FTP service in Linux
1, Introduction to FTP
(1)FTP service - the protocol used to transfer files
FTP is the English abbreviation of File Transfer Protocol. It is one of the protocols in TCP/IP protocol group. Used for two-way transfer of control files on the Internet. At the same time, it is also an Application. There are different FTP applications based on different operating systems, and all these applications follow the same protocol to transfer files.
FTP protocol consists of two parts, one is FTP server, the other is FTP client. The FTP server is used to store files, and users can use the FTP client to access the resources on the FTP server through the FTP protocol.
(2)FTP port
- By default, the FTP server uses ports 20 and 21 of TCP protocol to communicate with customers
- Port 20 is used to establish data connection and transfer file data
- Port 21 is used to establish a control connection and transmit FTP control commands
(3)FTP data connection mode
**Active mode: * * the server actively initiates a link from port 20 to the client. Control port 21; Data transmission port 20
Process: the client sends a request from any non privileged PORT N (N > 1024) to the command PORT (21 by default) of the FTP server. The server accepts the connection and establishes a command link. When it is necessary to transmit data, the client starts listening to PORT N+1 and sends PORT N+1 to the FTP server with the PORT command on the command link, so the server will send a connection request from its own data PORT (20) to the data PORT (N+1) specified by the client to establish a data link to transmit data.
**Passive mode: * * the server passively waits for a port and the client links within the specified range. Control port 21; Random data transmission port
Process: the client sends a request from any non privileged port N (N > 1024) to the command port (21 by default) of the FTP server. The server accepts the connection and establishes a command link. When data needs to be transmitted, the client sends it with PASV command on the command link. Therefore, the server will open an arbitrary non privileged port P (P > 1024) and send the port to the client on the command link, and then the client will send a connection request from its own data port (N+1) to the server's data port (P) to establish a data link to transmit data.
2, Related configuration
(1) Install FTP service
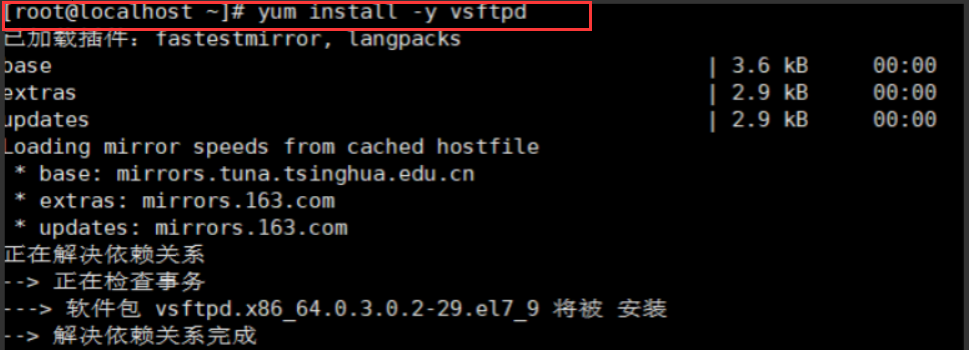
yum install -y vsftpd #yum one click Install
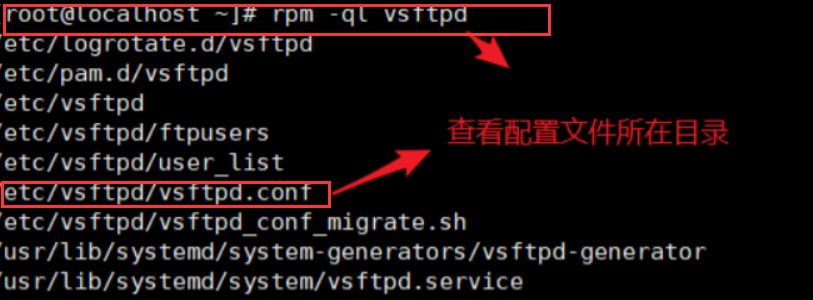
cd /etc/vsftpd/ #Switch to ftp configuration directory
cp vsftpd.conf vsftpd.conf.bak
or cp vsftpd.conf{,.bak} #Backup the original configuration file
(2) Set FTP service for anonymous user access (maximum permission)
① Modify profile
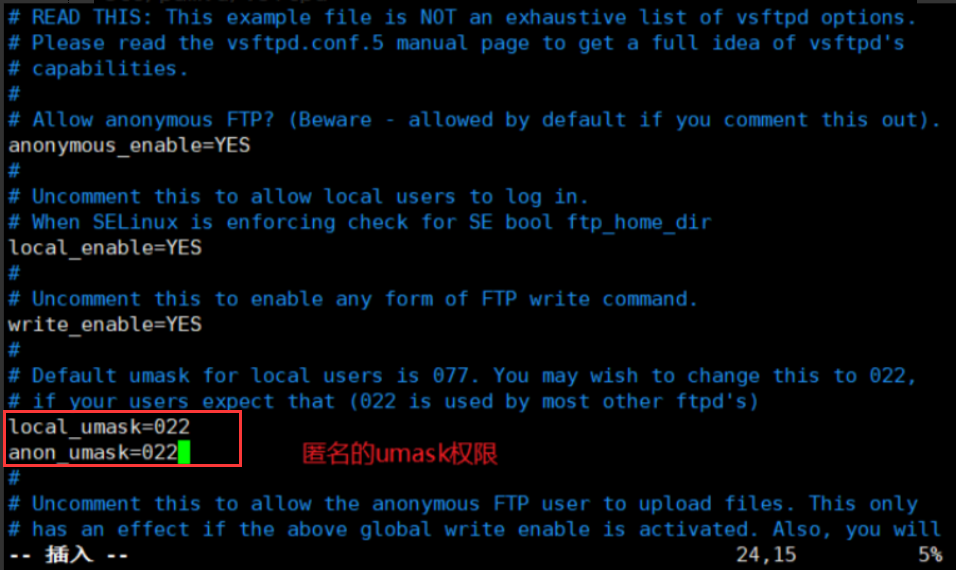
vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf anonymous_enable=YES #Enable anonymous user access. It is enabled by default write_enable=YES #Open the write permission of the server (to upload, it must be enabled). It is enabled by default anon_umask=022 #Set the permission mask (unmask) of data uploaded by anonymous users anon_upload_enable=YES #Anonymous users are allowed to upload files. They are annotated by default and need to be uncommented anon_mkdir_write_enable=YES #Allow anonymous users to create (upload) directories. It is annotated by default and needs to be uncommented anon_other_write_enable =YES #Delete, rename, overwrite and other operations are allowed, which need to be added
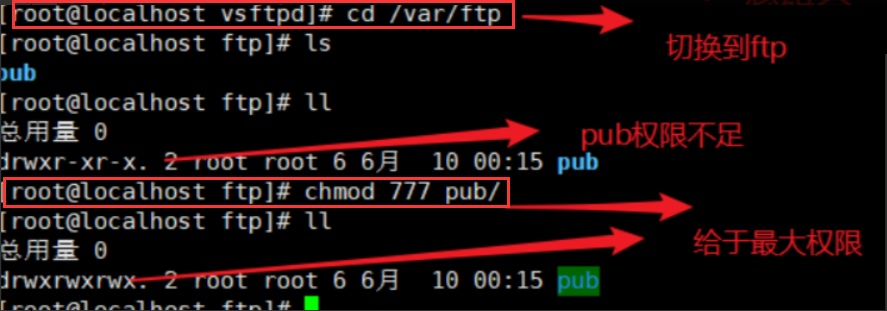
② Set the maximum permission for anonymous access to the pub subdirectory under the root directory of FTP so that anonymous users can upload data
chmod 777 /var/ftp/pub
③ Turn on services, turn off firewalls and enhanced security features
systemctl start vsftpd #Open service systemctl stop firewalld #Turn off firewall setenforce 0 #Turn off system security
④ Anonymous access test
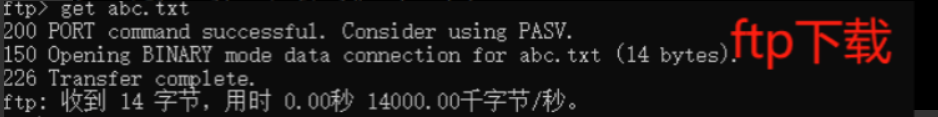
win10 Open in cmd command prompt ftp 192.168.184.50 #Establish ftp connection ftp> pwd #The root directory of anonymous FTP access is / var/ftp / directory of Linux system ftp> ls #View current directory ftp> cd pub #Switch to the pub directory ftp> get file name #Download files to the Current Windows local directory ftp> put file name #Upload files to ftp directory ftp> quit #sign out
⑤ Set local user authentication access to ftp and prohibit switching to directories other than ftp (the default login root directory is the local user's home directory)
vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf local_enable=Yes #Enable local users anonymous_enable=NO #Turn off anonymous user access write_enable=YES #Open the write permission of the server (to upload, it must be enabled) anon_umask=077 #You can set the permission (unmask) that only the host user has the uploaded file chroot_local_user=YES #Imprison access in the user's host directory allow_writeable_chroot=YES #Allow restricted user home directory to have write permission systemctl restart vsftpd #Restart service
⑥ Modify the default root directory for anonymous users and local users
anon_root=/var/www/html #anon_root for anonymous users local_root=/var/www/html #local_root for system users
⑦ Use user_list user list file and set whitelist and blacklist
vim /etc/vsftp/user_list //Add zhangan user at the end zhansgan vim /etc/vsftpd/vsftpd.conf userlist_enable=YES #Enable user_list user list file userlist_deny=NO #Set the white list. Only users are allowed_ User access to the list file. The default value is YES. It is a blacklist and disabled
Three. Simulation experiment 1 (upload and download of FTP services)
(1) Install FTP and backup configuration files
(2) Modify profile
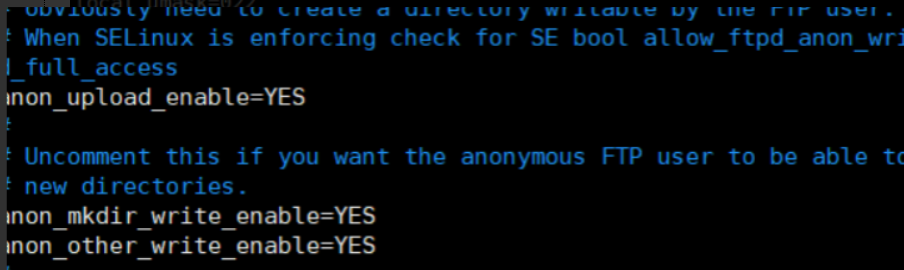
(3) Turn on the service and turn off the firewall and enhanced security features
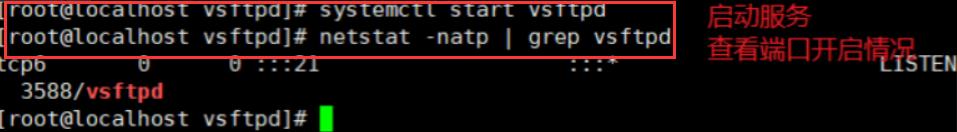

(4) FTP connectivity test on win10

(5) Give maximum permission
(6) Upload files on win10 (close firewall)
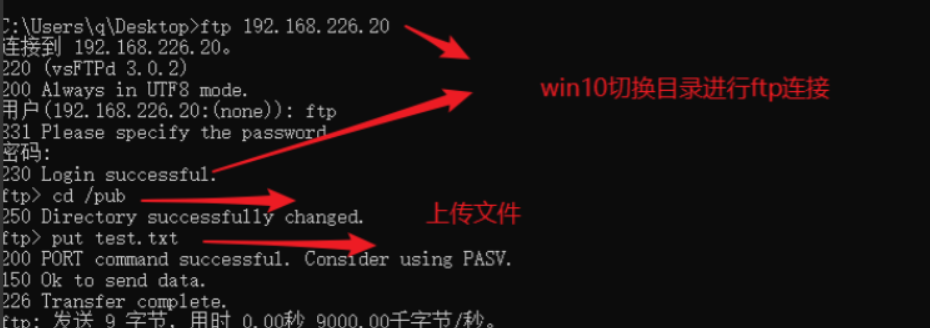
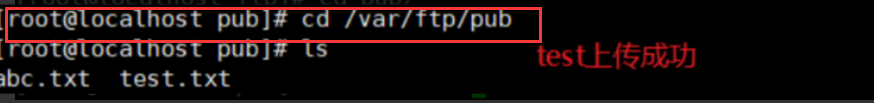
(7) Check whether the upload is successful
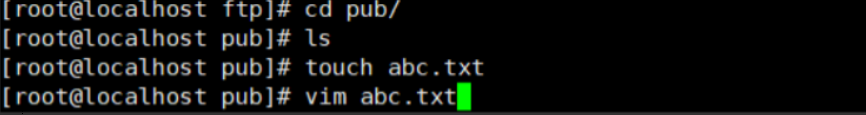
(8) Create a new file containing content in the pub directory
(9) Download FTP service in win10 and check whether the file is downloaded successfully