1, What is XML
XML is extensible markup language and HTML is hypertext markup language
Markup language is a syntax format that organizes data through tags one by one
Compared with HTMl hypertext language, XML, an extensible language, defines its own tags
Self defined tags in XML represent:
For example: < tag name attribute 1 = "attribute value" attribute 2 = "attribute value" ···· > specific data < / tag end >
< tag name > -- start tag
< tag name attribute 1 = "attribute value" attribute 2 = "attribute value"... >-- Start tag
< / tag name > -- end tag
2, What is the role of XML
A grammatical format in which data is stored
It can also be a packet exchange format
3, How to write an XML file
Now we need to organize a java object into data in xml format. Let's talk about the specific methods.
public class Student{
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
private int stuage;
private String stuaddress;
```````
getXXX()/setXXX()
}
Student student=new Student();
student.setStuid(1001);
student.setStuname("zhangsan");
student.setStuage(23);
student.setStuaddress("Xi'an");
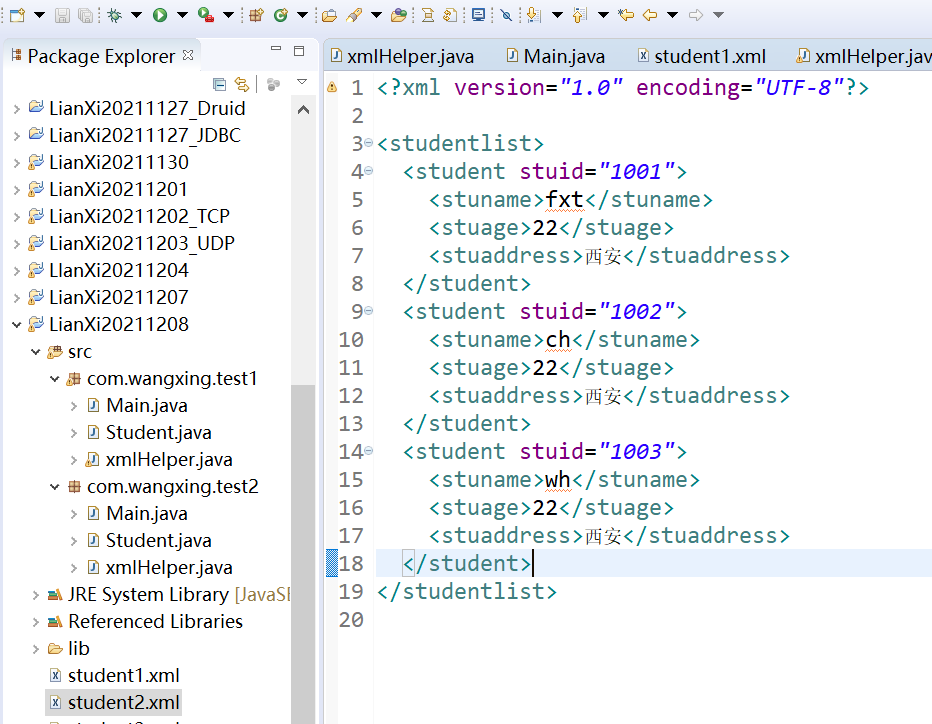
XML type data / file [student.xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
< students > ----- root element of XML [essential]
< student study = "1001" > ----- a child element of XML. Study = "1001" is an attribute of the current child element
< stuname > zhangsan < / stuname > -- the child [grandson] element of XML, and the specific value of zhangsan
< stuage > 23 < / stuage > - sub [grandson] element of XML, 23 specific data values
Sub [grandson] element of < stuaddress > Xi'an < / stuaddress > - XML, Xi'an specific data value
</student>
</students>
Note: 1. <? xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> Not less
2. There is only one root element, which is essential
3. The specific data values are saved by sub elements / sub [grandson] elements.
4. If it is a file, the suffix of the file is ". xml"
Now we need to organize a collection / array with java objects into xml data. Let's take a look at the specific methods.
public class Student{
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
private int stuage;
private String stuaddress;
.....
getXXX()/setXXX()
}
Student student1=new Student();
student1.setStuid(1001);
student1.setStuname("zhangsan");
student1.setStuage(23);
student1.setStuaddress("Xi'an");
Student student2=new Student();
student2.setStuid(1002);
student2.setStuname("lisi");
student2.setStuage(24);
student2.setStuaddress("Beijing");
Student student3=new Student();
student3.setStuid(1003);
student3.setStuname("wangwu");
student3.setStuage(25);
student3.setStuaddress("Shanghai");
List<Student> studentlist=new ArrayList<Student>();
studentlist.add(student1);
studentlist.add(student2);
studentlist.add(student3);
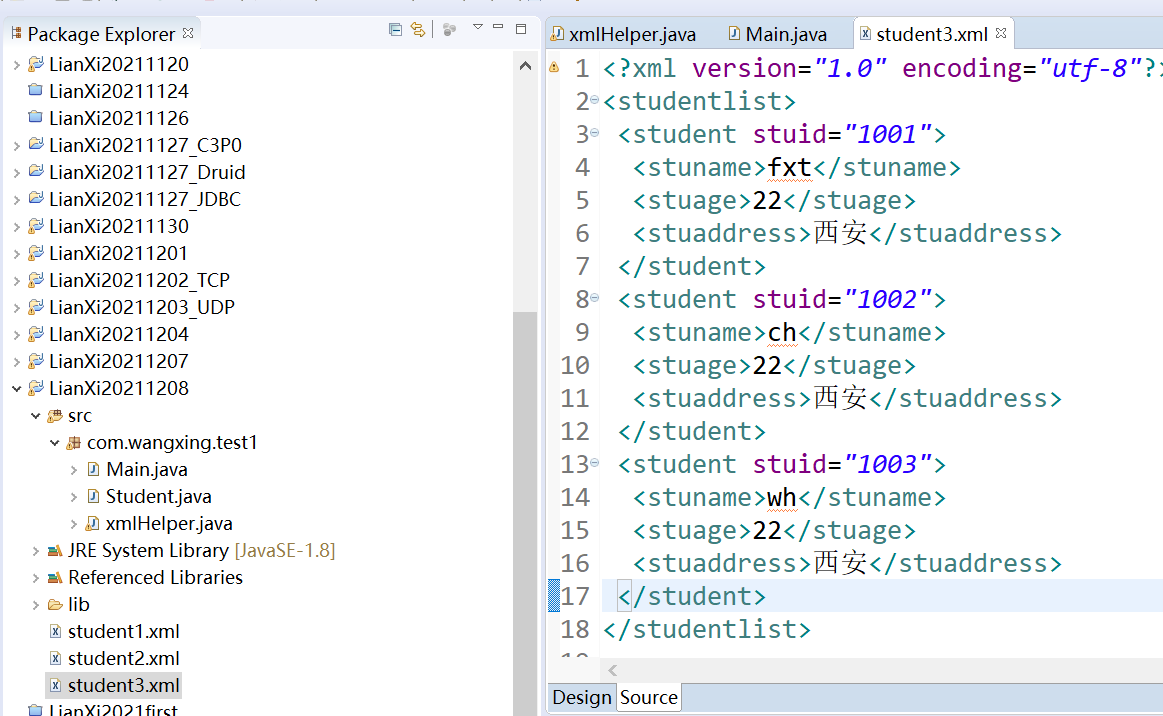
Organize the above student list into xml data / file [student.xml]
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<studentlist>
<student stuid="1001">
<stuname>zhangsan</stuname>
<stuage>23</stuage>
< stuaddress > Xi'an < / stuaddress >
</student>
<student stuid="1002">
<stuname>lisi</stuname>
<stuage>24</stuage>
< stuaddress > Beijing < / stuaddress >
</student>
<student stuid="1003">
<stuname>wangwu</stuname>
<stuage>25</stuage>
< stuaddress > Shanghai < / stuaddress >
</student>
</studentlist>
Note: 1 Tags are self-defined, and there are no fixed specific tags
2. There can be multiple child elements and child elements.
4, Generation of XML files
1.Dom generation
1.1 default dom generation method of java [java class provided by jdk]
For example:
Create the student class to create the student's xml file
package com.wangxing.test1;
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
private int stuage;
private String stuaddress;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public int getStuage() {
return stuage;
}
public void setStuage(int stuage) {
this.stuage = stuage;
}
public String getStuaddress() {
return stuaddress;
}
public void setStuaddress(String stuaddress) {
this.stuaddress = stuaddress;
}
}Create a class with methods to get xml files
package com.wangxing.test1;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.transform.OutputKeys;
import javax.xml.transform.Transformer;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory;
import javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Element;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* 1.java Default dom generation method [java class provided by jdk]
*/
public static void createXml1(ArrayList<Student> stulist) throws Exception{
//Get DOM parser factory
DocumentBuilderFactory factory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//Create DocumentBuilder object
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder=factory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Create Document object
Document document=documentBuilder.newDocument();
//Sets the header of the document object
document.setXmlStandalone(true);
//Create root element
Element rootElment=document.createElement("studentlist");
//Traversal set
for(Student student:stulist){
//Create child element
Element studentElement=document.createElement("student");
//Set attributes for child elements
studentElement.setAttribute("stuid",String.valueOf(student.getStuid()));
//Create child element
Element stunameElement=document.createElement("stuname");
//Set specific values for child elements
stunameElement.setTextContent(student.getStuname());
//Create child element
Element stuageElement=document.createElement("stuage");
//Set specific values for child elements
stuageElement.setTextContent(String.valueOf(student.getStuage()));
//Create child element
Element stuaddressElement=document.createElement("stuaddress");
//Set specific values for child elements
stuaddressElement.setTextContent(student.getStuaddress());
//Add child elements to child elements
studentElement.appendChild(stunameElement);
studentElement.appendChild(stuageElement);
studentElement.appendChild(stuaddressElement);
//Add child elements to the root element
rootElment.appendChild(studentElement);
}
//Add the root element to the Document object
document.appendChild(rootElment);
//Write out the document object to a file
File file=new File("student1.xml");
//Create a TransformerFactory object
TransformerFactory tff=TransformerFactory.newInstance();
//Create Transformer object
Transformer tf=tff.newTransformer();
//Whether to use line feed for output content
tf.setOutputProperty(OutputKeys.INDENT,"yes");
//Create xml file and write content
tf.transform(new DOMSource(document),new StreamResult(file));
}
}test
package com.wangxing.test1;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Student student1=new Student();
student1.setStuid(1001);
student1.setStuname("fxt");
student1.setStuage(22);
student1.setStuaddress("Xi'an");
Student student2=new Student();
student2.setStuid(1002);
student2.setStuname("ch");
student2.setStuage(22);
student2.setStuaddress("Xi'an");
Student student3=new Student();
student3.setStuid(1003);
student3.setStuname("wh");
student3.setStuage(22);
student3.setStuaddress("Xi'an");
//Create collection
ArrayList<Student> stulist=new ArrayList<Student>();
stulist.add(student1);
stulist.add(student2);
stulist.add(student3);
xmlHelper.createXml1(stulist);
}
}Get results
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?><studentlist> <student stuid="1001"> <stuname>fxt</stuname> <stuage>22</stuage> <stuaddress>Xi'an</stuaddress> </student> <student stuid="1002"> <stuname>ch</stuname> <stuage>22</stuage> <stuaddress>Xi'an</stuaddress> </student> <student stuid="1003"> <stuname>wh</stuname> <stuage>22</stuage> <stuaddress>Xi'an</stuaddress> </student> </studentlist>
1.2 use the third-party development package [download in advance]
dom4j
For example:
package com.wangxing.test1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import javax.xml.transform.OutputKeys;
import javax.xml.transform.Transformer;
import javax.xml.transform.TransformerFactory;
import javax.xml.transform.dom.DOMSource;
import javax.xml.transform.stream.StreamResult;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
//import org.jdom.Document;
//import org.jdom.Element;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
//import org.w3c.dom.Document;
//import org.w3c.dom.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* Using third-party development packages
* dom4j
* @param studentlist
*/
public static void createXml2(ArrayList<Student> stulist) throws Exception{
//Create Document object
Document document=DocumentHelper.createDocument();
//Create root element
Element rootElement=document.addElement("studentlist");
//Traversal set
for(Student student:stulist){
//Create child elements and add them directly to the root element
Element studentElement=rootElement.addElement("student");
studentElement.addAttribute("stuid", String.valueOf(student.getStuid()));
//Create and add child elements
Element stunameElement=studentElement.addElement("stuname");
stunameElement.setText(student.getStuname());
Element stuageElement=studentElement.addElement("stuage");
stuageElement.setText(String.valueOf(student.getStuage()));
Element stuaddressElement=studentElement.addElement("stuaddress");
stuaddressElement.setText(student.getStuaddress());
}
//Format the generated xml
OutputFormat format=OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint();
//Set encoding format
format.setEncoding("UTF-8");
//Create xml character output stream
XMLWriter writer=new XMLWriter(new FileOutputStream(new File("student2.xml")),format);
//Set whether to escape. Escape characters are used by default
writer.setEscapeText(false);
//Write out Document objects
writer.write(document);
//Close flow
writer.close();
}
}
jdom
For example:
package com.wangxing.test1;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import org.jdom.Document;
import org.jdom.Element;
import org.jdom.output.Format;
import org.jdom.output.XMLOutputter;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* jdom
* @param studentlist
*/
public static void createXml3(ArrayList<Student> stulist) throws Exception{
//Create root element
Element rootElement=new org.jdom.Element("studentlist");
//Traversal set
for(Student student:stulist){
//Create child element
Element studentElement=new Element("student");
//Set attributes for child elements
studentElement.setAttribute("stuid", String.valueOf(student.getStuid()));
//Create child element
Element stunameElement=new Element("stuname");
stunameElement.setText(student.getStuname());
Element stuageElement=new Element("stuage");
stuageElement.setText(String.valueOf(student.getStuage()));
Element stuaddressElement=new Element("stuaddress");
stuaddressElement.setText(student.getStuaddress());
//Put child elements into child elements
studentElement.addContent(stunameElement);
studentElement.addContent(stuageElement);
studentElement.addContent(stuaddressElement);
//Put the child element into the root element
rootElement.addContent(studentElement);
}
//Create a Document object and put the root element in it
Document document=new Document(rootElement);
//Output Document object
Format format=Format.getCompactFormat();
//Set the newline Tab or newline and encoding format
format.setIndent(" ");
format.setEncoding("utf-8");
//Create an object for XMLOutputter
XMLOutputter outputter=new XMLOutputter(format);
//Write Document
outputter.output(document, new FileOutputStream(new File("student3.xml")));
}
}
2. By splicing strings [not recommended, error prone]
For example:
public static void createXML4(List<Person> personlist)throws Exception{
//Define a string variable that holds the spliced string
String xmlcontent=null;
//To make it easier to splice strings, we use the stringbuilder class to splice strings
StringBuilder stringBuilder=new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
stringBuilder.append("<personlist>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
//Traverse the collection that needs to be generated into an xml file
for(Person person:personlist){
stringBuilder.append("\t<person perid=\""+person.getPerid()+"\">");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
stringBuilder.append("\t\t<pername>"+person.getPername()+"</pername>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
stringBuilder.append("\t\t<perage>"+person.getPerage()+"</perage>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
stringBuilder.append("\t\t<peraddress>"+person.getPeraddress()+"</peraddress>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
stringBuilder.append("\t</person>");
stringBuilder.append("\r\n");
}
stringBuilder.append("<personlist>");
xmlcontent=stringBuilder.toString();
System.out.println(xmlcontent);
//Create an output stream object and save the created xml to a file
File file=new File("F:"+File.separator+"personlist.xml");
BufferedWriter out=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
out.write(xmlcontent);
out.close();
}5, Parsing of XML files
1.DOM (Document Object Model) parsing
1.1 Java default Dom parsing xml
For example:
Create a class that receives student object values
package com.wangxing.test2;
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
private int stuage;
private String stuaddress;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public int getStuage() {
return stuage;
}
public void setStuage(int stuage) {
this.stuage = stuage;
}
public String getStuaddress() {
return stuaddress;
}
public void setStuaddress(String stuaddress) {
this.stuaddress = stuaddress;
}
}Create a class that parses xml files
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
import org.w3c.dom.Document;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* java The default Dom parses xml
* @param filename
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static List<Student> getstudentXML(String filename) throws Exception{
//Create the Student object finally parsed and put it into the collection
List<Student> stulist=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Get parser factory
DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//Get resolution object
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder=builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Create Document object
Document document=documentBuilder.parse(new File(filename));
//Get a collection of all child elements
NodeList studentNodeList=document.getElementsByTagName("student");
//Traversal of the resulting set
for(int i=0;i<studentNodeList.getLength();i++){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the tag node of a collection of sub elements
Node studentElement=studentNodeList.item(i);
//Get the attribute value of each child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.getAttributes().item(0).getNodeValue());
//Set the student object to get the student each time
student.setStuid(stuid);
//Gets the collection of child element tag nodes from the tag nodes of child elements
NodeList childElement=studentElement.getChildNodes();
//Traverse child elements
for(int j=0;j<childElement.getLength();j++){
//Get each tag node of the child element
Node elementName=childElement.item(j);
//Get the tag content of each child element
String info=elementName.getTextContent();
//Get the desired tag content by getting the tag name of each tag node
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuname")){
student.setStuname(info);
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuage")){
student.setStuage(Integer.parseInt(info));;
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuaddress")){
student.setStuaddress(info);;
}
}
//Each time the outer child element is cycled, the Student object obtained from each child element is put into the collection
stulist.add(student);
}
return stulist;
}
}Test:
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
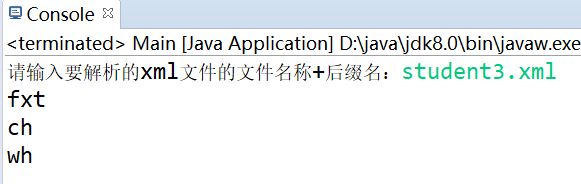
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("Please enter the to resolve xml File name of the file+Suffix:");
String filename=reader.readLine();
List<Student> stulist=xmlHelper.getstudentXML(filename);
for(Student student:stulist){
System.out.println(student.getStuname());
}
}
}
1.2 dom4j
For example;
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* java The default Dom parses xml
* @param filename
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
/*
public static List<Student> getstudentXML(String filename) throws Exception{
//Create the Student object finally parsed and put it into the collection
List<Student> stulist=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Get parser factory
DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//Get resolution object
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder=builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Create Document object
Document document=documentBuilder.parse(new File(filename));
//Get a collection of all child elements
NodeList studentNodeList=document.getElementsByTagName("student");
//Traversal of the resulting set
for(int i=0;i<studentNodeList.getLength();i++){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the tag node of a collection of sub elements
Node studentElement=studentNodeList.item(i);
//Get the attribute value of each child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.getAttributes().item(0).getNodeValue());
//Set the student object to get the student each time
student.setStuid(stuid);
//Gets the collection of child element tag nodes from the tag nodes of child elements
NodeList childElement=studentElement.getChildNodes();
//Traverse child elements
for(int j=0;j<childElement.getLength();j++){
//Get each tag node of the child element
Node elementName=childElement.item(j);
//Get the tag content of each child element
String info=elementName.getTextContent();
//Get the desired tag content by getting the tag name of each tag node
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuname")){
student.setStuname(info);
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuage")){
student.setStuage(Integer.parseInt(info));;
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuaddress")){
student.setStuaddress(info);;
}
}
//Each time the outer child element is cycled, the Student object obtained from each child element is put into the collection
stulist.add(student);
}
return stulist;
}
*/
/**
* dom4j
* @param filename
* @return
*/
public static List<Student> getstudentXML(String filename) throws Exception{
List<Student> stulst=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Create SAXReader object
SAXReader saxread=new SAXReader();
//Read the xml file and create a document object through SAXReader
Document document=saxread.read(new File(filename));
//Get the root element object through the document object
Element rootElement=document.getRootElement();
//Through the root element, we can get the collection composed of each child element with the tag name of student (including the child elements inside)
List<Element> studentElementList=rootElement.elements("student");
//Traversal of the resulting collection of child elements
for(Element studentElement:studentElementList){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the attribute value of the child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.attributeValue("stuid"));
//Get the child element stuname element object in the child element
Element stunameElement=studentElement.element("stuname");
String stuname=stunameElement.getText();
Element stuageElement=studentElement.element("stuage");
int stuage=Integer.parseInt(stuageElement.getText());
Element stuaddressElement=studentElement.element("stuaddress");
String stuaddress=stuaddressElement.getText();
student.setStuid(stuid);
student.setStuname(stuname);
student.setStuage(stuage);
student.setStuaddress(stuaddress);
stulst.add(student);
}
return stulst;
}
}
1.3jdom
For example:
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.ArrayList;
//import java.util.List;
import java.util.List;
import org.jdom.Document;
import org.jdom.Element;
import org.jdom.input.SAXBuilder;
//import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilder;
//import javax.xml.parsers.DocumentBuilderFactory;
//import org.dom4j.Document;
//import org.dom4j.Element;
//import org.dom4j.io.SAXReader;
//import org.w3c.dom.Document;
//import org.w3c.dom.Node;
//import org.w3c.dom.NodeList;
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* java The default Dom parses xml
* @param filename
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
/*
public static List<Student> getstudentXML1(String filename) throws Exception{
//Create the Student object finally parsed and put it into the collection
List<Student> stulist=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Get parser factory
DocumentBuilderFactory builderFactory=DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance();
//Get resolution object
DocumentBuilder documentBuilder=builderFactory.newDocumentBuilder();
//Create Document object
Document document=documentBuilder.parse(new File(filename));
//Get a collection of all child elements
NodeList studentNodeList=document.getElementsByTagName("student");
//Traversal of the resulting set
for(int i=0;i<studentNodeList.getLength();i++){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the tag node of a collection of sub elements
Node studentElement=studentNodeList.item(i);
//Get the attribute value of each child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.getAttributes().item(0).getNodeValue());
//Set the student object to get the student each time
student.setStuid(stuid);
//Gets the collection of child element tag nodes from the tag nodes of child elements
NodeList childElement=studentElement.getChildNodes();
//Traverse child elements
for(int j=0;j<childElement.getLength();j++){
//Get each tag node of the child element
Node elementName=childElement.item(j);
//Get the tag content of each child element
String info=elementName.getTextContent();
//Get the desired tag content by getting the tag name of each tag node
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuname")){
student.setStuname(info);
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuage")){
student.setStuage(Integer.parseInt(info));;
}
if(elementName.getNodeName().equals("stuaddress")){
student.setStuaddress(info);;
}
}
//Each time the outer child element is cycled, the Student object obtained from each child element is put into the collection
stulist.add(student);
}
return stulist;
}
*/
/**
* dom4j
* @param filename
* @return
*/
/*
public static List<Student> getstudentXML2(String filename) throws Exception{
List<Student> stulst=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Create SAXReader object
SAXReader saxread=new SAXReader();
//Read the xml file and create a document object through SAXReader
Document document=saxread.read(new File(filename));
//Get the root element object through the document object
Element rootElement=document.getRootElement();
//Through the root element, we can get the collection composed of each child element with the tag name of student (including the child elements inside)
List<Element> studentElementList=rootElement.elements("student");
//Traversal of the resulting collection of child elements
for(Element studentElement:studentElementList){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the attribute value of the child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.attributeValue("stuid"));
//Get the child element stuname element object in the child element
Element stunameElement=studentElement.element("stuname");
String stuname=stunameElement.getText();
Element stuageElement=studentElement.element("stuage");
int stuage=Integer.parseInt(stuageElement.getText());
Element stuaddressElement=studentElement.element("stuaddress");
String stuaddress=stuaddressElement.getText();
student.setStuid(stuid);
student.setStuname(stuname);
student.setStuage(stuage);
student.setStuaddress(stuaddress);
stulst.add(student);
}
return stulst;
}
*/
/**
* jdom
* @param filename
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public static List<Student> getstudentXML3(String filename)throws Exception{
List<Student> stulist=new ArrayList<Student>();
//Create SAXReader object
SAXBuilder saxBuilder=new SAXBuilder();
//Read the xml file and create a document object through SAXReader
Document document=saxBuilder.build(new File(filename));
Element rootElement=document.getRootElement();
//Get his collection of child / child element objects through the root element object
List<Element> childElement=rootElement.getChildren();
//ergodic
for(Element studentElement:childElement){
Student student=new Student();
//Get the attribute value of the child element
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(studentElement.getAttributeValue("stuid"));
//Get the tag object of the child element
Element stuidElement=studentElement.getChild("stuname");
String stuname=stuidElement.getText();
Element stuageElement=studentElement.getChild("stuage");
int stuage=Integer.parseInt(stuageElement.getText());
Element stuaddressElement=studentElement.getChild("stuaddress");
String stuaddress=stuidElement.getText();
student.setStuid(stuid);
student.setStuname(stuname);
student.setStuage(stuage);
student.setStuaddress(stuaddress);
stulist.add(student);
}
return stulist;
}
}
The principle of DOM (Document Object Model) parsing is to read the xml file to be parsed into a Document tree [Document Object], get the root element from the Document tree according to the provided development class library and method, and then get the sub element from the root element, from the sub element to the sub element, and then get the specific data value.
Advantages: clear structure.
Disadvantages: it usually needs to load the whole XML document to construct the hierarchy, which consumes a lot of resources
2.SAX (Simple API for XML) parsing
DefaultHandler is the default class. You need to inherit this class to use it
For example:
Create student class
package com.wangxing.test2;
public class Student {
private int stuid;
private String stuname;
private int stuage;
private String stuaddress;
public int getStuid() {
return stuid;
}
public void setStuid(int stuid) {
this.stuid = stuid;
}
public String getStuname() {
return stuname;
}
public void setStuname(String stuname) {
this.stuname = stuname;
}
public int getStuage() {
return stuage;
}
public void setStuage(int stuage) {
this.stuage = stuage;
}
public String getStuaddress() {
return stuaddress;
}
public void setStuaddress(String stuaddress) {
this.stuaddress = stuaddress;
}
}Create an xml parsing class to get the SAX parser object, which uses the methods in the DefaultHandler class to parse
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.File;
import java.util.List;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParser;
import javax.xml.parsers.SAXParserFactory;
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
public class xmlHelper {
/**
* 2.SAX(Simple API for XML)analysis
* @param filename
* @return
*/
public static List<Student> getstudentXML4(String filename) throws Exception{
//Get SAX parser factory
SAXParserFactory saxFactroy=SAXParserFactory.newInstance();
//Get the parser object from the factory
SAXParser saxparser=saxFactroy.newSAXParser();
MyDefaultHandler myDefaultHandler=new MyDefaultHandler();
System.out.println(myDefaultHandler);
saxparser.parse(new File(filename), myDefaultHandler);
return myDefaultHandler.getStudentList();
}
}Create a subclass that inherits the DefaultHandler class
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import org.xml.sax.Attributes;
import org.xml.sax.SAXException;
import org.xml.sax.helpers.DefaultHandler;
public class MyDefaultHandler extends DefaultHandler{
//Save each accepted student object
private List<Student> studentlist=null;
private Student student=null;
//Create saved element tag name
private String ElementName=" ";
/**
* Get the parsed data set
* @return
*/
public List<Student> getStudentList() {
return studentlist;
}
/**
* Document start
*/
@Override
public void startDocument() throws SAXException {
//Build set object
studentlist=new ArrayList<Student>();
}
/**
* End of document
*/
@Override
public void endDocument() throws SAXException {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.endDocument();
}
/**
* Element start
*/
@Override
public void startElement(String uri, String localName, String qName, Attributes attributes) throws SAXException {
//Create a student object when the label name of the element is student
if (qName.equals("student")) {
student=new Student();
int stuid=Integer.parseInt(attributes.getValue("stuid"));
student.setStuid(stuid);
}
if (qName.equals("stuname")) {
ElementName=qName;
}
if (qName.equals("stuage")) {
ElementName=qName;
}
if (qName.equals("stuaddress")) {
ElementName=qName;
}
}
/**
* End of element
*/
@Override
public void endElement(String uri, String localName, String qName) throws SAXException {
ElementName=" ";
if (qName.equals("student")) {
studentlist.add(student);
student=null;
}
}
/**
* Get data value
*/
@Override
public void characters(char[] ch, int start, int length) throws SAXException {
String info=new String(ch,start,length);
if (ElementName.equals("stuname")) {
student.setStuname(info);
}
if (ElementName.equals("stuage")) {
student.setStuage(Integer.parseInt(info));
}
if (ElementName.equals("stuaddress")) {
student.setStuaddress(info);
}
}
}Test:
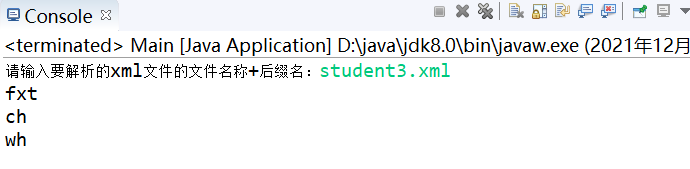
package com.wangxing.test2;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.List;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader reader=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
System.out.print("Please enter the to resolve xml File name of the file+Suffix:");
String filename=reader.readLine();
//List<Student> stulist=xmlHelper.getstudentXML1(filename);
//List<Student> stulist=xmlHelper.getstudentXML2(filename);
//List<Student> stulist=xmlHelper.getstudentXML3(filename);
List<Student> stulist=xmlHelper.getstudentXML4(filename);
for(Student student:stulist){
System.out.println(student.getStuname());
}
}
}
SAX (Simple API for XML) the principle of parsing XML files is based on the event model. It can trigger a series of events when parsing XML documents. When a given tag is found, it can activate a callback method to tell the method that the specified tag has been found. If there are data values in the specified tag, we can parse it. If there are no data values, we don't need to process it. Read an element and determine which element of the XML file this element belongs to [document start / document end / mark start / mark end / text element]. Different elements trigger different methods to parse data. If there is no data value in the current element, skip reading the next element.
Advantages: 1. Check the data only when reading the data and do not need to be saved in memory
2. You can stop parsing when a certain condition is met without parsing the whole document.
3. High efficiency and performance, able to parse documents larger than the system memory.
Disadvantages: there is no clear analytical structure
A parsing method similar to SAX parsing pull parsing