Install redis
https://redis.io/download cd /opt wget http://download.redis.io/releases/redis-6.2.3.tar.gz yum install gcc-c++ tar xzf redis-6.2.3.tar.gz mv /opt/redis-6.2.3 /usr/local/redis cd /usr/local/redis make make PREFIX=/usr/local/redis install
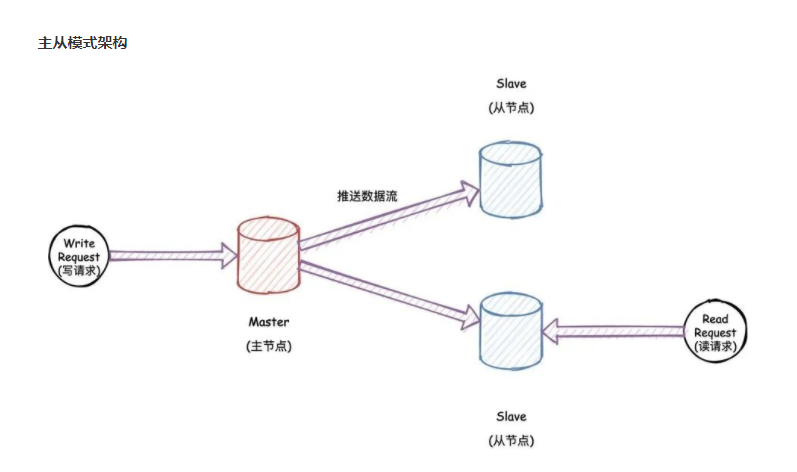
Setup of master-slave redis mode
cd /opt
mkdir redis-sentinel
cd redis-sentinel
mkdir {redis-6380,redis-6381,redis-6382}
cp /usr/local/redis/redis.conf redis-6380
cp /usr/local/redis/redis.conf redis-6381
cp /usr/local/redis/redis.conf redis-6382
Change redis Conf configuration file
The configuration of redis-6381 and redis-6382 is similar to that of redis-6380. The following is the redis of redis-6380 Conf configuration modification:
cd /opt/redis-sentinel/redis-6380/ vi redis.conf daemonize yes pidfile /var/run/redis_6380.pid port 6380 bind 127.0.0.1 #Optional. All requests are processed by default. logfile "./redis-6380.log" redis To configure the password, the following configuration is required masterauth "123456" requirepass "123456" appendonly yes
be careful:
Focus (error prone)
1,protected-mode no
Whether to enable the protection mode. It is enabled by default. If the bind and password are not specified in the configuration. After this parameter is enabled, redis will only access locally and refuse external access. If the password and bind are enabled, it can be set to yes. Otherwise, it is better to turn it off and set it to no.
2,bind
Many explanations on the Internet are wrong. It doesn't mean which IPS are allowed to access redis services!!!
Easy to understand: for the ip configured in the bind, others have to access the ip configured in the bind to access the redis service
Start redis
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /opt/redis-sentinel/redis-6380/redis.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /opt/redis-sentinel/redis-6381/redis.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-server /opt/redis-sentinel/redis-6382/redis.conf
Check to see if it starts
ps -aux | grep redis /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6380 -a 123456
slave join master
# redis-6381 joins redis-6380 as a slave /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6381 -a 123456 SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6380 exit # redis-6382 joins redis-6380 as a slave /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6382 -a 123456 SLAVEOF 127.0.0.1 6380 exit
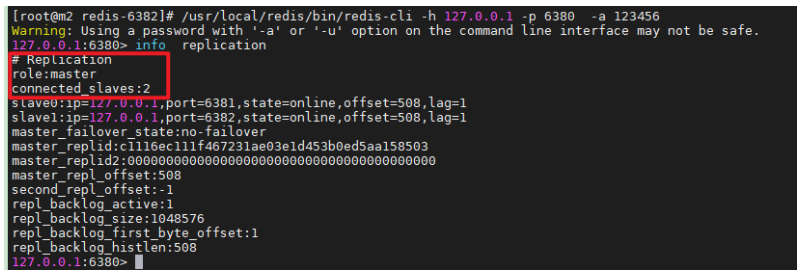
Verify master-slave
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6380 -a 123456 info replication
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6380 -a 123456 set name zhangsan /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6381 -a 123456 get name

Sentinel mode setup
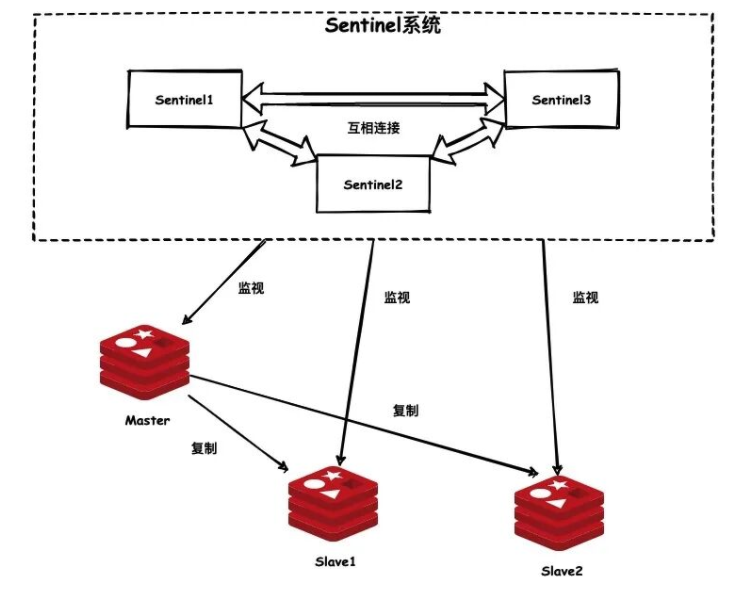
The sentinel mechanism of Redis is a highly available (HA) scheme officially recommended. When we use the master-slave structure of Redis, if the master node hangs up, we cannot automatically switch between master and standby and notify the client that the master node goes offline.
Redis sentinel mechanism mainly uses three functions:
(1) Monitoring: constantly monitor whether Redis master-slave nodes are installed and run as expected
(2) Reminder: if Redis runs with problems, you can notify the client or cluster administrator according to the configuration items in the configuration file
(3) Automatic failover: when the master node goes offline, the Sentry can select a master node from multiple slave nodes of the master node and update the configuration file and the master node information of other slave nodes.
cd /opt/redis-sentinel
mkdir {sentinel-7380/workdir,sentinel-7381/workdir,sentinel-7382/workdir}
cp /usr/local/redis/sentinel.conf /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7380
cp /usr/local/redis/sentinel.conf /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7381
cp /usr/local/redis/sentinel.conf /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7382
Change sentinel Conf configuration file
The configuration of sentinel-7381 and sentinel-7382 is similar to that of sentinel-7380. The following is the sentinel of sentinel-7380 Conf configuration modification:
cd /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7380 vim sentinel.conf daemonize yes port 7380 #assign work directory dir /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7380/workdir logfile "./sentinel.log" #Specify the number of port sentinels of the alias master node address (several sentinels monitor that the master node is down and perform the transfer) sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6380 2 #If the sentinel does not receive the heartbeat of the primary node within 10s, the sentinel will think that the primary node is down. The default is 30 seconds sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 10000 #After selecting a new master node, the number of slave nodes that can be connected at the same time sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1 #If the master still doesn't come back to life after 30 seconds, start failover. The default is 180s sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 30000 #Configure the password of the primary node connecting to redis sentinel auth-pass mymaster 123456
mymaster is followed by the ip and port of the master. The last '2' means I want to start. As long as two sentinels think that the master is offline, they think that the master is offline objectively. Start failover and elect a new master. Usually, the last parameter cannot be more than the number of sentinel instances started. It is recommended to start at least three sentinel instances.
Activate the sentry
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-sentinel /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7380/sentinel.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-sentinel /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7381/sentinel.conf /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-sentinel /opt/redis-sentinel/sentinel-7382/sentinel.conf
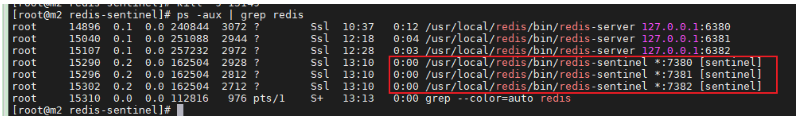
Verification sentry
ps -aux | grep redis kill -9 14896 ps -aux | grep redis
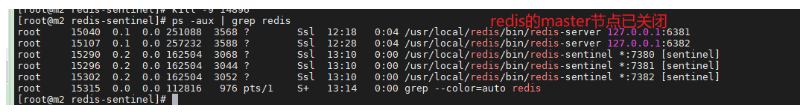
/usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6381 -a 123456 info replication exit /usr/local/redis/bin/redis-cli -h 127.0.0.1 -p 6382 -a 123456 info replication exit
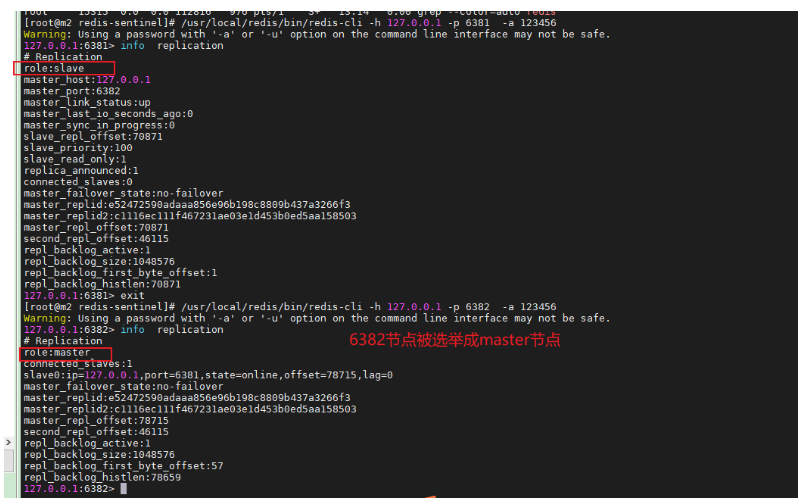
Look at sentinel The configuration of the master in conf has also changed to 6382

summary
This paper mainly introduces two cluster modes of Redis and summarizes them
The master-slave mode can realize read-write separation and data backup. But it's not "highly available"
Sentinel mode can be regarded as the "highly available" version of master-slave mode, which introduces sentinel to monitor the whole Redis service cluster. However, since there is only one master node, there is still a write bottleneck.