What is a file?
Files in a computer are a collection of data stored on external media (usually disk), which are divided into text files and binary files.
Open and close files
The os.Open() function can open a file and return a *File and an error.Calling the close() method on the resulting file instance closes the file.
func main(){
file,err := os.Open("./main.go")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("open file failed!,err",err)
return
}
fmt.Println("cool!")
file.Close()
}To prevent the file from forgetting to close, we usually use defer to register the file close statement.
read file
file.Read()
Basic Use
The method of Read is defined as follows:
func(f *File) Read(b []byte)(n int, err error)
It receives a byte slice, returns the number of bytes read and possible specific errors, and returns 0 and io.EOF at the end of the file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"io"
)
func main(){
file,err := os.Open("./main.go")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("open file failed!,err", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
var tmp = make([]byte,128)
n, err := file.Read(tmp)
if err == io.EOF {
fmt.Println("File Read Out")
return
}
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("read file failed,err",err)
return
}
fmt.Printf("Read%d Byte data of\n",n)
fmt.Println(string(tmp[:n]))
}Loop Read
Use a for loop to read all the data in the file.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"io"
)
func main(){
file, err := os.Open("./main.go")
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("open file failed!, err", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
var content []byte
var tmp = make([]byte,128)
for {
n ,err := file.Read(tmp)
if err == io.EOF{
fmt.Println("File Read Out")
break
}
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("read file failed,err",err)
return
}
content = append(content,tmp[:n]...)
}
fmt.Println(string(content))
}bufio Read File
bufio encapsulates an API based on file to support more functions.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"os"
"io"
"bufio"
)
func main(){
file , err := os.Open("./main.go")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("open file failed,err",err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
reader := bufio.NewReader(file)
for {
line, err := reader.ReadString('\n')
if err == io.EOF{
fmt.Println("File Read Out")
break
}
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("read file failed!,err",err)
return
}
fmt.Println(line)
}
}Use ioutil to read the entire file
The ReadFile method of the io/ioutil package reads the entire file, simply passing in the file name as a parameter.
package main
import (
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
)
func main(){
content, err := ioutil.ReadFile("./main.go")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("read file failed,err:",err)
return
}
fmt.Println(string(content))
}File Write Operation
The os.OpenFile() function can open a file in a specified mode, thereby enabling file writing.
func OpenFile(name string, flag int, perm FileMode) (*File, error){
....
}Where:
Name is the name of the file to be opened, flag is the mode in which the file is opened. There are several modes:
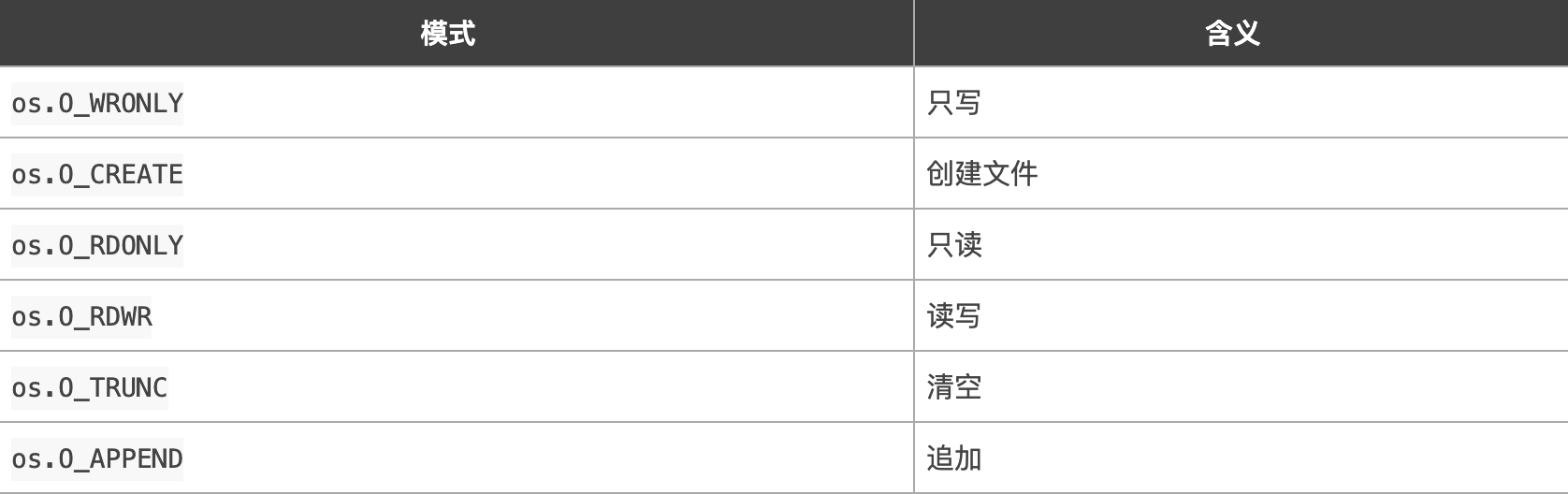
perm file permissions, an octal number.R (read) 04, w (write) 02, x (execute) 01.
Write and WriteString
func main() {
file, err := os.OpenFile("xx.txt", os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC|os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("open file failed, err:", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
str := "hello Shahe River"
file.Write([]byte(str)) //Write Byte Slice Data
file.WriteString("hello Princeling") //Write string data directly
}bufio.NewWriter
import (
"io"
"fmt"
)
func main() {
file, err := os.OpenFile("xx.txt", os.O_CREATE|os.O_TRUNC|os.O_WRONLY, 0666)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("open file failed, err:", err)
return
}
defer file.Close()
writer := bufio.NewWriter(file)
for i := 0; i < 10; i++ {
writer.WriteString("hello Shahe River\n") //Write data to cache first
}
writer.Flush() //Write the contents of the cache to a file
}ioutil.WriteFile
func main() {
str := "hello Shahe River"
err := ioutil.WriteFile("./xx.txt", []byte(str), 0666)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("write file failed, err:", err)
return
}
}Practice
copyFile
func CopyFile(dstName, srcName string)(written int64,err error){
src,err := os.Open(srcName)
if err != nil{
fmt.Printf("open %s failed,err: %v.\n", srcName,err)
return
}
defer src.Close()
dst ,err := os.OpenFile(dstName,os.O_CREATE|os.O_WRONLY,0644)
if err != nil{
fmt.Printf("open %s failed,err:%v.\n",dstName,err)
return
}
defer dst.Close()
return io.Copy(dst,src)
}
func main(){
_,err := CopyFile("dst.txt","src.txt")
if err != nil{
fmt.Println("copy file failed,err",err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Copy done!")
}