1, Why unit testing
First, let's take a look at the standard software development process
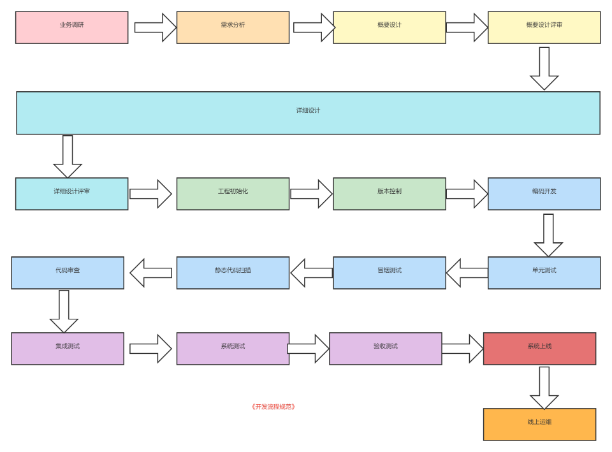
As can be seen from the figure, unit testing, as an important part of the development process, is actually an important part to ensure the robustness of the code. However, for various reasons, in daily development, we often don't pay attention to this step and don't write it or write it irregularly. So why unit testing? Xiao Qi thinks there are the following points:
- It is convenient for later reconstruction. Unit testing can provide guarantee for code reconfiguration. As long as all unit tests pass after code reconfiguration, it largely means that no new BUG is introduced into this reconfiguration. Of course, this is based on complete and effective unit test coverage.
- Optimize the design. Writing unit tests will enable users to observe and think from the perspective of the caller, especially the development method of TDD driven development, which will enable users to design the program to be easy to call and testable, and decouple the software.
- Documentation. Unit testing is an invaluable document. It is the best document to show how functions or classes are used. This document is compiled, runnable, up-to-date and always synchronized with the code.
- It is regressive. Automated unit testing avoids code regression. After writing, you can quickly run the test anytime and anywhere, rather than deploying the code to the device and then manually covering various execution paths. This behavior is inefficient and wastes time.
Many students write unit tests to directly call interface methods, just like running swagger and postMan. In this way, they only verify whether there are errors in the current method and cannot form a unit test network.
For example, the following code
@Test
public void Test1(){
xxxService.doSomeThing();
}
Next, Xiao Qi will discuss with you how to write a simple unit test.
Xiao Qi thinks that the following points should be paid attention to when writing a unit test:
1. Unit testing mainly focuses on the logic of the test method, not just the results.
2. The methods to be tested should not rely on other methods, that is, each unit is independent.
3. No matter how many times it is executed, the result is constant, that is, unit tests need idempotency.
4. Unit tests should also be maintained iteratively.
2, jar package to be referenced for unit test
For the springboot project, we only need to reference its starter
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
The dependencies contained in this start are posted below
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd" xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starters</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<name>Spring Boot Test Starter</name>
<description>Starter for testing Spring Boot applications with libraries including
JUnit, Hamcrest and Mockito</description>
<url>https://projects.spring.io/spring-boot/#/spring-boot-parent/spring-boot-starters/spring-boot-starter-test</url>
<organization>
<name>Pivotal Software, Inc.</name>
<url>https://spring.io</url>
</organization>
<licenses>
<license>
<name>Apache License, Version 2.0</name>
<url>http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0</url>
</license>
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer>
<name>Pivotal</name>
<email>info@pivotal.io</email>
<organization>Pivotal Software, Inc.</organization>
<organizationUrl>http://www.spring.io</organizationUrl>
</developer>
</developers>
<scm>
<connection>scm:git:git://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot.git/spring-boot-starters/spring-boot-starter-test</connection>
<developerConnection>scm:git:ssh://git@github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot.git/spring-boot-starters/spring-boot-starter-test</developerConnection>
<url>http://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/spring-boot-starters/spring-boot-starter-test</url>
</scm>
<issueManagement>
<system>Github</system>
<url>https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/issues</url>
</issueManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-test-autoconfigure</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.jayway.jsonpath</groupId>
<artifactId>json-path</artifactId>
<version>2.4.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.assertj</groupId>
<artifactId>assertj-core</artifactId>
<version>3.11.1</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mockito</groupId>
<artifactId>mockito-core</artifactId>
<version>2.23.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-core</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.hamcrest</groupId>
<artifactId>hamcrest-library</artifactId>
<version>1.3</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.skyscreamer</groupId>
<artifactId>jsonassert</artifactId>
<version>1.5.0</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2.RELEASE</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.xmlunit</groupId>
<artifactId>xmlunit-core</artifactId>
<version>2.6.2</version>
<scope>compile</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>
3, Unit test analysis and skills
1. Annotation analysis of unit test class
The following are notes that appear very frequently:
/* * The function of this annotation is not to directly execute the unit test when executing the unit test * Because some preparations need to be done before those methods are executed, it needs to initialize a spring container first * Therefore, we have to find the SpringRunner class to prepare the spring container first, and then execute various test methods */ @RunWith(SpringRunner.class) /* * The function of this annotation is to find a class annotated with @ SpringBootApplication annotation, that is, the startup class * Then the main method of the startup class will be executed, and the spring container can be created to provide a complete environment for later unit tests */ @SpringBootTest /* * The function of this annotation is to put each method in a transaction * The addition, deletion and modification operations performed by the unit test method are all one-time */ @Transactional /* * The function of this annotation is to roll back if an exception occurs to ensure the purity of database data * The default is true */ @Rollback(true)
2. Common assertions
All Junit assertions are contained in the Assert class.
| void assertEquals(boolean expected, boolean actual) | Check whether two variables or equations are balanced |
|---|---|
| void assertTrue(boolean expected, boolean actual) | Check condition is true |
| void assertFalse(boolean condition) | The inspection condition is false |
| void assertNotNull(Object object) | Check object is not empty |
| void assertNull(Object object) | Check object is empty |
| void assertArrayEquals(expectedArray, resultArray) | Check whether the two arrays are equal |
| void assertSame(expected, actual) | Check whether the references of two objects are equal. It is similar to using "= =" to compare two objects |
| assertNotSame(unexpected, actual) | Check whether the references of two objects are not equal. It is similar to comparing two objects with "! =" |
| fail() | Let the test fail |
| static T verify(T mock, VerificationMode mode) | Verify the number of calls, which is generally used for void methods |
3. Test with return value method
@Test
public void haveReturn() {
// 1. Initialization data
// 2. Simulated behavior
// 3. Call method
// 4. Assert
}
4. Test of method without return value
@Test
public void noReturn() {
// 1. Initialization data
// 2. Simulated behavior
// 3. Call method
// 4. Verification execution times
}
4, Unit test example
Taking the common spring mvc3 layer architecture as an example, we show how the three-layer architecture can do simple unit testing. The business scenario is the addition, deletion, modification and query of user user.
(1) Unit test of dao layer
In general, we should not rely on the external Dao layer until the development of the unit layer. But we should not rely on the external Dao layer for testing.
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Transactional
@Rollback
public class UserMapperTest {
/**
* Persistence layer, no need to use mock objects
*/
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* Test case: query all user information
*/
@Test
public void testListUsers() {
// Initialization data
initUser(20);
// Call method
List<User> resultUsers = userMapper.listUsers();
// Assertion is not empty
assertNotNull(resultUsers);
// Assertion size greater than 0
Assert.assertThat(resultUsers.size(), is(greaterThanOrEqualTo(0)));
}
/**
* Test case: query a user by ID
*/
@Test
public void testGetUserById() {
// Initialization data
User user = initUser(20);
Long userId = user.getId();
// Call method
User resultUser = userMapper.getUserById(userId);
// Assert object equality
assertEquals(user.toString(), resultUser.toString());
}
/**
* Test case: new user
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() {
initUser(20);
}
/**
* Test case: modify user
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() {
// Initialization data
Integer oldAge = 20;
Integer newAge = 21;
User user = initUser(oldAge);
user.setAge(newAge);
// Call method
Boolean updateResult = userMapper.updateUser(user);
// Is the assertion true
assertTrue(updateResult);
// Call method
User updatedUser = userMapper.getUserById(user.getId());
// Are assertions equal
assertEquals(newAge, updatedUser.getAge());
}
/**
* Test case: delete user
*/
@Test
public void testRemoveUser() {
// Initialization data
User user = initUser(20);
// Call method
Boolean removeResult = userMapper.removeUser(user.getId());
// Is the assertion true
assertTrue(removeResult);
}
private User initUser(int i) {
// Initialization data
User user = new User();
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(i);
// Call method
userMapper.saveUser(user);
// Assertion id is not empty
assertNotNull(user.getId());
return user;
}
}
(2) Unit test of service layer
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserServiceImplTest {
@Autowired
private UserService userService;
/**
* The annotation table name. The object is a mock object. It will replace the object marked by @ Autowired
*/
@MockBean
private UserMapper userMapper;
/**
* Test case: query all user information
*/
@Test
public void testListUsers() {
// Initialization data
List<User> users = new ArrayList<>();
User user = initUser(1L);
users.add(user);
// mock behavior
when(userMapper.listUsers()).thenReturn(users);
// Call method
List<User> resultUsers = userService.listUsers();
// Are assertions equal
assertEquals(users, resultUsers);
}
/**
* Test case: query a user by ID
*/
@Test
public void testGetUserById() {
// Initialization data
Long userId = 1L;
User user = initUser(userId);
// mock behavior
when(userMapper.getUserById(userId)).thenReturn(user);
// Call method
User resultUser = userService.getUserById(userId);
// Are assertions equal
assertEquals(user, resultUser);
}
/**
* Test case: new user
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() {
// Initialization data
User user = initUser(1L);
// Default behavior (this line can be left blank)
doNothing().when(userMapper).saveUser(any());
// Call method
userService.saveUser(user);
// Verification execution times
verify(userMapper, times(1)).saveUser(user);
}
/**
* Test case: modify user
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() {
// Initialization data
User user = initUser(1L);
// Simulated behavior
when(userMapper.updateUser(user)).thenReturn(true);
// Call method
Boolean updateResult = userService.updateUser(user);
// Is the assertion true
assertTrue(updateResult);
}
/**
* Test case: delete user
*/
@Test
public void testRemoveUser() {
Long userId = 1L;
// Simulated behavior
when(userMapper.removeUser(userId)).thenReturn(true);
// Call method
Boolean removeResult = userService.removeUser(userId);
// Is the assertion true
assertTrue(removeResult);
}
private User initUser(Long userId) {
User user = new User();
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(20);
user.setId(userId);
return user;
}
}
(3) Unit test of controller layer
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
@Slf4j
public class UserControllerTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@InjectMocks
private UserController userController;
@MockBean
private UserService userService;
/**
* Pre method, which generally executes initialization code
*/
@Before
public void setup() {
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(userController).build();
}
/**
* Test case: query all user information
*/
@Test
public void testListUsers() {
try {
List<User> users = new ArrayList<User>();
User user = new User();
user.setId(1L);
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(20);
users.add(user);
when(userService.listUsers()).thenReturn(users);
mockMvc.perform(get("/user/"))
.andExpect(content().json(JSONArray.toJSONString(users)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Test case: query a user by ID
*/
@Test
public void testGetUserById() {
try {
Long userId = 1L;
User user = new User();
user.setId(userId);
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(20);
when(userService.getUserById(userId)).thenReturn(user);
mockMvc.perform(get("/user/{id}", userId))
.andExpect(content().json(JSONObject.toJSONString(user)));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Test case: new user
*/
@Test
public void testSaveUser() {
Long userId = 1L;
User user = new User();
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(20);
when(userService.saveUser(user)).thenReturn(userId);
try {
mockMvc.perform(post("/user/").contentType("application/json").content(JSONObject.toJSONString(user)))
.andExpect(content().string("success"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Test case: modify user
*/
@Test
public void testUpdateUser() {
Long userId = 1L;
User user = new User();
user.setId(userId);
user.setName("Test user");
user.setAge(20);
when(userService.updateUser(user)).thenReturn(true);
try {
mockMvc.perform(put("/user/{id}", userId).contentType("application/json").content(JSONObject.toJSONString(user)))
.andExpect(content().string("success"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
/**
* Test case: delete user
*/
@Test
public void testRemoveUser() {
Long userId = 1L;
when(userService.removeUser(userId)).thenReturn(true);
try {
mockMvc.perform(delete("/user/{id}", userId))
.andExpect(content().string("success"));
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
5, Other
1. Xiaoqi thinks that there is no need to unit test private methods.
2. dubbo's interface will be proxied by dubbo's class during initialization, and the mock of single test is two classes, which will lead to the failure of mock. At present, no good solution has been found.
3. Unit test coverage report
(1) Add dependency
<dependency>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.2</version>
</dependency>
(2) Add plug-in
<plugin>
<groupId>org.jacoco</groupId>
<artifactId>jacoco-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>0.8.2</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>pre-test</id>
<goals>
<goal>prepare-agent</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
<execution>
<id>post-test</id>
<phase>test</phase>
<goals>
<goal>report</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
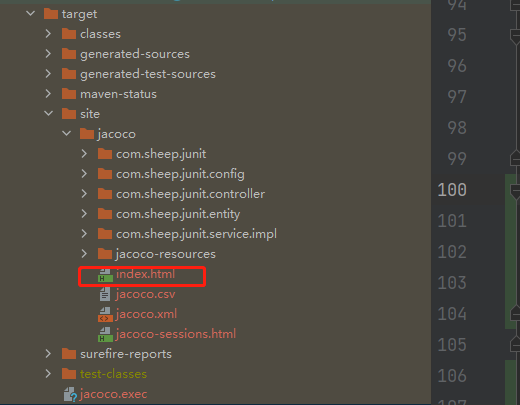
(3) Execute mvn test command
Report generation location
4. Abnormal test
This sharing is mainly for the forward process, and the abnormal conditions are not handled. Interested students can view the relevant documents in the appendix and study by themselves.
6, Appendix
1. user create table statement:
CREATE TABLE `user` ( `id` INT(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY COMMENT 'Primary key', `name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL UNIQUE COMMENT 'user name', `age` INT(3) NOT NULL COMMENT 'Age' ) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COMMENT='user Example table';
2. Source code address of article small example: https://gitee.com/diqirenge/sheep-web-demo/tree/master/sheep-web-demo-junit
3. mockito official website: https://site.mockito.org/
4. mockito Chinese document: https://github.com/hehonghui/mockito-doc-zh