First acquaintance of C language
The video comes from station b
Geng Bo is just to serve as a learning note... No intention of embezzlement
1. Write c language code:
1. Create project
2. Create files
3. Execute Ctrl + F5
#include "stdio.h"
int main()
{
printf("hello world/n");
return 0;
}
4. Set linker:
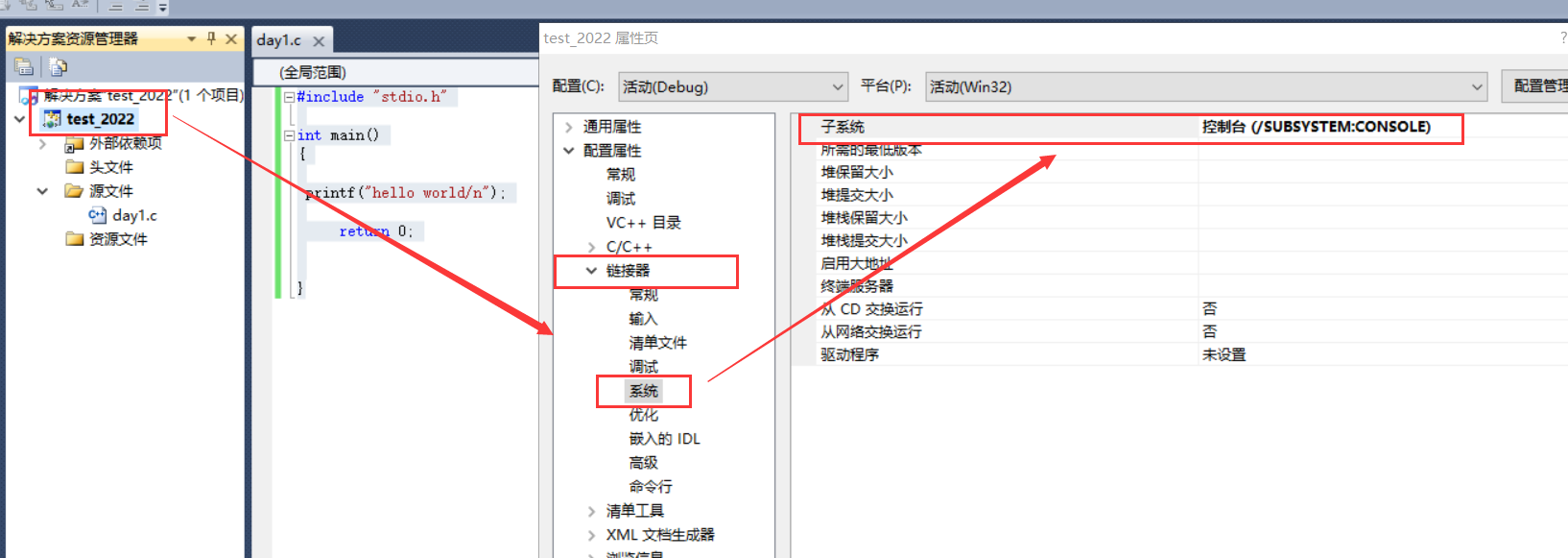
5. Set line number:
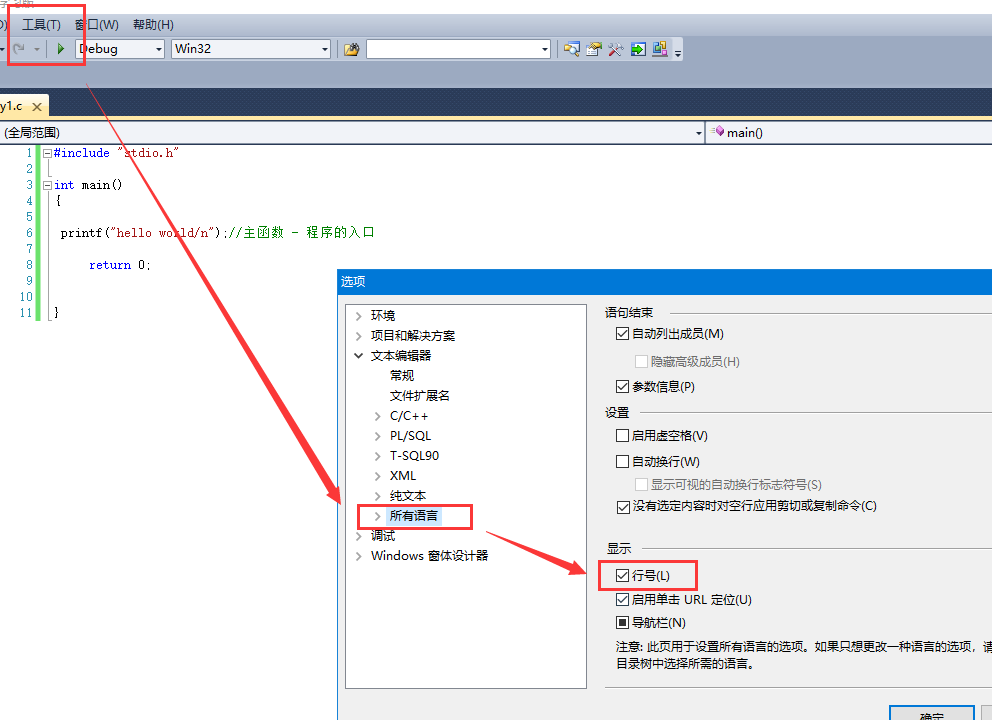
6.
//include contains a file called "stdio.h"
//std - standard stadanard input output
#include "stdio.h"
//int means integer
//The int in front of main indicates that the main function call returns an integer value
int main()//Main function - the entry of the program, with and only one
{
printf("hello world/n");//Here, complete the task, output hello world on the screen, function - print function-printf - print function
//Library function - the function provided by C language itself for us to use
// Other people's things - say hello
// #include
return 0;//Return to '0'
}
2. Data type:
// char - character data type
// Short - short integer
// int - integer
// Long long integer
// long long longer integer
// float single precision floating point number
// Double double precision floating point number
//%c - print character format data
//%d - print integer decimal data
//%f - print floating point numbers - print decimals
//%lf - print double data
//%p - print as address
//%x - print hex
//%o ....
int main()
{
char ch = 'A';
printf("%c\n",ch);
return 0;
}
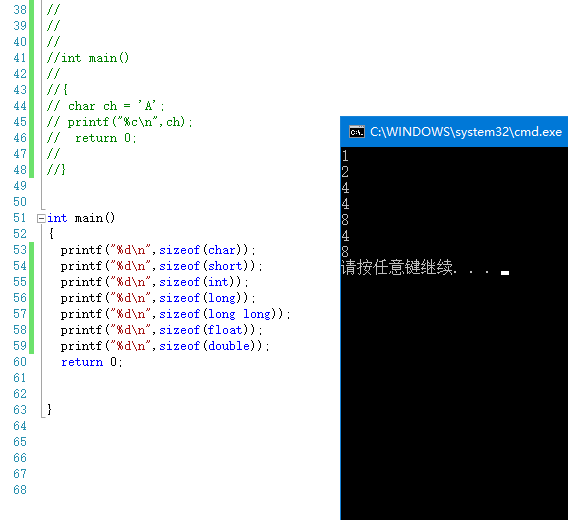
3.
int main()
{
short age = 20;//Apply for 2 bytes = 16bit from the memory to store 20 bytes
printf("%d\n",age);
return 0;
}
4. Variables:
4.1 definition:
int age =150; float weight =45.5f; char ch = "w";
4.2 local / global variables:
Global variables: variables defined outside {...};
Local variables: variables defined within {...};
//It is recommended that the names of local variables and global variables should not be the same - it is easy to misunderstand
//Local variables are limited when the names of local variables and global variables are repeated
int main()
{
//Calculate the sum of two numbers
int num1 = 0;
int num2 = 0;
int sum =0;
// Input data - use input functions
scanf("%d%d",&num1,&num2);// &Get address symbol
//C language should be defined at the front of the current code segment;
sum = num1 + num2;
printf("sum = %d\n",sum);
return 0;
}
6. Scope and life cycle of variables:
6.1
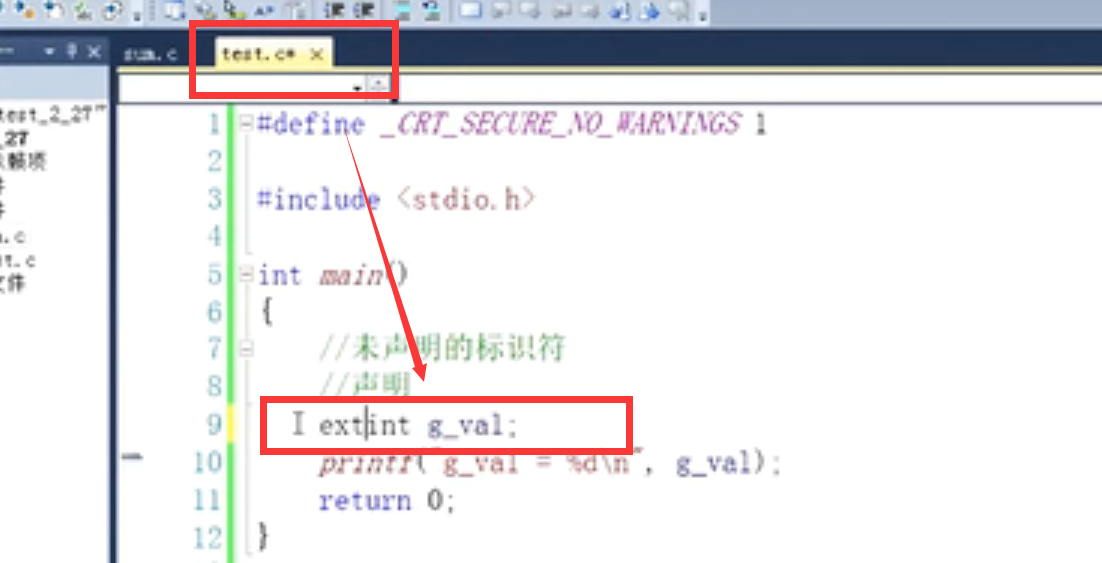
Scope: where can I use this "variable" and where can I not
int main()
{
{ int num =0;}
printf("num = %d\n",num);
return 0;
}
6.2
6.3
Life cycle: a period of time from variable creation to destruction
1. Life cycle of local variables: start the life cycle of entering scope and end the life cycle of exiting scope
2. Life cycle of global variable: the life cycle of the whole program
3. Ignore warnings
Add a sentence before the code:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1 //Add to the first line of the source file
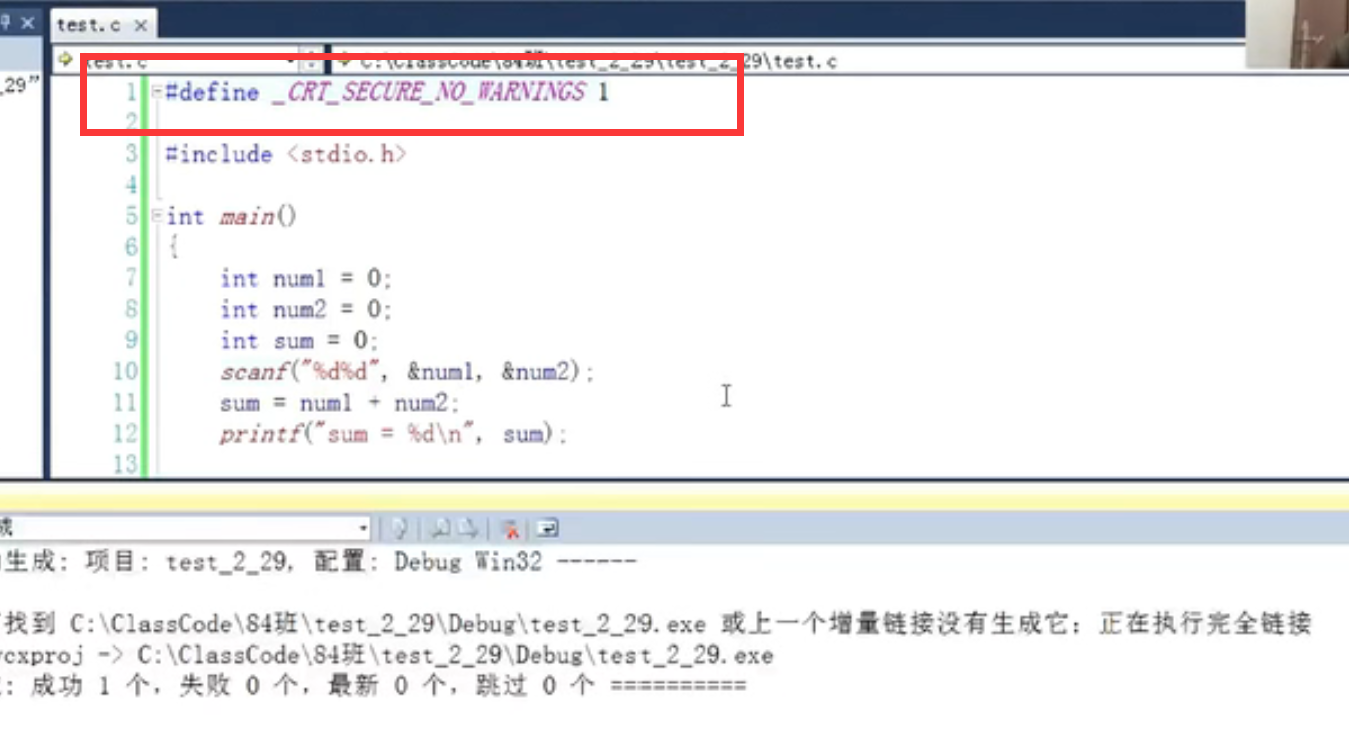
2. These library functions are considered unsafe
//scanf //strcpy //strlen //strcat //... //Unsafe //strcpy_s
4. Automatic header (TIPS)
1. First find the absolute path to install VC:
D:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft Visual Studio 10.0\VC\vcprojectitems
2. Find the file NEWC + + file cpp:
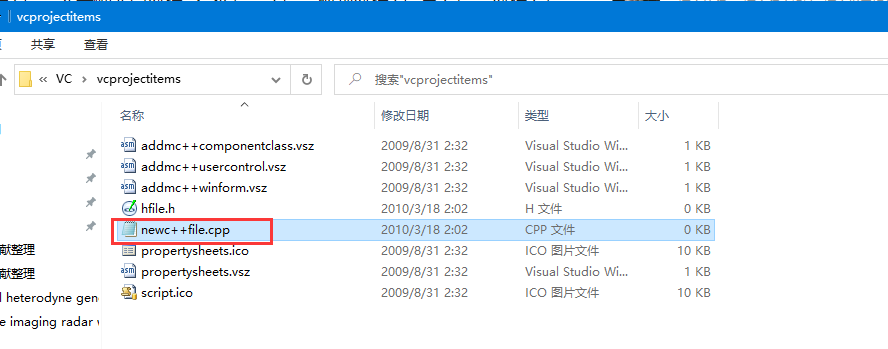
3. Open edit save:
5. Constant:
1. Type of constant:
1. Literal constant:
Written directly... For example: 3, 4, 5
2.const modified constant:



3.#define defined identifier constants:

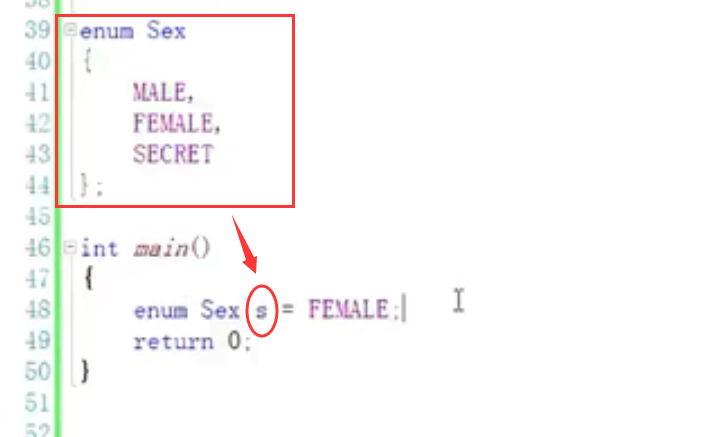
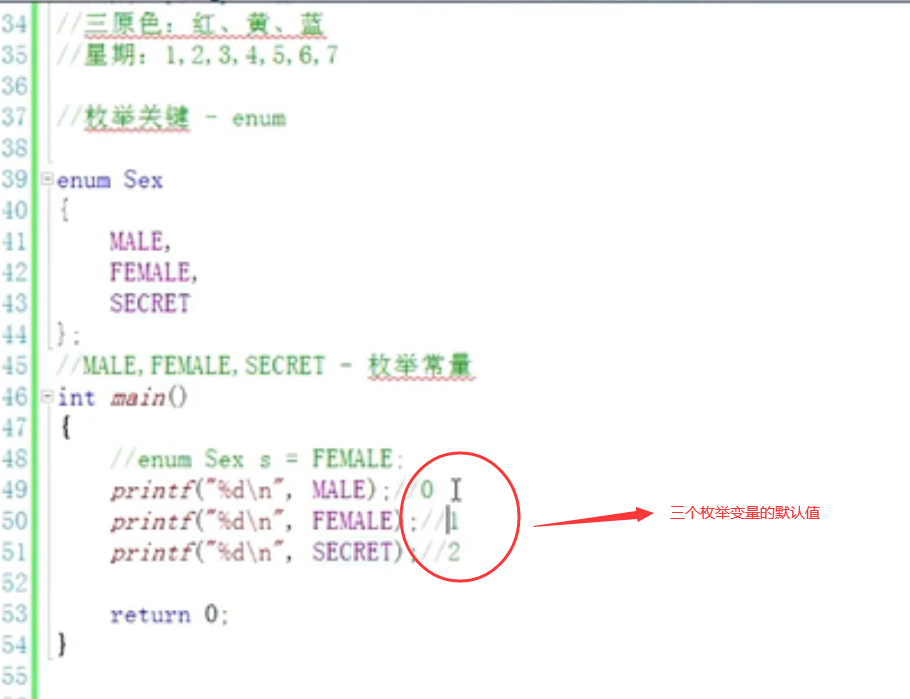
4. Enumeration constants:

enum Sex
{
MALE,
FEMALE,
SECRET
};//Ale female secret -- Enumeration constant

6. String + escape character + comment:
1. String:
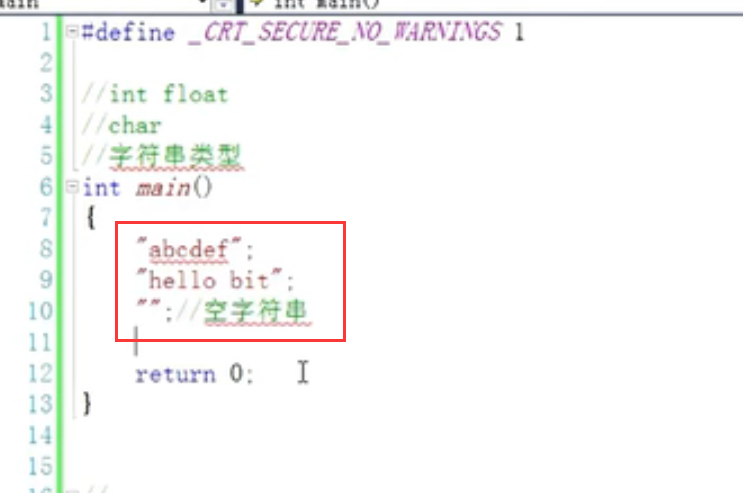
2. Storage string:
1. char array to store string:

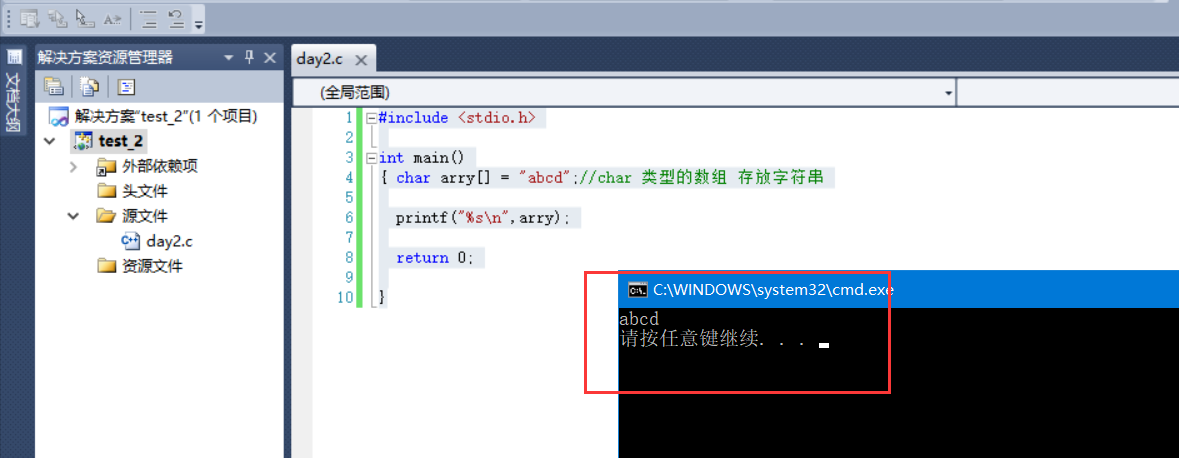
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
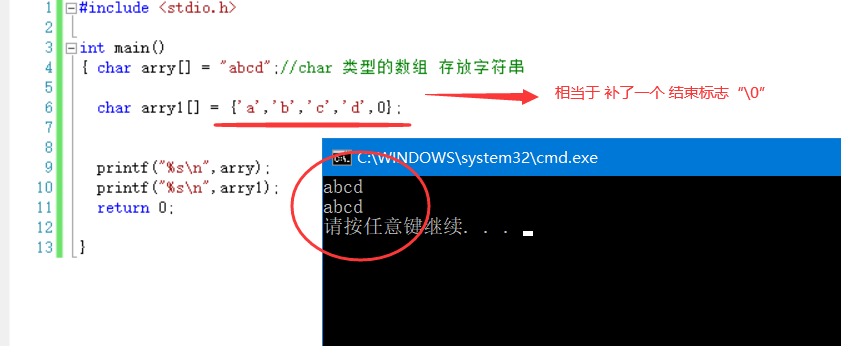
{ char arry[] = "abcd";//An array of type char holds strings
printf("%s\n",arry);
return 0;
}
2. Debug if the printed results are inconsistent:
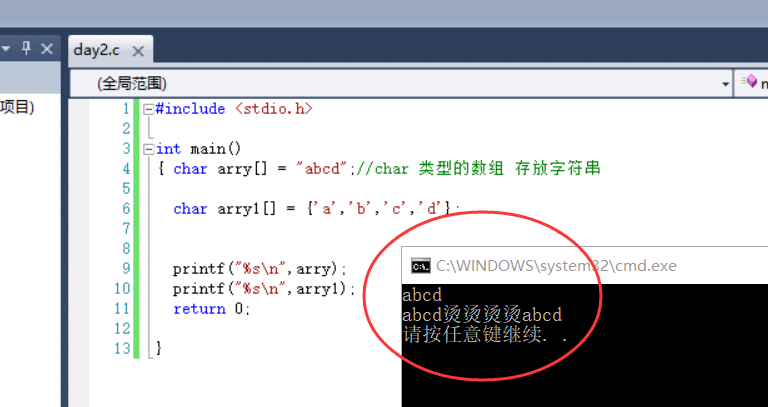
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{ char arry[] = "abcd";//An array of type char holds strings
char arry1[] = {'a','b','c','d'};
printf("%s\n",arry);
printf("%s\n",arry1);
return 0;
}
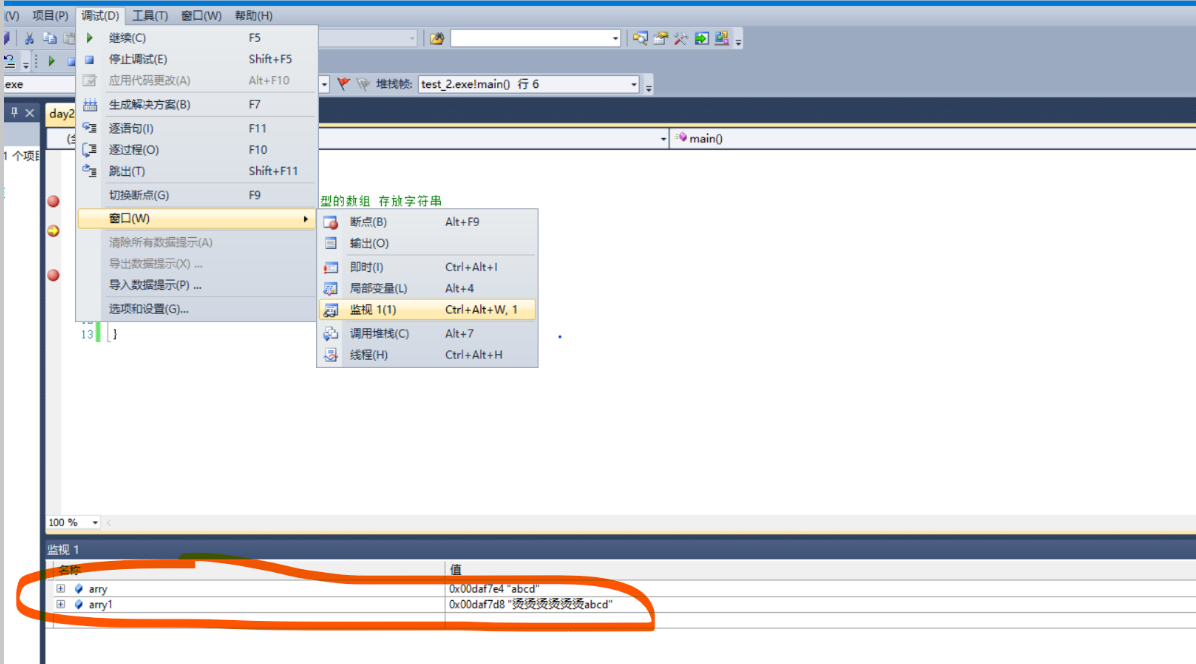
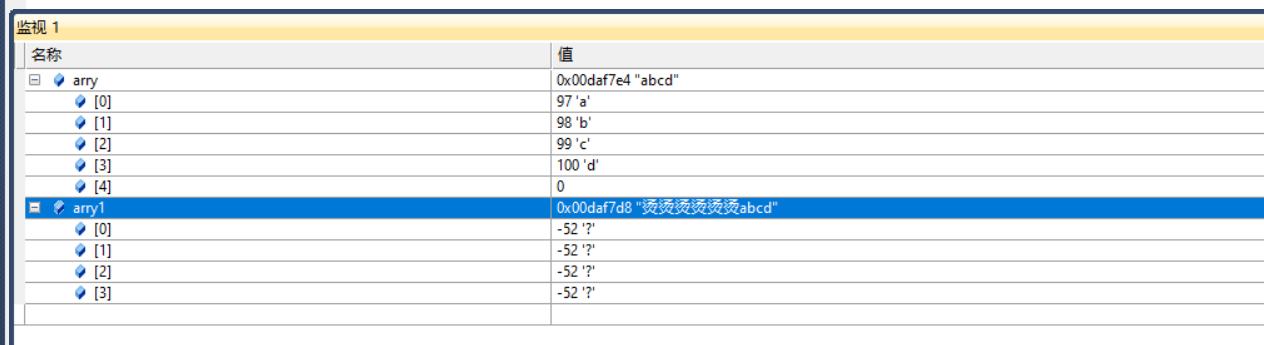
3. Complement 0 to play the role of "\ 0" Terminator:

4. The results are consistent:
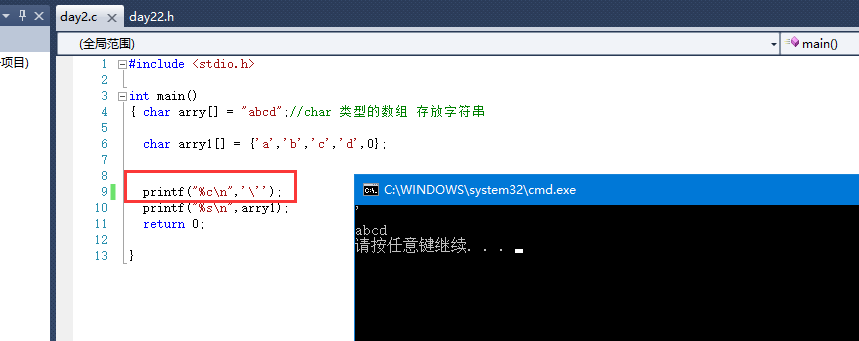
5. String definition

6. Output string length:

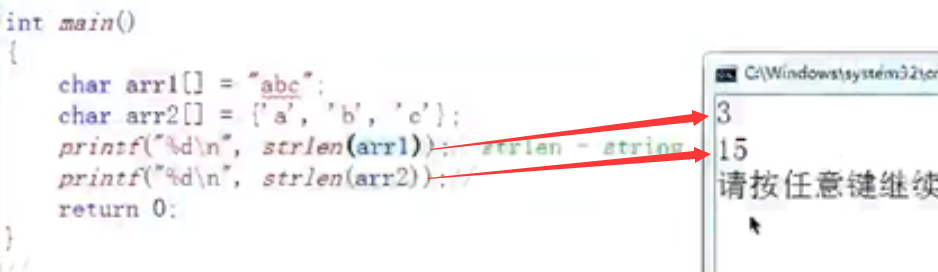
arry1 '\ 0' is not a length
There is no "\ 0" in arry2, which is filled with random numbers, so the length is increased
Then the answer is: 3 and random value
7. Escape character (change the original meaning):
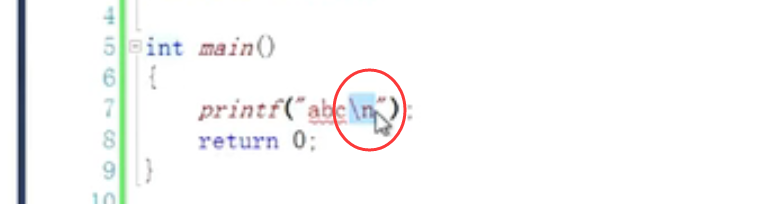
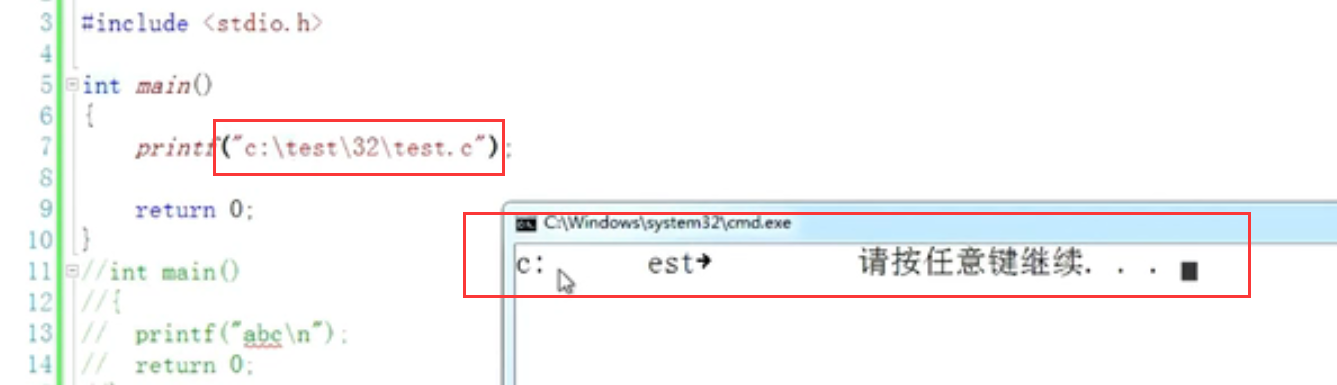
8.strlen():
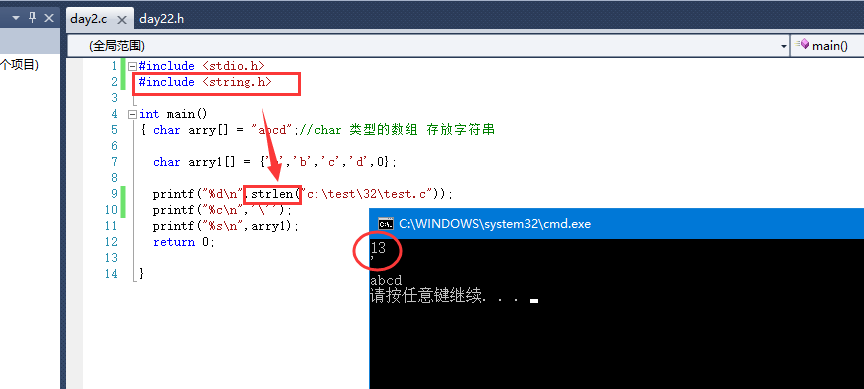
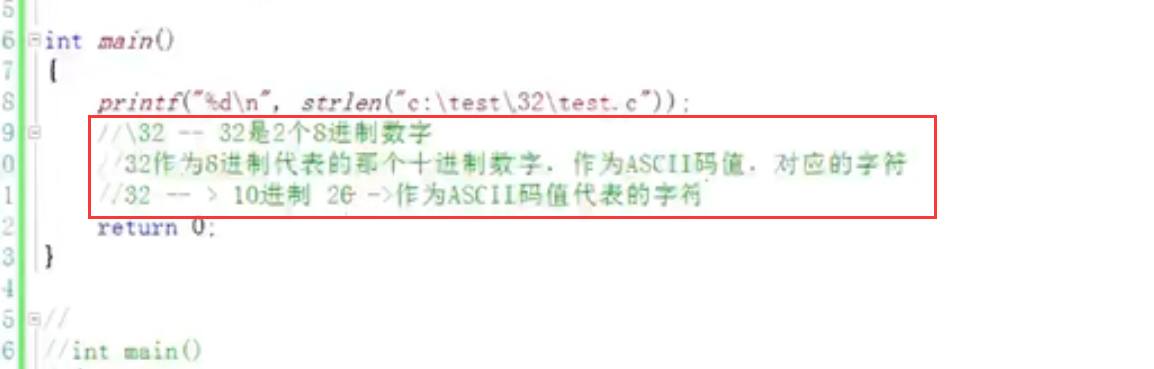
printf("%c\n",'\x61');// x61 hexadecimal 61 corresponds to 97, i.e. "a"
3. Differences between \ 0, 0 and "0":
7. Notes:
1. "\"
2."/* */"

3. Multiline comments:
CTRL + K + C > > > multiline comment
CTRL + K + U > > > uncomment multiple lines
8. Conditional statements:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main()
{
int input = 0 ;//Store the input variable input
printf("Add bit\n");
printf("Do you want to study hard?(1/0):");
scanf("%d",&input);// 1/0
if(input == 1)
printf("good offer\n");
else
printf("Selling sweet potatoes\n");
}
int main()
{
int line = 0;
printf("Add bit\n");
while(line<20000)
{
printf("Type one line of code:%d\n",line);
line ++;
if(line>=20000)
printf("good offer\n");
}
9. Function
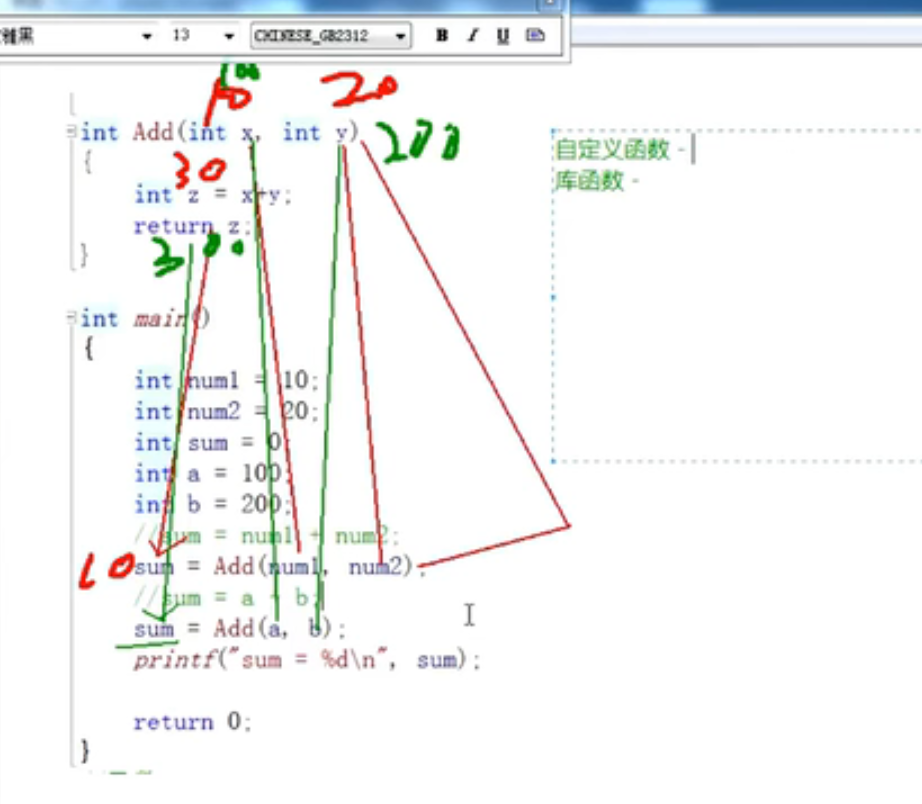
1. int ADD(int x,int y)
Functions that can achieve the same function
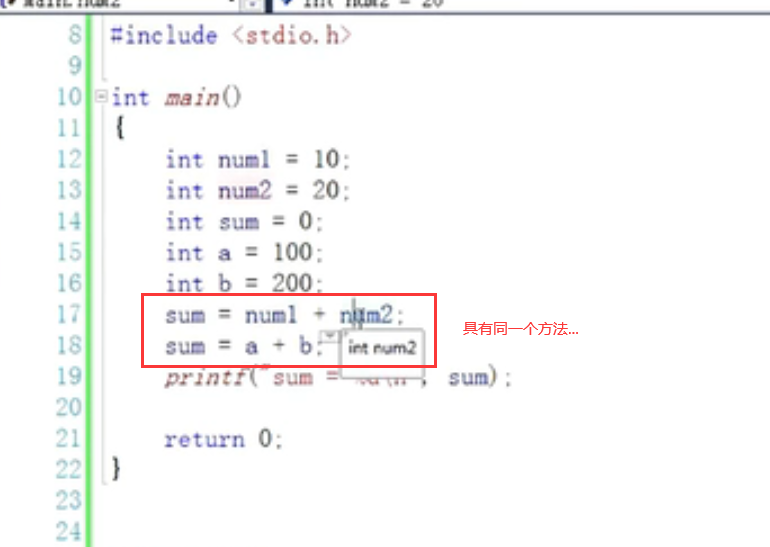
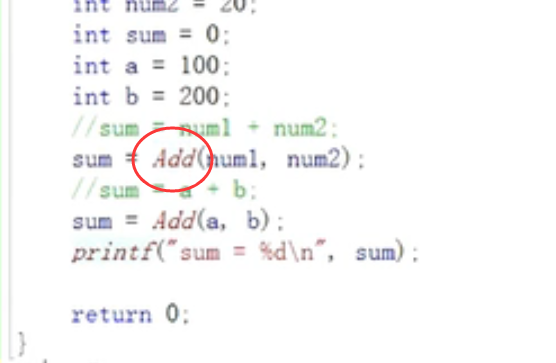
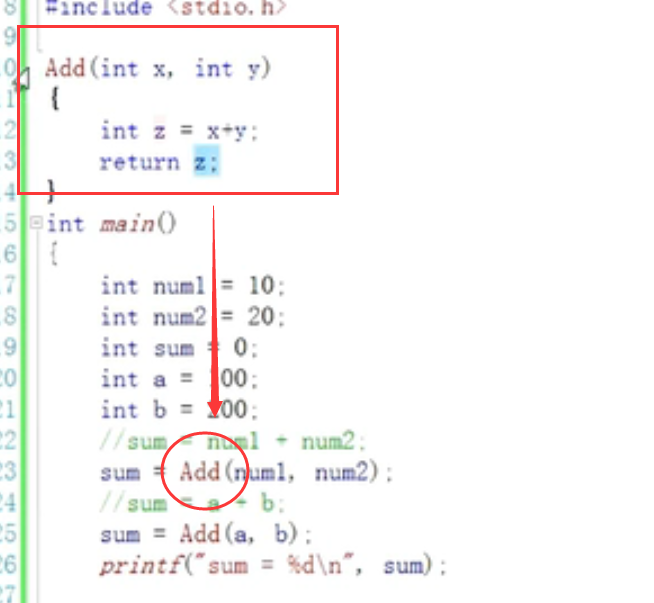
int ADD(int x,int y)
{
int z =x+y;
return z;
}
int main()
{
int a=10;
int b =10;
int sum =0;
sum = ADD(a,b);
}
2. Function for maximum value:
The first is written directly in the main() function:

int main()
{
int num = 1;
int num1 = 2;
if(num>num1)
{
printf("The maximum value is:%d\n",num);
}
else
printf("The maximum value is:%d\n",num1);
return 0;
}
The second method is to call sub functions:
int max(int x,int y)
{
if(x>y)
return x;
else
return y;
}
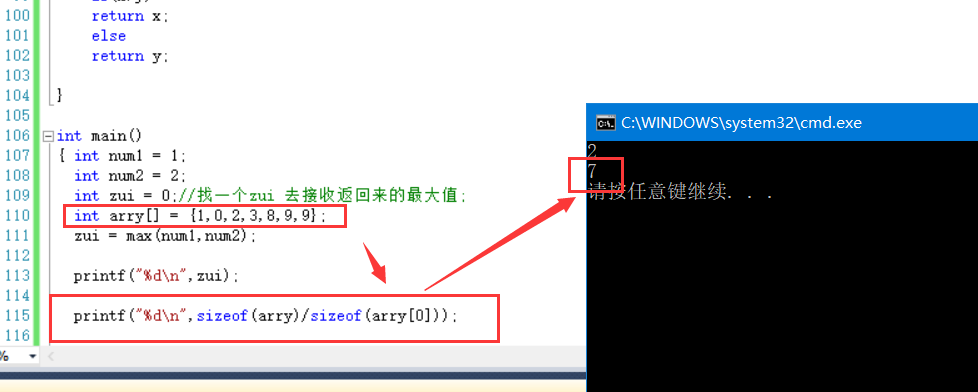
int main()
{ int num1 = 1;
int num2 = 2;
int zui = 0;//Find a zui to receive the maximum value returned;
zui = max(num1,num2);
printf("%d\n",zui);
return 0;
}
10. Array
1. Basic definition of array:

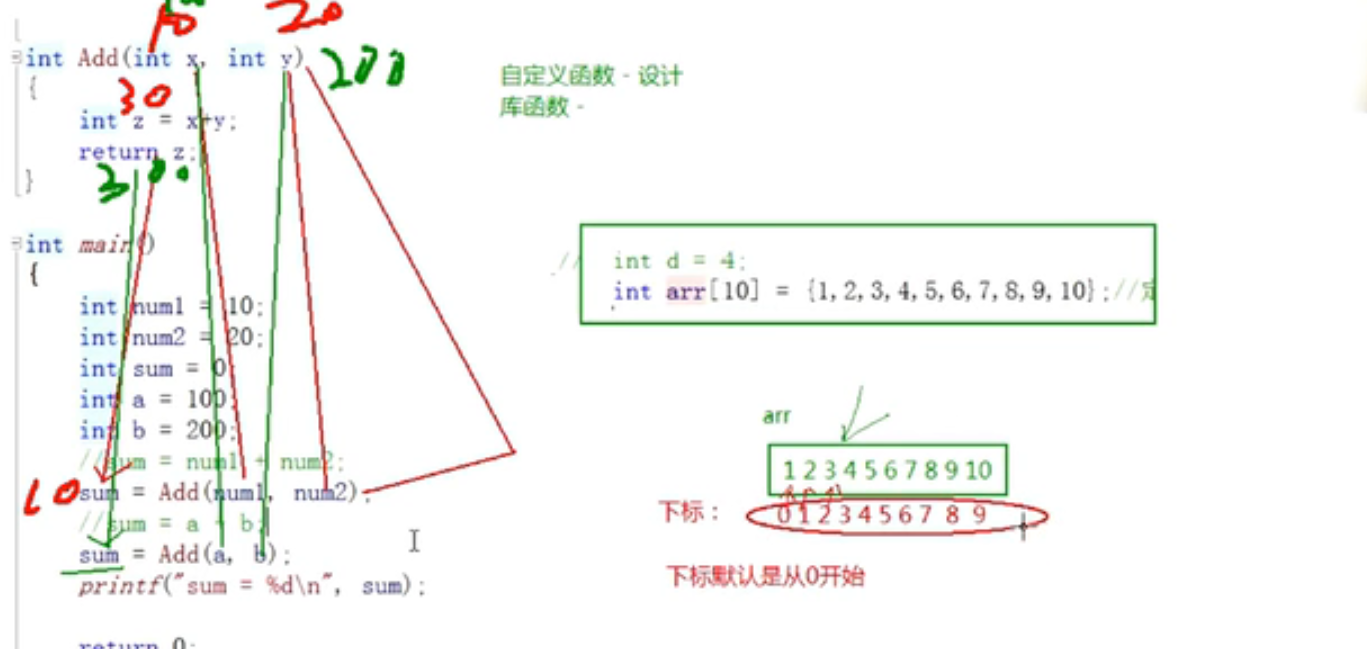
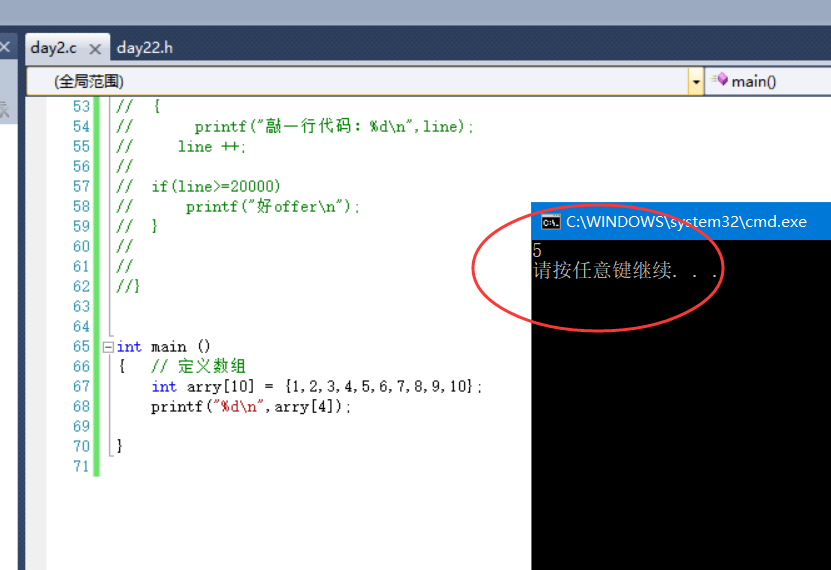
int main ()
{ // Define array
int arry[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
printf("%d\n",arry[4]);
}
int main ()
{ // Define array
int arry[10] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int i = 0;
printf("%d\n",arry[4]);
while(i<10)
{
printf("%d\n",arry[i]);
i++;
}
}

2. Meaning of int arry:
In int array, int defines the type of data in the data, and the array has its own type;
11. Operator
1. Arithmetic operator:
"+" "-" "*" "/"% "addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
2. Shift operator
"> >" "< <" move right and left
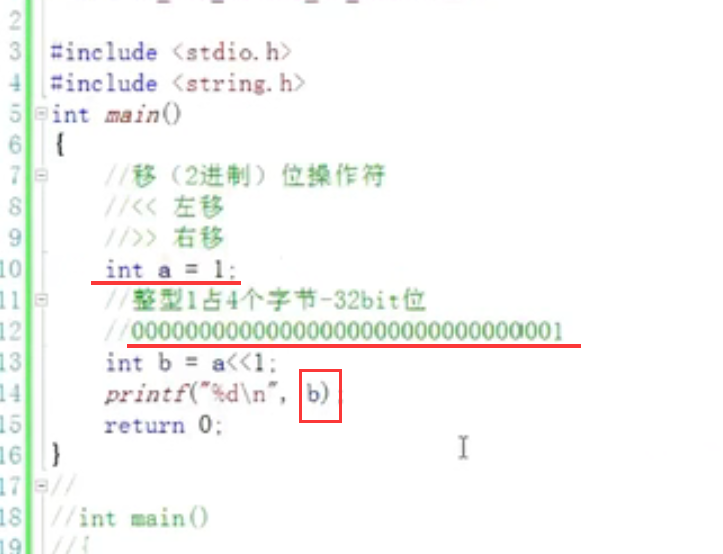
3. Bitwise operator
"&" "|" "^" and or XOR
XOR: 0 if the binary bits are the same / 1 if the binary bits are different
4. Assignment:
a = a + 10 / a += 10
...
a -= 20, a & = 20... / / compound assignment character
5. Unary operator (one operand)
Binocular operator (two operands)
Ternary operator (three operands)
! Logical negation
...

5.1 calculating array size:
Total array size / size of each element
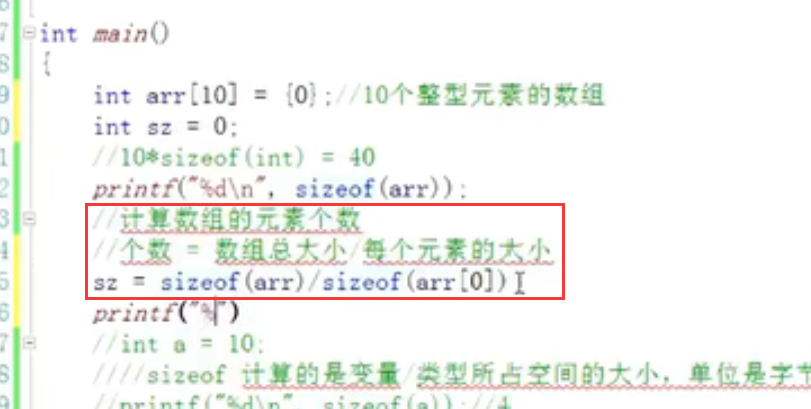
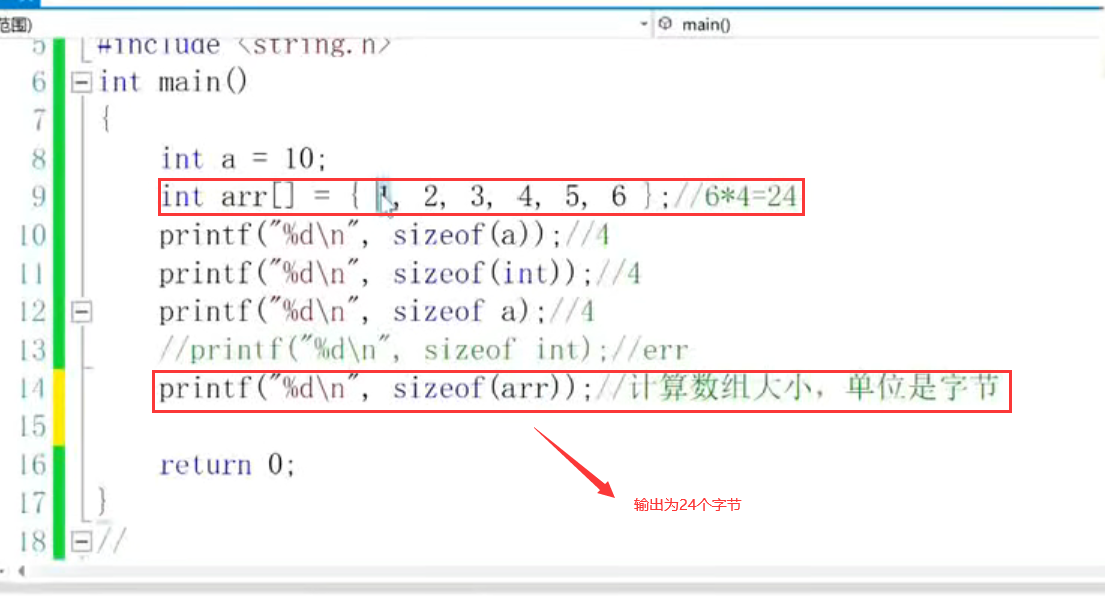
12.size of ( ):
1. Example:
2. There are several elements in the array:
13. "~" is inverted by binary:
1. Code:
int main()
{
int a = 0;//4 bytes, 32bit 00000000 000000000 000000000 000000000
int b =~a;// 11111111 11111111 11111111 11111111
printf("%d\n",b);
return 0;
}
2. Analysis:
a should not be 11111111111111111111111111111111111111111111