1. rsync Server
1. Introduction to Rsync
- Rsync remote synchronization is a tool primarily for fast incremental backups; Simply put, replication can be used for local replication or for replication between users across hosts (ssh/rsync host synchronization); Official website: https://rsync.samba.org/
- rsync is an open source, fast, multifunctional tool that enables full and incremental synchronous backup of local or remote data. The backup and migration characteristics of the data can be achieved without changing the attribute information of the original data.
- It can replicate locally, remotely, or in a remote daemon fashion. It provides a large number of parameters to control all aspects of its behavior and allows a very flexible way to transfer and replicate files.
2. Synchronization method
1 Full backup
- All original data transferred
- Transfer old and new files together
- Full copy, inefficient
Incremental backup
- Before transferring data, use some algorithms to transfer different data over the network by comparing what you have with what I have.
- Incremental replication with high efficiency
3.rsync command
rsync [option] Original location Target location
| Common Options | Explain |
|---|---|
| -r | Recursive mode, including all files in directories and subdirectories |
| -l | Copy symbolic link files as symbolic link files |
| -v | Show details of the synchronization process |
| -z | Compress when transferring files |
| -a | Archive mode, recursive and preserves object attributes, equivalent to -rlptgoD |
| -p | Keep permission flags for files |
| -t | Keep time stamps for files |
| -g | Keep group tags for files (superuser only) |
| -o | Keep the owner tag of the file (superuser only) |
| -H | Keep Hard Linked Files |
| -A | Preserve ACL attribute information |
| -D | Keep device files and other special files |
| - - delete | Delete files that have destination location but not original location |
| - - checksum | Decide whether to skip files based on the object's checksum |
2. EXPERIMENTS
1. rsync Local Replication
[root@localhost ~]# mkdir /abc [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /bcd [root@localhost ~]# mkdir /cde [root@localhost ~]# cd /abc [root@localhost abc]# touch 1.txt [root@localhost abc]# Rsync-avz/abc/ /bcd //Copy/abc files to/bcd directory sending incremental file list ./ 1.txt sent 103 bytes received 38 bytes 282.00 bytes/sec total size is 0 speedup is 0.00 [root@localhost abc]# Rsync-avz/abc/cde //Copy/abc files with/abc to/dce sending incremental file list abc/ abc/1.txt sent 115 bytes received 39 bytes 308.00 bytes/sec total size is 0 speedup is 0.00 [root@localhost abc]# ls /bcd /cde /bcd: 1.txt /cde: abc [root@localhost abc]# The cp-a/abc/opt //cp command copies the directory itself whether or not it is followed [root@localhost abc]# ls /opt/ abc rh [root@localhost abc]# rm -rf /opt/abc/ [root@localhost abc]# cp -a /abc/ /opt [root@localhost abc]# ls /opt/ abc rh [root@localhost abc]#
2. Remote Replication
Environmental Science Server 192.168.30.7 Client 192.168.30.8
2.1 Configure rsync Server
[root@localhost /]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf uid = nobody #root gid = nobody #root use chroot = yes #Confined in Source Directory address = 192.168.30.7 #Listening Address port 873 #Listening port tcp/udp 873, viewable through cat/etc/services | grep Rsync log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log #Log file location pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid #File location to store process ID hosts allow = 192.168.30.0/24 #Allowed Client Address [wwwroot] ##First shared module path = /var/www/html #Actual path to source directory comment = Document Root of www.ljm.com read only = yes #readonly dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z #File types that are no longer compressed during synchronization auth users = backuper #Authorized accounts, multiple accounts separated by spaces secrets file = /etc/rsyncd_users.db #Data file holding account information
2.2 Create data files for backup accounts
[root@localhost /]# vim /etc/user.db [root@localhost /]# cat /etc/user.db backuper:abc123 [root@localhost /]# Chmod 600/etc/user. DB //must be granted 600 permissions or an error will be reported
@ERROR: auth failed on module wwwroot rsync error: error starting client-server protocol (code 5) at main.c(1648) [Receiver=3.1.2]
2.3 Create shared directories
[root@localhost /]# mkdir -p /var/www/html [root@localhost /]# chmod +r /var/www/html/ [root@localhost /]# ls -ld /var/www/html/ drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 6 8 January 1019:10 /var/www/html/ [root@localhost /]# Echo "hello world" > /var/www/html/1. Txt //Create synchronized documents [root@localhost /]# rsync --daemon //Start rsync [root@localhost /]# netstat -natp | grep rsync tcp 0 0 192.168.30.7:873 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 27641/rsync
2.4 Client Synchronization
[root@localhost ~]# rsync -avz backuper@192.168.30.7::wwwroot /abc/ Password: receiving incremental file list ./ 1.txt sent 46 bytes received 119 bytes 47.14 bytes/sec total size is 12 speedup is 0.07 [root@localhost ~]# ls /abc 1.txt [root@localhost ~]# cat /abc/1.txt hello world [root@localhost ~]#
2.5 Client-Free Interaction
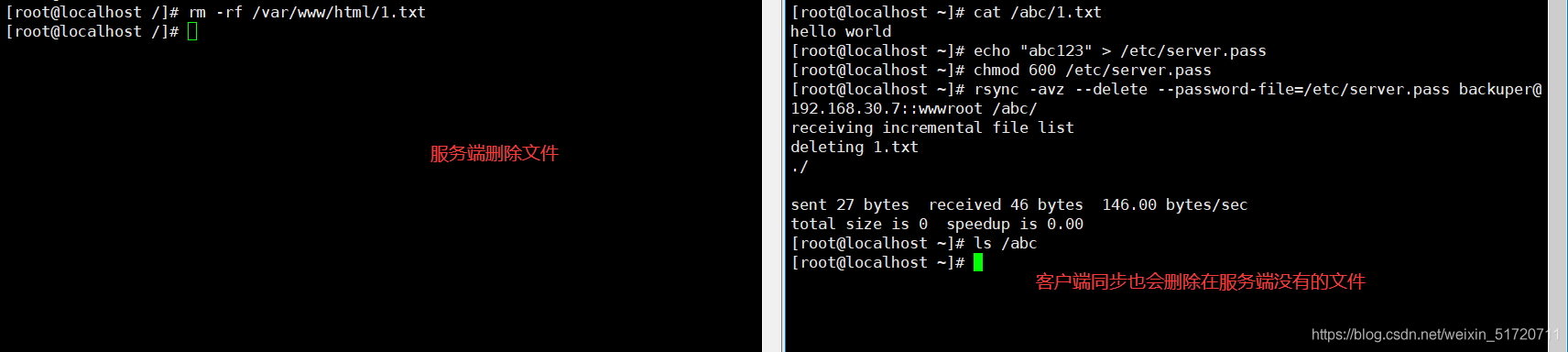
3.rsync + inotify
Monitor file system changes and synchronize files to rsync server
3.1 Install inotify
[root@localhost opt]# yum -y install gcc gcc-c++ Plugins loaded: fastestmirror, langpacks Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirrors.aliyun.com * extras: mirrors.aliyun.com * updates: mirrors.aliyun.com software package gcc-4.8.5-44.el7.x86_64 Installed and up to date software package gcc-c++-4.8.5-44.el7.x86_64 Installed and up to date No processing required [root@localhost opt]# tar xf inotify-tools-3.14.tar.gz [root@localhost opt]# cd inotify-tools-3.14/ [root@localhost inotify-tools-3.14]# ./configure && make && make install
3.2 Modify inotify kernel parameters
[root@localhost ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf [root@localhost ~]# sysctl -p fs.inotify.max_queued_events = 32768 #Monitor time queue, default 16384 fs.inotify.max_user_instances = 1024 #Maximum number of monitoring instances, default 128 fs.inotify.max_user_watches = 1048576 #Maximum number of monitoring files per instance, default is 8192
3.3 Write trigger synchronization scripts
[root@localhost ~]# cat /opt/inotify.sh
#!/bin/bash
#Execute the "inotifywait" command, then add files to/abc directory on the client side, move files, and track screen output
INOTIFY_CMD="inotifywait -mrq -e create,delete,move,modify,attrib /abc/"
RSYNC_CMD="rsync -apzH --delete --password-file=/etc/server.pass backuper@192.168.30.7::wwwroot/ /abc/"
$INOTIFY_CMD | while read DIRECTORY EVENT FILE
do
if [ $(pgrep rsync | wc -l) -le 0 ] ; then
$RSYNC_CMD
fi
done
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /opt/inotify.sh
[root@localhost ~]# chmod +x /etc/rc.d/rc.local
[root@localhost ~]# echo "/opt/inotify.sh" >> /etc/rc.d/rc.local
3.4 Modify rsync profile
[root@localhost /]# vim /etc/rsyncd.conf uid = root gid = root use chroot = yes address = 192.168.30.7 port 873 log file = /var/log/rsyncd.log pid file = /var/run/rsyncd.pid hosts allow = 192.168.30.0/24 [wwwroot] path = /var/www/html comment = Document Root of www.ljm.com read only = no //Turn off read-only, upstream synchronization requires writable permissions dont comperss = *.gz *.bz2 *.tgz *.zip *.rar *.z auth users = backuper secrets file = /etc/user.db
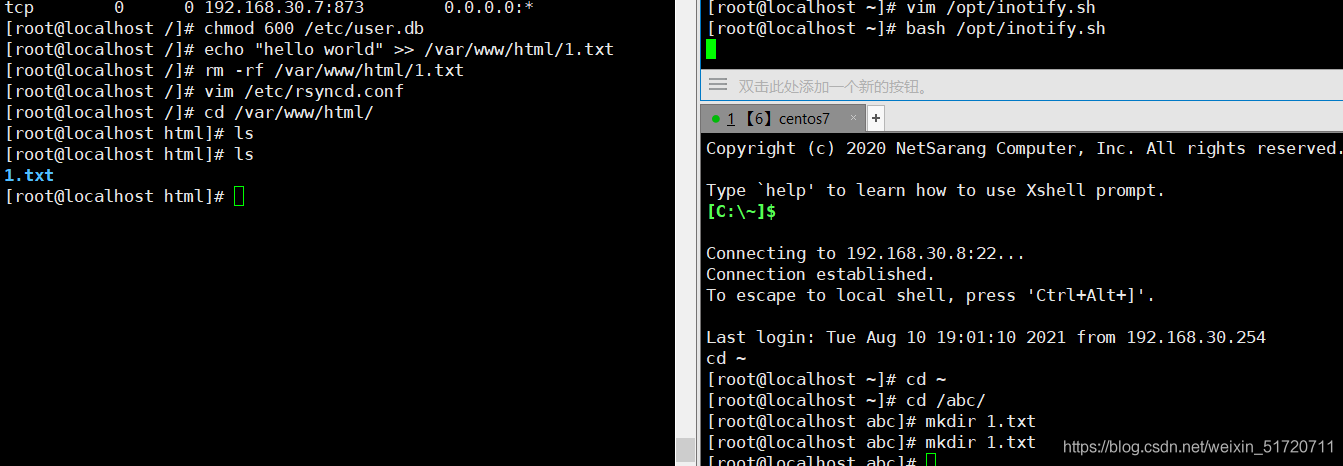
3.5 Test
Create files on client side, view server side
Summary
rsync is a fast and very convenient file copying tool. It can replicate locally, remotely, or as a remote daemon, and it provides a large number of
Parameters control all aspects of its behavior and allow very flexible ways to transfer and copy files