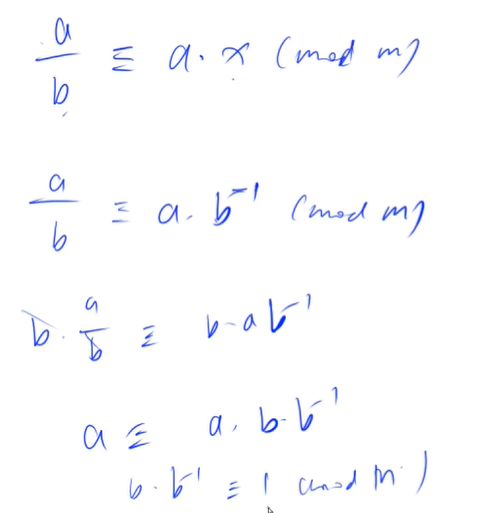Euler function
Solving Euler function by formula method
Basic principle: O(n √ ai)
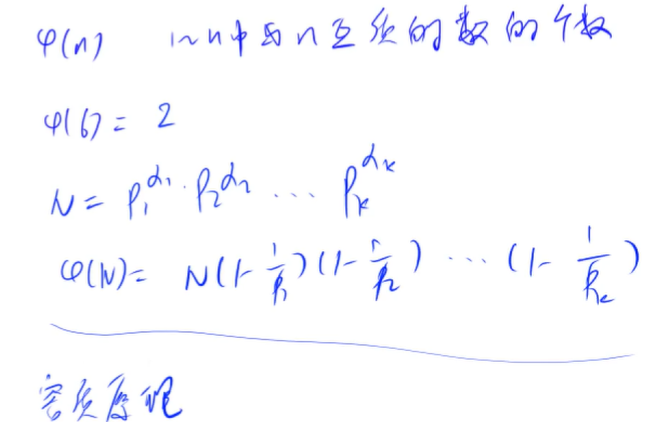

Example: Euler function
given n positive integers ai, please find the Euler function of each number.
Definition of Euler function
1 ∼ N and N The number of Coprime numbers is called the Euler function and is written as ϕ (N)
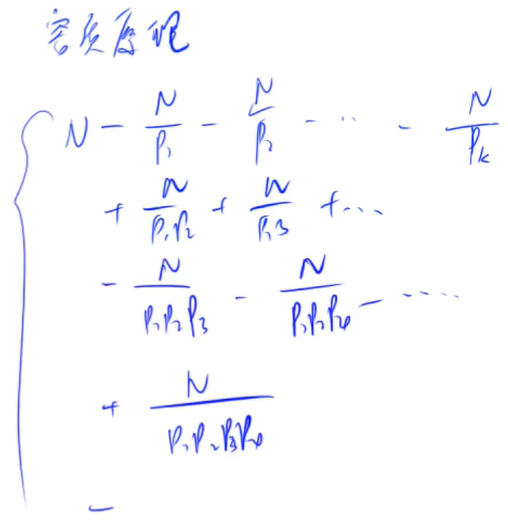
If in the basic theorem of arithmetic, N=pa11pa22... pamm, then:
ϕ(N) = N×p1−1p1×p2−1p2×...×pm−1pm
Input format
The first line contains integers n.
next n Rows, each containing a positive integer ai.
Output format
Output common n Rows, each row outputs a positive integer Euler function of ai.
Data range
1≤n≤100
1≤ai≤2×109
Input example:
3 3 6 8
Output example:
2 2 4
Problem solving Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >>n;
while(n--)
{
int a;
cin>>a;
int res=a;
for(int i=2;i<=a/i;i++)//Decomposition quality factor
if(a%i==0)//a is the prime factor of i
{
res=res/i*(i-1);//formula
while(a%i==0) a/=i;//Remove the i
}
if(a>1) res=res/a*(a-1);
cout<<res<<endl;
}
return 0;
}Finding Euler function by sieve method

Example:
Given a positive integer n. Beg Sum of Euler functions of each number in 1 ∼ n.
Input format
A total of one line, including an integer n.
Output format
A total of one line, including an integer, representing Sum of Euler functions of each number in 1 ∼ n.
Data range
1≤n≤106
Input example:
6
Output example:
12
Problem solving Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N=1000010;
int primes[N],cnt;//primes stores every prime number, cnt stores the subscript of prime number
bool st[N];//Indicates whether it has been screened out
int phi[N];//Euler function
LL get_eulers(int n)
{
phi[1]=1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++)//Linear sieve method
{
if(!st[i])
{
primes[cnt++]=i;
//If it's prime
phi[i]=i-1;
}
for(int j=0;primes[j]<=n/i;j++)
{
st[primes[j]*i]=true;//Sift out the product of the current prime number and i each time
if(i%primes[j]==0)
{
phi[primes[j]*i]=primes[j]*phi[i];
break;
}
phi[primes[j]*i]=phi[i]*(primes[j]-1);
}
}
LL res=0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) res+=phi[i];
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin>>n;
cout<<get_eulers(n)<<endl;
return 0;
}Euler function function:
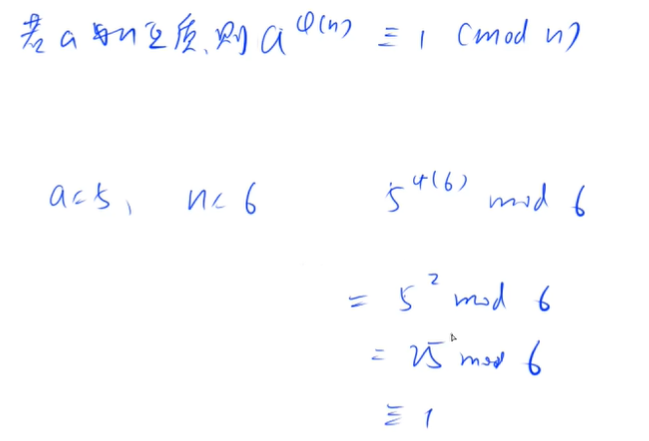
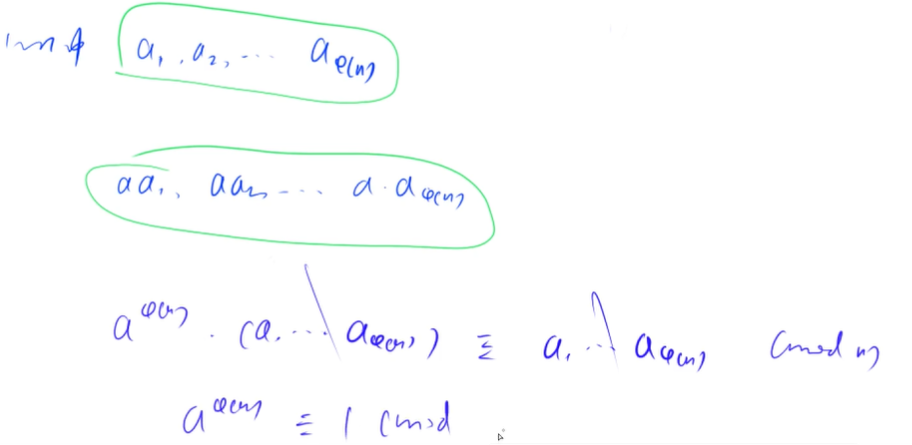
Proof of Euler's theorem:
Fermat theorem
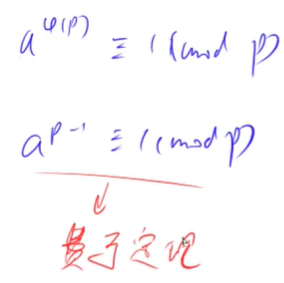
Counting

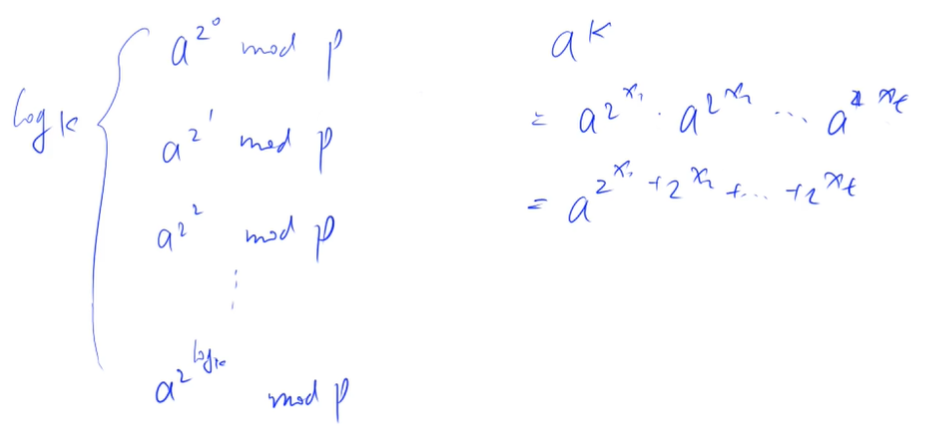
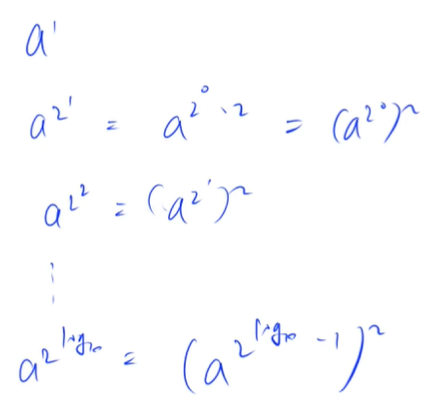
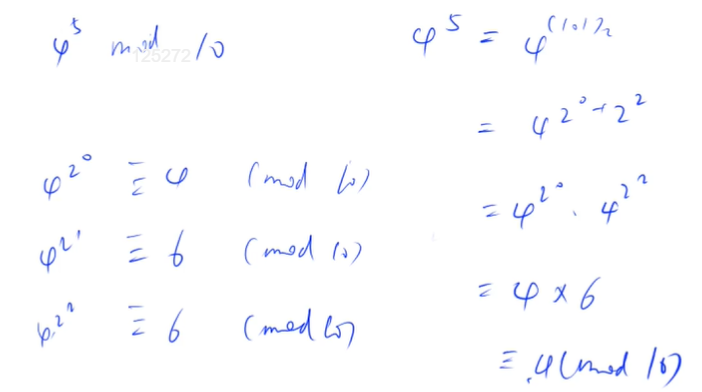
Example: fast power
given n group ai,bi,pi, for each set of data, find abii mod pi value.
Input format
The first line contains integers n.
next n Rows, each containing three integers ai,bi,pi
Output format
For each group of data, a result is output, representing abii mod pi value.
One line for each result.
Data range
1≤n≤100000
1≤ai,bi,pi≤2×109
Input example:
2 3 2 5 4 3 9
Output example:
4 1
Problem solving Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
//Find a ^ B% p
LL qmi(int a, int b, int p)
{
LL res = 1 % p;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) res = res * a % p;//%p prevent overflow
a = a * (LL)a % p;
b >>= 1;//Delete the last bit of b
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
int a, b, p;
scanf("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &p);
printf("%lld\n", qmi(a, b, p));
}
return 0;
}
Example: fast power inverse element
given n group ai,pi, where pi It's a prime number. Find ai module pi If the inverse element does not exist, it will be output impossible.
Note: please return to Inverse element between 0 ∼ p − 1.
Definition of multiplicative inverse
If integer b. M coprime, and for any integer a. If satisfied b|a, there is an integer x. Make a/b≡a × x(modm) is called X is b Module of m The inverse of multiplication is written as b−1(modm)
b The necessary and sufficient condition for the existence of multiplicative inverse is b And modulus m Coprime. When modulus m When it is a prime number, bm − 2 is b Multiplicative inverse of.
Input format
The first line contains integers n.
next n Rows, each containing an array ai,pi, data assurance pi Is a prime number.
Output format
Output common n Row, each group of data outputs a result, and each result occupies one row.
if ai model pi If the multiplicative inverse of exists, an integer is output to represent the inverse, otherwise it is output impossible.
Data range
1≤n≤105
1≤ai,pi≤2∗109
Input example:
3 4 3 8 5 6 3
Output example:
1 2 impossible
Problem solving ideas:
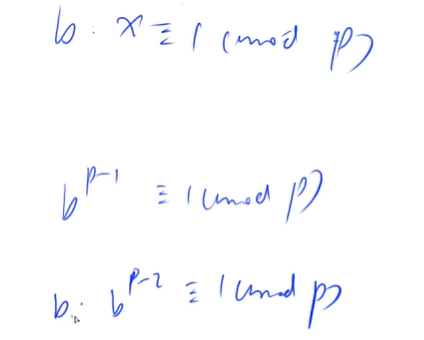
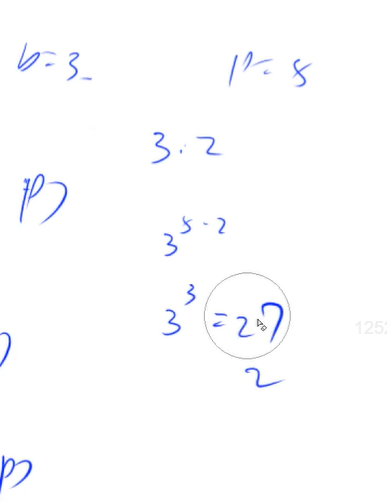
Problem solving Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
//Find a ^ B% p
LL qmi(int a, int b, int p)
{
LL res = 1 % p;
while (b)
{
if (b & 1) res = res * a % p;//%p prevent overflow
a = a * (LL)a % p;
b >>= 1;//Delete the last bit of b
}
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
int a, p;
scanf("%d%d%", &a, &p);
LL res=qmi(a, p-2, p);
if(a%p) printf("%lld\n", res);
else puts("impossible");
}
return 0;
}
extended euclidean algorithm
Pei Shu theorem:
For any positive integer a, b, there must be non-zero integers x, y such that:
ax+by = (a, b) / / (a, b) is a multiple of the greatest common divisor of a and B
That is, the smallest positive integer that a and b can round up is its maximum common divisor
The extended Euclidean algorithm is to find their coefficients, that is, x, y
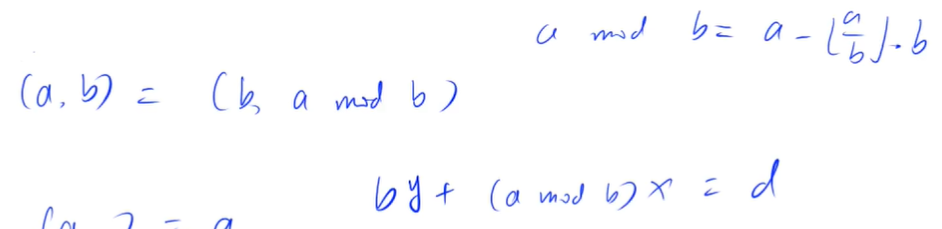
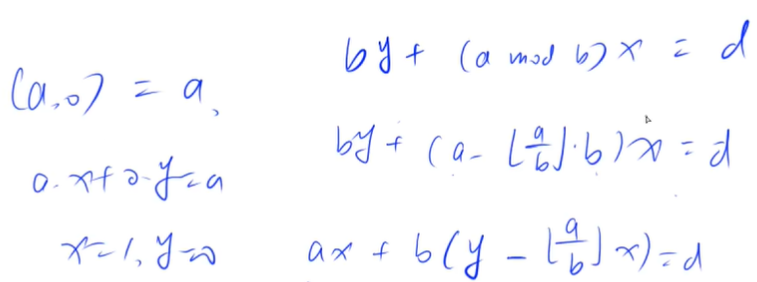
Example: extended Euclidean algorithm
given n Positive integer AI, Bi, for each logarithm, find a set xi,yi make it meet ai × xi+bi × yi=gcd(ai,bi)
Input format
The first line contains integers n.
next n Rows, each containing two integers ai,bi
Output format
Output common n Row, for each group ai,bi find a set of conditions xi,yi each group results in one row.
The answer to this question is not unique. Output any one that meets the conditions Either Xi or Yi.
Data range
1≤n≤105
1≤ai,bi≤2×109
Input example:
2 4 6 8 18
Output example:
-1 1 -2 1
Problem solving Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int exgcd(int a,int b,int &x,int &y)
{
if(!b)
{
x=1,y=0;
return a;
}
int d= exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=a/b *x;
return d;
}
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d",&n);
while(n --)
{
int a,b,x,y;
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
exgcd(a,b,x,y);
printf("%d %d\n",x,y);
}
return 0;
}Application: solving linear congruence equation
given n Group data ai,bi,mi find one for each group xi, make it meet ai × xi ≡ bi(mod mi) output if there is no solution impossible.
Input format
The first line contains integers n.
next n Rows, each containing a set of data ai,bi,mi
Output format
Output common n Row, each group of data outputs an integer, representing a condition satisfied xi, output if there is no solution impossible.
Each group of data results occupy one line, and the results may not be unique. Any result that meets the conditions can be output.
The output answer must be in int range.
Data range
1≤n≤105
1≤ai,bi,mi≤2×109
Input example:
2 2 3 6 4 3 5
Output example:
impossible -3
Problem solving:

Chinese remainder theorem
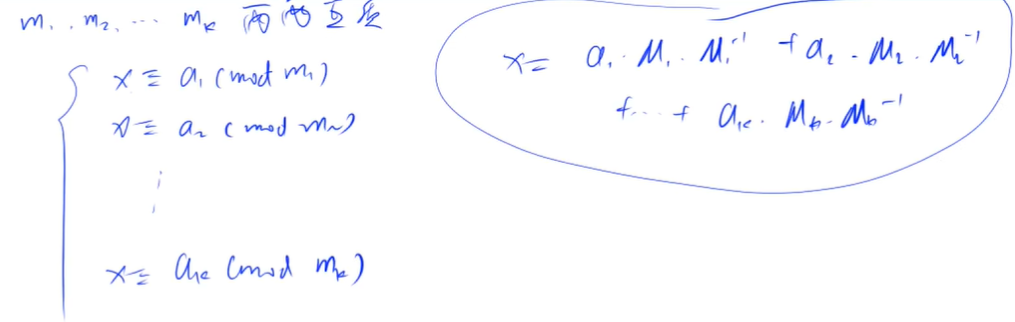

Example: strange way to express integers
given 2n Integer a1,a2,..., an and m1,m2,..., mn find a minimum nonnegative integer x. Satisfied ∀i∈[1,n],x≡mi(mod ai)
Input format
The first one The row contains integers n.
The first 2... n+1 lines: each i+1 The row contains two integers ai and mi, numbers are separated by spaces.
Output format
Output minimum nonnegative integer x. If x Not present, output −1.
If present x. Data assurance x Must be 64 bit integer range.
Data range
1≤ai≤231−1
0≤mi<ai
1≤n≤25
Input example:
2 8 7 11 9
Output example:
31
Problem solving:
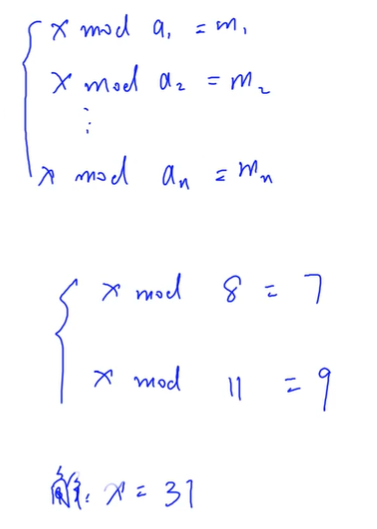

#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL exgcd(LL a,LL b,LL &x,LL &y)
{
if(!b)
{
x=1,y=0;
return a;
}
LL d=exgcd(b,a%b,y,x);
y-=a/b*x;
return d;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >>n;
bool has_answer =true;
LL a1,m1;
cin>>a1>>m1;
for(int i=0;i<n-1;i++)
{
LL a2,m2;
cin>>a2>>m2;
//Find the values of k1 and k2
LL k1,k2;
LL d=exgcd(a1,a2,k1,k2);
//The equation has a solution
if((m2-m1)%d)
{
has_answer=false;
break;
}
//Double K1 and K2 to m1 and m2
k1*=(m2-m1)/d;
LL t=a2/d;//Save the number first
k1=(k1%t+t)%t;//Turn k1 into the minimum positive integer solution of the equation
m1=a1*k1+m1;
a1=abs(a1/d*a2);
}
if(has_answer)
{
cout<<(m1%a1+a1)%a1 <<endl;
}
else puts("-1");
return 0;
}