preface
Hello, I'm sailing.
We may not be very familiar with the registry, because we usually use less; However, it is the core of Windows. Many software startup and logging are included in it. It can be said that it is a large database. Today, let's take a look at how Python operates the registry.
1, Registration form first meeting
There are many ways to enter the system registry. The most common way is to run the window and enter the command "regedit" to enter the registry:

Several menus in the registry correspond to the user information and local machine information logged in from the root directory of the machine, as well as user information and local configuration information.
2, Recognize the modules that operate the registry
There is such a magical module in Python, which can be used to operate the registry. It is -- "winreg", a module of Python's own to operate the registry.
3, Import
import winreg
1. Constant
”Winreg "always has many useful methods. Basically, it is to operate the keys in the registry. Let's pick some important ones. First, let's understand the constants in" winreg ":
1).HKEY_ constant
winreg.HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT #Store application and shell information winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_USER #Information customized by the current user winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE #All information of computer system winreg.HKEY_USERS #All user information winreg.HKEY_PERFORMANCE_DATA #performance data winreg.HKEY_CURRENT_CONFIG #Hardware profile of the local computer system winreg.HKEY_DYN_DATA #The version after Windows 98 cannot be used
2). Access rights
winreg.KEY_ALL_ACCESS #All permissions winreg.KEY_WRITE #Writable winreg.KEY_READ #readable winreg.KEY_EXECUTE #Executable equivalent to KEY_READ winreg.KEY_QUERY_VALUE #Query registry key winreg.KEY_SET_VALUE #Create, delete, or set a set of registry values winreg.KEY_CREATE_SUB_KEY #Create a registry key for a registry subkey winreg.KEY_ENUMERATE_SUB_KEYS #Enumerate registry keys required for registry subkeys winreg.KEY_NOTIFY #Tips for modifying registry keys winreg.KEY_CREATE_LINK #Create a link and reserve it for the system
3) . 64 bit application
winreg.KEY_WOW64_64KEY #The 64 bit Windows application should run in the 64 bit registry view winreg.KEY_WOW64_32KEY #The 64 bit Windows application should run in the 32-bit registry view
4). Value class
winreg.REG_BINARY #Binary data in any form winreg.REG_DWORD #Number of 32 bits winreg.REG_DWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN #32-bit numbers in low priority format, equivalent to REG_DWORD winreg.REG_DWORD_BIG_ENDIAN #32-bit numbers in high priority format winreg.REG_EXPAND_SZ #null terminated strings contain references to environment variables (%) winreg.REG_LINK #Unicode symbolic link winreg.REG_MULTI_SZ #A null terminated sequence of strings that ends with two null characters winreg.REG_NONE #No value type defined winreg.REG_QWORD #Number of 64 bits winreg.REG_QWORD_LITTLE_ENDIAN #Give priority to a 64 bit digital format in the low order, which is equivalent to REG_QWORD winreg.REG_RESOURCE_LIST #Device drive resource list winreg.REG_FULL_RESOURCE_DESCRIPTOR #hardware setup winreg.REG_RESOURCE_REQUIREMENTS_LIST #Hardware resource list winreg.REG_SZ #A null terminated string
4, Registry related operations
1. Connect to the remote computer registry
reg=winreg.ConnectRegistry('\\Computer name',winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)#The return value is the handle of the key being opened
#The first parameter refers to the remote computer name, and the second parameter refers to the key in the registry, such as HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE, which is a constant in winreg.However, we should note here that if the remote registry does not have system administrator privileges, it cannot access the registry normally. So we must first judge its access rights. Here we will use the method of judging whether the user is an administrator user in the "ctypes" module.
import ctypes
import sys
def admin():
aa=ctypes.windll.shell32.IsUserAnAdmin()
return aa
if admin()==1: #Have administrator privileges to open the remote registry
winreg.ConnectRegistry('\\Computer name',winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE)
else:
if sys.version_info[0]==3: #python version is more than 3
ctypes.windll.shell32.ShellExecuteW(None, "runas", sys.executable, __file__, None, 1)
else: #python2 version
ctypes.windll.shell32.ShellExecuteW(None, u"runas", unicode(sys.executable), unicode(__file__), None, 1)2. Close the connection registry
After connecting, we don't want to use it, so we have to close it. It's also very simple. As long as we get the handle to open the registry, we can close it.
winreg.CloseKey(reg)

You can see that the value of the handle is different.
In fact, there is another method, which is to use the method of registering processing objects to close.
reg.Close()
Registered objects also support context and separate processing object cycles:
reg.detach() #Returns an integer that records the life cycle of the current object. If the registration handle object is closed, it is 0
3. Open the registry key
#Open the specified key and return a processing object winreg.OpenKey(key, sub_key, reserved=0, access=winreg.KEY_READ) winreg.OpenKeyEx(key, sub_key, reserved=0, access=winreg.KEY_READ) #key:HKEY_ constant #sub_key: Specifies the subkey of the key #Reserved: a reserved certificate, which must be zero. The default value is zero #Access: access rights
4. Create a new registry key
winreg.CreateKey(key,sub_key) winreg.CreateKeyEx(key,sub_key,reserved=0,access=winreg.KEY_WRITE) #key:HKEY_ constant #sub_key: Specifies the subkey of the key #Reserved: a reserved certificate, which must be zero. The default value is zero #Access: access rights

5. Delete the key specified in the registry
winreg.DeleteKey( key,sub_key) #Keys with children cannot be deleted winreg.DeleteKeyEx(key,sub_key,reserved=0,access=winreg.KEY_WOW64_64KEY)#Keys with children cannot be deleted winreg.DeleteValue(key, value)#Deletes a named value entry from a registration key #The usage is the same as above, but the result is deletion

You can see that "cnm" has been deleted. If the key does not exist, the deletion will report an error.
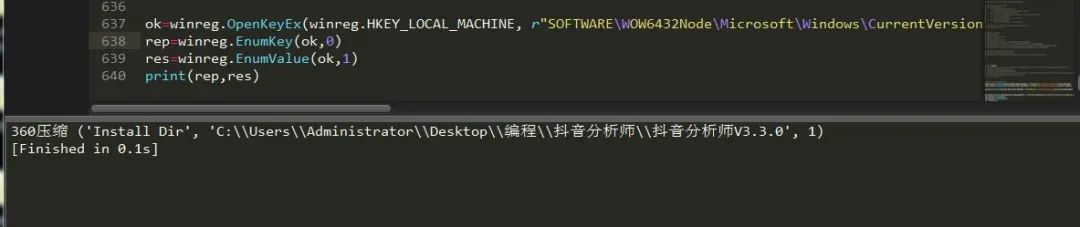
6. Enumerate registry keys
winreg.EnumKey(key,index) #Enumerates the subkeys of open registry keys and returns a string winreg.EnumValue(key,index)#Enumerates the open registry keys and returns a tuple #Index: an integer that identifies the index of the obtained key
7. Refresh registry key
winreg.FlushKey(key) #Synchronize all properties of a key to write to the registry
8. Read the registry
winreg.LoadKey(key,sub_key,file_name) #file_name: file name of reading registry data
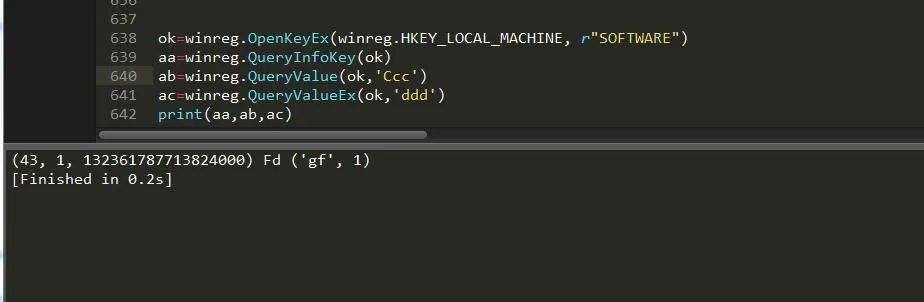
9. Find registry key
winreg.QueryInfoKey(key) #Returns information about the key of a 3-element tuple winreg.QueryValue(key,sub_key) #Use a string to retrieve the value of a key winreg.QueryValueEx(key,value_name) #Retrieves the data type and name of the specified value associated with an open registry key
10. Save registry key
winreg.SaveKey(key, file_name) #Saves the specified key and registry subkeys of all specified files
11. Enable or disable the registry
winreg.DisableReflectionKey(key) #Disable winreg.EnableReflectionKey(key) #Enable
12. Is the reflection status disabled
winreg.QueryReflectionKey(key) #If the result is True, it means disabled
13. Associate values on specified keys
winreg.SetValue(key, sub_key, type, value) #Add keys and values winreg.SetValueEx(key,value_name,reserved,type,value)#Store data in an open registry key field #value_name: the registry subkey of the string name #Type: value type #Value: the key value of the subkey
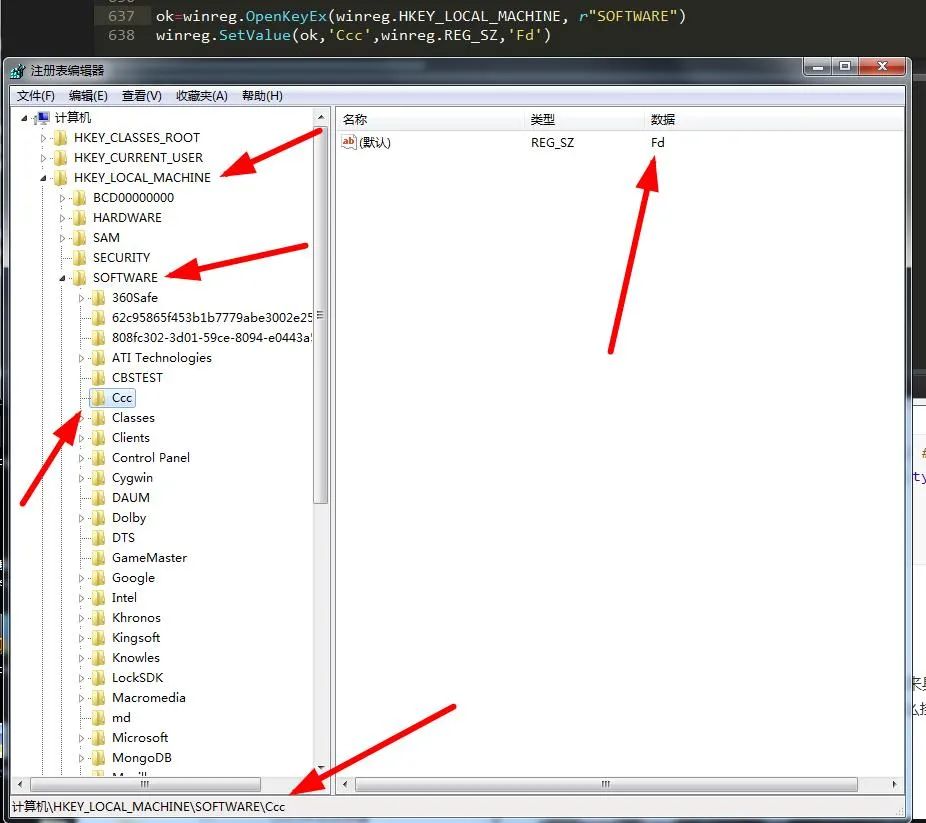
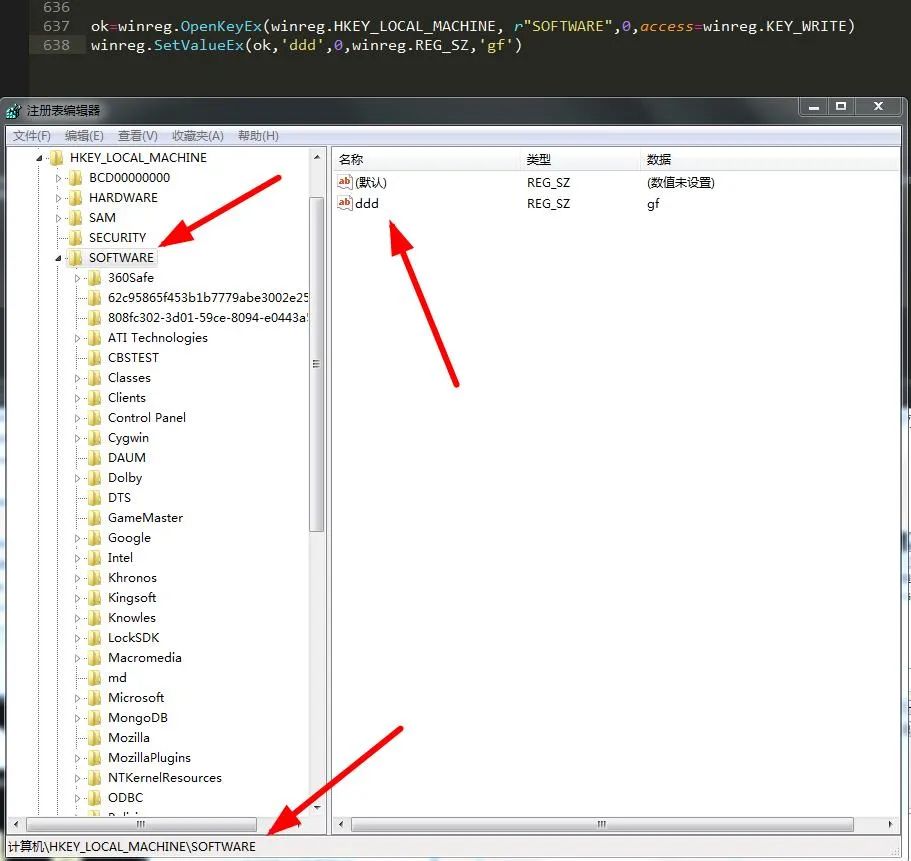
You can see the difference between them, and the value type of the former can only be specified as "winreg.REG_SZ", while the latter can be of any type.
14. Find the location of the application and open it
Previously, we introduced almost all the methods of "winreg". Now let's do an application training. Take our 360 security guard as an example. We try to find its location through the registry and then open it. Then Xiaobian began to perform:
1). Locate the registry key of 360 security guard:
1)). Open the system registry editor and search for keywords:
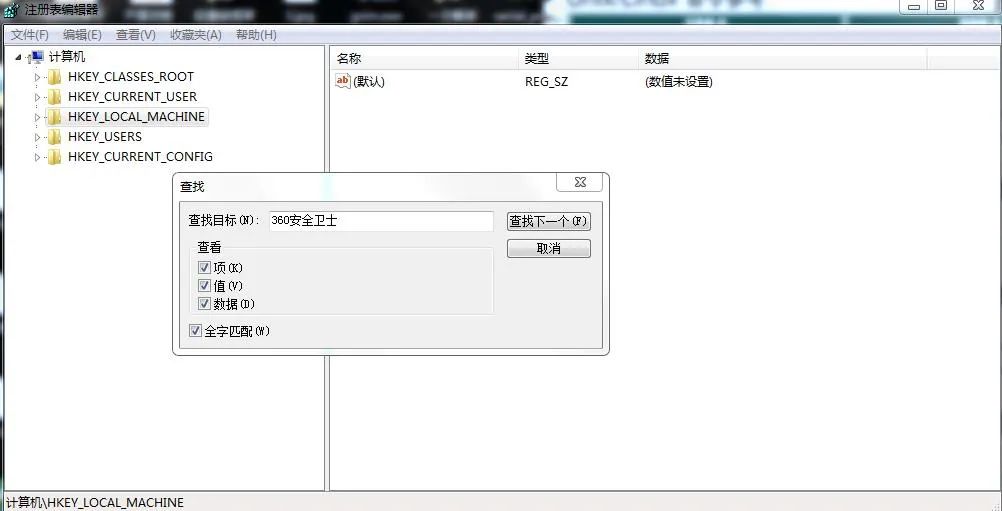
2)). Navigate to registry path

2). Open registry key
The handle "reg" of the processing object is obtained by finding the sub key and then searching it
reg=winreg.OpenKey(winreg.HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE,r"SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Microsoft\Windows\CurrentVersion\Uninstall\360 Security guard")
3). Find the absolute path of the application and print it
Find numeric data by numeric name,
path=winreg.QueryValueEx(reg,'DisplayIcon')
In this way, the absolute path of the application is found. The return value is an ancestor. We use the index to access:
path[0]

We can see that we have successfully printed out the absolute path of the application we are looking for, and then we can happily open it. There are many ways to open, such as "os", "subprocess", "ctypes","pywin32", a lot of methods, but Xiaobian still thinks "os" is the most convenient.
os.popen(path[0])

Finally, don't forget to close the object processing handle.
#Both methods can be turned off winreg.CloseKey(reg) reg.Close()
4, Summary
Using "winreg" can complete many operations. You can also set the system startup key and other operations through the registry. If you want to develop into hackers.

This is the end of the article. Thank you for watching
To be honest, I feel very happy every time I see some readers' responses in the background. I want to contribute some of my collection of programming dry goods to you and give back to every reader. I hope I can help you.
Dry goods mainly include:
① More than 2000 Python e-books (both mainstream and classic books should be available)
② Python standard library materials (the most complete Chinese version)
③ Project source code (forty or fifty interesting and classic hand training projects and source code)
④ Videos on basic introduction to Python, crawler, web development and big data analysis (suitable for Xiaobai)
5951 30847 7094 1002 30369 27756 517 13817 4456 10486 14004 7094 11497 27983 25378 30847 1002 9484
*If you can use it, you can take it directly. In my QQ technology exchange group, you can take it by yourself. The group number is 857113825*