catalogue
1. Introduction to flinksql integration Hive
2. Basic ways of integrating Hive
2.2. Use Flink to read and write Hive's table
0. Links to related articles
1. Introduction to flinksql integration Hive
Introduction to the official website: Apache Flink 1.12 Documentation: Hive
Zhihu case: Quick start of Flink integrated Hive -- with flink1 12 as an example - Zhihu
Using Hive to build data warehouse has become a common solution. At present, some common big data processing engines are compatible with Hive without exception. Flink supports integrated Hive from 1.9, but version 1.9 is beta and is not recommended for use in production environments. At flink1 In version 10, it marks the completion of the integration of Blink, and the integration of Hive also meets the requirements of production level. It is worth noting that different versions of Flink have different integration for Hive. Next, we will use the latest flink1 Take version 12 as an example to realize Flink integration Hive.
2. Basic ways of integrating Hive
2.1. Persistent metadata
Flink uses Hive's MetaStore as a persistent Catalog. We can store Flink metadata in different sessions in Hive Metastore through HiveCatalog. For example, we can use HiveCatalog to store its Kafka data source table in Hive Metastore, so that the metadata information of the table will be persisted to the metadata database corresponding to Hive Metastore, and we can reuse them in subsequent SQL queries.
2.2. Use Flink to read and write Hive's table
Flink opens up the integration with Hive. Just like using SparkSQL or Impala to operate the data in Hive, we can use Flink to directly read and write the tables in Hive. The design of HiveCatalog provides good compatibility with Hive. Users can access their existing Hive tables "out of the box". There is no need to modify the existing history Metastore, or change the data location or partition of the table.
3. Preparation
1. Add hadoop_classpath, add the following configuration in the / etc/profile environment variable
# Edit / etc/profile file vim /etc/profile # Add the following configuration export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=`hadoop classpath` # Refresh configuration source /etc/profile
2. Download the jar and upload it to the flink/lib directory
Download website: Apache Flink 1.12 Documentation: Hive
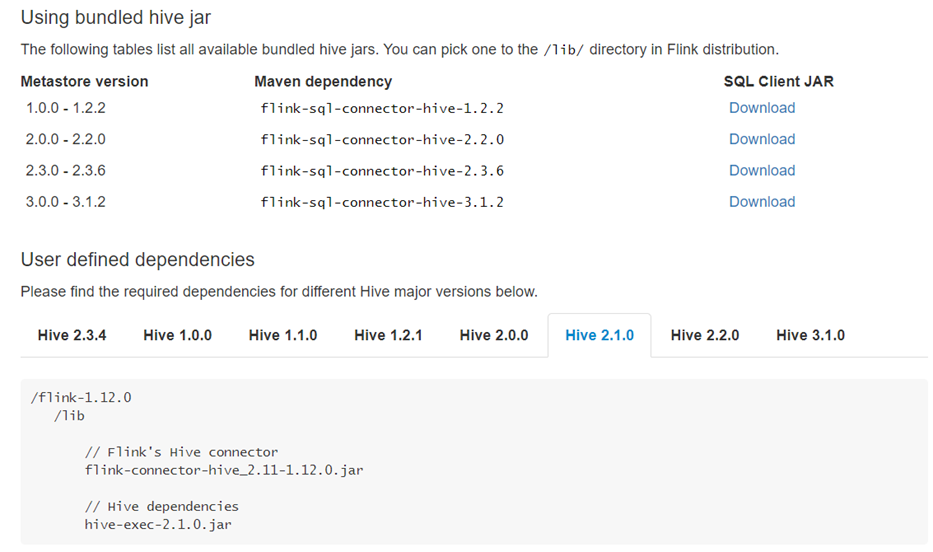
3. Modify hive configuration
# Edit the following file
vim /export/server/hive/conf/hive-site.xml
# Add the following configuration
<property>
<name>hive.metastore.uris</name>
<value>thrift://node3:9083</value>
</property>
4. Restart hive metadata service
nohup /export/server/hive/bin/hive --service metastore &
4. SQL CLI
1. Modify the SQL client defaults of the flinksql cluster Yaml configuration file, and add the following configuration
# Modify the following configuration file
vim /export/server/flink/conf/sql-client-defaults.yaml
# Add the following configuration
catalogs:
- name: myhive
type: hive
hive-conf-dir: /export/server/hive/conf
default-database: default
2. Start the flink cluster
/export/server/flink/bin/start-cluster.sh
3. Start the flynk SQL client
/export/server/flink/bin/sql-client.sh embedded
4. Execute the following sql
show catalogs; use catalog myhive; show tables; select * from person;
5. Code demonstration
import org.apache.flink.table.api.EnvironmentSettings;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.Table;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableResult;
import org.apache.flink.table.catalog.hive.HiveCatalog;
/**
* Desc
*/
public class HiveDemo {
public static void main(String[] args){
EnvironmentSettings settings = EnvironmentSettings.newInstance().useBlinkPlanner().build();
TableEnvironment tableEnv = TableEnvironment.create(settings);
String name = "myhive";
String defaultDatabase = "default";
String hiveConfDir = "./conf";
HiveCatalog hive = new HiveCatalog(name, defaultDatabase, hiveConfDir);
//Register catalog
tableEnv.registerCatalog("myhive", hive);
//Use registered catalog
tableEnv.useCatalog("myhive");
//Write data to Hive table
String insertSQL = "insert into person select * from person";
TableResult result = tableEnv.executeSql(insertSQL);
System.out.println(result.getJobClient().get().getJobStatus());
}
}
Note: this blog is adapted from the 2020 New Year video of a horse - > Website of station B
Note: links to other related articles go here - > Flink article summary