catalogue
1, Prerequisites for database programming
2, Database programming in Java: JDBC
4, Construction of development environment
1, Prerequisites for database programming
Programming languages, such as Java, C, C + +, Python and other databases, such as Oracle, mysql, SQL Server and other database driver packages: different databases provide different database driver packages corresponding to different programming languages. For example, MySQL provides Java driver package MySQL connector Java, which is required to operate MySQL based on Java. Similarly, to operate Oracle database based on Java, Oracle database driver package ojdbc is required.
2, Database programming in Java: JDBC
JDBC, namely Java Database Connectivity. Is a Java API for executing SQL statements. It is the database connection specification in Java. This API consists of Java sql.*, javax. sql.* It is composed of some classes and interfaces in the package. It provides a standard API for Java developers to operate the database, and can provide unified access to a variety of relational databases.
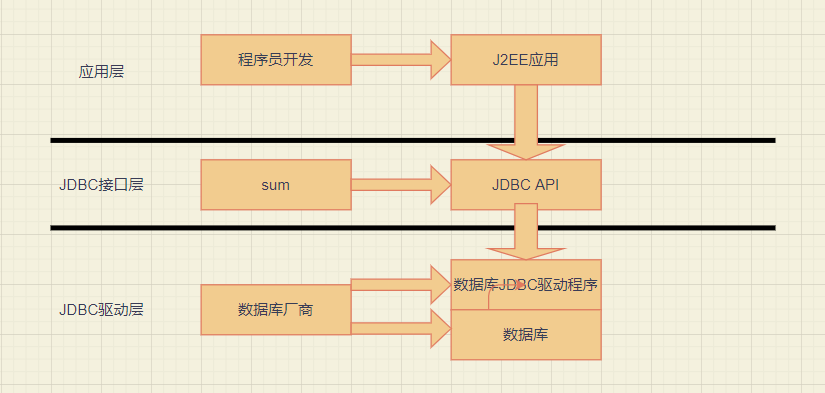
3, How JDBC works
DBC provides a unified access mode for a variety of relational databases. As a high-level abstraction of database access API for specific manufacturers, it mainly contains some general interface classes.
JDBC access database hierarchy:
4, Construction of development environment
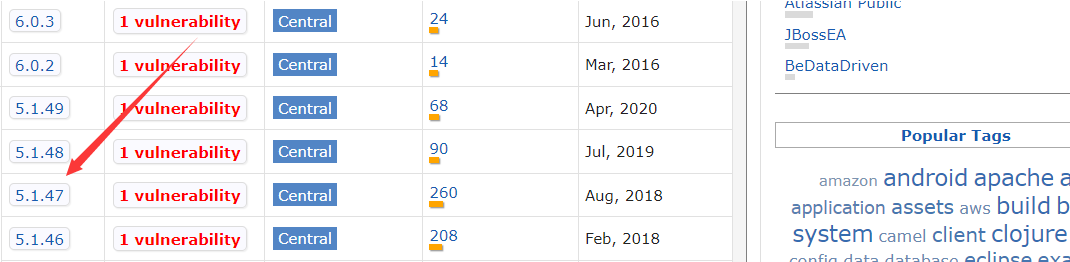
First check your MySQL version in the computer service, and then enter the maven warehouse
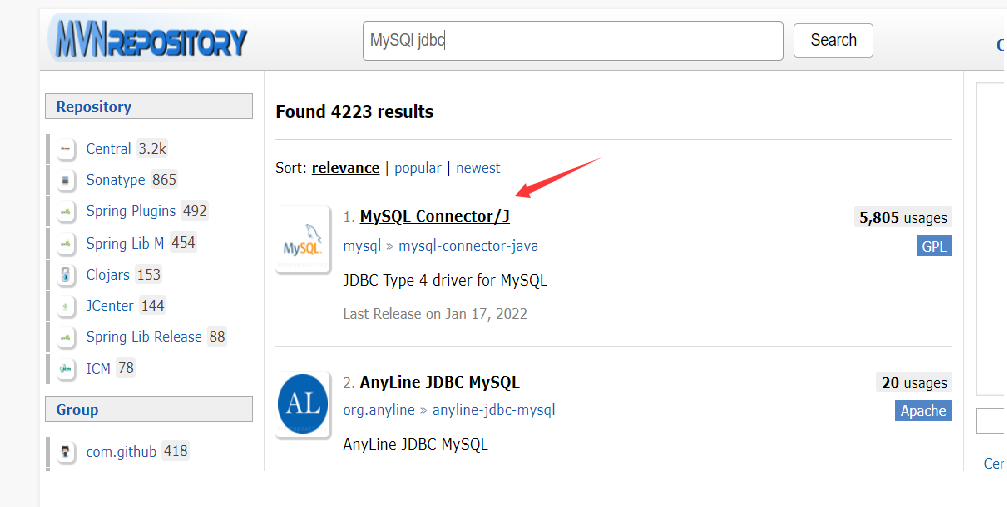
Because my own version is after 5.0, I choose 5.1.47, and the large version should be consistent
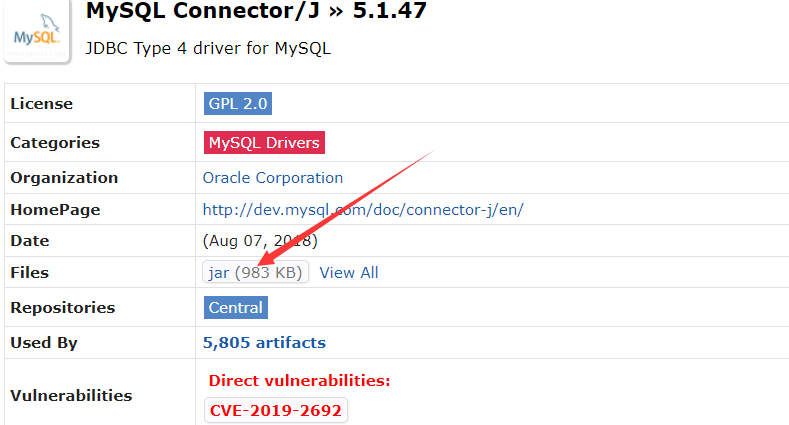
Just download the jar. Remember, the jar package cannot be decompressed
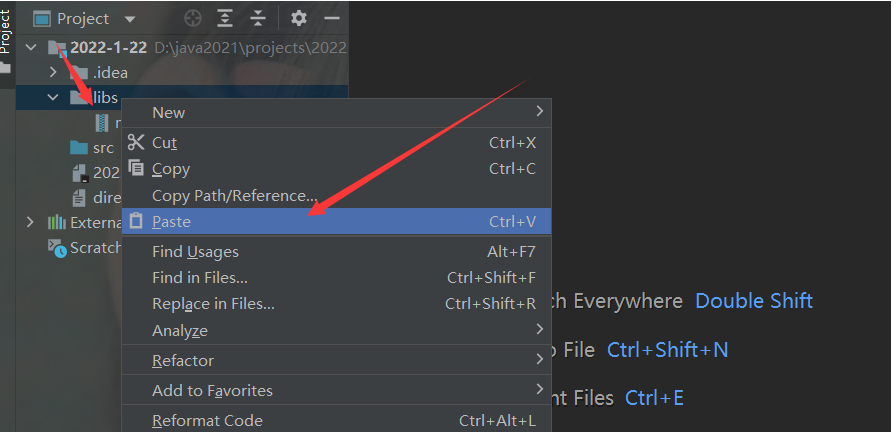
Next, create a folder in the root directory of idea, and then import the jar package
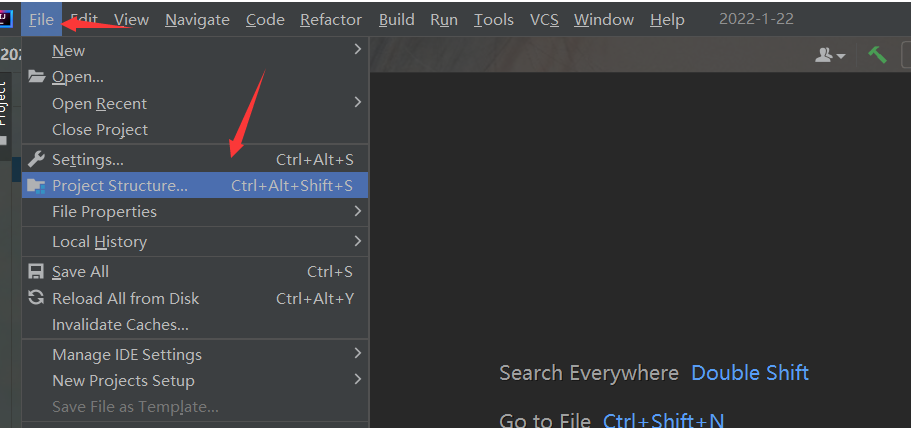
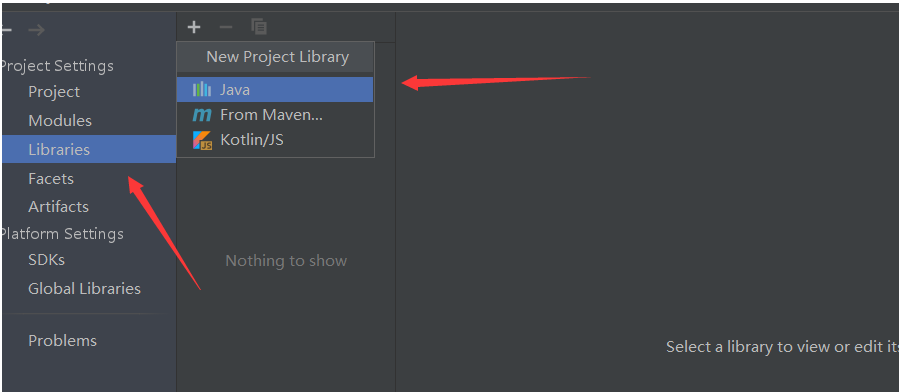
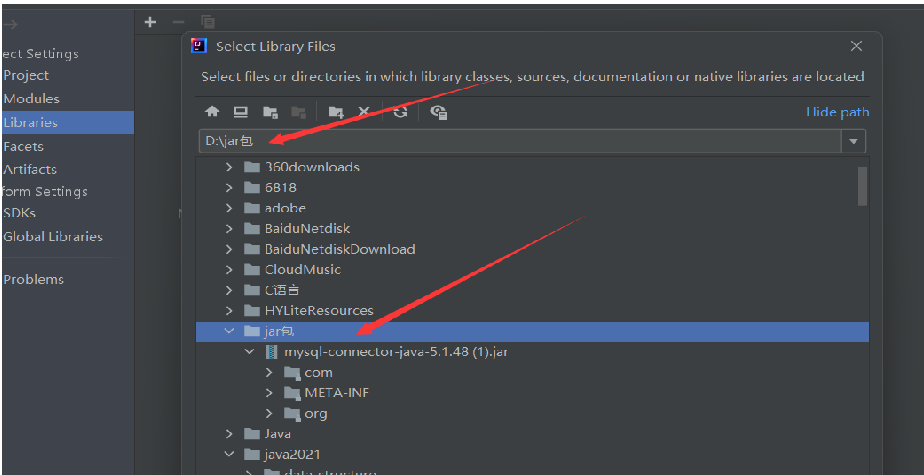
No error is reported. If you continue to OK, there will be no problem. It indicates that the import is successful
5, JDBC programming in MySQL
1. Five step process
Establish database connection
// Load JDBC Driver: reflection, so call initialization com mysql. jdbc. Driver class, which loads the class into the JVM method
And execute the static method blocks and static attributes of this class.
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
// Create database connection
Connection connection =
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test?
user=root&password=root&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8");
//The URL parameter format of MySQL data connection is as follows: jdbc:mysql://Server address: port / database name? Parameter name = parameter value
Create action command (Statement)
Statement statement = connection.createStatement();
Execute SQL statement
ResultSet resultSet= statement.executeQuery(
"select id, sn, name, qq_mail, classes_id from student");Processing result set
while (resultSet.next()) {
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String sn = resultSet.getString("sn");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
int classesId = resultSet.getInt("classes_id");
System.out.println(String.format("Student: id=%d, sn=%s, name=%s,
classesId=%s", id, sn, name, classesId));
}
Release resources (close result set, command, connection)
//Close result set
if (resultSet != null) {
try {
resultSet.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//close command
if (statement != null) {
try {
statement.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//Close connection command
if (connection != null) {
try {
connection.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}2. Add information
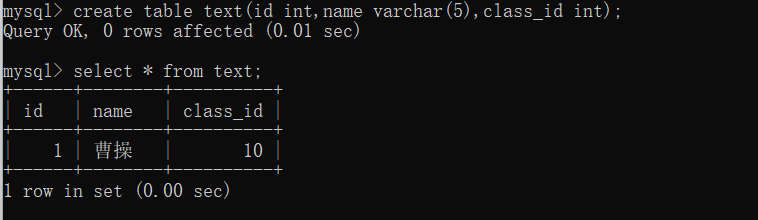
First create a database and create a table
create database java122;
create table text(id int,name varchar(5),class_id int);
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
public class TextJDBC {
//DataSource
//Connection
//PrepareStatement
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException{
//1. Create DataSource object
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
//Set related content
//URL User password
//Transition down to the ip address of the database protocol name to access the address
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java122?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("180210");
//2. And database connection Make subsequent connections
//connect has a short life cycle
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3. Assemble SQL statements
int id = 1;
String name = "Cao Cao";
int class_id = 10;
//? Is a placeholder that can replace the value of a specific variable with?
String sql = "insert into text values(?,?,?)";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//1 2 3 is equivalent to? Subscript of
statement.setInt(1,id);
statement.setString(2,name);
statement.setInt(3,class_id);
System.out.println("statement:" + statement);
//4. Execute SQL statement
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
System.out.println("ret:" + ret);
//5. Close related resources
//Those created later are released first. The order cannot be wrong
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
3. Query information
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import javax.xml.transform.Source;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Text1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//1. Create real columns
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java122?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource)dataSource).setPassword("180210");
//2. Database connection
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3. Construct SQL statement
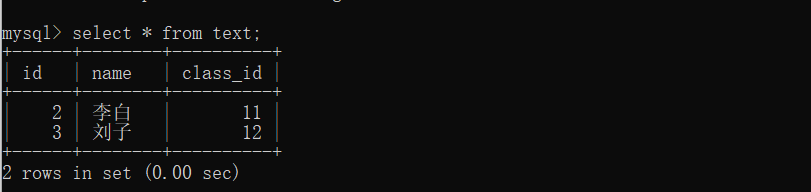
String sql ="select * from text";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//4. Execute SQL statement
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
int id = resultSet.getInt("id");
String name = resultSet.getString("name");
int class_id = resultSet.getInt("class_id");
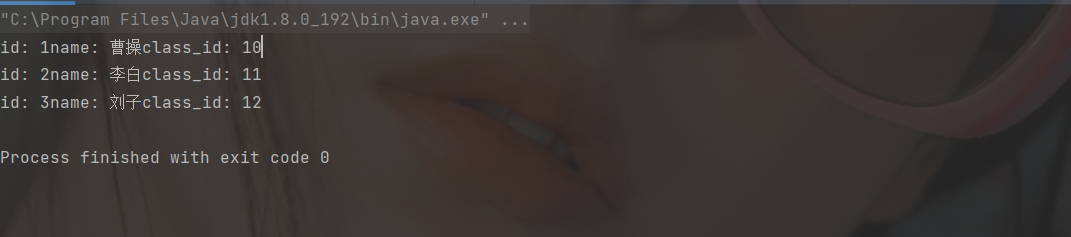
System.out.println("id: " + id + "name: " + name + "class_id: " + class_id);
}
//5. Close relevant resources
resultSet.close();
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
4. Delete information
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Textur2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
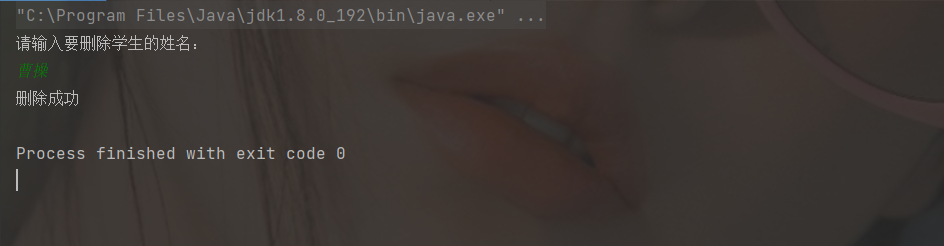
System.out.println("Please enter the name of the student to delete:");
String name = scanner.next();
//1. Create a real column
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java122?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("180210");
//2. Database connection
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3. Construct SQL statements
String sql = "delete from text where name = ?";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
//4. Execute SQL
int ret = statement.executeUpdate();
if (ret == 1){
System.out.println("Delete succeeded");
}else {
System.out.println("Deletion failed");
}
//5. Close resources
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}
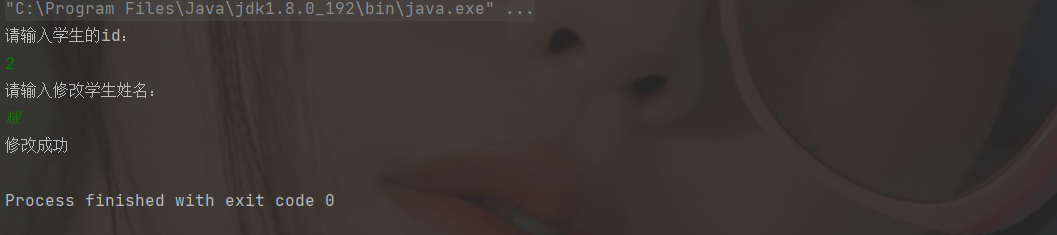
5. Modify information
import com.mysql.jdbc.jdbc2.optional.MysqlDataSource;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import java.sql.Connection;
import java.sql.PreparedStatement;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Text4 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws SQLException {
//Modify information
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("Please enter the student's id: ");
int id = scanner.nextInt();
System.out.println("Please enter and modify student name:");
String name = scanner.next();
//1. Create a real column
DataSource dataSource = new MysqlDataSource();
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setURL("jdbc:mysql://127.0.0.1:3306/java122?characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setUser("root");
((MysqlDataSource) dataSource).setPassword("180210");
//2. Database connection
Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
//3. Assemble SQL
String sql = "update text set name = ? where id = ?";
PreparedStatement statement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
statement.setString(1,name);
statement.setInt(2,id);
//4. Execute SQL
int set = statement.executeUpdate();
if (set == 1){
System.out.println("Modified successfully");
}else {
System.out.println("Modification failed");
}
//5. Close resources
statement.close();
connection.close();
}
}