gradle build tool learning series
Sometimes you may want to execute code when a specific lifecycle event occurs. A lifecycle event may occur before, during, or after a construction phase. The lifecycle event that occurs after the execution phase is the completion of the build.
Internal representation of Task execution diagram
During configuration, Gradle determines the order of tasks to be run in the execution phase, and the internal structure representing the internal dependencies shall be constructed as a directed acyclic graph (DAG). Each task in the graph is called a node, and each node is connected through a directed edge.
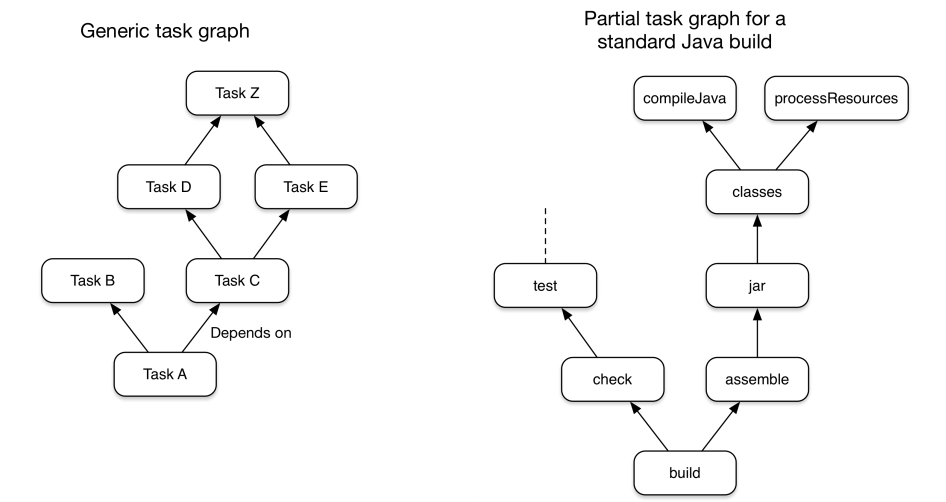
In general, connections between these nodes are created by declaring dependsOn relationships or by using implicit task dependent intervention mechanisms. It is important that DAG does not have a closed loop, that is, a previously executed task will never be executed again.
Attaching a Task to a Task execution diagram
As shown in the figure below, the so-called task execution diagram actually refers to TaskExecutionGraph Class.
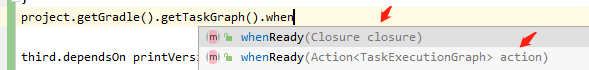
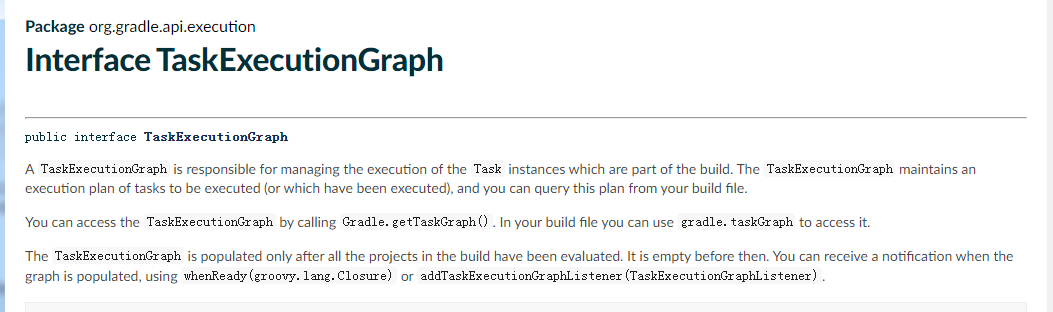
There are two ways to write callback lifecycle events (the whenReady method above)
- closure
- It is implemented through the listener interface provided by Gradle API
The build script is extended by calling the whenReady method to register a closure. After the task graph is generated, it will be executed immediately. As shown in the figure below
gradle.taskGraph.whenReady { TaskExecutionGraph taskGraph ->
if (taskGraph.hasTask(release)) {
if (!version.release) {
version.release = true
ant.propertyfile(file: versionFile) {
entry(key: 'release', type: 'string', operation: '=', value: 'true')
}
}
}
}
The life cycle hook registered in the above code is called after the task graph is generated. Check whether the branch graph contains the release d task, and then perform the corresponding operation of modifying the file. The following is the completed code
apply plugin: 'war'
ext.versionFile = file('version.properties')
task loadVersion {
project.version = readVersion()
}
ProjectVersion readVersion() {
logger.quiet 'Reading the version file.'
if (!versionFile.exists()) {
throw new GradleException("Required version file does not exit: $versionFile.canonicalPath")
}
Properties versionProps = new Properties()
versionFile.withInputStream { stream ->
versionProps.load(stream)
}
new ProjectVersion(versionProps.major.toInteger(), versionProps.minor.toInteger(), versionProps.release.toBoolean())
}
gradle.taskGraph.whenReady { TaskExecutionGraph taskGraph ->
if (taskGraph.hasTask(release)) {
if (!version.release) {
version.release = true
ant.propertyfile(file: versionFile) {
entry(key: 'release', type: 'string', operation: '=', value: 'true')
}
}
}
}
task createDistribution(type: Zip) {
from war.outputs.files
from(sourceSets*.allSource) {
into 'src'
}
from(rootDir) {
include versionFile.name
}
}
task backupReleaseDistribution(type: Copy) {
from createDistribution.outputs.files
into "$buildDir/backup"
}
task release(dependsOn: backupReleaseDistribution) {
doLast{
logger.quiet 'Releasing the project...'
}
}
tasks.addRule("Pattern: increment<Classifier>Version – Increments the project version classifier.") { String taskName ->
if (taskName.startsWith('increment') && taskName.endsWith('Version')) {
task(taskName){
doLast {
String classifier = (taskName - 'increment' - 'Version').toLowerCase()
String currentVersion = version.toString()
switch (classifier) {
case 'major': ++version.major
break
case 'minor': ++version.minor
break
default: throw new GradleException("Invalid version type '$classifier. Allowed types: ['Major', 'Minor']")
}
String newVersion = version.toString()
logger.info "Incrementing $classifier project version: $currentVersion -> $newVersion"
ant.propertyfile(file: versionFile) {
entry(key: classifier, type: 'int', operation: '+', value: 1)
}
}
}
}
}
class ProjectVersion {
Integer major
Integer minor
Boolean release
ProjectVersion(Integer major, Integer minor) {
this.major = major
this.minor = minor
this.release = Boolean.FALSE
}
ProjectVersion(Integer major, Integer minor, Boolean release) {
this(major, minor)
this.release = release
}
@Override
String toString() {
"$major.$minor${release ? '' : '-SNAPSHOT'}"
}
}
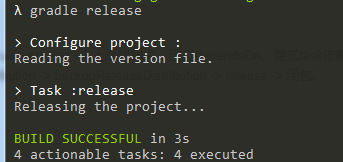
In the above code, the execution sequence is ensured through dependsOn, implicit task dependency and hook task execution diagram: createdistribution - > backupreleasedistribution - > release - > closure.
The execution effect is as follows