The basic concept of map can be turned over
catalogue
Concrete class implementation of adjacency matrix
The second storage method of graph adjacency table
Adjacency table establishment algorithm!
Generally speaking, there are four kinds of graph storage, but because of the examination and I am a person, I only discuss the adjacency matrix and adjacency table
Template base class of graph
const int maxWeight = ......; //Value of infinity (= )
const int DefaultVertices = 30; //Maximum number of vertices (= n)
template <class T, class E>
class Graph { //Class definition of graph
protected:
int maxVertices; //Maximum number of vertices in graph
int numEdges; //Current number of sides
int numVertices; //Current vertex number
int getVertexPos (T vertex);
//Give the position of vertex in the graph
public:
Graph (int sz = DefaultVertices); //Constructor
~Graph(); //Destructor
bool GraphEmpty () const //Judge whether the drawing is empty or not
{ return numEdges == 0; }
int NumberOfVertices () { return numVertices; }
//Returns the current vertex count
int NumberOfEdges () { return numEdges; }
//Returns the current number of edges
virtual T getValue (int i); //Take the value of vertex i
virtual E getWeight (int v1, int v2); //Take the weight on the edge
virtual int getFirstNeighbor (int v); //Take the first adjacent vertex of vertex v
virtual int getNextNeighbor (int v, int w);
//Take the next adjacent vertex of the adjacent vertex w
virtual bool insertVertex (const T vertex);
//Insert a vertex
virtual bool insertEdge (int v1, int v2, E cost);
//Insert edge (v1,v2), weight cost
virtual bool removeVertex (int v);
//Delete vertex v and all associated edges
virtual bool removeEdge (int v1, int v2);
//Delete the edge (v1,v2) in the figure
};
The above is just a basic class. Just have a general understanding
adjacency matrix
Basic concepts


Generally speaking, the edge band weight of a directed graph is a network

Concrete class implementation of adjacency matrix
template <class T, class E>
class Graphmtx : public Graph<T, E> {
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Graphmtx<T, E>& G); //input
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, Graphmtx<T, E>& G); //output
private:
T *VerticesList; //Vertex table - > can be understood as vertex array
E **Edge; //The secondary pointer of adjacency matrix represents a two-dimensional array. Pay attention to it when applying for array space
int getVertexPos (T vertex) { //Give the position of vertex in the graph
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
if (VerticesList[i] == Vertex)
return i; //Return array subscript
return -1;
};
public:
Graphmtx (int sz = DefaultVertices); //Constructor
~Graphmtx () //Destructor
{ delete [ ]VerticesList; delete [ ]Edge; }
T getValue (int i) { //Take the value of vertex i, I is unreasonable, and return 0 [prevent crossing]
return i >= 0 && i <= numVertices ? VerticesList[i] : NULL;
}
E getWeight (int v1, int v2) { //Take the weight on the edge (v1,v2)
if(return v1 != -1 && v2 != -1 )
return Edge[v1][v2];
else
return 0;
}
int getFirstNeighbor (int v); //Take the first adjacent vertex of vertex v
int getNextNeighbor (int v, int w);
//Take the adjacent vertex of v and the next adjacent vertex of w
bool insertVertex (const T vertex);
//Insert vertex
bool insertEdge (int v1, int v2, E cost);
//Insert an edge (v1, v2) with a weight of cost
bool removeVertex (int v);
//Delete vertex v and all its associated edges
bool removeEdge (int v1, int v2);
//Delete the edge (v1,v2) in the figure
};
Implementation of adjacency matrix constructor (an adjacency matrix can be initialized based on this constructor)
Each edge in the constructor is initialized to a maximum value
template <class T, class E>
Graphmtx<T, E>::Graphmtx (int sz) { //Constructor
maxVertices = sz;
numVertices = 0; numEdges = 0;
int i, j;
VerticesList = new T[maxVertices]; //Create vertex table (vertex array)
Edge = (int **) new int *[maxVertices];
for (i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++)
Edge[i] = new int[maxVertices]; //Construct adjacency matrix to generate two-dimensional array
for (i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++) //The matrix is initialized to the maximum value
for (j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++)
Edge[i][j] = (i == j) ? 0 : maxWeight;
};
Find the first edge of a vertex
template <class T, class E>
int Graphmtx<T, E>::getFirstNeighbor (int v) {
//The position of the first adjacent vertex with vertex position v is given,
//If not found, the function returns - 1
if (v != -1) {
for (int col = 0; col < numVertices; col++)
if (Edge[v][col] && Edge[v][col] < maxWeight)
return col;
}
return -1;
};
Find the next edge of an edge of the adjacency matrix
template <class T, class E>
int Graphmtx<T, E>::getNextNeighbor (int v, int w) {
//Give the next adjacent vertex of an adjacent vertex w of vertex v
if (v != -1 && w != -1) {
for (int col = w+1; col < numVertices; col++)
if (Edge[v][col] && Edge[v][col] < maxWeight)
return col;
}
return -1;
};
The second storage method of graph adjacency table
Note: select the adjacency table to save space and the adjacency matrix to save time. The time complexity can be analyzed according to the characteristics of linked list and matrix
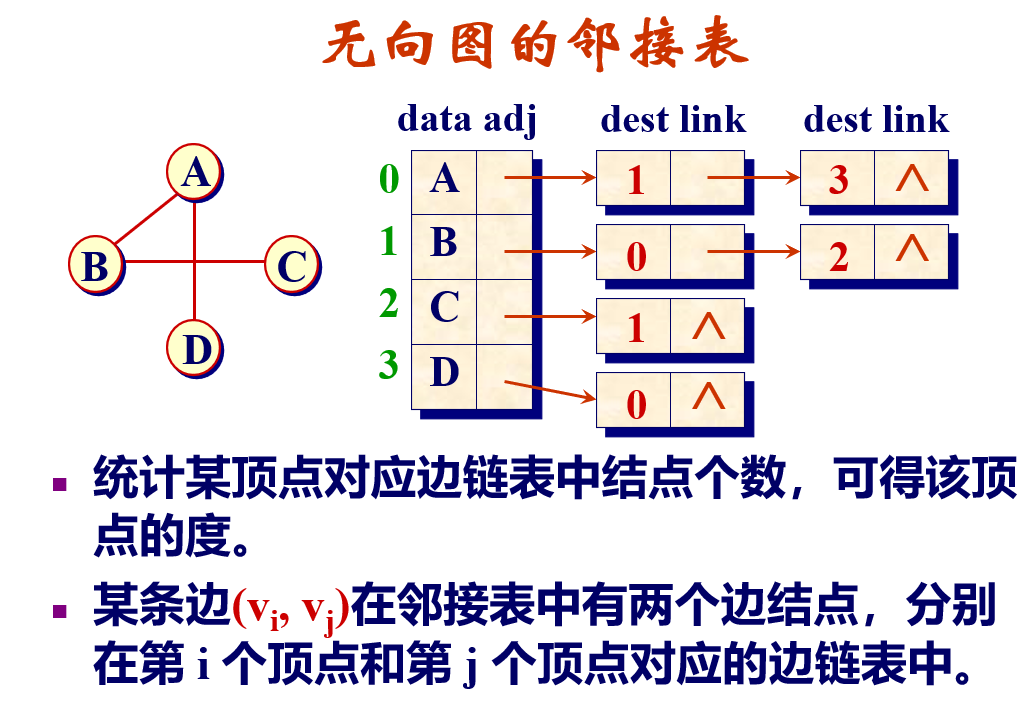

Constructor for each node of the adjacency table
template <class T, class E>
struct Edge { //Definition of edge node
int dest; //Another vertex position of the edge
E cost; //Weight on edge
Edge<T, E> *link; //Next side chain pointer
Edge () {} //Constructor
Edge (int num, E cost) //Constructor
: dest (num), weight (cost), link (NULL) { }
bool operator != (Edge<T, E>& R) const
{ return dest != R.dest; } //Edge judgment, etc
};
Vertex definition of adjacency table
template <class T, class E>
struct Vertex { //Definition of vertices
T data; //The name of the vertex
Edge<T, E> *adj; //Header pointer of side linked list
};
Definition of adjacency table class
template <class T, class E>
class Graphlnk : public Graph<T, E> { //Class definition of graph
friend istream& operator >> (istream& in, Graphlnk<T, E>& G); //input
friend ostream& operator << (ostream& out, Graphlnk<T, E>& G); //output
private:
Vertex<T, E> *NodeTable;
//Vertex list (the head node of each side linked list)
int getVertexPos (const T vertx) {
//Give the position of vertex in the graph
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++)
if (NodeTable[i].data == vertx) return i;
return -1;
}
public:
Graphlnk (int sz = DefaultVertices); //Constructor
~Graphlnk(); //Destructor
T getValue (int i) { //Take the value of vertex i
return (i >= 0 && i < NumVertices) ? NodeTable[i].data : 0;
}
E getWeight (int v1, int v2); //Weight of edge (v1,v2)
bool insertVertex (const T& vertex);
bool removeVertex (int v);
bool insertEdge (int v1, int v2, E cost);
bool removeEdge (int v1, int v2);
int getFirstNeighbor (int v);
int getNextNeighbor (int v, int w);
};
Adjacency table constructor
template <class T, class E>
Graphlnk<T, E>::Graphlnk (int sz) {
//Constructor: create an empty adjacency table
maxVertices = sz;
numVertices = 0; numEdges = 0;
NodeTable = new Vertex<T, E>[maxVertices]; //Create vertex table array
if (NodeTable == NULL)
{ cerr << "Wrong storage allocation!" << endl; exit(1); }
for (int i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++)
NodeTable[i].adj = NULL;
};
template <class T, class E>
Graphlnk<T, E>::~Graphlnk() {
//Destructor: delete an adjacency table
for (int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++ ) {
Edge<T, E> *p = NodeTable[i].adj;
while (p != NULL) {
NodeTable[i].adj = p->link;
delete p; p = NodeTable[i].adj;
}
}
delete [ ]NodeTable; //Delete vertex table array
};
template <class T, class E>
int Graphlnk<T, E>::getFirstNeighbor (int v) {
//The position of the first adjacent vertex with vertex position v is given,
//If not found, the function returns - 1
if (v != -1) { //Vertex v exists
Edge<T, E> *p = NodeTable[v].adj; //The first edge node of the corresponding edge linked list
if (p != NULL) return p->dest; //Exists, returns the first adjacent vertex
}
return -1; //The first adjacent vertex does not exist
};
template <class T, class E>
int Graphlnk<T, E>::getNextNeighbor (int v, int w) {
//The position of the next adjacent vertex of the adjacent vertex w of the top point v is given,
//If there is no next adjacent vertex, the function returns - 1
if (v != -1) { //Vertex v exists
Edge<T, E> *p = NodeTable[v].adj;
while (p != NULL && p->dest != w)
p = p->link;
if (p != NULL && p->link != NULL)
return p->link->dest; //Returns the next adjacent vertex
}
return -1; //The next adjacent vertex does not exist
};

Adjacency table establishment algorithm!
template<class T , class E>
void Graphlnk<T,E>::CreateNodeTable(void){
int n,i,j,m;
Edge<T,E> *p;
cin>>n;//Number of nodes
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
NodeTable[i].adj=0;
cin>>NodeTable[i].data;//Enter node value
cin>>m; //Number of adjacent points of each node
for(j=0;j<m;j++){
p=new Edge<T,E>;
cin>>p->dest; //Establish the edge node and input the node value to dest field
p->link=NodeTable[i].adj;
//The weighted graph adds an additional weight input CIN > > p - > cost;
NodeTable[i].adj=p; //Head interpolation establishment
}
}
}