1. GraphSAGE import
-
Thesis title: Inductive Representation Learning on Large Graphs
-
Author: William L. Hamilton, Rex Ying and Jure Leskovec
Graph neural network methods proposed before GraphSAGE, such as DeepWalk and GCN, belong to transmissive models. When the structure of the network changes a little, such models need to be retrained, which can not meet the needs of real-time and rapid generation of network node embedding. In order to solve this problem, the authors of this paper propose an inductive model, GraphSAGE method. The goal of this method is to train an aggregator to aggregate the information of the neighbors of the target node, so as to quickly generate the low-dimensional vector representation of the unknown node.
-
The basic process of GraphSAGE is shown in the following figure:
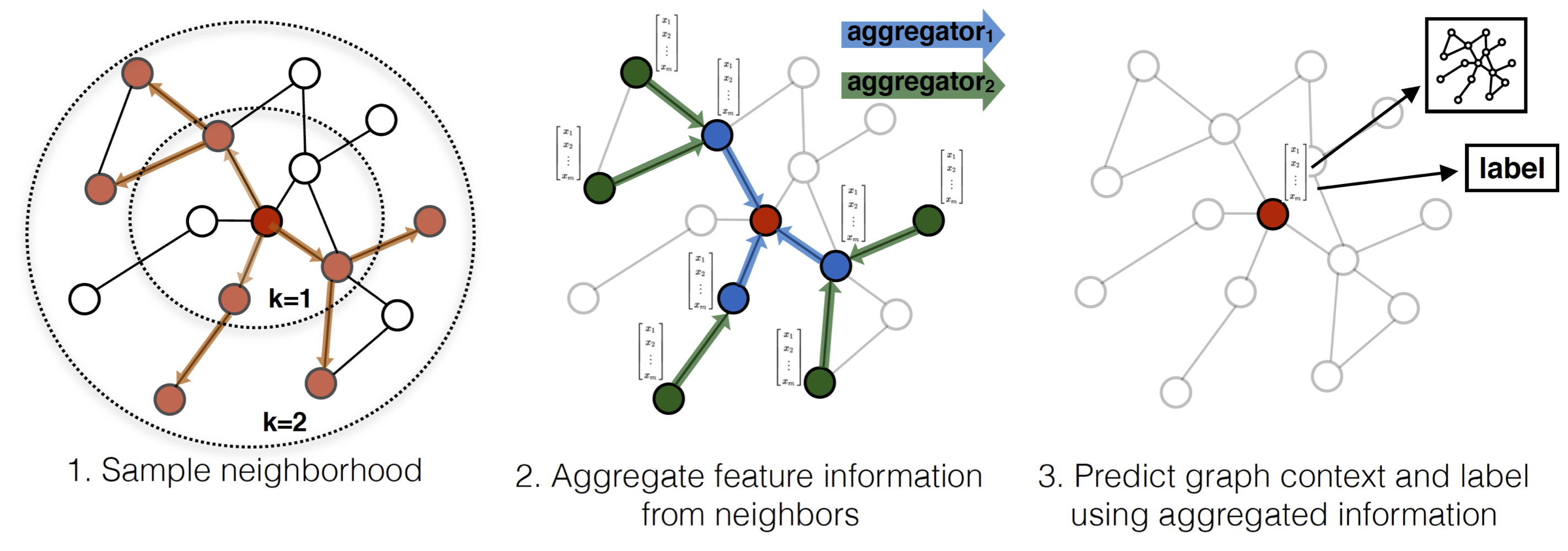
1) Firstly, the neighborhood network of fixed size is obtained by random walk. 2) then the characteristics of finite order neighbor nodes are aggregated to the target node by aggregator. The pseudo code is as follows

As can be seen from the pseudo code above, the input of GraphSAGE is: target network G G G. Eigenvectors of nodes x v x_v xv. Weight matrix W k W^k Wk, nonlinear activation function σ \sigma σ, aggregator function and neighbor function N N N. 1) first h 0 h_0 h0 ¢ is the eigenvector of the node, cyclic K K K step 2) traverse each node. For each node, first aggregate neighbor nodes k − 1 k-1 The characteristics of k − 1 time, and then compare the aggregation result with the current node k − 1 k-1 concat the characteristics at time k − 1 and pass through an activation function 3) make a command after K steps of the cycle h k h_k hk divided by ∣ ∣ h k ∣ ∣ 2 ||h_k||_2 ∣∣ hk ∣∣ 2 get the low dimensional representation of the node. -
Aggregators: it can be seen from the above flowchart and pseudo code that GraphSAGE needs aggregators. What is this aggregator? What role does it play? In fact, the function of aggregator is to aggregate the neighbor information of the target node. The author gives three different aggregators in this paper, which are:
1) Mean aggregator: this strategy averages the values of eigenvectors of neighbor nodes and target nodes
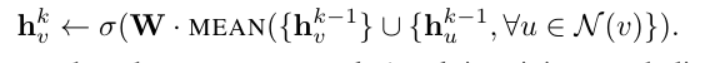
2) LSTM aggregator: use LSTM to aggregate the information of neighbor nodes.
3) Pooling aggregator: when using the pooling aggregator, the characteristics of each neighbor node pass through a full connection layer one by one, so as to carry out pooling operation
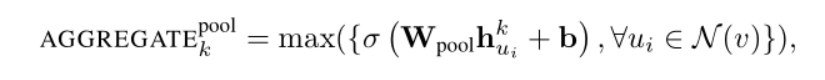
Here Max is an element wise max
2. Code analysis
- Code reference address: graphSAGE-pytorch
- Import required libraries
import numpy as np import pandas as pd import os,sys import argparse import torch import torch.nn as nn import torch.nn.functional as F import torch.optim as optim import random import math from sklearn.utils import shuffle from sklearn.metrics import f1_score from collections import defaultdict
2.1 loading data
- The data cora used in this code contains two files: cora_content and cora_cite. For detailed data description, please refer to the link: Cora dataset description
class DataCenter(object):
"""Load dataset
Parameter:
file_paths:{Data file storage address 1,Data file storage address 2}
"""
def __init__(self,file_paths):
"""file_paths:{name:root,...,}"""
super(DataCenter,self).__init__()
self.file_paths = file_paths
def load_Dataset(self,dataset='cora'):
"""Read the data set stored in the specified path"""
feat_list = [] # List for storing eigenvectors of each node
label_list = [] # It is used to store the list of corresponding categories of each node
node_map = {} # Recoding nodes
label_map = {} # Map label to number
if dataset == 'cora':
content = file_paths['cora_content'] # Get Cora_ Address of content
cite = file_paths['cora_cite'] # Get cora_cite's address
with open(content) as f1:
for i,each_sample in enumerate(f1.readlines()): # Traverse the characteristics of each sample
sample_clean = each_sample.strip().split()
# Extract the features of each sample, in which the first element and the last element are the sample name and the corresponding label
feat_list.append(sample_clean[1:-1])
# Mapping node names to node numbers
node_map[sample_clean[0]]=i
label = sample_clean[-1]
if label not in label_map.keys():
# Convert label to number
label_map[label] = len(label_map)
label_list.append(label_map[label])
feat_list = np.asarray(feat_list,dtype=np.float64)
label_list = np.asarray(label_list,dtype=np.int64)
# Obtain the neighbors of each node {V0: [neighbor set of V0], V1: [neighbor set of V1]}
adj_lists = defaultdict(set)
with open(cite) as f2:
for j,each_pair in enumerate(f2.readlines()):
pair = each_pair.strip().split()
assert len(pair) == 2
adj_lists[node_map[pair[0]]].add(node_map[pair[1]])
adj_lists[node_map[pair[1]]].add(node_map[pair[0]])
assert len(feat_list) == len(label_list) == len(adj_lists)
train_index,test_index,val_index = self._split_data(feat_list.shape[0])
# Use getattr() to get the data
setattr(self,dataset+'_test',test_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_val',val_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_train',train_index)
setattr(self,dataset+'_feats',feat_list)
setattr(self,dataset+'_labels',label_list)
setattr(self,dataset+'_adj_lists',adj_lists)
def _split_data(self,number_of_nodes,test_split=3,val_split=6):
"""Obtain training set, verification set and test set"""
# Disorder order
rand_indices = np.random.permutation(number_of_nodes)
test_size = number_of_nodes // test_split
val_size = number_of_nodes // val_split
test_index = rand_indices[:test_size]
val_index = rand_indices[test_size:test_size+val_size]
train_index = rand_indices[test_size+val_size:]
return train_index,test_index,val_index
2.2 Unsupervised Loss
The Loss function defined by GraphSAGE is as follows:,
J
G
(
z
u
)
=
−
l
o
g
(
σ
(
z
u
T
z
v
)
)
−
Q
E
v
n
P
n
(
v
)
l
o
g
(
σ
(
−
z
u
T
z
v
n
)
)
J_G(z_u)=-log(\sigma(z_u^Tz_v))-QE_{v_n ~ P_n(v)}log(\sigma(-z_u^Tz_{v_n}))
JG(zu)=−log(σ(zuTzv))−QEvn Pn(v)log(σ(−zuTzvn))
Among them,
Q
Q
Q is the number of negative samples. The former is Loss calculated based on positive samples, and the latter is Loss calculated based on negative samples
class UnsupervisedLoss(object):
"""docstring for UnsupervisedLoss"""
def __init__(self, adj_lists, train_nodes, device):
"""Initialization parameters"""
super(UnsupervisedLoss, self).__init__()
self.Q = 10 # Number of negative samples
self.N_WALKS = 6 # Number of random walks per node
self.WALK_LEN = 1 # Step size of each random walk
self.N_WALK_LEN = 5 # Each negative sample randomly walks several nodes
self.MARGIN = 3
self.adj_lists = adj_lists #{V0: [neighbor set of V0], V1: [neighbor set of V1],..., VN: [neighbor set of VN]}
self.train_nodes = train_nodes # Training node
self.device = device # cpu or gpu
self.target_nodes = None
self.positive_pairs = [] # Store positive example samples [(positive example nodes sampled in V0 and V0 neighbors),...,]
self.negtive_pairs = [] # Store negative example samples [(negative example nodes sampled in V0 and V0 neighbors),....,]
self.node_positive_pairs = {} # {v0:[(v0, positive example node sampled from v0), (v0, positive example node sampled from v0)],..., vn:[(vn, positive example node sampled from vn)]}
self.node_negtive_pairs = {} # {v0:[(v0, negative example node sampled from v0), (v0, negative example node sampled from v0)],..., vn:[(vn, negative example node sampled from vn)]}
self.unique_nodes_batch = [] # All nodes used in a batch and their neighbors
def get_loss_sage(self, embeddings, nodes):
"""Calculate the loss function according to the formula in the paper"""
assert len(embeddings) == len(self.unique_nodes_batch) #Judge whether each node has embeddings
assert False not in [nodes[i]==self.unique_nodes_batch[i] for i in range(len(nodes))] # Judge whether the nodes in the target node set and unique set are 1 one-to-one corresponding
node2index = {n:i for i,n in enumerate(self.unique_nodes_batch)} # Recode nodes
nodes_score = []
assert len(self.node_positive_pairs) == len(self.node_negtive_pairs) # Determine whether the number of positive and negative node pairs is the same
for node in self.node_positive_pairs: # Traverse all nodes
pps = self.node_positive_pairs[node] # Obtain the corresponding positive example [(v0,v0 positive example sample 1),(v0,v0 positive example sample 2),...,(v0,v0 positive example sample n)]
nps = self.node_negtive_pairs[node] # Obtain the corresponding negative example of each node [(v0,v0 negative example sample 1),(v0,v0 negative example sample 2),...,(v0,v0 negative example sample n)]
if len(pps) == 0 or len(nps) == 0: # Judge whether there are positive and negative cases
continue
# Q * Exception(negative score) calculates the Loss of the negative sample, that is, the latter term of the Loss function
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*nps)] # [[source node,..., source node], [sampled negative node 1,..., sampled negative node n]]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]] # Get the number of the source node
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]] # Number of negative sample node
neg_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs]) # Calculate cosine similarity
neg_score = self.Q*torch.mean(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(-neg_score)), 0) # Calculate the latter item of loss
#print(neg_score)
# multiple positive score calculates the Loss of the positive sample, that is, the previous term of the Loss function
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*pps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
pos_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
pos_score = torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score)) # Previous item for calculating loss
#print(pos_score)
nodes_score.append(torch.mean(- pos_score - neg_score).view(1,-1)) # Add the loss of each node to the list
loss = torch.mean(torch.cat(nodes_score, 0)) # Average
return loss
def get_loss_margin(self, embeddings, nodes):
assert len(embeddings) == len(self.unique_nodes_batch)
assert False not in [nodes[i]==self.unique_nodes_batch[i] for i in range(len(nodes))]
node2index = {n:i for i,n in enumerate(self.unique_nodes_batch)}
nodes_score = []
assert len(self.node_positive_pairs) == len(self.node_negtive_pairs)
for node in self.node_positive_pairs:
pps = self.node_positive_pairs[node]
nps = self.node_negtive_pairs[node]
if len(pps) == 0 or len(nps) == 0:
continue
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*pps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
pos_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
pos_score, _ = torch.min(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score)), 0)
indexs = [list(x) for x in zip(*nps)]
node_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[0]]
neighb_indexs = [node2index[x] for x in indexs[1]]
neg_score = F.cosine_similarity(embeddings[node_indexs], embeddings[neighb_indexs])
neg_score, _ = torch.max(torch.log(torch.sigmoid(neg_score)), 0)
nodes_score.append(torch.max(torch.tensor(0.0).to(self.device), neg_score-pos_score+self.MARGIN).view(1,-1))
# nodes_score.append((-pos_score - neg_score).view(1,-1))
loss = torch.mean(torch.cat(nodes_score, 0),0)
# loss = -torch.log(torch.sigmoid(pos_score))-4*torch.log(torch.sigmoid(-neg_score))
return loss
def extend_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg=6):
"""Obtain the positive and negative samples of the target node set, and output the set of these nodes"""
self.positive_pairs = []
self.node_positive_pairs = {}
self.negtive_pairs = []
self.node_negtive_pairs = {}
self.target_nodes = nodes
self.get_positive_nodes(nodes)
# print(self.positive_pairs)
self.get_negtive_nodes(nodes, num_neg)
# print(self.negtive_pairs)
self.unique_nodes_batch = list(set([i for x in self.positive_pairs for i in x]) | set([i for x in self.negtive_pairs for i in x]))
assert set(self.target_nodes) < set(self.unique_nodes_batch)
return self.unique_nodes_batch
def get_positive_nodes(self, nodes):
return self._run_random_walks(nodes) # Positive samples are obtained by random walk
def get_negtive_nodes(self, nodes, num_neg):
"""
Generate negative samples, that is, make the nodes far away from the target node form a negative example
"""
for node in nodes: # Traverse each node
neighbors = set([node])
frontier = set([node])
for i in range(self.N_WALK_LEN):
current = set()
for outer in frontier:
current |= self.adj_lists[int(outer)] #Get all neighbor nodes in the frontier
frontier = current - neighbors #Remove source node
neighbors |= current # Source node + neighbor node
far_nodes = set(self.train_nodes) - neighbors # Subtract train_ Source node and its first-order neighbor in nodes
neg_samples = random.sample(far_nodes, num_neg) if num_neg < len(far_nodes) else far_nodes # Start sampling from second-order neighbors
self.negtive_pairs.extend([(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples])
self.node_negtive_pairs[node] = [(node, neg_node) for neg_node in neg_samples]
return self.negtive_pairs
def _run_random_walks(self, nodes):
for node in nodes: # Traverse each node
if len(self.adj_lists[int(node)]) == 0: # Skip if the node has no neighbors
continue
cur_pairs = [] # Create a
for i in range(self.N_WALKS): # Each node will have n_ Random walk of walks times
curr_node = node #
for j in range(self.WALK_LEN): # Walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk walk_ Length of len
neighs = self.adj_lists[int(curr_node)]
next_node = random.choice(list(neighs))
# self co-occurrences are useless
if next_node != node and next_node in self.train_nodes:
self.positive_pairs.append((node,next_node))
cur_pairs.append((node,next_node))
curr_node = next_node
self.node_positive_pairs[node] = cur_pairs
return self.positive_pairs
2.3 Models
- Classification model
class Classification(nn.Module):
"""A simplest one-tier classification model
Parameters:
input_size:Input dimension
num_classes:Number of categories
return:
logists:Label corresponding to maximum probability
"""
def __init__(self,input_size,num_classes):
super(Classification,self).__init__()
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(input_size,num_classes) # Define an input_ size*num_ Linear layer of classes
self.init_params() # Initialize weight parameters
def init_params(self):
for param in self.parameters():
if len(param.size()) == 2: # Reinitialize if the parameter is a matrix
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(param)
def forward(self,x):
logists = torch.log_softmax(self.fc1(x),1) # Using log_softmax to get the category of the final output
return logists
- GraphSAGE
class SageLayer(nn.Module):
"""
First floor SageLayer
"""
def __init__(self, input_size, out_size, gcn=False):
super(SageLayer, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.gcn = gcn
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(out_size, self.input_size if self.gcn else 2 * self.input_size)) #Initialize the weight parameter w * input T
self.init_params() # Adjust weight parameter distribution
def init_params(self):
for param in self.parameters():
nn.init.xavier_uniform_(param)
def forward(self, self_feats, aggregate_feats, neighs=None):
"""
Parameters:
self_feats:Eigenvector of source node
aggregate_feats:Characteristics of aggregated neighbor nodes
"""
if not self.gcn: # If it is not gcn, concatenate it
combined = torch.cat([self_feats, aggregate_feats], dim=1)
else:
combined = aggregate_feats
combined = F.relu(self.weight.mm(combined.t())).t()
return combined
class GraphSage(nn.Module):
"""Define a GraphSage Model"""
def __init__(self, num_layers, input_size, out_size, raw_features, adj_lists, device, gcn=False, agg_func='MEAN'):
super(GraphSage, self).__init__()
self.input_size = input_size
self.out_size = out_size
self.num_layers = num_layers # Layers of Graphsage
self.gcn = gcn
self.device = device
self.agg_func = agg_func
self.raw_features = raw_features
self.adj_lists = adj_lists
# Define the input and output of each layer
for index in range(1, num_layers+1):
layer_size = out_size if index != 1 else input_size
setattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index), SageLayer(layer_size, out_size, gcn=self.gcn))#Except for layer 1, the input is input_size, the input and output of other layers are outsize
def forward(self, nodes_batch):
"""
Generate embedded representations for a batch of nodes
Parameters:
nodes_batch:Node of target batch
"""
lower_layer_nodes = list(nodes_batch) # Initialize layer 1 nodes
nodes_batch_layers = [(lower_layer_nodes,)] # Store node information of each layer
for i in range(self.num_layers):
lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict, lower_layer_nodes= self._get_unique_neighs_list(lower_layer_nodes) # Obtain the next layer node according to the current layer node
nodes_batch_layers.insert(0, (lower_layer_nodes, lower_samp_neighs, lower_layer_nodes_dict))
assert len(nodes_batch_layers) == self.num_layers + 1
pre_hidden_embs = self.raw_features # Initialize h0
for index in range(1, self.num_layers+1):
nb = nodes_batch_layers[index][0] #All neighbor nodes
pre_neighs = nodes_batch_layers[index-1] # Neighbor node of upper layer
aggregate_feats = self.aggregate(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
sage_layer = getattr(self, 'sage_layer'+str(index))
if index > 1:
nb = self._nodes_map(nb, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs)
# self.dc.logger.info('sage_layer.')
cur_hidden_embs = sage_layer(self_feats=pre_hidden_embs[nb],
aggregate_feats=aggregate_feats)
pre_hidden_embs = cur_hidden_embs
return pre_hidden_embs
def _nodes_map(self, nodes, hidden_embs, neighs):
layer_nodes, samp_neighs, layer_nodes_dict = neighs
assert len(samp_neighs) == len(nodes)
index = [layer_nodes_dict[x] for x in nodes]
return index
def _get_unique_neighs_list(self, nodes, num_sample=10):
_set = set
to_neighs = [self.adj_lists[int(node)] for node in nodes] # Get all neighbor nodes of the target node set [[neighbor of v0], [neighbor of v1], [neighbor of v2]]
if not num_sample is None: # If num_ If sample is a real number
_sample = random.sample
samp_neighs = [_set(_sample(to_neigh, num_sample)) if len(to_neigh) >= num_sample else to_neigh for to_neigh in to_neighs] # [set (randomly sampled neighbor set), set(),set()]
# Traverse all neighbor sets if the number of neighbor nodes > = num_sample, which randomly samples num from the neighbor node set_ Sample is a neighbor node. Otherwise, put the neighbor node set directly
else:
samp_neighs = to_neighs
samp_neighs = [samp_neigh | set([nodes[i]]) for i, samp_neigh in enumerate(samp_neighs)] # Put the source node in, too
_unique_nodes_list = list(set.union(*samp_neighs)) #Flatten
i = list(range(len(_unique_nodes_list))) # Renumber
unique_nodes = dict(list(zip(_unique_nodes_list, i)))
return samp_neighs, unique_nodes, _unique_nodes_list
def aggregate(self, nodes, pre_hidden_embs, pre_neighs, num_sample=10):
"""Aggregate neighbor node information
Parameters:
nodes:A collection of nodes starting from the outermost layer
pre_hidden_embs:Node embedding of the upper layer
pre_neighs:Node of the upper layer
"""
unique_nodes_list, samp_neighs, unique_nodes = pre_neighs # The source node of the upper layer,
assert len(nodes) == len(samp_neighs)
indicator = [(nodes[i] in samp_neighs[i]) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))] # Judge whether each node appears in the neighbor node
assert (False not in indicator)
if not self.gcn:
# If gcn is not applicable, remove the source node
samp_neighs = [(samp_neighs[i]-set([nodes[i]])) for i in range(len(samp_neighs))]
if len(pre_hidden_embs) == len(unique_nodes):
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs
else:
embed_matrix = pre_hidden_embs[torch.LongTensor(unique_nodes_list)]
# self.dc.logger.info('3')
mask = torch.zeros(len(samp_neighs), len(unique_nodes))
column_indices = [unique_nodes[n] for samp_neigh in samp_neighs for n in samp_neigh]
row_indices = [i for i in range(len(samp_neighs)) for j in range(len(samp_neighs[i]))]
mask[row_indices, column_indices] = 1 # Each source node is a row, and 1 in a row of elements corresponds to the location of neighbor nodes
if self.agg_func == 'MEAN':
num_neigh = mask.sum(1, keepdim=True) # Calculate how many neighbor nodes each source node has
mask = mask.div(num_neigh).to(embed_matrix.device) #
aggregate_feats = mask.mm(embed_matrix)
elif self.agg_func == 'MAX':
# print(mask)
indexs = [x.nonzero() for x in mask==1]
aggregate_feats = []
for feat in [embed_matrix[x.squeeze()] for x in indexs]:
if len(feat.size()) == 1:
aggregate_feats.append(feat.view(1, -1))
else:
aggregate_feats.append(torch.max(feat,0)[0].view(1, -1))
aggregate_feats = torch.cat(aggregate_feats, 0)
return aggregate_feats
2.4 evaluation and model use
def evaluate(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1, name, cur_epoch):
"""
Test the performance of the model
Parameters:
datacenter:Created datacenter Opposite image
ds:The name of the dataset
graphSage: Trained graphSage Opposite image
classification:Trained classificator
"""
test_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_test') # Get test set
val_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_val') # Get validation set
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels') # Get label
models = [graphSage, classification]
params = [] # Store the parameters of the two models in a list
for model in models:
for param in model.parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
param.requires_grad = False
params.append(param)
embs = graphSage(val_nodes)
logists = classification(embs)
_, predicts = torch.max(logists, 1)
labels_val = labels[val_nodes]
assert len(labels_val) == len(predicts)
comps = zip(labels_val, predicts.data)
vali_f1 = f1_score(labels_val, predicts.cpu().data, average="micro")
print("Validation F1:", vali_f1)
if vali_f1 > max_vali_f1:
max_vali_f1 = vali_f1
embs = graphSage(test_nodes)
logists = classification(embs)
_, predicts = torch.max(logists, 1)
labels_test = labels[test_nodes]
assert len(labels_test) == len(predicts)
comps = zip(labels_test, predicts.data)
test_f1 = f1_score(labels_test, predicts.cpu().data, average="micro")
print("Test F1:", test_f1)
for param in params:
param.requires_grad = True
torch.save(models, './model_best_{}_ep{}_{:.4f}.torch'.format(name, cur_epoch, test_f1))
for param in params:
param.requires_grad = True
return max_vali_f1
def get_gnn_embeddings(gnn_model, dataCenter, ds):
"""use GraphSage Get the embedded representation of the node"""
print('Loading embeddings from trained GraphSAGE model.')
features = np.zeros((len(getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')), gnn_model.out_size))
nodes = np.arange(len(getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels'))).tolist()
b_sz = 500
batches = math.ceil(len(nodes) / b_sz)
embs = []
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
embs_batch = gnn_model(nodes_batch)
assert len(embs_batch) == len(nodes_batch)
embs.append(embs_batch)
# if ((index+1)*b_sz) % 10000 == 0:
# print(f'Dealed Nodes [{(index+1)*b_sz}/{len(nodes)}]')
assert len(embs) == batches
embs = torch.cat(embs, 0)
assert len(embs) == len(nodes)
print('Embeddings loaded.')
return embs.detach()
def train_classification(dataCenter, graphSage, classification, ds, device, max_vali_f1, name, epochs=800):
"""Training classifier"""
print('Training Classification ...')
c_optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(classification.parameters(), lr=0.5)
# train classification, detached from the current graph
#classification.init_params()
b_sz = 50
train_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_train')
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')
features = get_gnn_embeddings(graphSage, dataCenter, ds)
for epoch in range(epochs):
train_nodes = shuffle(train_nodes)
batches = math.ceil(len(train_nodes) / b_sz)
visited_nodes = set()
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = train_nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
visited_nodes |= set(nodes_batch)
labels_batch = labels[nodes_batch]
embs_batch = features[nodes_batch]
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss /= len(nodes_batch)
# print('Epoch [{}/{}], Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}, Dealed Nodes [{}/{}] '.format(epoch+1, epochs, index, batches, loss.item(), len(visited_nodes), len(train_nodes)))
loss.backward()
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(classification.parameters(), 5)
c_optimizer.step()
c_optimizer.zero_grad()
max_vali_f1 = evaluate(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1, name, epoch)
return classification, max_vali_f1
def apply_model(dataCenter, ds, graphSage, classification, unsupervised_loss, b_sz, unsup_loss, device, learn_method):
test_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_test')
val_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_val')
train_nodes = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_train')
labels = getattr(dataCenter, ds+'_labels')
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
num_neg = 6
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
num_neg = 100
else:
print("unsup_loss can be only 'margin' or 'normal'.")
sys.exit(1)
train_nodes = shuffle(train_nodes)
models = [graphSage, classification]
params = []
for model in models:
for param in model.parameters():
if param.requires_grad:
params.append(param)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(params, lr=0.7)
optimizer.zero_grad()
for model in models:
model.zero_grad()
batches = math.ceil(len(train_nodes) / b_sz)
visited_nodes = set()
for index in range(batches):
nodes_batch = train_nodes[index*b_sz:(index+1)*b_sz]
# extend nodes batch for unspervised learning
# no conflicts with supervised learning
nodes_batch = np.asarray(list(unsupervised_loss.extend_nodes(nodes_batch, num_neg=num_neg)))
visited_nodes |= set(nodes_batch)
# get ground-truth for the nodes batch
labels_batch = labels[nodes_batch]
# feed nodes batch to the graphSAGE
# returning the nodes embeddings
embs_batch = graphSage(nodes_batch)
if learn_method == 'sup':
# superivsed learning
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss_sup = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss_sup /= len(nodes_batch)
loss = loss_sup
elif learn_method == 'plus_unsup':
# superivsed learning
logists = classification(embs_batch)
loss_sup = -torch.sum(logists[range(logists.size(0)), labels_batch], 0)
loss_sup /= len(nodes_batch)
# unsuperivsed learning
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_margin(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_sage(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
loss = loss_sup + loss_net
else:
if unsup_loss == 'margin':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_margin(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
elif unsup_loss == 'normal':
loss_net = unsupervised_loss.get_loss_sage(embs_batch, nodes_batch)
loss = loss_net
print('Step [{}/{}], Loss: {:.4f}, Dealed Nodes [{}/{}] '.format(index+1, batches, loss.item(), len(visited_nodes), len(train_nodes)))
loss.backward()
for model in models:
nn.utils.clip_grad_norm_(model.parameters(), 5)
optimizer.step()
optimizer.zero_grad()
for model in models:
model.zero_grad()
return graphSage, classification
2.5 Main
file_paths = {'cora_content':'./cora.content','cora_cite':'./cora.cites'}
datacenter = DataCenter(file_paths)
datacenter.load_Dataset()
feature_data = torch.FloatTensor(getattr(datacenter, 'cora'+'_feats'))
label_data = torch.from_numpy(getattr(datacenter,'cora'+'_labels')).long()
adj_lists = getattr(datacenter,'cora'+'_adj_lists')
random.seed(824)
np.random.seed(824)
torch.manual_seed(824)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(824)
learn_method = 'sup'
ds = 'cora'
epochs = 50
max_vali_f1=0
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
graphSage = GraphSage(2, feature_data.size(1), 128, feature_data, getattr(datacenter, ds+'_adj_lists'), device, gcn='store_true', agg_func='MEAN')
num_labels = len(set(getattr(datacenter, ds+'_labels')))
classification = Classification(128, num_labels)
unsupervised_loss = UnsupervisedLoss(getattr(datacenter, ds+'_adj_lists'), getattr(datacenter, ds+'_train'), device)
if learn_method == 'sup':
print('GraphSage with Supervised Learning')
elif learn_method == 'plus_unsup':
print('GraphSage with Supervised Learning plus Net Unsupervised Learning')
else:
print('GraphSage with Net Unsupervised Learning')
for epoch in range(epochs):
print('----------------------EPOCH %d-----------------------' % epoch)
graphSage, classification = apply_model(datacenter, ds, graphSage, classification, unsupervised_loss, 20, 'normal', device, learn_method)
if (epoch+1) % 2 == 0 and learn_method == 'unsup':
classification, max_vali_f1 = train_classification(datacenter, graphSage, classification, ds, device,max_vali_f1, 'debug')
if learn_method != 'unsup':
max_vali_f1 = evaluate(datacenter, ds, graphSage, classification, device, max_vali_f1 , 'debug', epoch)
- The output results are as follows:
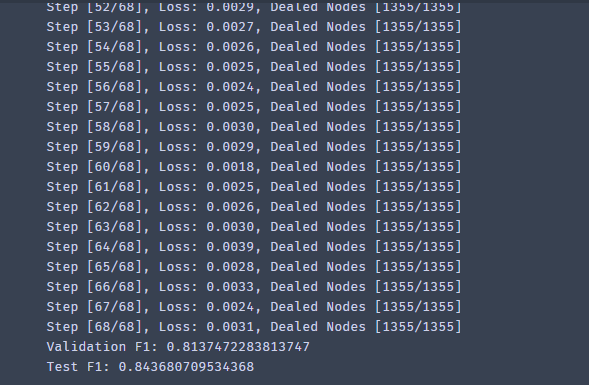
reference material
[1] Hamilton W L, Ying R, Leskovec J. Inductive representation learning on large graphs[J]. arXiv preprint arXiv:1706.02216, 2017.
[2] https://github.com/twjiang/graphSAGE-pytorch