Write in front
This time, we use gRPC implementation to obtain user information
1. Installation
1.1 grpc
grpc can be installed directly by go get
go get google.golang.org/grpc
1.2 proto
Download proto. I downloaded this.

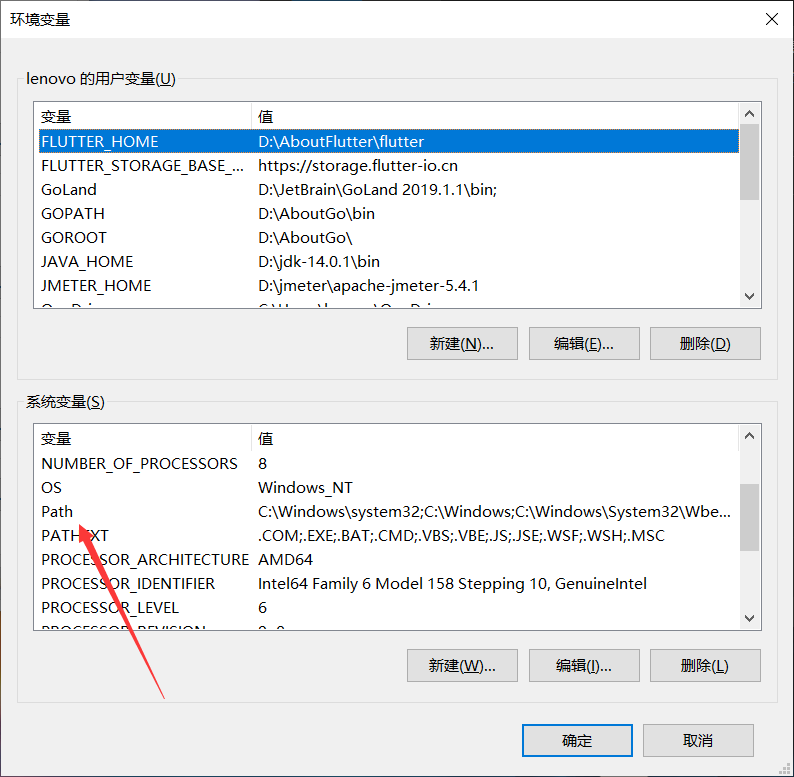
Then extract it and put the bin directory directly in the system variable

1.3 protobuf
We're at the terminal
go get github.com/golang/protobuf
If you can't get down like me, you can directly git clone source code
Then enter the protocol Gen go folder and open cmd under this folder
implement
go build

You'll find one more executable
Then put the executable file in the proto folder just mentioned in 1.2
Open cmd and enter protoc ol
That's it
2. Write code
2.1 initialization items
- Create a new folder gRPC, and then create the proto folder and client go,server.go file
2.2 writing proto
Create a user under proto proto
Note the proto syntax:
- A message type definition describes the message format of a request or response, and can contain multiple types of fields.
- For example, define the message format of a search request. Each request includes query string, page number and number of pages.
- The field name is in lowercase and automatically becomes uppercase after being converted to go file. message is equivalent to a structure.
Determine the version number first:
syntax = "proto3";
Then the output path
option go_package = "./";
Define client request format
message UserRequest{
// Define request parameters
string name = 1;
}
Specifies the name of the generated package
package proto;
Define the server response format
message UserResponse{
// Define response parameters
int32 id = 1;
string name = 2;
int32 age = 3;
// Field modifier
// repeated represents a variable array, similar to the slice type
repeated string hobby = 4;
}
Define service interface
service UserInfoService{
// Methods within the interface
// Define the request parameter as UserRequest and the response parameter as UserResponse
rpc GetUserInfo (UserRequest) returns (UserResponse){
}
}
Then execute
protoc --go_out=plugins=grpc:. user.proto

Generate Pb Go file
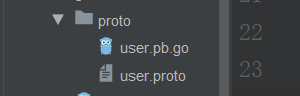
2.3 writing server
- Define service object
type UserInfoService struct {
}
var u = UserInfoService{}
- Implementation method of server
func (service *UserInfoService)GetUserInfo(ctx context.Context,req *pb.UserRequest)(resp *pb.UserResponse,err error) {
name := req.Name
// Query user information in database
if name == "zs" {
resp = &pb.UserResponse{
Id: 1,
Name: name,
Age: 19,
// Slice field
Hobby :[]string{"FanOne","FanOneTwo"},
}
}
err = nil
return
}
- Implement listening connection
// 1. Monitoring
address := "127.0.0.1:8080"
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", address)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Listening exception ",err)
return
}
fmt.Println("Listening succeeded")
- Instantiate rpc
s := grpc.NewServer()
- Register microservices on gRPC
// The first type is the service, and the second type is the variable of the interface pb.RegisterUserInfoServiceServer(s,&u)
- Start gRPC server
_ = s.Serve(lis)
2.4 implementation of client
- Create a connection with gRPC server
conn, err := grpc.Dial("127.0.0.1:8080", grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Connection exception",err)
}
defer conn.Close()
- Instantiate gRPC client
client := pb.NewUserInfoServiceClient(conn)
- Assemble the parameter, New a requested parameter, and then send the object
req := new(pb.UserRequest) req.Name="zs"
- Call the interface to get the response
resp ,err := client.GetUserInfo(context.Background(),req)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println("Abnormal response",err)
}
fmt.Println("Response results",resp)
3. Presentation
- Open the server listening port first
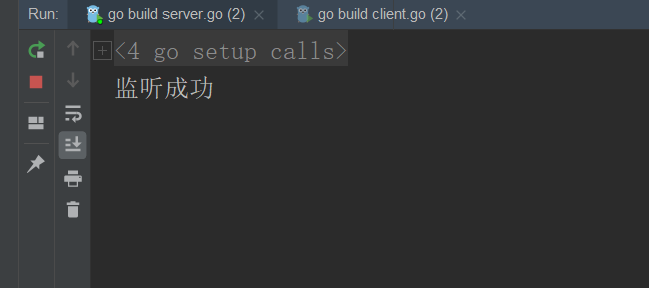
- Enable client to send request
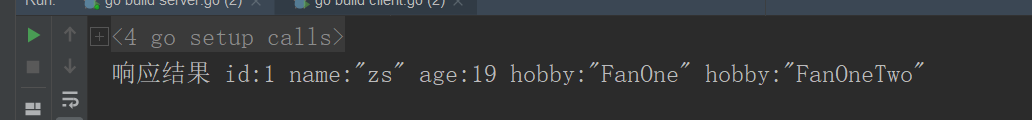
Then you can get the server information.
Note:
The call of rpc is that the memory of one machine calls the memory of another machine, so we need to pass the form of pointer.