1, Security technology and firewall
1.1 safety technology
- Intrusion detection systems: it is characterized by not blocking any network access, quantifying and locating from internal and external networks
The threat situation is mainly to provide alarm and post supervision, and provide targeted guidance measures and safety decision-making basis. Similar to the monitoring system, it generally adopts bypass deployment (looking at you silently). - Intrusion prevention system: it works in a transparent mode and analyzes the contents of data packets, such as overflow attack and denial of service
Conduct accurate analysis and judgment on denial of service attacks, Trojans, worms and system vulnerabilities, and block them immediately after they are determined to be attacks
The effective protection of network security, - generally adopts online deployment. (the only way) - Firewall: the isolation function works at the edge of the network or host and checks the data packets entering and leaving the network or host based on fixed rules
Query and processed by the behavior defined by the rule when matching a rule -- the components of group functions are basically closed by default
Close all pass through access and only open the access allowed policy, which will place the hosts that want access from the external network in the DMZ (demilitarized zone) network
1 waterproof wall
2 waterproof wall in a broad sense: compared with firewall, waterproof wall 1 is a security product to prevent internal information leakage. Network, peripheral interface, storage medium and printer constitute all ways of information leakage. For these four ways of leakage, the waterproof wall shall be fully protected before, during and after the event. Together with anti-virus products and external security products, it constitutes a complete network security system.
1.2 classification of firewall
Divided by protection scope:
- Host firewall: the service scope is the current host
- Network firewall: the service scope is the LAN on one side of the firewall
Divided by implementation mode:
- Hardware firewall: a firewall that realizes some functions at the dedicated hardware level; Another part of the function is based on software implementation, such as Huawei, Shanshi hillstone, Tianrongxin, Qiming star, Lvmeng, etc.
- Software firewall: application software of firewall running on general hardware platform, Windows firewall ISA – > forefront TMG
By network protocol:
-
Network layer firewall: four layers under OSI model, also known as packet filtering firewall
-
Application firewall / proxy server: proxy proxy gateway, OSI model, seven layers
Packet filtering firewall
The network layer selects the data packet based on the filtering logic set in the system, which is called access control list (ACL). It determines whether to allow the data packet to pass through by checking the source address, destination address, port number and protocol status of each data in the data stream, or their combination
Advantages: transparent to users. Fast processing speed and easy maintenance disadvantages: unable to check application layer data, such as viruses
But low: unable to check application layer data, such as viruses
Application layer firewall
Application layer firewall / proxy service firewall, also known as Proxy Server, divides all network communication links across the firewall into two sections
Both internal and external network users access through the "link" on the proxy server. Advantages: it is safer to check the data in the application layer
Disadvantages: increase the load of firewall
2, Firewall tools
2.1 Iptables
The command line tool provided by the software package iptables works in the user space to write rules. The written rules are sent to netfilter to tell the kernel how to process information packets
[root@localhost ~]# iptables --version iptables v1.4.21
2.2 firewalld
New front-end management tools have been introduced since CentOS version 7
Software package:
firewalld
firewalld-config
Management tools:
Firewall CMD command line tool
Firewall config graphics
2.3 nftables
nftables is a new packet classification framework and a new linux Firewall manager, which aims to replace the existing {ip,ip6,arp,eb}_tables. In short:
- It is available when the Linux kernel version is higher than 3.13.
- It has a new command-line tool ntf, and its syntax is different from iptables.
- It also includes a compatibility layer that lets you run iptables commands on top of the new nftables kernel framework.
- It provides a common collection foundation that allows you to establish mappings and associations. You can use this new feature to classify your rule set into a multidimensional tree, which greatly reduces the number of rules to check before finding the final behavior of the package.
2.4 nftables features
-
Have some advanced programming language like capabilities, such as defining variables and including external files, that is, the ability to use additional scripts. nftables can also be used to filter and process a variety of address clusters.
-
Unlike iptables, nftables does not contain any built-in tables. It is up to the administrator to decide which tables are needed and add processing rules for these tables.
-
The table contains a rule chain, which contains rules.
2.5 five hook functions and message flow direction in Netfilter
Netfilter selects five locations in the kernel and puts five hook functions (input, OUTPUT, FORWARD
Preouting and POSTROUTING), and these five hook function s are open to users through a command tool
(iptables) write rules to it
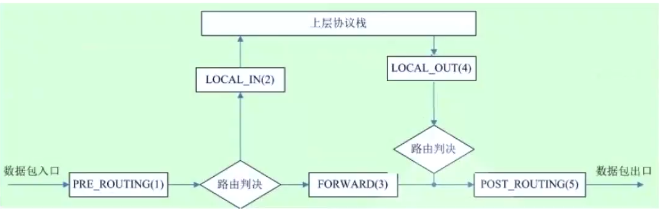
2.5.1 Netfilter overview
Netfilter/IPTables yes Linux2.4.x After a new generation Linux Firewall mechanism, yes linux A subsystem of the kernel. Netfilter It adopts modular design and has good scalability. Its important tool module IPTables From user status iptables Connected to kernel state Netfilter In our architecture, Netfilter And IP The protocol stack fits seamlessly and allows users to filter, address translate, process and other operations on datagrams.
2.5.2 three message flows
- Inflow to the local machine: preempting -- > input – > user space process (accessing my service)
- Out of the machine: user space process -- > output – > postrouting (through me)
- Forwarding: forwarding -- > forward -- > postrouting
chain:
Built in chain: each built-in chain corresponds to a hook function
User defined chain: used to extend or supplement the built-in chain to realize a more flexible rule organization and management mechanism; Hook hook only
It takes effect only when the user-defined chain is used.
INPUT,OUTPUT,FORWARD,PREROUTING,POSTROUTING
. five tables tble: filter, nat, mangle, raw and security
Filter: filter rule table, which filters qualified packets according to predefined rules. The default table is
nat: network address translation rule table
mangle: modify data tag bit rule table
raw: turn off the enabled connection tracking mechanism to speed up the packet passing through the firewall
3, firewalld service
3.1 introduction to firewalld
Firewalld is a new user space software tool for managing netfilter launched by CentOS 7.0. It is also supported by Ubuntu version 18.04 or above (apt install firewalld can be installed)
Firewalld is a system daemon that configures and monitors firewall rules. The functions of iptables, IP6 tables and ebtables can be implemented. Firewalld service is provided by firewalld package
**Classification order of zone:
- First, according to the source address in the packet, it is included as a zone
- It is the zone to which the network interface belongs
- Include the default zone, which is public by default. Administrators can change it to other zones
- The network card belongs to the public zone by default, and the lo network interface belongs to the trusted zone
firewalld supports the division of regional zones, and each zone can set independent firewall rules
- The zone already exists
- Using firewall is to associate specific traffic to a zone
-
Associate zone s through source network segments
-
Associate zone area through network card
-
If there is no associated data message between them, it will go to the default zone
3firewalld zone classification
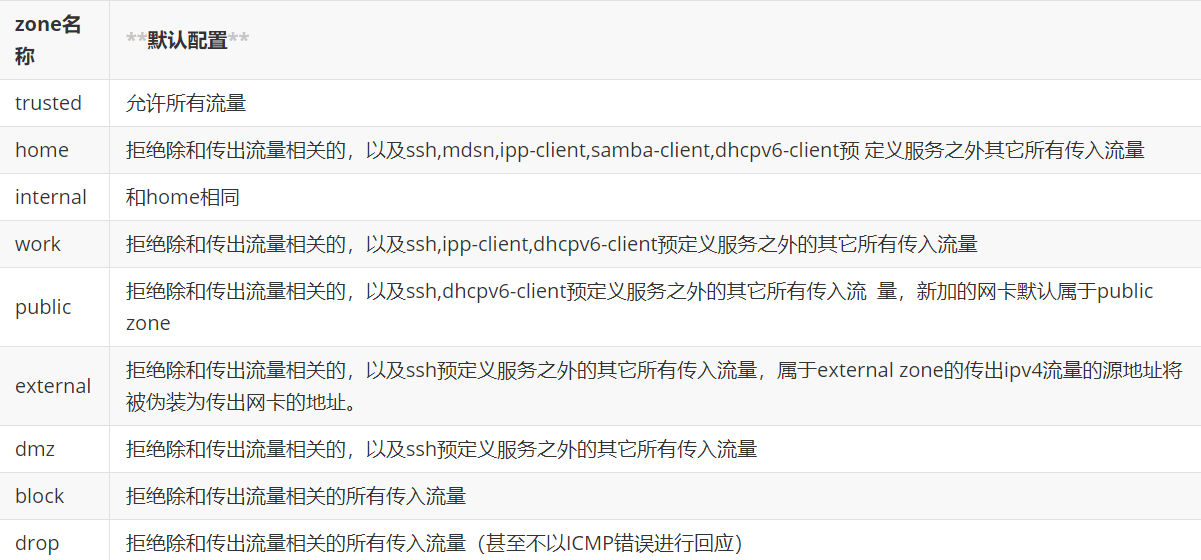
Predefined Services
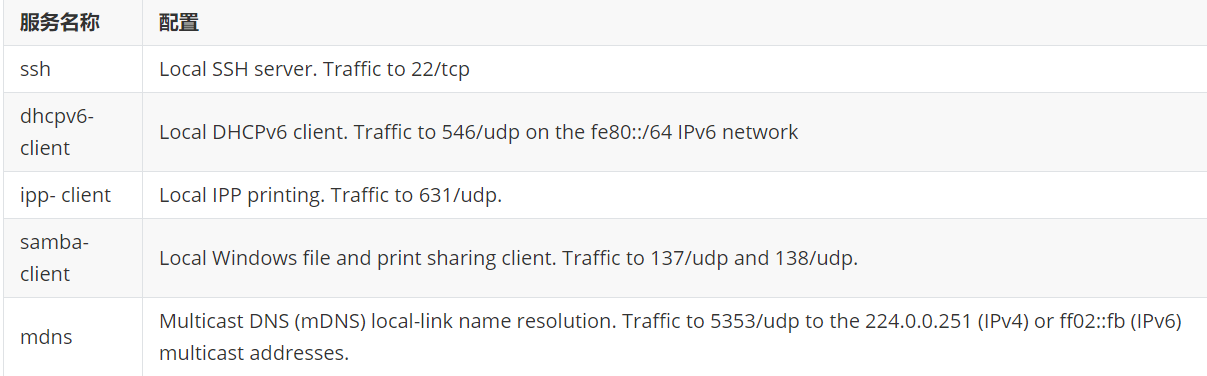
firewalld predefined service configuration -
Firewall CMD -- get services view a list of predefined services
-
/usr/lib/firewalld/services/*.xml configuration of predefined services
Three configuration methods of firewalld
- Firewall config graphical tool: firewall config package needs to be installed
- Firewall CMD command line tool: firewalld package, installed by default
- /The / etc/firewalld / configuration file is generally not recommended, such as: / etc/firewalld/zones/public.xml
3.2 viewing existing firewall settings
[root@localhost ~]#systemctl start firewalld #open [root@localhost ~]#systemctl stop firewalld.service #close [root@localhost ~]#systemctl status firewalld #View status [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --list-all public (active) target: default icmp-block-inversion: no interfaces: ens33 sources: services: ssh dhcpv6-client ports: protocols: masquerade: no forward-ports: source-ports: icmp-blocks: rich rules: [root@localhost ~]#Firewall CMD -- list all -- zones = zone name
3.3 setting the default viewing area
[root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --zone= #Viewing area block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --get-default-zone #View default area [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --set-default-zone block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --set-default-zone block dmz drop external home internal public trusted work [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --set-default-zone home success [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --get-default-zone home
3.4 add source address (network segment), port and service
[root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp #Add 80 ports [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --permanent --add-port=80/tcp --zone=home #You can specify an area success [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --add-service=http #Allow http services [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --permanent --add-icmp-block=echo-request #Prohibit ping success [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --reload success [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --permanent --add-source=192.168.100.0/24 # The basic command takes effect permanently. Add the subnet mask of the source network segment [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --reload success [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --list-all #View effective policies Small experiment Try opening httpd service ####Delete source [root@localhost ~]#firewall-cmd --zone=home --remove-source=192.168.91.0/24 --remove-source=192.168.50.0/24 --remove-source=192.168.100.0/24 --permanent
3.5 rich management rules
rich rules are more powerful than the basic firewalld syntax. They can not only allow / deny, but also log syslog and syslog
auditd can also realize port forwarding, camouflage and rate limiting
Rule implementation sequence:
Port forwarding and camouflage rules in this area
Log rules for this area
Allow rules for this area
Reject rules for this area
Each matching rule takes effect. All rules do not match. The default rules in this area take effect
rich syntax:
rule [source] [destination] service|port|protocol|icmp-block|masquerade|forward-port [log] [audit] [accept|reject|drop]
4, bond
4.1 nmli command
nmcli con add help #Configuring the network using nmcli nmcli con show #Show all active connections nmcli con show --active #Display network connection configuration nmcli con show "System eth0" #Display device status nmcli dev status #Display network interface properties nmcli dev show eth0 #Create a new connection default, and the IP is automatically obtained through dhcp nmcli con add con-name default type Ethernet ifname eth0 #Delete connection nmcli con del default #Create a new connection static, specify a static IP, and do not connect automatically nmcti con add con-name static ifname eth0 autoconnect no type Ethernet ipv4.addresses 172.25.X.10/24 ipv4.gateway 172.25.X.254 #Enable static connection configuration nmcli con up static #Enable default connection configuration nmcli con up default #Modify connection settings nmcli con mod "static" connection.autoconnect no nmcli con mod "static" ipv4.dns 172.25.X.254 nmcli con mod "static" +ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8 nmcli con mod "static" -ipv4.dns 8.8.8.8 nmcli con mod "static" ipv4.addresses "172.16.X.10/24 172.16.X.254" nmcli con mod "static" +ipv4.addresses 10.10.10.10/16 #DNS settings are stored in / etc/resolv.conf. PEERDNS=no indicates that DNS is still manually set when IP is automatically obtained through dhcp, Do not get automatically is equivalent to the following command nmcli con mod "system eth0" ipv4.ignore-auto-dns yes
#Add binding interface nmcli con add type bond con-name mybond0 ifname bond0 mode active-backup ipv4.method manual ipv4.addresses 192.168.91.100/24 #Add slave interface nmcli con add type bond-slave ifname ens7 master bond0 nmcli con add type bond-slave ifname ens33 master bond0 #Note: if no connection name is provided for the dependent interface, the name is composed of interface name and type #To start binding, you must first start the slave interface nmcli con up bond-slave-ens33 nmcli con up bond-slave-ens37 #Start binding nmcli con up mybond0
5.2 practical operation
[root@localhost ~]#nmcli connection add con-name mybond0 ifname bond0 type bond ipv4.method manual ipv4.addresses 192.168.91.100/24 mode active-backup Connect“ mybond0"(422ba65f-12cd-4edd-9d4d-367b6c205823) Successfully added. [root@localhost network-scripts]#ls ifcfg-ens33 ifdown-isdn ifup-bnep ifup-routes ifcfg-ens37 ifdown-post ifup-eth ifup-sit ifcfg-lo ifdown-ppp ifup-ib ifup-Team ifcfg-mybond0 ifdown-routes ifup-ippp ifup-TeamPort ifdown ifdown-sit ifup-ipv6 ifup-tunnel ifdown-bnep ifdown-Team ifup-isdn ifup-wireless ifdown-eth ifdown-TeamPort ifup-plip init.ipv6-global ifdown-ib ifdown-tunnel ifup-plusb network-functions ifdown-ippp ifup ifup-post network-functions-ipv6 ifdown-ipv6 ifup-aliases ifup-ppp [root@localhost network-scripts]#cat ifcfg-mybond0 DEVICE=bond0 BONDING_OPTS=mode=active-backup TYPE=Bond BONDING_MASTER=yes PROXY_METHOD=none BROWSER_ONLY=no BOOTPROTO=none IPADDR=192.168.91.100 PREFIX=24 DEFROUTE=yes IPV4_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6INIT=yes IPV6_AUTOCONF=yes IPV6_DEFROUTE=yes IPV6_FAILURE_FATAL=no IPV6_ADDR_GEN_MODE=stable-privacy NAME=mybond0 UUID=422ba65f-12cd-4edd-9d4d-367b6c205823 ONBOOT=yes [root@localhost network-scripts]#nmcli connection add type bond-slave ifname ens37 master bond0 Connect“ bond-slave-ens37"(386628bb-94b5-4c98-9023-f3fab154943d) Successfully added. [root@localhost network-scripts]#nmcli connection add type bond-slave ifname ens33 master bond0 Connect“ bond-slave-ens33"(c97d22d5-23c2-472f-891e-dff378b7f69f) Successfully added. [root@localhost network-scripts]#nmcli connection name UUID type equipment ens33 12156d92-6495-4c69-82e9-c0e22f532f76 802-3-ethernet ens33 mybond0 422ba65f-12cd-4edd-9d4d-367b6c205823 bond bond0 virbr0 335fcf86-189c-4513-9deb-da344ff280dd bridge virbr0 Wired connection 1 d62f0f08-f45b-3548-815d-30dbca7821f6 802-3-ethernet ens37 bond-slave-ens33 c97d22d5-23c2-472f-891e-dff378b7f69f 802-3-ethernet -- bond-slave-ens37 386628bb-94b5-4c98-9023-f3fab154943d 802-3-ethernet -- [root@localhost network-scripts]#nmcli connection up bond-slave-ens33 The connection was successfully activated( D-Bus Active path:/org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/24) [root@localhost network-scripts]#nmcli connection up bond-slave-ens37 The connection was successfully activated( D-Bus Active path:/org/freedesktop/NetworkManager/ActiveConnection/25) [root@localhost network-scripts]#cat /proc/net/bonding/bond0 Ethernet Channel Bonding Driver: v3.7.1 (April 27, 2011) Bonding Mode: fault-tolerance (active-backup) Primary Slave: None Currently Active Slave: ens33 MII Status: up MII Polling Interval (ms): 100 Up Delay (ms): 0 Down Delay (ms): 0 Slave Interface: ens33 MII Status: up Speed: 1000 Mbps Duplex: full Link Failure Count: 0 Permanent HW addr: 00:0c:29:fe:e5:bf Slave queue ID: 0 Slave Interface: ens37 MII Status: up Speed: 1000 Mbps Duplex: full Link Failure Count: 0 Permanent HW addr: 00:0c:29:fe:e5:c9 Slave queue ID: 0