Flash get post request parameters
Today, let's continue to talk about how to obtain post request parameters using flash web application.
summary
There are several ways for post requests. The content type entity header is used to indicate the MIME type of the resource media type .
Content type is the field of http request header. As a request header (post or put), the client tells the server the type of data actually sent.
The data sent by different content types are different. For the server side, how to obtain the data and correctly parse the data are also different.
Several common content types are listed below
-
application/json
-
application/x-www-form-urlencoded
-
multipart/form-data
-
text/plain
-
text/xml
-
text/html
1. application/json
At present, there are still many content type APIs in this way. At present, the mainstream front-end and back-end interaction APIs use application/json to transmit data. It is mainly proud of the development of json and the perfect library support at the front and back ends, which makes this method more common.
Take the login login interface as an example
The format of http request message is as follows:
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:5000
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 59
{
"username":"frank",
"password":"jsdofjdsofjsdo"
}
Use curl
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login' \
--header 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{
"username":"frank",
"password":"jsdofjdsofjsdo"
}'
postman request
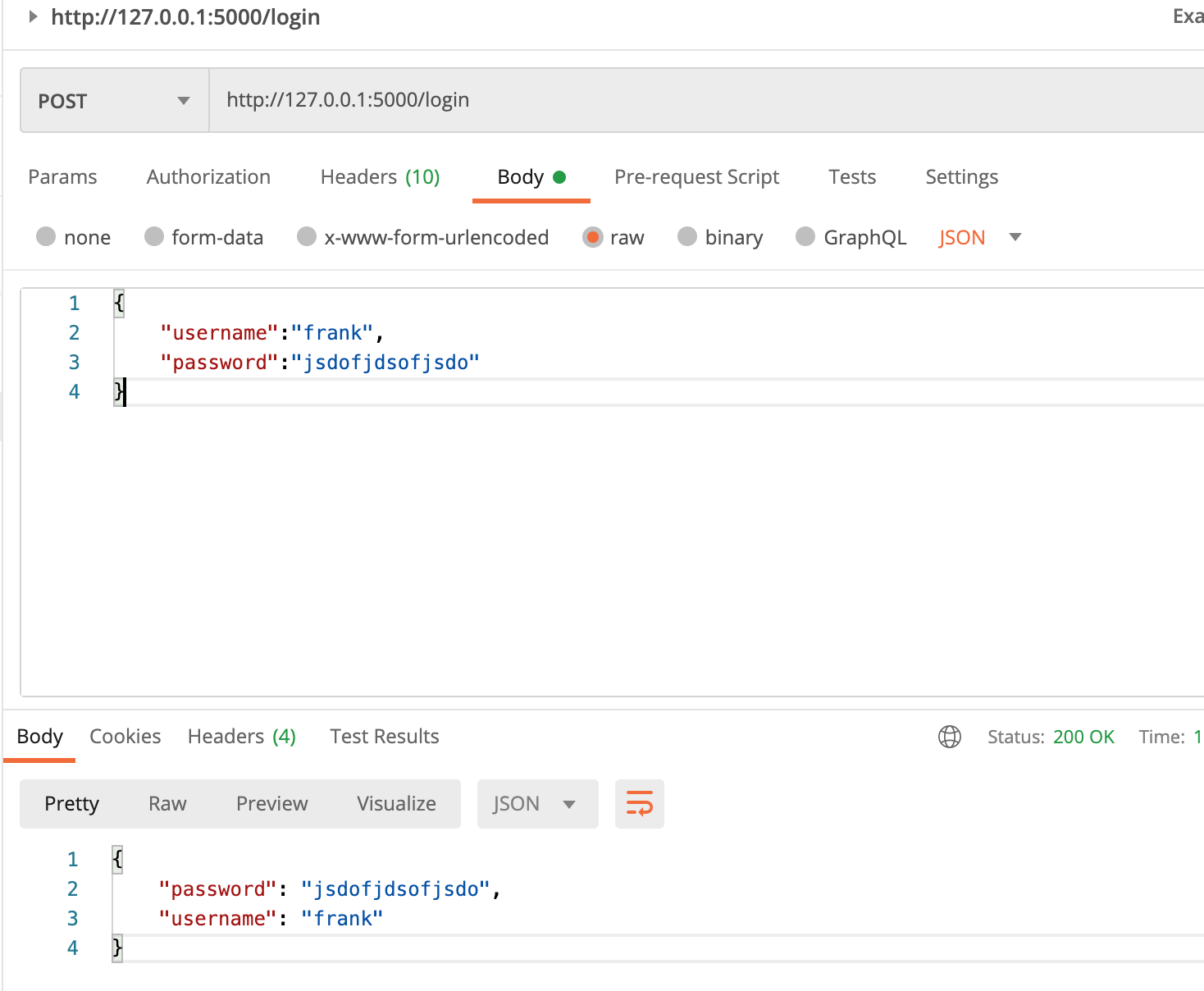
How does flash get the request body
For this request mode, how does flash get the content of the requested body?
# main.py
from flask import Flask
from flask import request
from flask import jsonify
# pip install pysimple-log
from simplelog import logger
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login', methods=[ 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
# So you can get it
json_data = request.json
logger.info(f"json_data:{json_data}")
return jsonify(json_data)
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=5000, debug=True)
We can directly obtain parameters through the request object provided by flash. request.json can get the content of the request body through this attribute. Isn't it convenient.
2. application/x-www-form-urlencoded
This method is the default submission method for browser native form
http request message format
POST /login HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:5000 Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded Content-Length: 38 username=frank&password=jsdofjdsofjsdo
Using curl requests
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login' \ --header 'Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' \ --data-urlencode 'username=frank' \ --data-urlencode 'password=jsdofjdsofjsdo'
How does flash get the request body
For content type, we can use request Form returns an immutable dictionary type. Then you can get the request body.
# Omit
@app.route('/login', methods=[ 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
json_data = request.form
logger.info(f"json_data:{json_data}")
return jsonify(json_data)
3. multipart/form-data
This is another common way of POST data submission. When we upload a file using a form, we must make the enctype of the form equal to multipart / form data. Let's take a direct look at an example of a request:
Here I'm just demonstrating that it corresponds to the http message
http request message
POST /login HTTP/1.1 Host: 127.0.0.1:5000 Content-Type: multipart/form-data; boundary=----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW Content-Length: 239 ----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW Content-Disposition: form-data; name="username" frank ----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW Content-Disposition: form-data; name="password" 111111sfsfsafsafas== ----WebKitFormBoundary7MA4YWxkTrZu0gW
Using curl requests
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login' \ --form 'username="frank"' \ --form 'password="111111sfsfsafsafas=="'
postman request
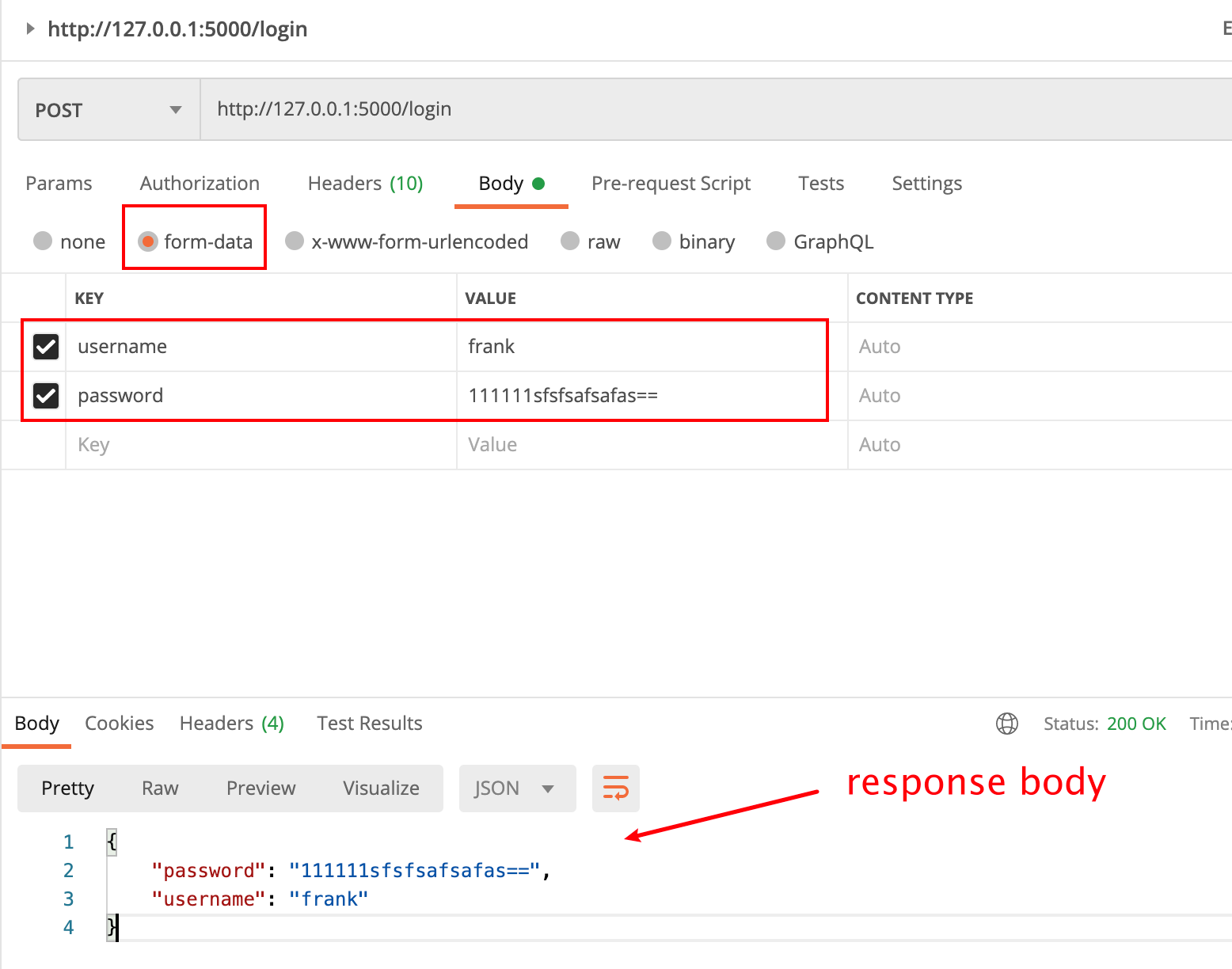
How does flash get the request body
For this method, you can still use request From to get the parameters
# ... ellipsis
@app.route('/login', methods=[ 'POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
json_data = request.form
logger.info(f"json_data:{json_data}")
return jsonify(json_data)
4. text/plain
Send data in plain text
http request message is as follows
POST /login HTTP/1.1
Host: 127.0.0.1:5000
Content-Type: text/plain
Content-Length: 59
{
"username":"frank",
"password":"jsdofjdsofjsdo"
}
Using curl requests
curl --location --request POST 'http://127.0.0.1:5000/login' \
--header 'Content-Type: text/plain' \
--data-raw '{
"username":"frank",
"password":"jsdofjdsofjsdo"
}'
postman request
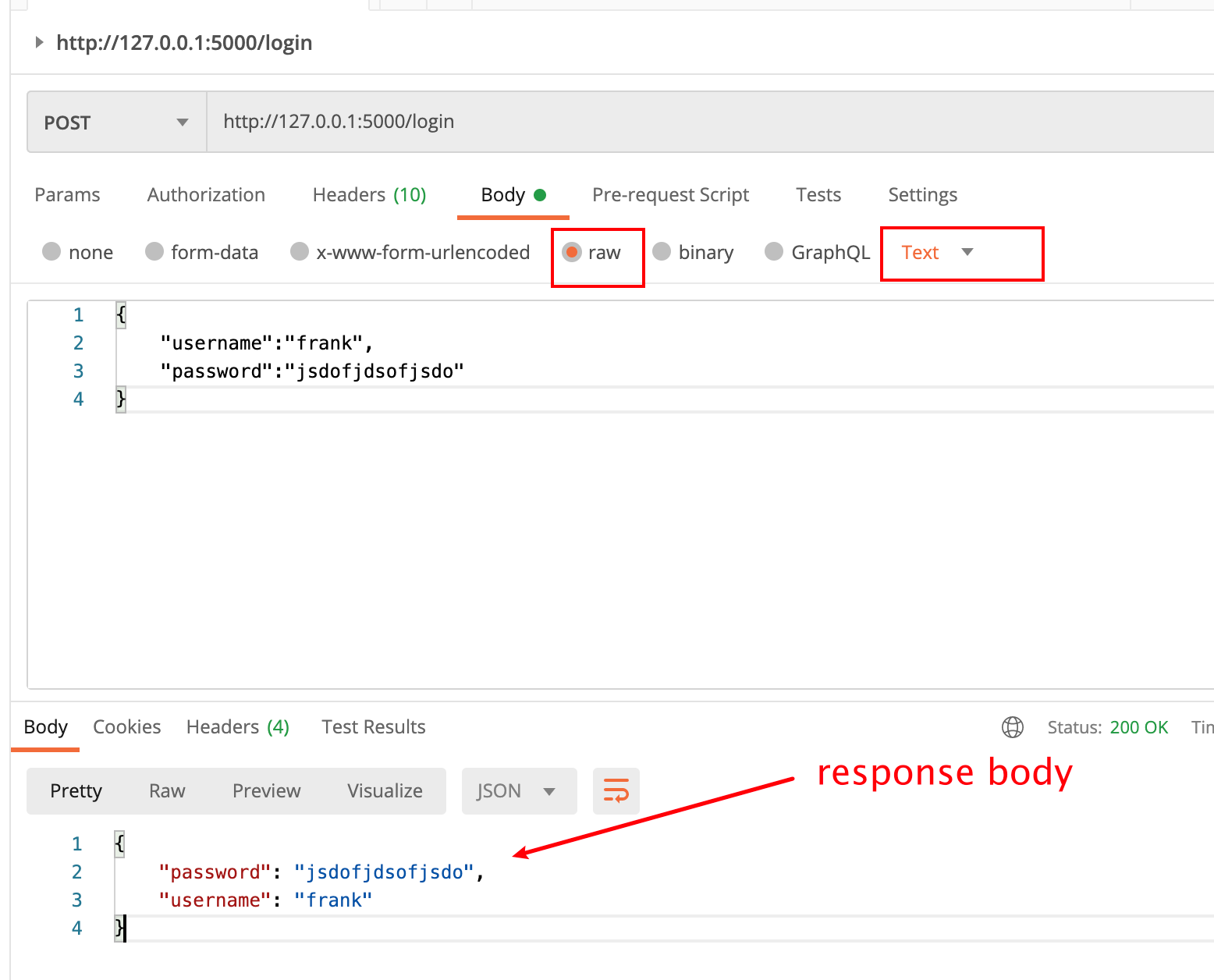
How does flash get the request body
How does flash receive data normally? The native request data will be placed in request In data, the type is bytes, which needs to be converted into a string, and then converted into a dictionary through the json module.
import json
from flask import Flask
from flask import request
from flask import jsonify
# pip install pysimple-log
from simplelog import logger
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/login', methods=['POST'])
def login():
if request.method == 'POST':
# bytes type
raw_data = request.data
logger.info(f'raw_data:{raw_data}')
json_data = json.loads(raw_data.decode())
logger.info(f"json_data:{json_data},type:{type(json_data)}")
return jsonify(json_data)
The results are as follows:
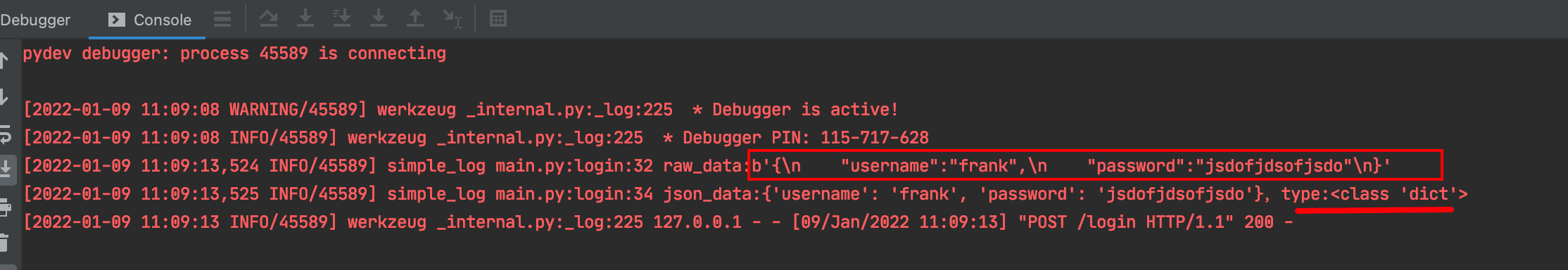
It can be seen that the data can be parsed normally and returned in the form of json.
summary
This article mainly explains that if you use the flash framework to obtain the common post request body data, that's all for today's sharing.