The course recommended by Wu Haiyang of wanmen university is very clear. The content of this blog is basically the content of the course.
1, Environment configuration
git configuration
// Configure user name and mailbox git config --global user.name "yourname" git config --global user.email "your@email" //View profile git config --list //View a configuration git config user.name //view help git help git help order of the day //View detailed description
git initialization
// initialization git init //Create folder and initialize git init file name //View all files in the folder ls -la file name
git tracking
//View git status git status //Add files to staging area git add file name //Add all files git add .
git undo tracking
//Withdraw the file from the staging area and cancel tracking git rm --cached File name (multiple file names can be written)
git submit to local warehouse
//After commit, the version number is generated and saved git commit git commit -m Submit information //Do add and commit at the same time, but only take effect for the tracked files git commit -am
2, Version tracking
log tracking of git
//Command parameters can be combined git log //View the difference between the last two submissions git log -p -2 git log --author="" //View branch diagram git log --graph git log --pretty=oneline //The printed information is complete //Custom print format,% h represents hash value,% an represents author,% ar represents time, and% s represents description. git log --pretty=format: "%h - %an, %ar : %s"
git tracks the difference between before and after file modification
//Before git commit, check whether there is a problem with the current version. If there is no problem, you can submit it directly git diff //You can specify a file name. By default, it shows the changes of all files //If the file has been added to the temporary storage area, you cannot use git diff to directly view the difference. You need to add the staged parameter. git diff --staged
git file deletion, renaming and moving
//To delete, you can delete the original file and add again, which is equivalent to git deletion git rm filename //rename git mv oldname newname //Move, move is essentially to delete the old and create a new one git mv filename route/file name
git file ignored
//Yes Add the file name to gitignore //Ignore node_ All files under the modules file //Ignore different files and wrap lines /node_modules //Ignore log end file *.log //Delete tracked files //Empty folders will not be found and will be prompted not to be tracked. Empty files will be prompted not to be tracked //Bring out all the files in the cache and Add files to gitignore, and then add commit push. git rm -r --cached .
3, Restore changes
git one click Restore
//Local modification, not add ed yet //Discard local changes git checkout -- filename //The newly created file has not been tracked and cannot be restored with checkout. You can delete it directly rm -rf filename
git undo tracking and one click Restore
//Files that have been added to the cache //reset to the last operation of this file git reset HEAD filename //Return to the status of not add ed, abandon the local modification, and return to the previous status git checkout --filename
git version fallback
//Forced fallback git reset --hard HEAD^ //Fallback to previous version git reset --hard HEAD^^ //Back to previous version git reset --hard HEAD of hash number //Fallback to the specified hash version git reflog // View the change of pointer
git back to the old version
Version fallback: the future version is deleted and cannot be returned to the future
Back to the old version: pull a certain version from the past to the present, and keep all the existing versions
// git log git checkout hash number -- filename git checkout hash number -- . //Restore all files to the previous version and commit again
4, Branch merge
When the current branch is not processed, the content of other branches will not be changed.
Switch branches when the current branch is working tree clean
git new switch delete branch
git branch //View branch git branch name //New branch git checkout branch_name //Switch branch git checkout -b branch_name //Create and switch branches git branch -d name //To delete a branch, you need to switch to another branch first git branch -D name //Forcibly delete branches. Unconsolidated branches cannot be deleted with - D, but can be forcibly deleted with - D //After a branch is deleted by mistake, it can be retrieved as long as there is the hash number of the branch git branch Branch name hash number
git merge branch
First switch to the main branch, and then git merge the branches to be merged
git merge branch_name git merge --no-ff --no-commit branch_name //Do not submit after merging. Submit after the test is OK, -no-ff do not need to switch to the fast mode. You can see all versions git merge --no-ff --squash branch_name //--No FF and -- squash cannot be used at the same time git merge --squash branch_name //Compress branches and commit after compression git reset --hard ORIG_HEAD //Back to the original version
git conflict resolution
git merge --abort //Abandon merge
< < < < < < < indicates the current branch
=======Indicates separation
>>>>>>>Represents the branch to be merged
git view the version line diagram through the command
git log git log --oneline git log --oneline --graph git log --oneline --graph --all //View all branches git log --oneline --graph -number //View recent versions of the line graph
git fast rotation mechanism
When the previous version is the same as this version, it is not necessary to keep the two same versions. Use the fast rotation mechanism to erase the previous version directly
git merge branch_name --no-ff //Fast rotation mechanism is not used
git deletes all unwanted branches at once
git branch --merged //Show all merged content git branch --no-merged //Show all unmerged content git branch --merged | egrep -v "(^\*|master|develop)"|xargs git branch -d //In parentheses are the branches to keep git branch --no-merged | egrep -v "(^\*|master|develop)"|xargs git branch -D //In parentheses are the branches to be retained. Delete the unconsolidated branches with capital D
5, github usage
Push git local warehouse to remote warehouse
git init //Generate local warehouse git add . git commit -m "message" git remote add origin Remote web address //After setting, use origin to replace the remote URL git push --set-upstream origin master //Connection required for first submission git push -u origin master //Abbreviation of the last command
git main warehouse as server
1,The project name is owner_name.github.io 2,Remove the original connection git remote remove origin 3,Establish a new connection git remote add origin Remote web address
git get remote project
Do not download the zip file and then use git init, which will cause all branch information to be lost.
git clone Remote warehouse address item name (optional)//Clone the remote warehouse and automatically check out to the master //Add the item name parameter to rename the item git clone --no-checkout //Clone, but do not automatically check ou to the master git clone --bare Remote warehouse address //Clone a naked warehouse, only git file If you need to obtain the following code git clone Naked warehouse address item name
6, git multi person collaborative development
git push
git push git push -u origin git push --set-upstream origin branch_name //The first upload should correspond to the remote branch, and then you can directly use git push git push --all //All branches are uploaded at one time git branch -a //You can view remote trace branches
git pull
git pull = git fetch + git merge //git pull before work git fetech git merge gitr pull After pulling a remote branch that does not exist locally, there is only the remote tracking branch of the branch locally, but there is no such branch, Not at this time checkout Tracing a branch to the far end generates a split head pointer. If you want to checkout Can directly git checkout The corresponding remote branch name will be automatically created locally.
git Delete remote branch, warehouse migration
git push origin --delete branch_name //Delete remote branch and remote tracking branch git remote set-url origin New address of remote warehouse //After the warehouse is migrated and the new address is set, git push --all can be used.
git demo
developer A Create warehouse and upload git init //Initialize local warehouse code .gitignore //Open with vs code gitignore file git add . git commit -m 'first commit' git remote add origin Remote warehouse name git push -u origin master developer B Pull project and develop git clone --bare Remote warehouse address git clone --no-checkout Naked warehouse address item name rm -rf Bare warehouse git checkout master git checkout -b developB //Create your own branch and develop code . git add . git commit -m 'developB' git checkout master git merge --no-ff developB git log --oneline --graph git remote set-url Remote warehouse address git remote -v git push --all developer A Develop git pull git checkout -b developA code . git add . git commit -m 'developA' git checkout master git merge developA git push //Only the master is pushed. If you need to push others, you can git push --all or switch to other branches, GIT push origin developepa
7, git server deployment
git uses ssh to connect to github
cd ~ //Switch to default folder ls -la ssh-keygen //Generate public and private keys cat id_rsa.pub //Open the public key and put it on the server ssh git@github.com //Connect to github server
git is automatically deployed to alicloud server
1,Submit project to github 2,use github of actions Automatically deploy, select according to language and function CI,Deploy with rsync The plug-in implements the function of automatic deployment to the server. Parameter in settings--secrets Add in. 3,Generate public and private keys ssh-keygen -t rsa -C auto -f deployment //Customize the generation, add the description, give the project name, and finally generate the deployment and deployment pub Add private key to github of secrets In the variable Add private key to local ssh In the folder cd .ssh/ cp ~/deployment . Add the public key to the default folder of the remote server scp deployment.pub user name@Public network ip: . 4,Connect to remote server ssh root@Public network ip address //Local connection server Write public key to.ssh Folder authorized_keys In the file Press dd Delete original content cat deployment.pub >> ~/.ssh/authorized_keys 5,Initiate automatic deployment go back to github,click start commit.
8, gitlab usage
gitlab
Private warehouse free of charge, operation and github identical
fork use
It is used for collaboration among multiple developers, or the addition and testing of new functions of the project fork Modify in your own warehouse Then launch merge request
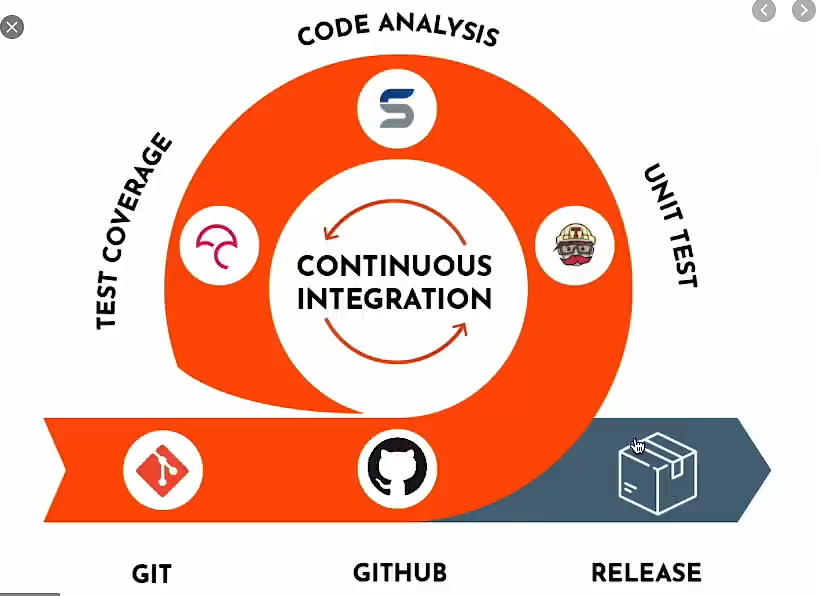
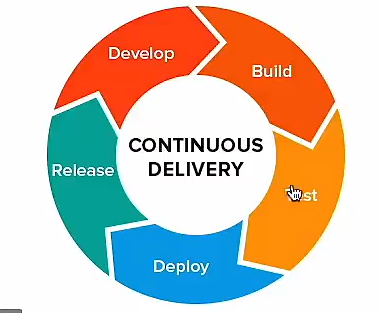
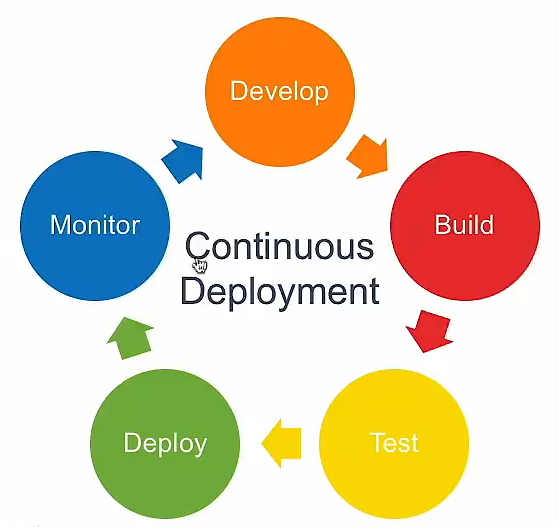
CI and CD
Continuous Intergration //unit testing Continuous Delivery // Continuous Deployment // Continuous integration, continuous delivery, continuous integration
gitlab runner
The installation tutorial is conducted according to the official website gitlab-runner --version //Check whether the installation is successful
gitlab CI/CD
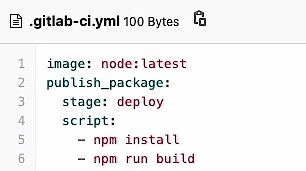
establish .gitlab-ci.yml function CI/CD Pipelines