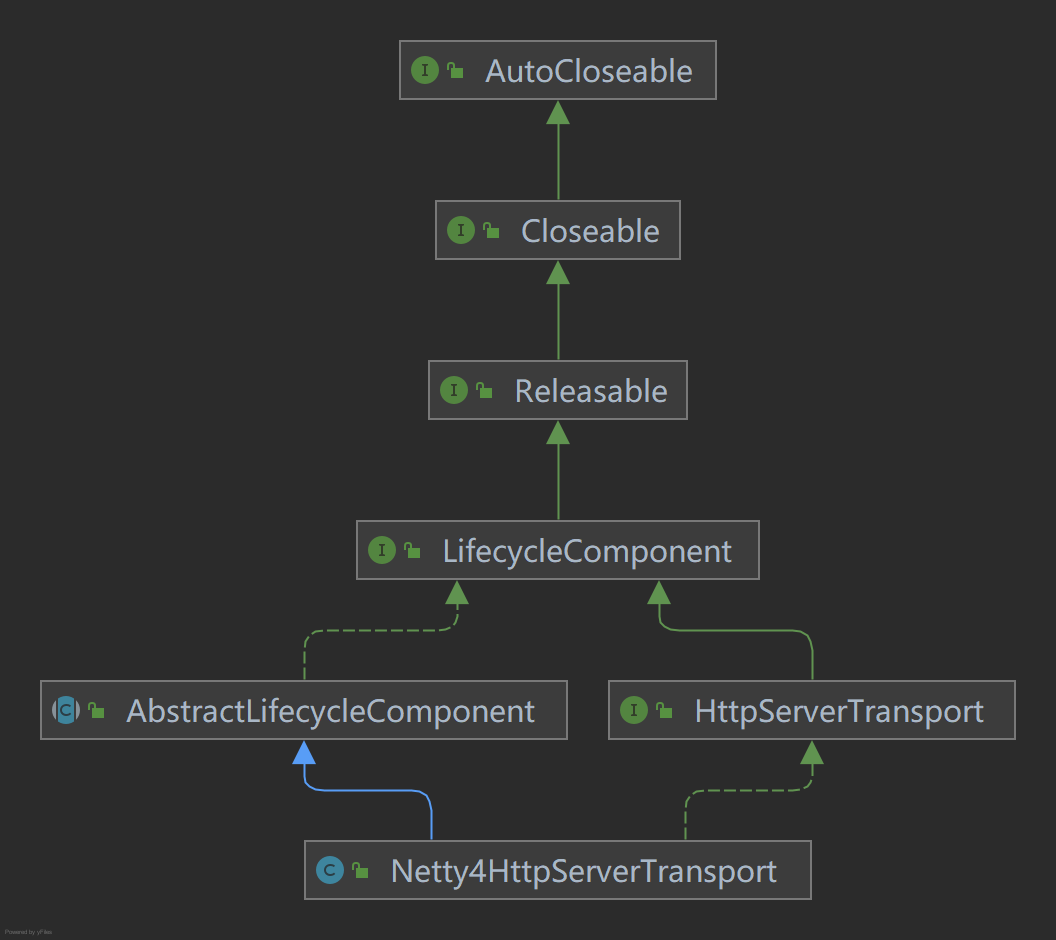
According to the class diagram, it is found that Netty4HttpServerTransport inherits abstractlifecycle component and implements HttpServerTransport at the same time.
The abstract method of doStart is also implemented to start the HTTP Server service. The listening port and processor are configured in the HTTP Server service. In fact, Netty4 should be used to complete the transport layer under the HTTP protocol.
@Override
protected void doStart() {
...
// The requested processing class HttpChannelHandler is configured
serverBootstrap.childHandler(configureServerChannelHandler());
...
// Bind port as HTTP listening port
this.boundAddress = createBoundHttpAddress();
...
}
An HttpChannelHandler object is built in the configureServerChannelHandler method. The constructor of HttpChannelHandler has two member variables Netty4HttpServerTransport and netty4httprequehandler. When a request is received, dispatchRequest will be called to perform corresponding processing on different requests. dispatchRequest is a method in the internal interface Dispatcher of the HttpServerTransport class. It is mainly used to forward requests. Its main implementation class is RestController.
TransportService
During Node startup, a TransportService will be built based on Transport after Transport is initialized. The newTransportService method actually calls the TransportService constructor.
public TransportService(Settings settings, Transport transport, ThreadPool threadPool, TransportInterceptor transportInterceptor, Function<BoundTransportAddress, DiscoveryNode> localNodeFactory, @Nullable ClusterSettings clusterSettings, Set<String> taskHeaders) {
this(settings, transport, threadPool, transportInterceptor, localNodeFactory, clusterSettings, taskHeaders,
// Create connection manager
new ConnectionManager(settings, transport));
}
ConnectionManager is the management class of Node transport connection, and the ConnectionManager of this class connectToNode(Node, connectionProfile, connectionValidator(Node)); Resolve the connection profile to create an internal connection. Calling ConnectionProfile. in the constructor of ConnectionManager Builddefault connection profile (settings), this method will create a connection according to the information provided in the configuration file. In transportrequestoptions Classification of connections found in type.
public class TransportRequestOptions {
...
...
...
public enum Type {
RECOVERY, // For recovery
BULK, // For batch writing
REG, // Not very clear. One is cluster registration
STATE, // Status of the transport cluster
PING // ping request
}
}
The total number of TCP connections found in the TransportSettings class is 13 by default.
public final class TransportSettings {
...
...
...
public static final Setting<Integer> CONNECTIONS_PER_NODE_RECOVERY =
intSetting("transport.connections_per_node.recovery", 2, 1, Setting.Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Integer> CONNECTIONS_PER_NODE_BULK =
intSetting("transport.connections_per_node.bulk", 3, 1, Setting.Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Integer> CONNECTIONS_PER_NODE_REG =
intSetting("transport.connections_per_node.reg", 6, 1, Setting.Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Integer> CONNECTIONS_PER_NODE_STATE =
intSetting("transport.connections_per_node.state", 1, 1, Setting.Property.NodeScope);
public static final Setting<Integer> CONNECTIONS_PER_NODE_PING =
intSetting("transport.connections_per_node.ping", 1, 1, Setting.Property.NodeScope);
...
...
...
}
public TransportService(Settings settings, Transport transport, ThreadPool threadPool, TransportInterceptor transportInterceptor,
Function<BoundTransportAddress, DiscoveryNode> localNodeFactory, @Nullable ClusterSettings clusterSettings,
Set<String> taskHeaders, ConnectionManager connectionManager) {
// The only time we do not want to validate node connections is when this is a transport client using the simple node sampler
this.validateConnections = TransportClient.CLIENT_TYPE.equals(settings.get(Client.CLIENT_TYPE_SETTING_S.getKey())) == false ||
TransportClient.CLIENT_TRANSPORT_SNIFF.get(settings);
this.transport = transport;
this.threadPool = threadPool;
this.localNodeFactory = localNodeFactory;
this.connectionManager = connectionManager;
this.clusterName = ClusterName.CLUSTER_NAME_SETTING.get(settings);
setTracerLogInclude(TransportSettings.TRACE_LOG_INCLUDE_SETTING.get(settings));
setTracerLogExclude(TransportSettings.TRACE_LOG_EXCLUDE_SETTING.get(settings));
tracerLog = Loggers.getLogger(logger, ".tracer");
// Task manager service, which is used to track the currently running tasks on the node
taskManager = createTaskManager(settings, threadPool, taskHeaders);
this.interceptor = transportInterceptor;
// Asynchronous sender - sends communication requests between cluster nodes
this.asyncSender = interceptor.interceptSender(this::sendRequestInternal);
// Remote cluster -- CCR
this.connectToRemoteCluster = RemoteClusterService.ENABLE_REMOTE_CLUSTERS.get(settings);
remoteClusterService = new RemoteClusterService(settings, this);
responseHandlers = transport.getResponseHandlers();
if (clusterSettings != null) {
clusterSettings.addSettingsUpdateConsumer(TransportSettings.TRACE_LOG_INCLUDE_SETTING, this::setTracerLogInclude);
clusterSettings.addSettingsUpdateConsumer(TransportSettings.TRACE_LOG_EXCLUDE_SETTING, this::setTracerLogExclude);
if (connectToRemoteCluster) {
remoteClusterService.listenForUpdates(clusterSettings);
}
}
// Register the mapping between heartbeat Action and handler
registerRequestHandler(
HANDSHAKE_ACTION_NAME,
() -> HandshakeRequest.INSTANCE,
ThreadPool.Names.SAME,
false, false,
(request, channel) -> channel.sendResponse(
new HandshakeResponse(localNode, clusterName, localNode.getVersion())));
}
It will be called at the end of Node initialization to register and map RestHandler. The initialization part of the communication module is over.