Spring MVC overview
-
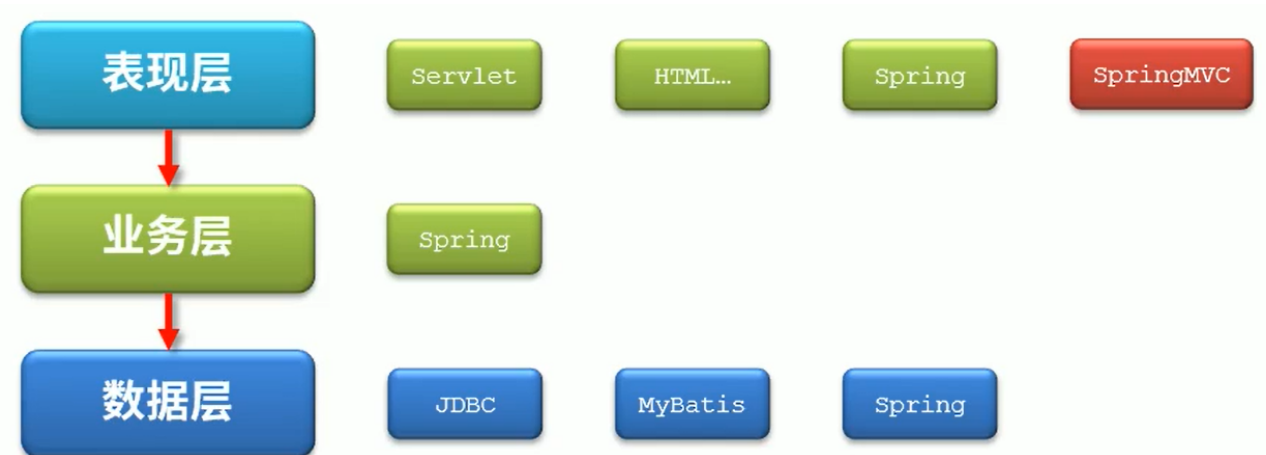
Three layer structure
-
summary
- Spring MVC is a lightweight Web framework based on Java to implement MVC model.
- Spring MVC has become one of the most popular MVC frameworks, and with spring 3 0, comprehensively surpassing struts 2 and becoming the best MVC framework. Through a set of annotations, it makes a simple Java class a controller for processing requests without implementing any interface. It also supports RESTful programming style requests.
Introduction to spring MVC
-
Development steps
- ① Introduce related dependencies
- ② Write web xml
- Configure dispatcher servlet and load spring MVC xml . Similar to ModelBaseServlet
- ③ Write spring MVC xml
- Scan annotation
- Configure the view parser. Similar to ViewBaseServlet
- ④ Write UserController
- ⑤ Code test
-
① Introduce related dependencies
<properties> <maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source> <maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target> <junit.version>4.13.2</junit.version> <lombok.version>1.18.22</lombok.version> <spring.version>5.3.13</spring.version> <logback.version>1.2.7</logback.version> <slf4j.version>1.7.32</slf4j.version> <servlet.version>4.0.1</servlet.version> </properties> <dependencies> <!--web start--> <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>${servlet.version}</version> </dependency> <!--web end--> <!--logback start--> <dependency> <groupId>ch.qos.logback</groupId> <artifactId>logback-classic</artifactId> <version>${logback.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.slf4j</groupId> <artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId> <version>${slf4j.version}</version> </dependency> <!--logback end--> <!--junit start--> <dependency> <groupId>junit</groupId> <artifactId>junit</artifactId> <version>${junit.version}</version> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <!--junit end--> <!--lombok start--> <dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>${lombok.version}</version> </dependency> <!--lombok end--> <!--spring start--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-test</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-aspects</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>${spring.version}</version> </dependency> <!--spring end--> </dependencies> -
② Write web xml
<!DOCTYPE web-app PUBLIC "-//Sun Microsystems, Inc.//DTD Web Application 2.3//EN" "http://java.sun.com/dtd/web-app_2_3.dtd" > <web-app> <!--be similar to ModelBaseServlet--> <servlet> <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <!--load spring-mvc.xml--> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>mvc</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> </web-app> -
③ Write spring MVC xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd"> <!--Scan annotation--> <context:component-scan base-package="com.atguigu"></context:component-scan> <!--View parser, similar to ViewBaseServlet--> <bean id="viewResolver" class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.view.ThymeleafViewResolver"> <property name="order" value="1"/> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8"/> <property name="templateEngine"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.SpringTemplateEngine"> <property name="templateResolver"> <bean class="org.thymeleaf.spring5.templateresolver.SpringResourceTemplateResolver"> <!--View prefix--> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/templates/"/> <!--View suffix--> <property name="suffix" value=".html"/> <property name="templateMode" value="HTML5"/> <property name="characterEncoding" value="UTF-8" /> </bean> </property> </bean> </property> </bean> </beans> -
④ Write UserController
@Controller public class UserController { @RequestMapping("/selectUserList") public ModelAndView selectUserList(){ List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); userList.add(new User(1,"Chen Lei","alei")); userList.add(new User(2,"Tu'ao","tuAo")); //Store the data and jump to the page ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.addObject("userList",userList); modelAndView.setViewName("demo01"); return modelAndView; } } -
⑤ Code test
Execution process of spring MVC
-
Execution process
-

-
① The browser initiates a request (/ framework25/selectUserList) to the front-end controller DispatcherServlet
-
② The front-end controller DispatcherServlet queries all processor execution chains through the processor mapper
-
③ The processor mapper returns the processor execution chain
-
④ The front-end controller DispatcherServlet finds a matching processor through processor adaptation
-
⑤ If a matching processor is found, the processor Handler starts processing the request
-
⑥ The processor Handler returns a response (ModelAndView) to the processor adapter
-
⑦ The processor adapter returns the response (ModelAndView) to the front-end controller
-
⑧ The front-end controller DispatcherServlet sends the response (ModelAndView) to the view parser for parsing
-
⑨ The view parser returns the rendered page file to the front-end controller
-
⑩ The front-end controller displays the rendered page file response to the browser
-
Spring MVC core components
- Core components
- Dispatcher servlet: the front-end controller, which is responsible for scheduling other components
- Handler mapping: the processor mapper, which is responsible for obtaining the processor execution chain
- HandlerAdapter: processor adapter, which is responsible for adapting the corresponding processor to the request
- Handler: processor that handles requests
- ViewResolver: View parser, processing views (ModelAndView)
Spring MVC core component configuration
-
summary
- Spring MVC has configured HandlerMapping and HandlerAdapter by default
-
code implementation
<!--Processor mapper--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerMapping"></bean> <!--Processor adapter--> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter"></bean>
<!--Processor mapper, processor adapter, and other auxiliary components are also configured: type converter, etc--> <mvc:annotation-driven></mvc:annotation-driven>
Static resource release
-
Static resources
- Images, css, js, html, text, etc
-
Mode 1
<!--Release static resources--> <!-- mapping: Access path location: Disk path --> <mvc:resources mapping="/css/**" location="/css/"></mvc:resources> <mvc:resources mapping="/js/**" location="/js/"></mvc:resources> <mvc:resources mapping="/img/**" location="/img/"></mvc:resources> -
Mode II
<mvc:default-servlet-handler></mvc:default-servlet-handler>
@RequestMapping annotation overview
-
summary
- Annotation for mapping web requests onto methods in request-handling classes with flexible method signatures.
- Used to map requests to processor methods.
-
Common properties
- Path: sets the access path
- Method: set the request method
- params: sets the request parameters that must be carried
-
effect
- ① Set the access path of the processor
- ② Narrowing request
- ③ Limited request mode
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping(path = "/request/testRequestMapping" , params = "username") public ModelAndView testRequestMapping(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
@Access path of RequestMapping annotation
-
classification
- ① Exact match
- ② Fuzzy matching
-
① Exact match
-
② Fuzzy matching
/** * Fuzzy matching * @return */ @RequestMapping(path = "/myrequest/*") public ModelAndView testRequestMapping2(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
@Narrowing request for RequestMapping annotation
-
summary
- Apply the @ RequestMapping annotation to the class.
-
code implementation
@Controller @RequestMapping("/request") public class RequestController { }
@Request method of RequestMapping annotation
-
summary
- Common request methods are: get, post, put and delete
-
code implementation
/** * Process GET * @return */ @RequestMapping(path = "/request/testRequestMapping3",method = RequestMethod.GET) public ModelAndView testRequestMapping3(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; } /** * Process POST * @return */ @RequestMapping(path = "/request/testRequestMapping4",method = RequestMethod.POST) public ModelAndView testRequestMapping4(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }@GetMapping("/request/testRequestMapping3") public ModelAndView testRequestMapping3(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; } @PostMapping("/request/testRequestMapping4") public ModelAndView testRequestMapping4(){ ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
Request parameter binding overview
- summary
- Is to bind the request parameters on the page to java data.
- classification
- Simple type
- javabean
- container
- javabean wrapper class
- ...
Simple type of request parameter binding
-
code implementation
<form th:action="@{/request/testRequestParam1}" method="get"> account:<input type="text" name="userName" ><br> password:<input type="text" name="userPwd" ><br> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam1") public ModelAndView testRequestParam1(String userName ,String userPwd){ System.out.println("userName = " + userName); System.out.println("userPwd = " + userPwd); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
View controller tab
-
summary
- When a processor is only used to forward pages, view controller can be used instead.
-
code implementation
<mvc:view-controller path="/demo02.html" view-name="demo02"></mvc:view-controller> <mvc:view-controller path="/demo03.html" view-name="demo03"></mvc:view-controller>
@RequestParam annotation
-
summary
- Pass the parameter value of the specified name in the request to the formal parameter assignment in the controller
-
effect
- ① Set request parameter name
- ② Set whether the parameter is required
- ③ Set default values for parameters
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam2") public ModelAndView testRequestParam2(@RequestParam(value = "username" ,required = true ,defaultValue = "missing") String userName ){ System.out.println("userName = " + userName); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
JavaBean for request parameter binding
-
code implementation
<form th:action="@{/request/testRequestParam3}" method="get"> account:<input type="text" name="userName" ><br> password:<input type="text" name="userPwd" ><br> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam3") public ModelAndView testRequestParam3(User user ){ System.out.println("user = " + user); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; } -
matters needing attention
- The value of the name attribute in the form is related to the setXxx method name.
JavaBean wrapper class for request parameter binding
-
summary
- If a JavaBean class (object A) contains another JavaBean class (object B)
-
code implementation
public class UserWrapper { private User user; }<form th:action="@{/request/testRequestParam4}" method="get"> account:<input type="text" name="user.userName" ><br> password:<input type="text" name="user.userPwd" ><br> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam4") public ModelAndView testRequestParam4(UserWrapper userWrapper ){ System.out.println("userWrapper = " + userWrapper); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
Chinese garbled code of request parameters
-
review
- In tomcat8 0. There is no Chinese parameter garbled problem in get request and Chinese parameter garbled problem in post request.
- Previously, you can solve this problem by customizing characterencoding fitler.
- Similar filters are provided in the spring MVC framework to solve the problem of Chinese parameter scrambling.
-
code implementation
<filter> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class> <init-param> <param-name>encoding</param-name> <param-value>utf-8</param-value> </init-param> </filter> <filter-mapping> <filter-name>encoding</filter-name> <url-pattern>/*</url-pattern> </filter-mapping>
Container for request parameter binding
-
code implementation
<form th:action="@{/request/testRequestParam6}" method="post"> javase : <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="javase"><br> javame : <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="javame"><br> javaee : <input type="checkbox" name="hobbys" value="javaee"><br> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam5") public ModelAndView testRequestParam5(String[] hobbys){ System.out.println(Arrays.toString(hobbys)); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam6") public ModelAndView testRequestParam6(@RequestParam("hobbys") List<String> hobbys){ System.out.println(hobbys); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
Request parameter binding exercise
-
Environmental preparation
public class Student { private String stuName; private School school; private List<Subject> subjectList; private Subject[] subjectArray; private Map<String, Double> scores; }public class School { private String schoolName; }public class Subject { private String subjectName;//Discipline name } -
code implementation
<form th:action="@{/request/testRequestParam7}" method="post"> Student name: <input type="text" name="stuName"><br> School name: <input type="text" name="school.schoolName"><br> Discipline 1 name[List type]: <input type="text" name="subjectList[0].subjectName"><br> Discipline 2 name[List type]: <input type="text" name="subjectList[1].subjectName"><br> Discipline 3 name[List type]: <input type="text" name="subjectList[2].subjectName"><br> Discipline 1 name[Array type]: <input type="text" name="subjectArray[0].subjectName"><br> Discipline 2 name[Array type]: <input type="text" name="subjectArray[1].subjectName"><br> Discipline 3 name[Array type]: <input type="text" name="subjectArray[2].subjectName"><br> Subject 1 score: <input type="text" name="scores['javase']"><br> Subject 2 score: <input type="text" name="scores['javame']"><br> Subject 3 score: <input type="text" name="scores['javaee']"><br> <button type="submit">Submit</button> </form>@RequestMapping("/request/testRequestParam7") public ModelAndView testRequestParam7(Student student){ System.out.println(student); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
@RequestHeader annotation
-
summary
- Get the specific data in the request header through this annotation.
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/request/header") public ModelAndView getRequestHeader(@RequestHeader(value = "user-agent",defaultValue = "missing") String userAgent){ System.out.println(userAgent); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
@CookieValue annotation
-
summary
- Gets the Cookie data in the current request
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/request/cookie") public ModelAndView getCookie(@CookieValue(name = "JSESSIONID",defaultValue = "missing") String JSESSIONID){ System.out.println(JSESSIONID); ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView(); modelAndView.setViewName("index"); return modelAndView; }
Processor returns ModelAndView
- summary
- ModelAndView encapsulates data and logical view names
Processor return string
-
summary
- In general, it is the logical view name
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/response/testResponseStr") public String testResponseStr(Model model) { List<User> userList = new ArrayList<>(); userList.add(new User(1, "Chen Lei", "alei")); userList.add(new User(2, "Tu'ao", "tuAo")); model.addAttribute("userList", userList);//Store data return "demo01";//Jump to logical view }
Processor return value operation forwarding and redirection
-
summary
- By default, the processor can only jump pages within the directory set by the view parser;
- If you want to jump to resources outside the directory range, you need to use the prefix symbol!!!
-
code implementation
/** * Forward to resources outside the directory range * * @return */ @RequestMapping("/response/forward") public String response2Forward() { return "forward:/mydemo01.html"; } /** * Redirect to resources outside the directory range * * @return */ @RequestMapping("/response/redirect") public String response2Redirect() { return "redirect:/mydemo01.html"; } /** * Redirect to specific processor * @return */ @RequestMapping("/response/jump2Method") public String jump2Method(){ return "redirect:/response/testResponseStr"; } -
matters needing attention
- When using "redirect:" operation redirection, the MVC framework has built-in access path of the project.
Native servlet API object
- Native Servlet object
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpSession
- ServletContext
Get request and response objects
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/servlet/getRequestResponse") public String getRequestResponse(HttpServletRequest request , HttpServletResponse response){ System.out.println("request = " + request); System.out.println("response = " + response); return "index"; }
Get session object
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/servlet/getSession") public String getSession(HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("session = " + request.getSession()); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/servlet/getSession2") public String getSession2(HttpSession session){ System.out.println("session = " + session); return "index"; }
Get ServletContext object
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/servlet/getServletContext") public String getServletContext(HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("servletContext = " + request.getServletContext()); return "index"; } @Autowired private ServletContext servletContext; @RequestMapping("/servlet/getServletContext2") public String getServletContext2(){ System.out.println("servletContext = " + servletContext); return "index"; }
Elephant (Master)
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/servlet/getSession") public String getSession(HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("session = " + request.getSession()); return "index"; } @RequestMapping("/servlet/getSession2") public String getSession2(HttpSession session){ System.out.println("session = " + session); return "index"; }
Get ServletContext object
-
code implementation
@RequestMapping("/servlet/getServletContext") public String getServletContext(HttpServletRequest request){ System.out.println("servletContext = " + request.getServletContext()); return "index"; } @Autowired private ServletContext servletContext; @RequestMapping("/servlet/getServletContext2") public String getServletContext2(){ System.out.println("servletContext = " + servletContext); return "index"; }