background
Last time How to select online Spring Boot, Spring Cloud and Spring Cloud Alibaba versions as well as Zuul and Gateway request IO model comparison (WebFlux advantages) and Reactor model analysis
Select the Gateway in the micro service to use the Gateway. Next, let's build a simple Gateway to use
Introduction to spring cloud gateway
GitHub address: https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-gateway
Official website document address: https://spring.io/projects/spring-cloud-gateway#learn
Spring Cloud gateway is a new project of Spring Cloud. The project is a gateway developed based on Spring 5.0, Spring Boot 2.0 and Project Reactor. It aims to provide a simple and effective unified API routing management method for microservice architecture.
As a gateway in the Spring Cloud ecosystem, the goal of Spring Cloud gateway is to replace Zuul. In Spring Cloud versions above 2.0, the latest performance versions above Zuul 2.0 are not integrated, and the old version of non Reactor mode before Zuul 2.0 is still used. In order to improve the performance of the gateway, the Spring Cloud gateway is implemented based on the WebFlux framework, and the underlying WebFlux framework uses the high-performance Reactor mode communication framework Netty.
Why do you need a gateway to speak? Let's think about what we need to do with multiple services without a gateway?
First, the relationship between our client traffic entry calls may be like this
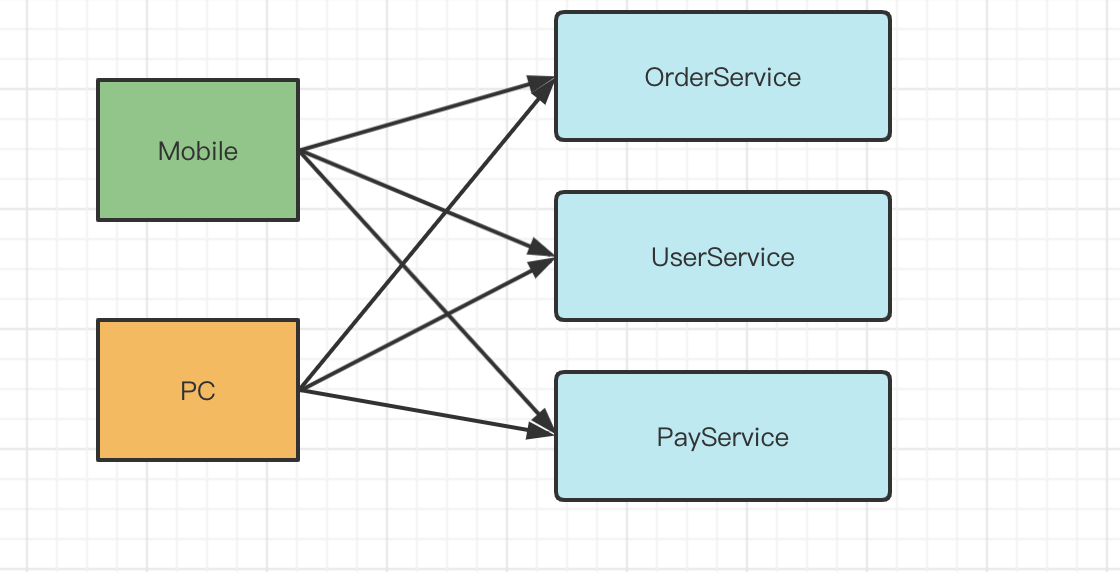
What are the problems?
- If the authentication function is added, each service needs to be modified
- Cross domain issues require the transformation of each service
- Cross domain issues require the transformation of each service
- Gray publishing and dynamic routing need to transform each service
- There is a security problem. The Endpoint exposed by each microservice is fixed, and the client access needs to know the real Endpoint of each microservice
If we add a layer of gateway before the service as the storage of all traffic, the whole architecture will become as follows
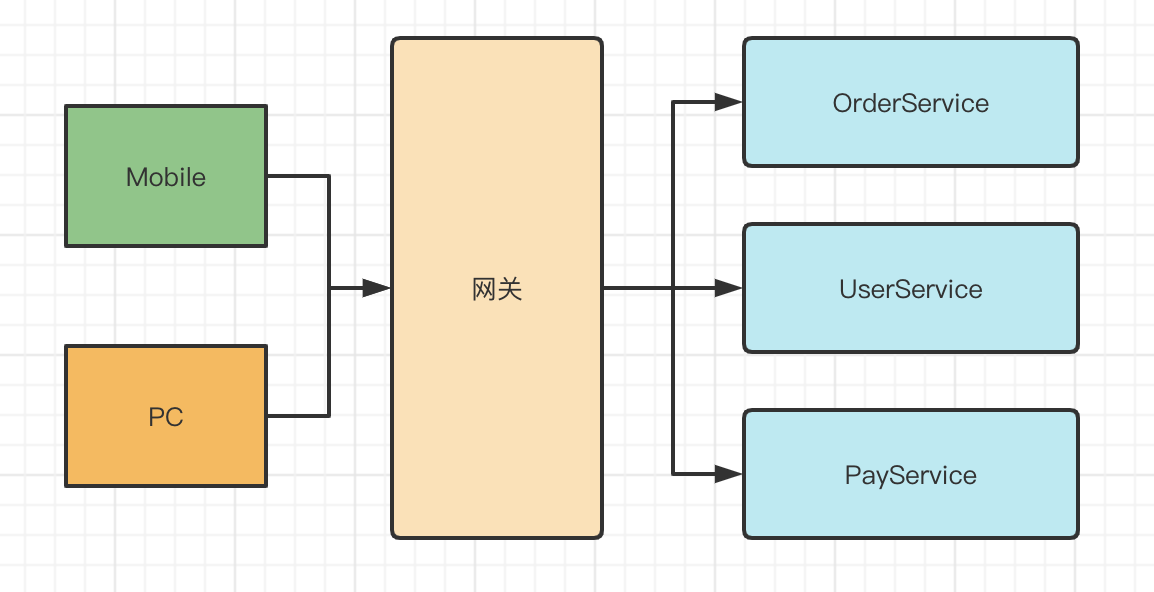
Then all the above problems can be implemented uniformly in the gateway, and each service does not need to be implemented
Gateway getting started
1. Create a SpringBoot project
2. Add dependency
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.2</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.wh</groupId>
<artifactId>gateway</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>gateway</name>
<description>gateway</description>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2020.0.1</spring-cloud.version>
<spring-cloud-alibaba.version>2021.1</spring-cloud-alibaba.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webflux</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-api</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.yomahub</groupId>
<artifactId>tlog-gateway-spring-boot-starter </artifactId>
<version>1.3.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-alibaba-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-alibaba.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
3. Configure routing forwarding
- Application.yml
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: gate-way
cloud:
gateway:
routes:
- id: plutus_route
uri: http://localhost:10080
predicates:
- Path=/plutus/**
Here, the startup port of the gateway is simply configured as 8080, and then a routing rule is configured
The routing rule configured here is to intercept all requests. The path prefix is / plutus, and then forward them to http://localhost:10080 route
A simple example:
The url of the gateway I access here is
localhost:8080/plutus/finance/v1/bill/exception
Then the actual access url will be forwarded to
http://localhost:10080/plutus/finance/v1/bill/exception
4. Add request log Filter
@Slf4j
@Component
@AllArgsConstructor
public class RequestLogFilter implements GlobalFilter, Ordered {
private static final String START_TIME = "startTime";
@Override
public Mono<Void> filter(ServerWebExchange exchange, GatewayFilterChain chain) {
String requestUrl = exchange.getRequest().getURI().getRawPath();
// Build a long log to avoid and distribute the log disorder
StringBuilder beforeReqLog = new StringBuilder(300);
// Log parameters
List<Object> beforeReqArgs = new ArrayList<>();
beforeReqLog.append("\n\n================ Cider Gateway Request Start ================\n");
// Print route
beforeReqLog.append("===> {}: {}\n");
// parameter
String requestMethod = exchange.getRequest().getMethodValue();
beforeReqArgs.add(requestMethod);
beforeReqArgs.add(requestUrl);
// Print request header
HttpHeaders headers = exchange.getRequest().getHeaders();
headers.forEach((headerName, headerValue) -> {
beforeReqLog.append("===Headers=== {}: {}\n");
beforeReqArgs.add(headerName);
beforeReqArgs.add(StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(headerValue));
});
beforeReqLog.append("================ Cider Gateway Request End =================\n");
// Print execution time
log.info(beforeReqLog.toString(), beforeReqArgs.toArray());
exchange.getAttributes().put(START_TIME, System.currentTimeMillis());
return chain.filter(exchange).then(Mono.fromRunnable(() -> {
ServerHttpResponse response = exchange.getResponse();
Long startTime = exchange.getAttribute(START_TIME);
long executeTime = 0L;
if (startTime != null) {
executeTime = (System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime);
}
// Build a long log to avoid and distribute the log disorder
StringBuilder responseLog = new StringBuilder(300);
// Log parameters
List<Object> responseArgs = new ArrayList<>();
responseLog.append("\n\n================ Cider Gateway Response Start ================\n");
// Print route 200 get: /mate*/xxx/xxx
responseLog.append("<=== {} {}: {}: {}\n");
// parameter
responseArgs.add(response.getStatusCode().value());
responseArgs.add(requestMethod);
responseArgs.add(requestUrl);
responseArgs.add(executeTime + "ms");
// Print request header
HttpHeaders httpHeaders = response.getHeaders();
httpHeaders.forEach((headerName, headerValue) -> {
responseLog.append("===Headers=== {}: {}\n");
responseArgs.add(headerName);
responseArgs.add(StringUtils.collectionToCommaDelimitedString(headerValue));
});
responseLog.append("================ Cider Gateway Response End =================\n");
// Print execution time
log.info(responseLog.toString(), responseArgs.toArray());
}));
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return 0;
}
}
5. Build test service
Here we build a simple plutus service and a simple spring boot project
configuration file
server:
port: 10080
servlet:
context-path: /plutus
Then write a simple interface
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/finance/v1")
@Slf4j
public class FinanceController {
@GetMapping("/bill/exception")
public String getFinanceExceptionVO() {
System.out.println("Route forwarding succeeded");
return "SUCCESS";
}
}
test
We visit
localhost:8080/plutus/finance/v1/bill/exception
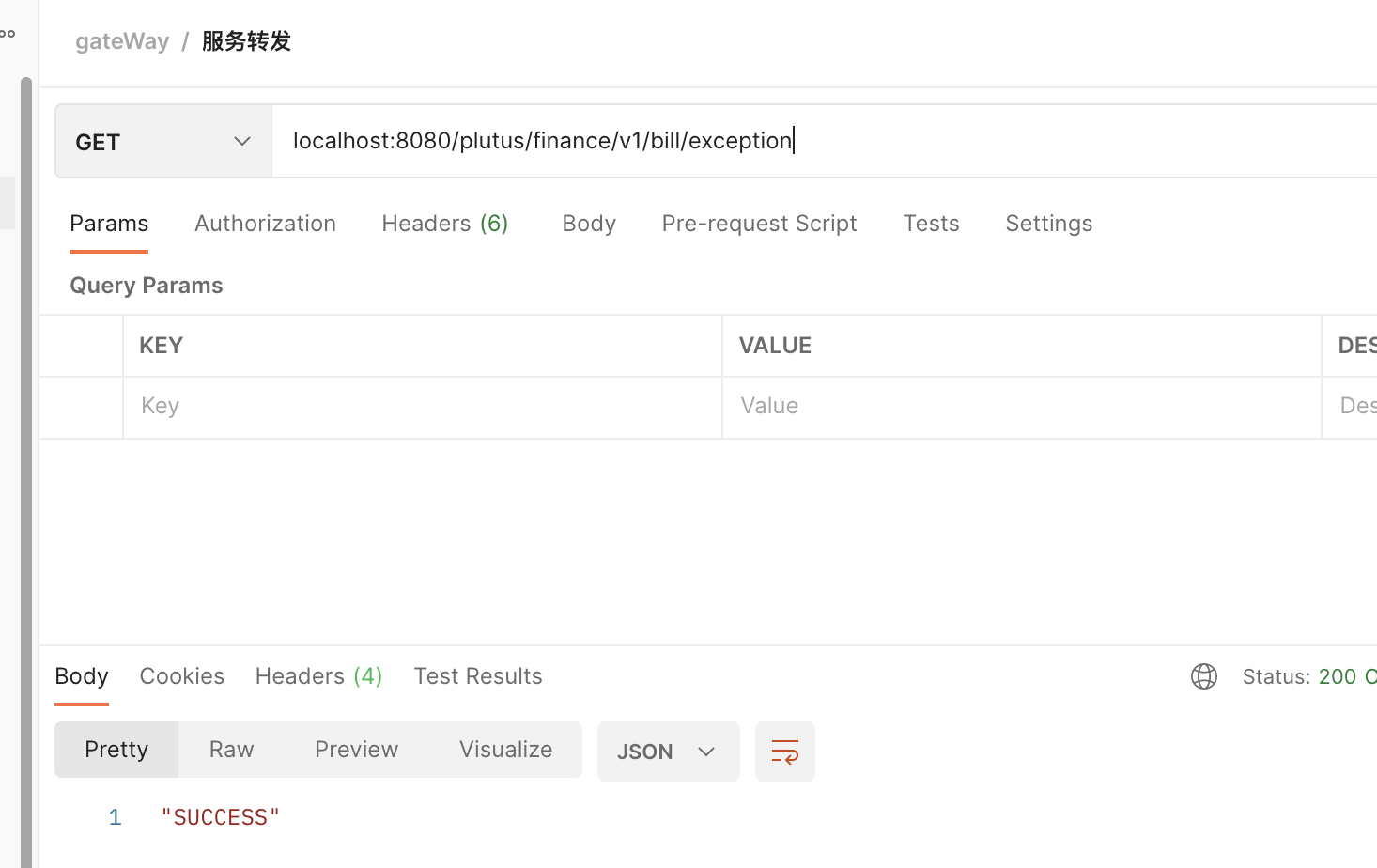
On the plutus project console, we can see that the output route is forwarded successfully, which means that the request is forwarded successfully
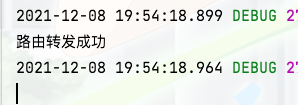
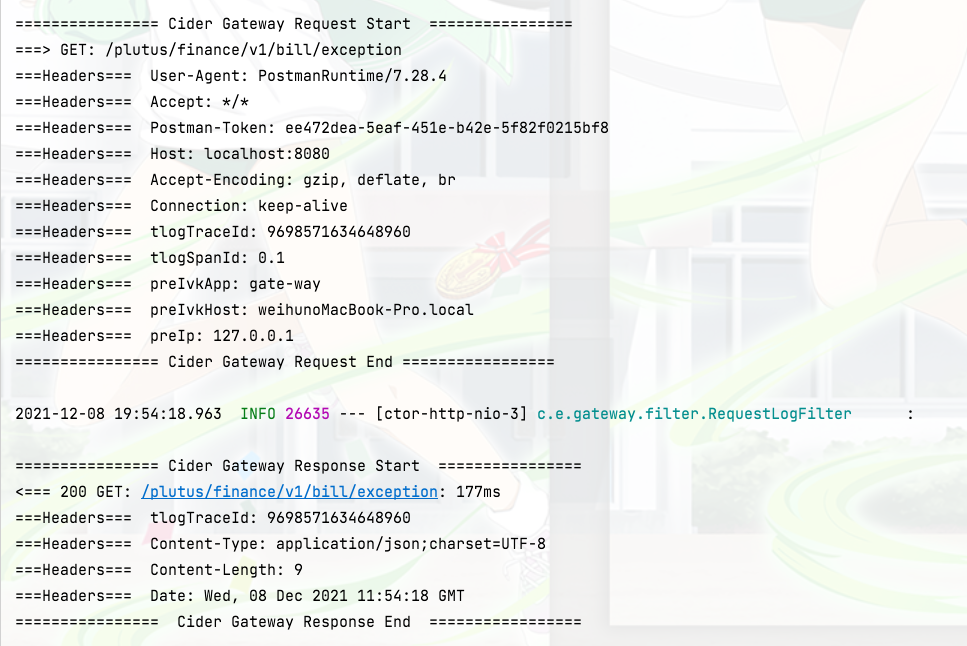
At the same time, we can also see that the gateway prints out the request log
About me
Pure technology dry goods blogger. It's not easy to be original. I think the article is good. Please scan the code and pay attention to me